Effects of the Substrate on Interfacial Polymerization: Tuning the Hydrophobicity via Polyelectrolyte Deposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Interfacial Polymerization on Substrates with Varied Hydrophilicity
2.2. Tuning the Hydrophilicity of Substrates via Polyelectrolyte Deposition
2.3. Membrane Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
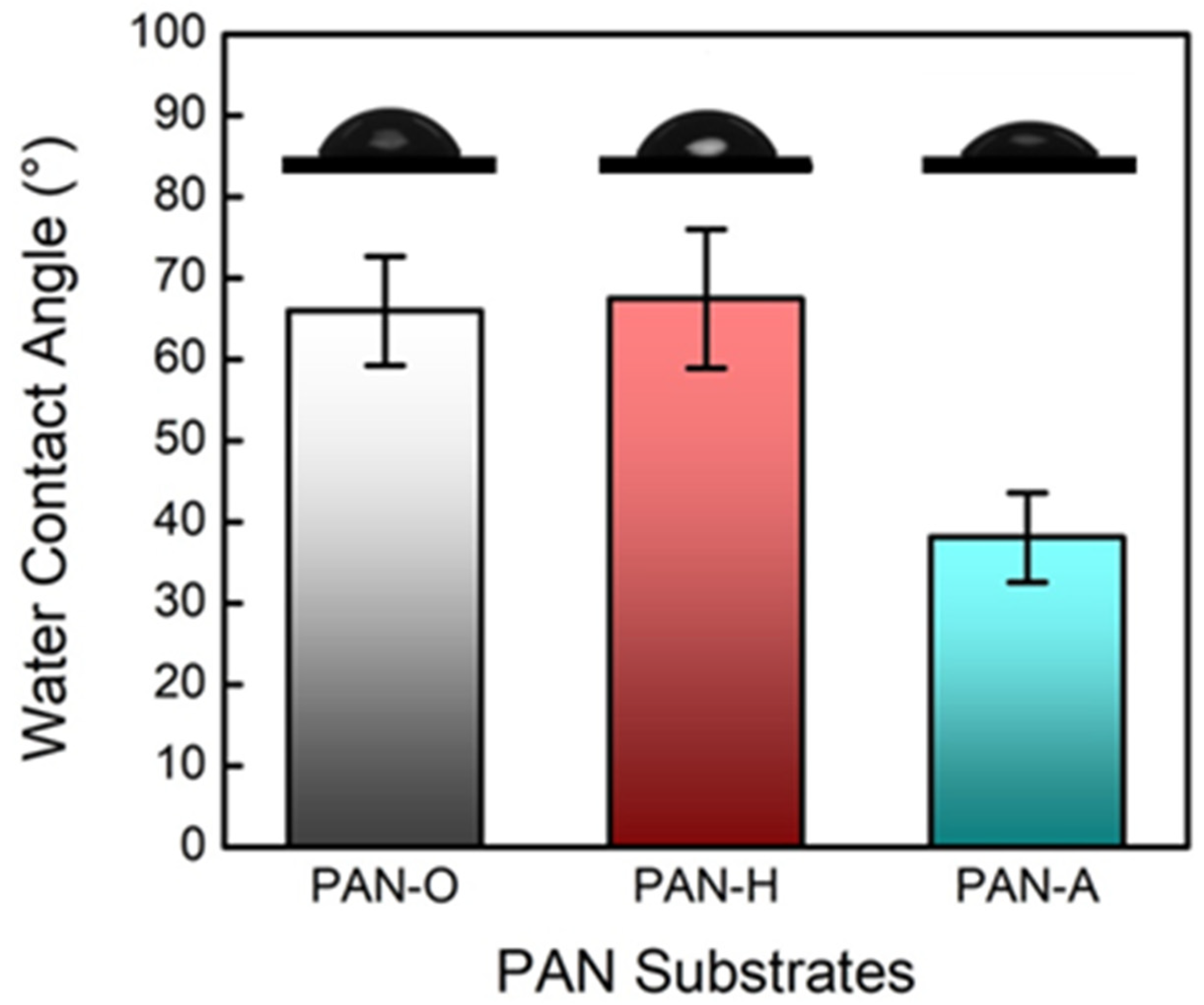
3.1. Effects of the Substrate Hydrophilicity on the IP-Film Formation
3.2. Effects of the Polyelectrolyte Deposition on the IP-Film Formation
4. Conclusions
- i.
- The PAN substrate with a relatively hydrophilic surface could result in delamination when it is employed in the formation of the TFC membrane via IP, whereas the integrity of the IP layer can be improved by decreasing the surface hydrophilicity.
- ii.
- The deposition of various polycations onto the surface of the PAN substrate modified with the alkaline treatment can change the wettability to different degrees (from ~38 to ~93 degrees), thereby offering a tool for the IP-based fabrication of TFC membranes with a hydrophilic PAN substrate.
- iii.
- The comparative study of the evaluation of the TFC membranes with different PAN substrates indicated that a relatively hydrophilic substrate would favor the enhancement of the water–flux efficiency with a factor of ~2 when it was employed in an osmotically-driven process.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yip, N.Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Phillip, W.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. High performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3812–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misdan, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Seawater Reverse Osmosis (SWRO) desalination by thin-film composite membrane-Current development, challenges and future prospects. Desalination 2012, 287, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadotte, J.E.; Petersen, R.J.; Larson, R.E.; Erickson, E.E. A new thin-film composite seawater reverse osmosis membrane. Desalination 1980, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. The upper bound of thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide membranes for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Padaki, M.; Hilal, N.; Matsuura, T.; Lau, W.J. Thin film composite membrane—Recent development and future potential. Desalination 2015, 356, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.P.; Joshi, S.V.; Trivedi, J.J.; Devmurari, C.V.; Shah, V.J. Structure-performance correlation of polyamide thin film composite membranes: Effect of coating conditions on film formation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mayyahi, A. Important approaches to enhance reverse osmosis (RO) thin film composite (TFC) membranes performance. Membranes 2018, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Hoek, E.M.V. Impacts of support membrane structure and chemistry on polyamide-polysulfone interfacial composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 336, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Zolotarev, A.; Plisko, T.; Burts, K.; Liamin, V.; Bildyukevich, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Effect of the formation of ultrathin selective layers on the structure and performance of thin-film composite chitosan/pan membranes for pervaporation dehydration. Membranes 2020, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Joshi, S.V.; Trivedi, J.J.; Devmurari, C.V.; Rao, A.P.; Ghosh, P.K. Probing the structural variations of thin film composite RO membranes obtained by coating polyamide over polysulfone membranes of different pore dimensions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSherbiny, I.M.A.; Ghannam, R.; Khalil, A.S.G.; Ulbricht, M. Isotropic macroporous polyethersulfone membranes as competitive supports for high performance polyamide desalination membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifakhr, M.; Trzaskus, K.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Roesink, H.D.W.; de Grooth, J. Increasing the success rate of interfacial polymerization on hollow fibers by the single-step addition of an intermediate layer. Desalination 2020, 491, 114581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsvik, I.L.; Hagg, M.B. Preparation of thin film composite membranes with polyamide film on hydrophilic supports. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, S. Novel insights into the interplay between support and active layer in the thin film composite polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Kim, S.S. Plasma treatment of polypropylene and polysulfone supports for thin film composite reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yu, Q.; Deng, B. Preparation and characterization of polyamide thin-film composite (TFC) membranes on plasma-modified polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Gorgojo, P.; Munoz-Ibanez, M.; Livingston, A.G. Beneath the surface: Influence of supports on thin film composite membranes by interfacial polymerization for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 448, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Yin, J.; Deng, B. Effects of Polysulfone (PSf) Support Layer on the Performance of Thin-Film Composite (TFC) Membranes. J. Chem. Process Eng. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of membrane support layer hydrophobicity on water flux in osmotically driven membrane processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R. Avoiding the Hype in Developing Commercially Viable Desalination Technologies. Joule 2019, 3, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Goh, K.; Li, X.; Setiawan, L.; Wang, R. Membranes and processes for forward osmosis-based desalination: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2018, 434, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, W.C.L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; McDougald, D.; Tang, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G. Effect of Pharmaceuticals on the Performance of a Novel Osmotic Membrane Bioreactor (OMBR). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 47, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castello, E.M.; McCutcheon, J.R. Dewatering press liquor derived from orange production by forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Elimelech, M. Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 2012, 488, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Jeon, S.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, H.; Park, Y.I.; Nam, S.E.; Lee, P.S.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.; Hong, S.; et al. Thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes prepared via layered interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kwon, S.J.; Kwon, H.E.; Shin, M.G.; Park, S.H.; Park, H.; Park, Y.I.; Nam, S.E.; Lee, J.H. Aromatic solvent-assisted interfacial polymerization to prepare high performance thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes based on hydrophilic supports. Polymer 2018, 144, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.E.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Shin, M.G.; Park, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Park, H.; Lee, J.H. High performance polyacrylonitrile-supported forward osmosis membranes prepared via aromatic solvent-based interfacial polymerization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.R.; Wang, S.H.; Zhao, H.L.; Wu, S.B.; Xu, J.M.; Li, L.; Liu, X.Y. Layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly technology as promising strategy for tailoring pressure-driven desalination membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Park, M.J.; Tijing, L.; Han, D.S.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Modification of nanofiber support layer for thin film composite forward osmosis membranes via layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte deposition. Membranes 2018, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Qi, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Cao, B.; Tang, C.Y. Synthesis and characterization of novel antibacterial silver nanocomposite nanofiltration and forward osmosis membranes based on layer-by-layer assembly. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Foo, L.X.; Li, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Cao, B.; Tang, C.Y. Fabrication and characterization of nanocomposite pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) membranes with excellent anti-biofouling property and enhanced water permeability. Desalination 2016, 389, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Wan, L.S.; Xu, Z.K. Surface engineerings of polyacrylonitrile-based asymmetric membranes towards biomedical applications: An overview. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H.; Kock, K. The formation mechanism of phase inversion membranes. Desalination 1977, 21, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, T.; Amano, K.; Fujii, A.; Ohmukai, Y.; Kamio, E.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Fouling reduction of reverse osmosis membrane by surface modification via layer-by-layer assembly. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 99, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, P.H.H.; Zuo, J.; Chung, T.S. Highly crosslinked layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte FO membranes: Understanding effects of salt concentration and deposition time on FO performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, C.; Reed, R.L. A method for estimating interfacial tensions and contact angles from sessile and pendant drop shapes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 91, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimanovich, D.L.; Vorobjova, A.I.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Kozlovskiy, A.L. Preparation and morphology-dependent wettability of porous alumina membranes. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, D.R. Reformulation of the solution-diffusion theory of reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R. Membrane technology for water: Microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. Treatise Water Sci. 2011, 301–335. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, C.; Wang, R.; Tang, C.Y. Influence of monomer concentrations on the performance of polyamide-based thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohokare, H.; Bhole, Y.; Taralkar, S.; Kharul, U. Poly(acrylonitrile) based ultrafiltration membranes: Optimization of preparation parameters. Desalination 2011, 282, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H.; Kock, K.; Amar, P.; Baker, R.W. The formation mechanism of asymmetric membranes. Desalination 1975, 16, 179–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.C.; Tong, J.H. Loose ultrafiltration of proteins using hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile hollow fiber. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 132, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-L.; Chao, W.-C.; Hung, W.-S.; An, Q.; De Guzman, M.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R. Physicochemical effects of hydrolyzed asymmetric polyacrylonitrile membrane microstructure on dehydrating butanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Guo, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Tuning roughness features of thin film composite polyamide membranes for simultaneously enhanced permeability, selectivity and anti-fouling performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, G.Y.; Krantz, W.B. Formation and characterization of polyamide membranes via interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 93, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyati, S.; Takagi, R.; Fujii, A.; Ohmukai, Y.; Matsuyama, H. Simultaneous improvement of the monovalent anion selectivity and antifouling properties of an anion exchange membrane in an electrodialysis process, using polyelectrolyte multilayer deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinska, M.; Warszynski, P. The effect of support material and conditioning on wettability of PAH/PSS multilayer films. Bioelectrochemistry 2005, 66, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.I.; Kwak, H.J.; Park, C.; Choi, C.; Sapkal, N.P.; Hong, J.; Kim, M.H. Wetting Criteria of Intrinsic Contact Angle To Distinguish between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Micro-/Nanotextured Surfaces: Experimental and Theoretical Analysis with Synchrotron X-ray Imaging. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, V.P.; Greenberg, A.R.; Krantz, W.B. Development of pendant drop mechanical analysis as a technique for determining the stress-relaxation and water-permeation properties of interfacially polymerized barrier layers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 2618–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freger, V.; Srebnik, S. Mathematical model of charge and density distributions in interfacial polymerization of thin films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qiu, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Synthesis and characterization of flat-sheet thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; She, Q.; Lay, W.C.L.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Coupled effects of internal concentration polarization and fouling on flux behavior of forward osmosis membranes during humic acid filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, N.; Wei, J.; Chin, T.W.; Tang, C.Y. Influence of the properties of layer-by-layer active layers on forward osmosis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423-424, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Deng, B.; Li, W. Effects of membrane morphology on the rejection of oil droplets: Theoretical analysis based on network modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Abbreviations | Modification Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| PAN substrates | PAN-O | original PAN substrate |
| PAN-H | PAN-O + heat treatment a | |
| PAN-A | PAN-O + alkaline treatment b | |
| PDADMAC-m | PAN-A + deposition of PDADMAC c | |
| PEI-m | PAN-A + deposition of PEI | |
| PAH-m | PAN-A + deposition of PAH | |
| TFC membranes | TFC-O | PAN-O + IP d |
| TFC-H | PAN-H + IP | |
| TFC-A | PAN-A + IP | |
| TFC-PDADMAC | PDADMAC-m + IP | |
| TFC-PEI | PEI-m + IP | |
| TFC-PAH | PAH-m + IP |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Deng, B. Effects of the Substrate on Interfacial Polymerization: Tuning the Hydrophobicity via Polyelectrolyte Deposition. Membranes 2020, 10, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100259
Liu X, Liu G, Li W, Wang Q, Deng B. Effects of the Substrate on Interfacial Polymerization: Tuning the Hydrophobicity via Polyelectrolyte Deposition. Membranes. 2020; 10(10):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100259
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Ge Liu, Weiyi Li, Qinyu Wang, and Baolin Deng. 2020. "Effects of the Substrate on Interfacial Polymerization: Tuning the Hydrophobicity via Polyelectrolyte Deposition" Membranes 10, no. 10: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100259
APA StyleLiu, X., Liu, G., Li, W., Wang, Q., & Deng, B. (2020). Effects of the Substrate on Interfacial Polymerization: Tuning the Hydrophobicity via Polyelectrolyte Deposition. Membranes, 10(10), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100259









