Adenovector 26 Encoded RSV Prefusion F Protein (Ad26.RSV.preF) Does Not Predispose to Enhanced Respiratory Disease in Preclinical Rodent Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Animal Handling
2.3. Viral Load Determination
2.3.1. By Plaque Assay
2.3.2. By Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Histopathology
2.5. RSV F Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Virus Neutralization Assay (VNA)
2.7. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. No Histopathological Signs of Enhanced Respiratory Disease Observed in Ad26.RSV.preF-Immunized Cotton Rats After Challenge with RSV A2
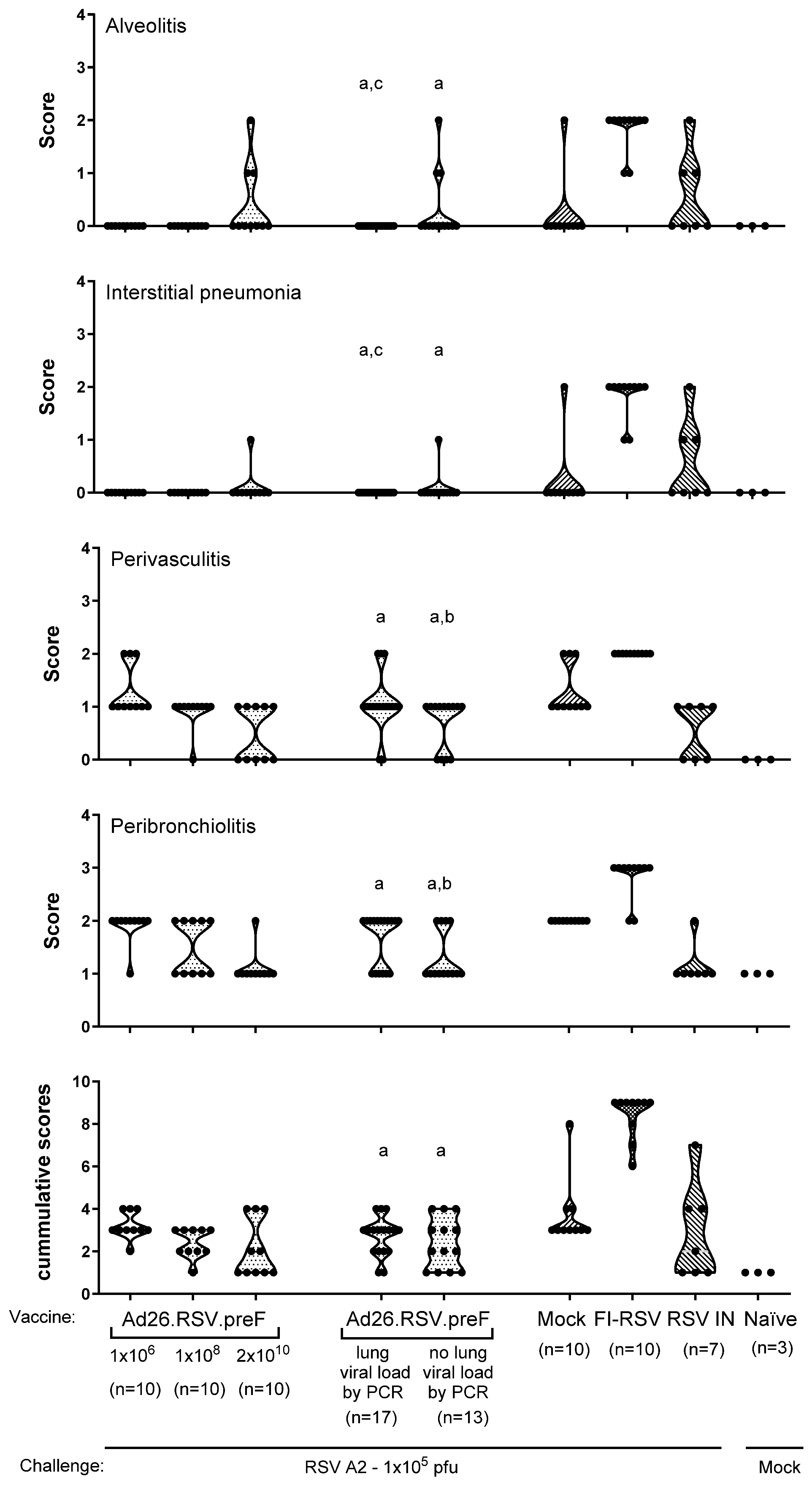
3.2. No Histopathological Alterations Characteristic for ERD Are Observed in Ad26.RSV.preF-Immunized Animals with Detectable RSV A2 Lung Viral Load After Challenge
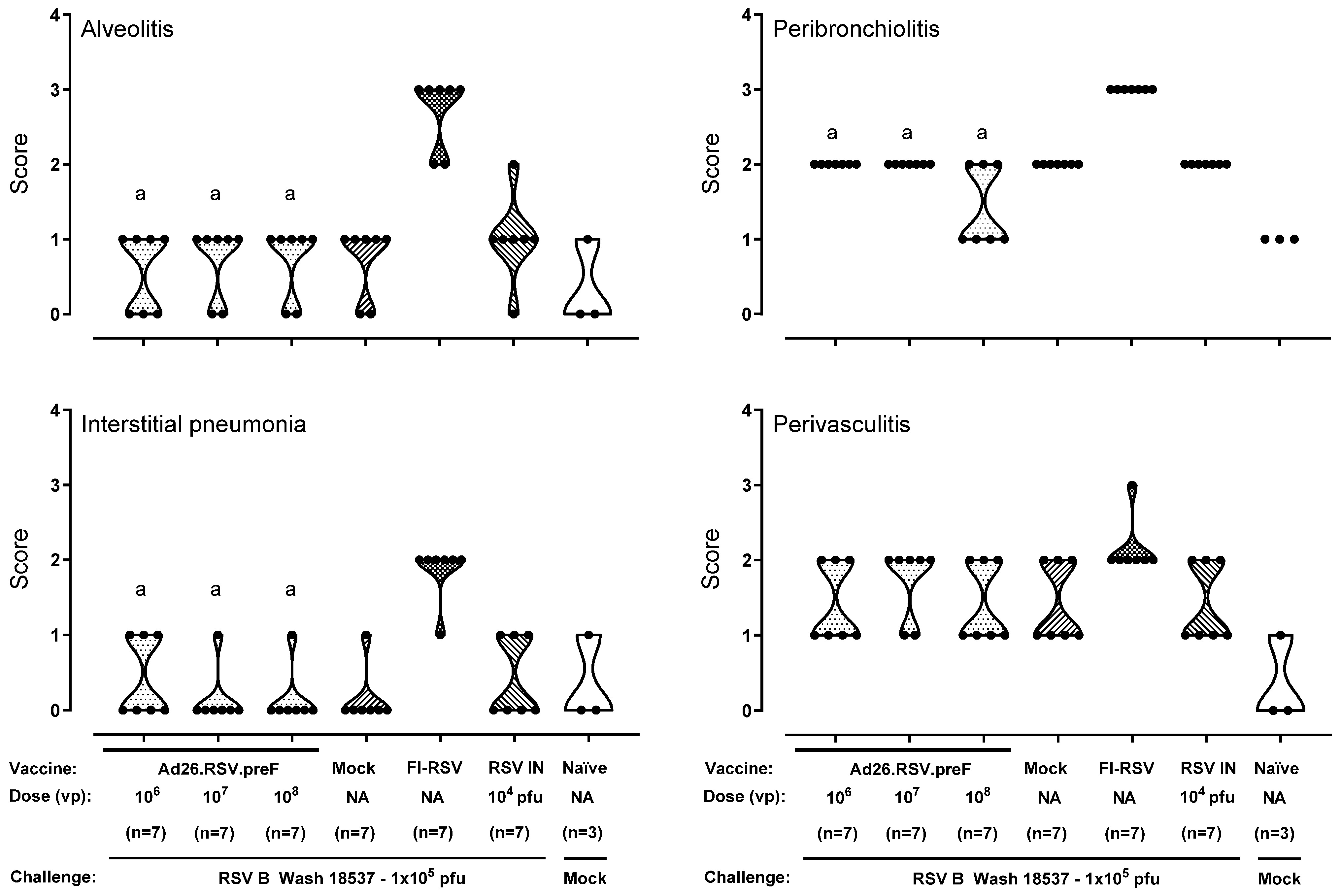
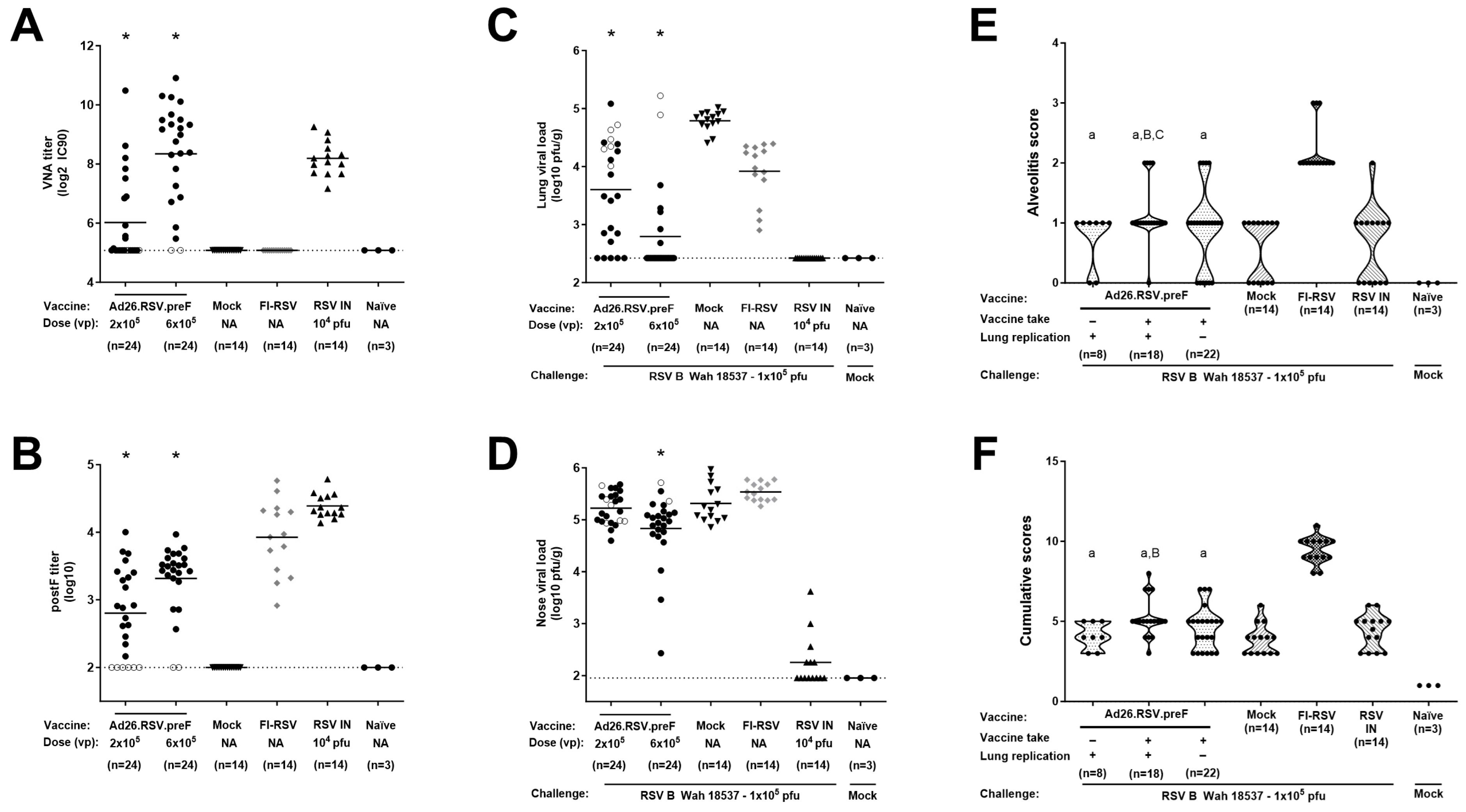
3.3. After Challenge with Vaccine Heterologous RSV B Wash 18537, No Signs of Enhanced Respiratory Disease Were Observed in Ad26.RSV.preF-Immunized Cotton Rats
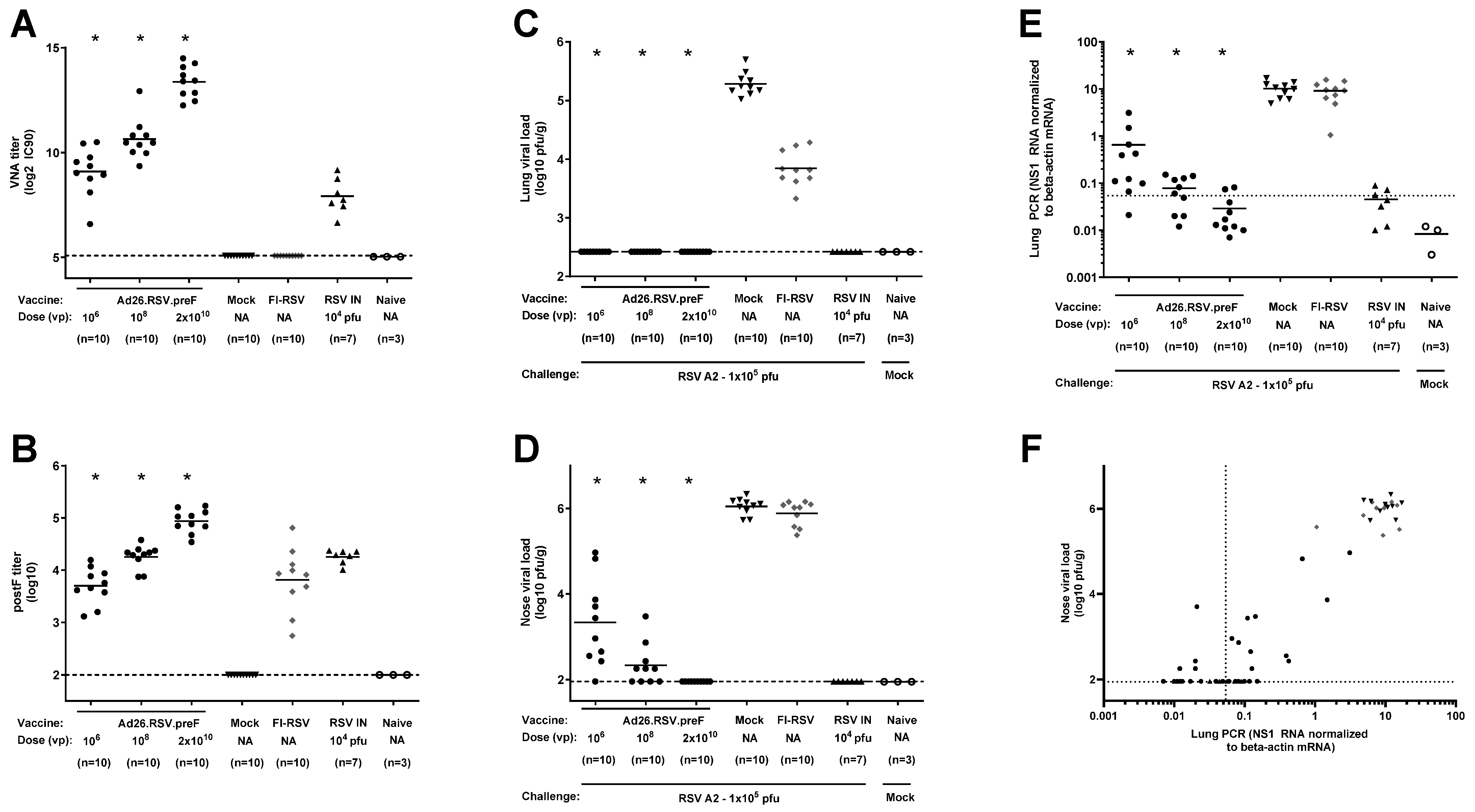
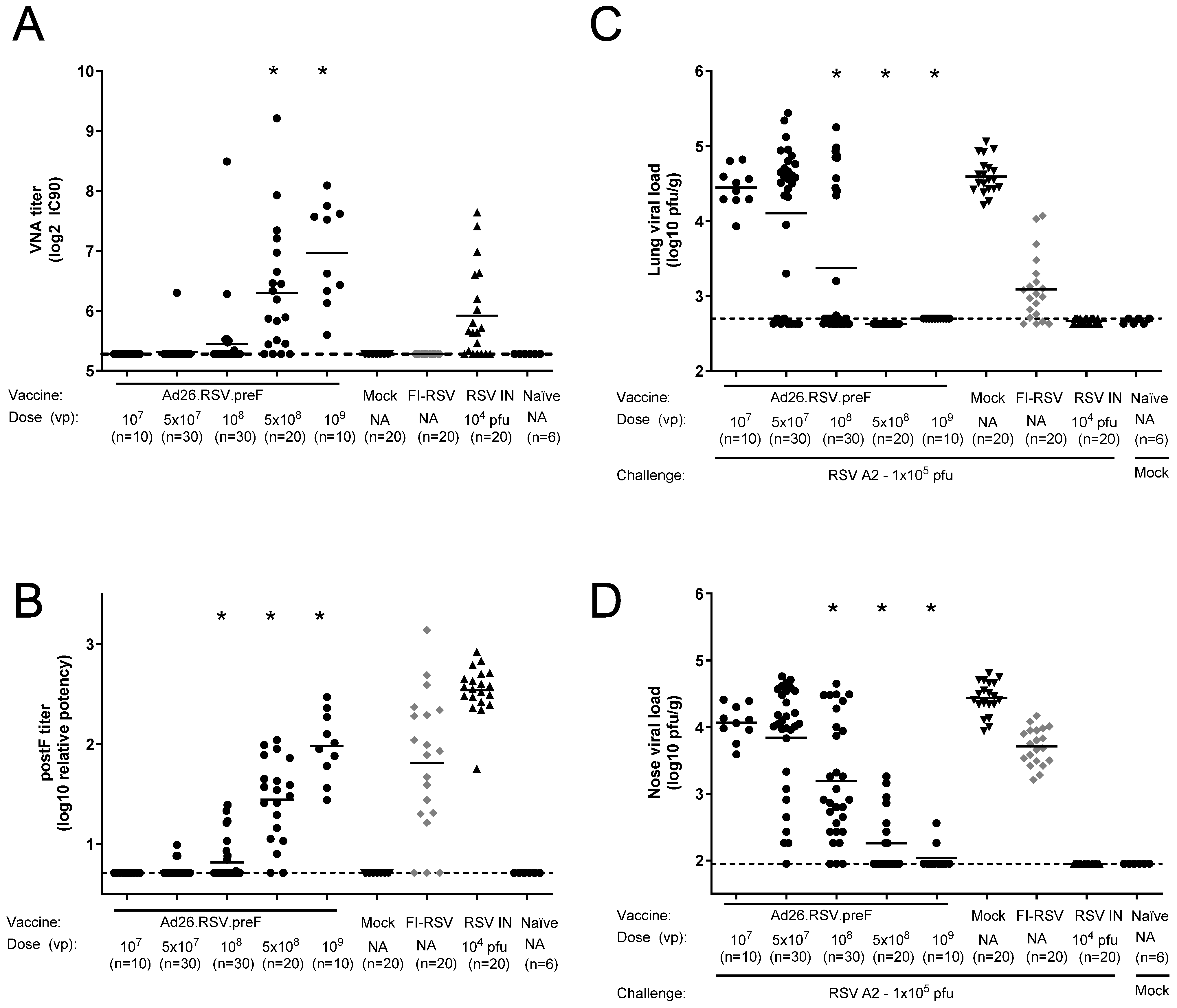
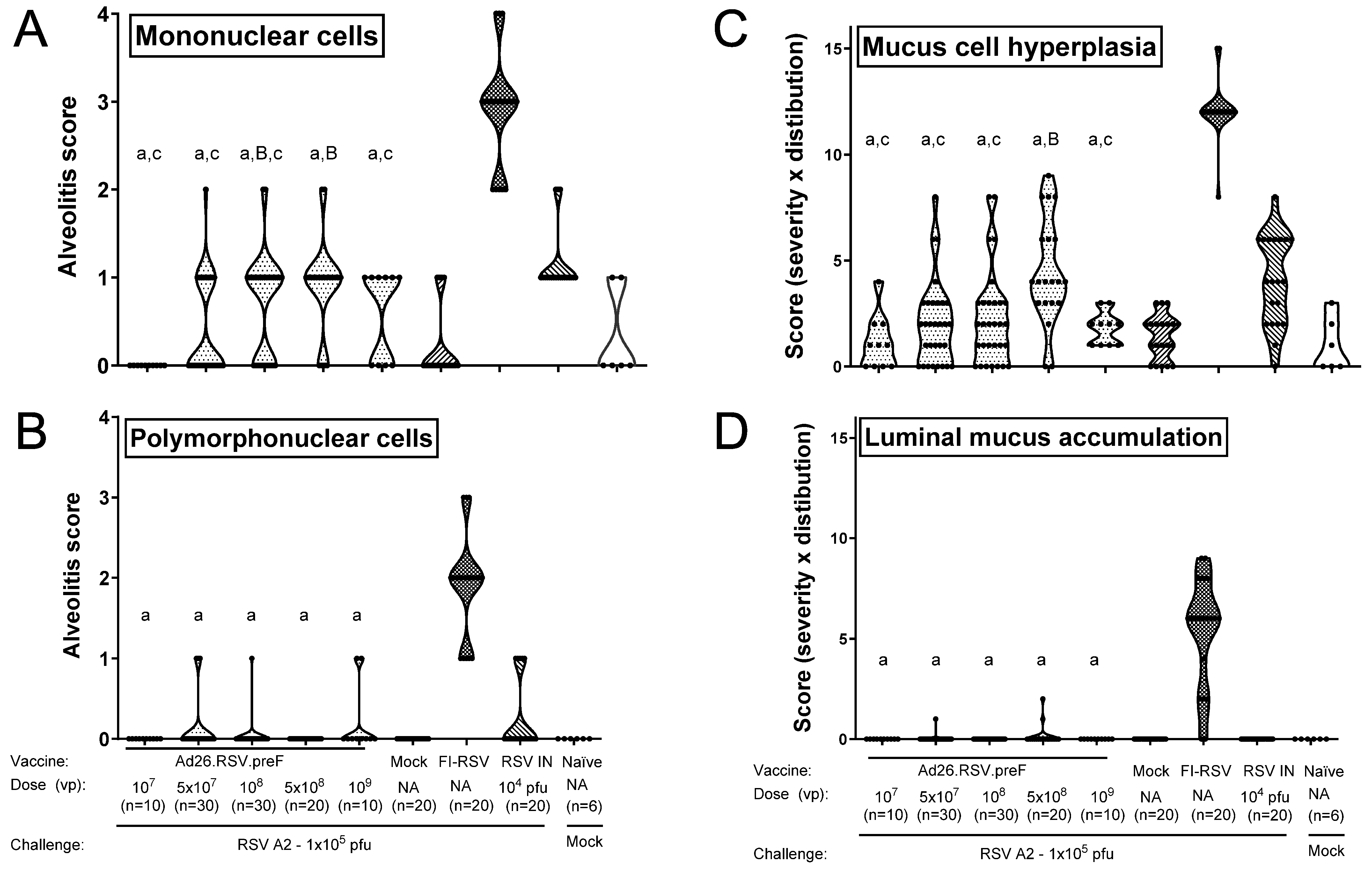
3.4. In Mice, Ad26.RSV.preF Dose-Dependently Induces Protection Against RSV A2, Without Any Signs of Predisposition to Enhanced Respiratory Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.M.; Caballero, M.T.; Feikin, D.R.; Gill, C.J.; Madhi, S.A.; Omer, S.B.; Simões, E.A.F.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fauroux, B.; Simões, E.A.F.; Checchia, P.A.; Paes, B.; Figueras-Aloy, J.; Manzoni, P.; Bont, L.; Carbonell-Estrany, X. The Burden and Long-term Respiratory Morbidity Associated with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Early Childhood. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2017, 6, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, S.J. Nirsevimab: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 83, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Subunit Vaccine: First Approval of a Maternal Vaccine to Protect Infants. Pediatr. Drugs 2023, 25, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, C.; Dondi, A.; Scarpini, S.; Rocca, A.; Vandini, S.; Poletti, G.; Lanari, M. Current State and Challenges in Developing Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines. Vaccines 2020, 8, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Canchola, J.G.; Brandt, C.D.; Pyles, G.; Chanock, R.M.; Jensen, K.; Parrott, R.H. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease in Infants Despite Prior Administration of Antigenic Inactivated Vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Mitchell, R.H.; Chanock, R.M.; Shvedoff, R.A.; Stewart, C.E. An Epidemiologic Study of Altered Clinical Reactivity to Respiratory Syncytial (RS) Virus Infection in Children Previously Vaccinated with an Inactivated RS Virus Vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulginiti, V.A.; Eller, J.J.; Sieber, O.F.; Joyner, J.W.; Minamitani, M.; Meiklejohn, G. Respiratory virus immunization. I. A field trial of two inactivated respiratory virus vaccines; an aqueous trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine and an alum-precipitated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Openshaw, P.J. Potential therapeutic implications of new insights into respiratory syncytial virus disease. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, P.L.; Caballero, M.T.; Polack, F.P. Brief History and Characterization of Enhanced Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, A.; Nakayama, T. Experimental animal model for analyzing immunobiological responses following vaccination with formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, A.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Immunopathogenesis associated with formaldehyde-inactivated RSV vaccine in preclinical and clinical studies. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 16, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, G.A.; Curtis, S.J.; Yim, K.C.; Porter, D.D. Vaccine-enhanced respiratory syncytial virus disease in cotton rats following immunization with Lot 100 or a newly prepared reference vaccine. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2881–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Ohrum, K.; Cayatte, C.; Bennett, A.S.; Rajani, G.M.; McTamney, P.; Nacel, K.; Hostetler, I.; Cheng, L.; Ren, K.; O’Day, T.; et al. Immunization with Low Doses of Recombinant Postfusion or Prefusion Respiratory Syncytial Virus F Primes for Vaccine-Enhanced Disease in the Cotton Rat Model Independently of the Presence of a Th1-Biasing (GLA-SE) or Th2-Biasing (Alum) Adjuvant. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02180-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, S.K.; Beeler, J.A.; Roberts, J.N. Summary of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee meeting held to consider evaluation of vaccine candidates for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus disease in RSV-naïve infants. Vaccine 2020, 38, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krarup, A.; Truan, D.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Bogaert, L.; Bouchier, P.; Bisschop, I.J.M.; Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Zahn, R.; Schuitemaker, H.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van der Fits, L.; Bolder, R.; Heemskerk-van der Meer, M.; Drijver, J.; van Polanen, Y.; Serroyen, J.; Langedijk, J.P.M.; Schuitemaker, H.; Saeland, E.; Zahn, R. Adenovector 26 encoded prefusion conformation stabilized RSV-F protein induces long-lasting Th1-biased immunity in neonatal mice. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Bastian, A.R.; Feldman, R.A.; Omoruyi, E.; de Paepe, E.; Hendriks, J.; van Zeeburg, H.; Godeaux, O.; Langedijk, J.P.M.; Schuitemaker, H.; et al. Phase 1 Safety and Immunogenicity Study of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine with an Adenovirus 26 Vector Encoding Prefusion F (Ad26.RSV.preF) in Adults Aged ≥60 Years. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; De Paepe, E.; DeVincenzo, J.; Gymnopoulou, E.; Menten, J.; Murray, B.; Bastian, A.R.; Vandebosch, A.; Haazen, W.; Noulin, N.; et al. Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Healthy Adults by a Single Immunization of Ad26.RSV.preF in a Human Challenge Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 226, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, A.S.V.; Virta, M.; Williams, K.; Seppa, I.; Hartvickson, R.; Greenland, M.; Omoruyi, E.; Bastian, A.R.; Haazen, W.; Salisch, N.; et al. Phase 1/2a Safety and Immunogenicity of an Adenovirus 26 Vector Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Encoding Prefusion F in Adults 18–50 Years and RSV-Seropositive Children 12–24 Months. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 227, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, J.M.; Nolan, T.M.; Rämet, M.; Richmond, P.C.; Filho, N.R.; Haazen, W.; Berg, S.P.H.v.D.; Williams, K.; Bastian, A.R.; Omoruyi, E.; et al. A Phase 1/2a Study Evaluating Safety and Immunogenicity of Ad26.RSV.preF in RSV-seronegative Toddlers Aged 12–24 Months. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeland, E.; van der Fits, L.; Bolder, R.; der Meer, M.H.-V.; Drijver, J.; van Polanen, Y.; Vaneman, C.; Tettero, L.; Serroyen, J.; Schuitemaker, H.; et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of adenoviral and subunit RSV vaccines based on stabilized prefusion F protein in pre-clinical models. Vaccine 2022, 40, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhvalova, M.S.; Yim, K.C.; Prince, G.A.; Blanco, J.C. Methods for Monitoring Dynamics of Pulmonary RSV Replication by Viral Culture and by Real-Time Reverse Transcription–PCR In Vivo: Detection of Abortive Viral Replication. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2010, 46, 26.6.1–26.6.19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotard, A.L.; Shaikh, F.Y.; Lee, S.; Yan, D.; Teng, M.N.; Plemper, R.K.; Crowe, J.E.; Moore, M.L. A stabilized respiratory syncytial virus reverse genetics system amenable to recombination-mediated mutagenesis. Virology 2012, 434, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, F.; Saeland, E.; Thoma, A.; Hoogen, W.v.D.; Tettero, L.; Drijver, J.; Vaneman, C.; van Polanen, Y.; Ritschel, T.; Bastian, A.R.; et al. RSV A2-Based Prefusion F Vaccine Candidates Induce RSV A and RSV B Cross Binding and Neutralizing Antibodies and Provide Protection against RSV A and RSV B Challenge in Preclinical Models. Vaccines 2023, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourassa, M.-H.; Lands, L.C. Preventative therapies for respiratory Syncytial virus (RSV) in children: Where are we now? Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2023, 49, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Weinberg, G.A.; Iwane, M.K.; Blumkin, A.K.; Edwards, K.M.; Staat, M.A.; Auinger, P.; Griffin, M.R.; Poehling, K.A.; Erdman, D.; et al. The Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Young Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanovich, J.L.; Eichinger, K.M.; Lipp, M.A.; Gidwani, S.V.; Brahmbhatt, D.; Yondola, M.A.; Perkins, T.N.; Empey, K.M. Exacerbated lung inflammation following secondary RSV exposure is CD4+ T cell-dependent and is not mitigated in infant BALB/c mice born to PreF-vaccinated dams. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1206026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karron, R.A.; Luongo, C.; Mateo, J.S.; Wanionek, K.; Collins, P.L.; Buchholz, U.J. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine RSV/ΔNS2/Δ1313/I1314L in RSV-Seronegative Children. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 222, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.A.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.; Jorquera, P.; Narayanan, E.; Elbashir, S.; Kaplonek, P.; Ma, L.; Hunter, N.; Hanahoe, E.; Ketova, T.; et al. Design and preclinical assessment of mRNA-1345 prefusion F glycoprotein-encoding mRNA vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus. Vaccine 2025, 63, 127589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
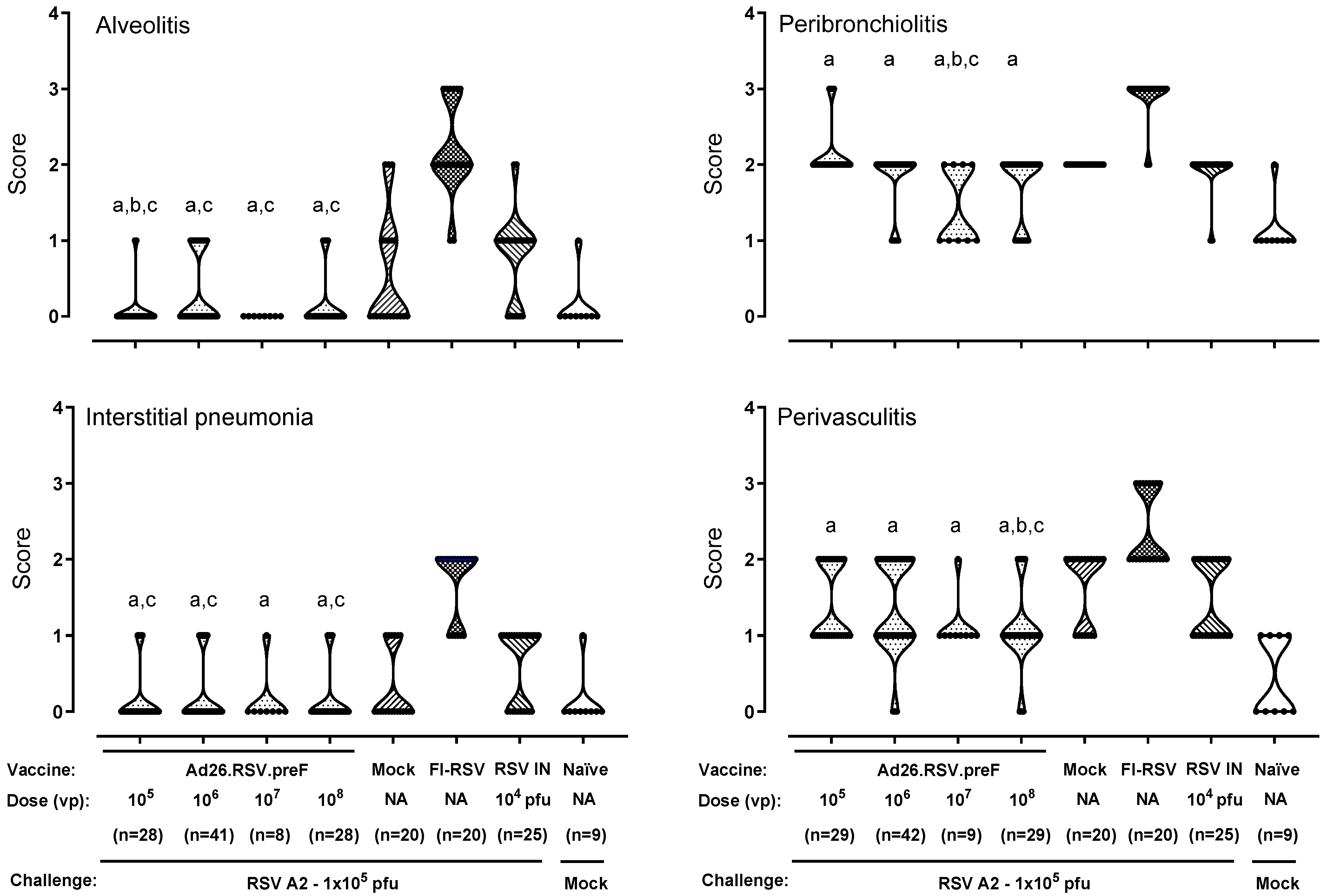
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Bolder, R.; King, S.B.S.; Zahn, R.C.; van der Fits, L. Adenovector 26 Encoded RSV Prefusion F Protein (Ad26.RSV.preF) Does Not Predispose to Enhanced Respiratory Disease in Preclinical Rodent Models. Vaccines 2026, 14, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines14010087
Bolder R, King SBS, Zahn RC, van der Fits L. Adenovector 26 Encoded RSV Prefusion F Protein (Ad26.RSV.preF) Does Not Predispose to Enhanced Respiratory Disease in Preclinical Rodent Models. Vaccines. 2026; 14(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines14010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolder, Renske, Susan B. S. King, Roland C. Zahn, and Leslie van der Fits. 2026. "Adenovector 26 Encoded RSV Prefusion F Protein (Ad26.RSV.preF) Does Not Predispose to Enhanced Respiratory Disease in Preclinical Rodent Models" Vaccines 14, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines14010087
APA StyleBolder, R., King, S. B. S., Zahn, R. C., & van der Fits, L. (2026). Adenovector 26 Encoded RSV Prefusion F Protein (Ad26.RSV.preF) Does Not Predispose to Enhanced Respiratory Disease in Preclinical Rodent Models. Vaccines, 14(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines14010087





