Chimeric VLPs Bearing VP60 from Two Serotypes of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Are Protective against Both Viruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Cell Culture and Baculoviruses
2.2. Construction of Recombinant Baculoviruses
2.3. Production of Recombinant Proteins in Insect Pupae
2.4. Protein Recovery from Infected Pupae
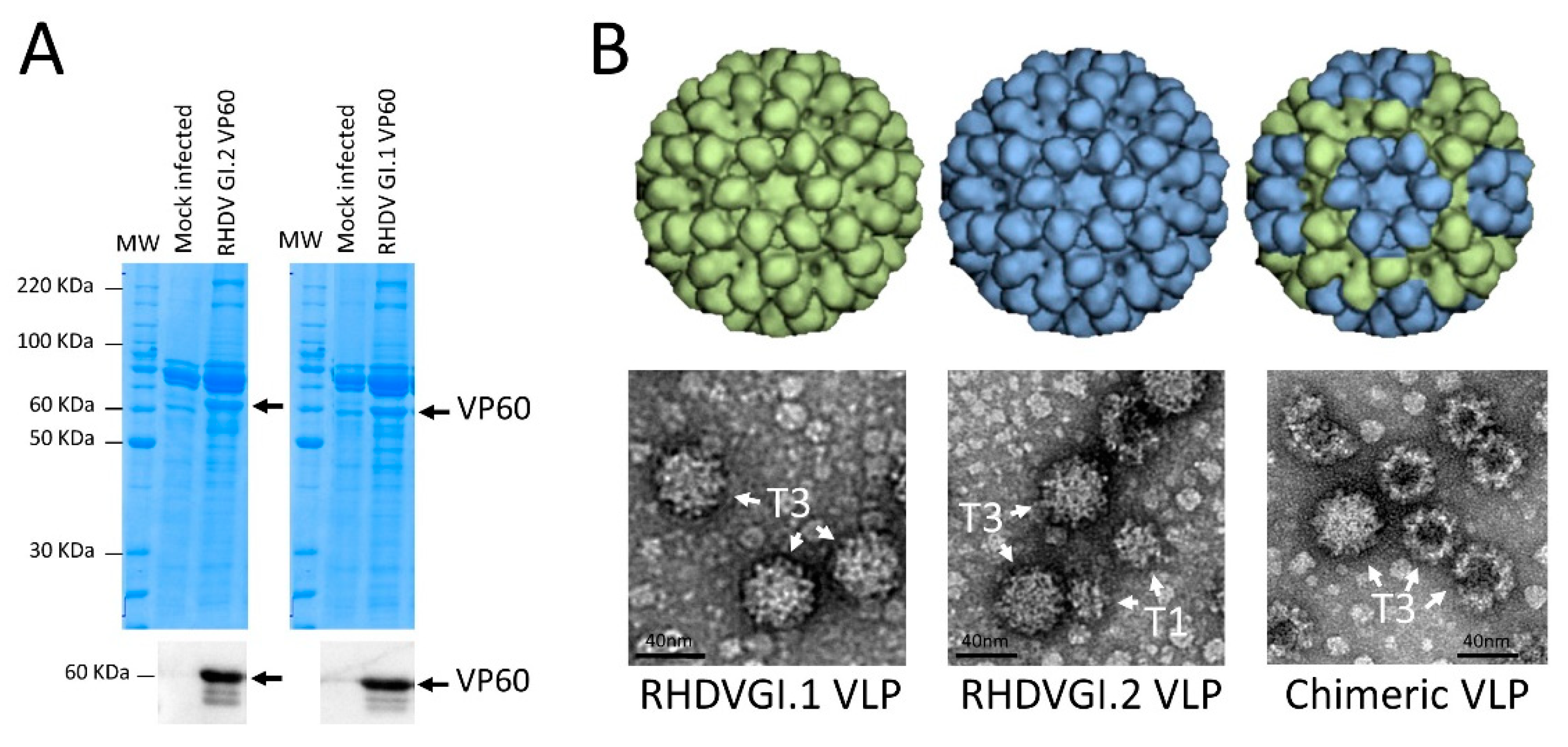
2.5. Electron Microscopy Analysis of VLP
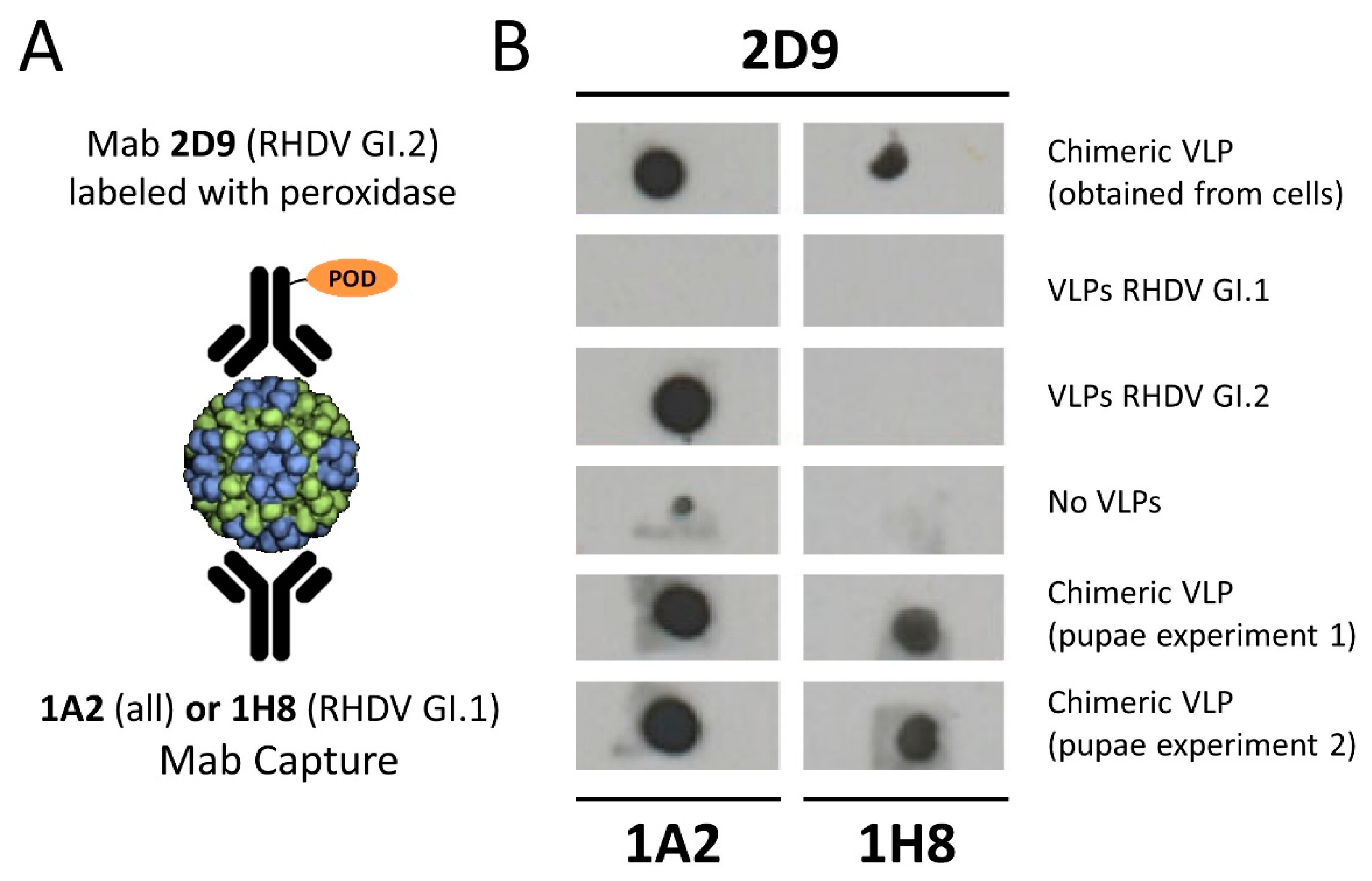
2.6. Dot Blot Analysis of Chimeric VLPs
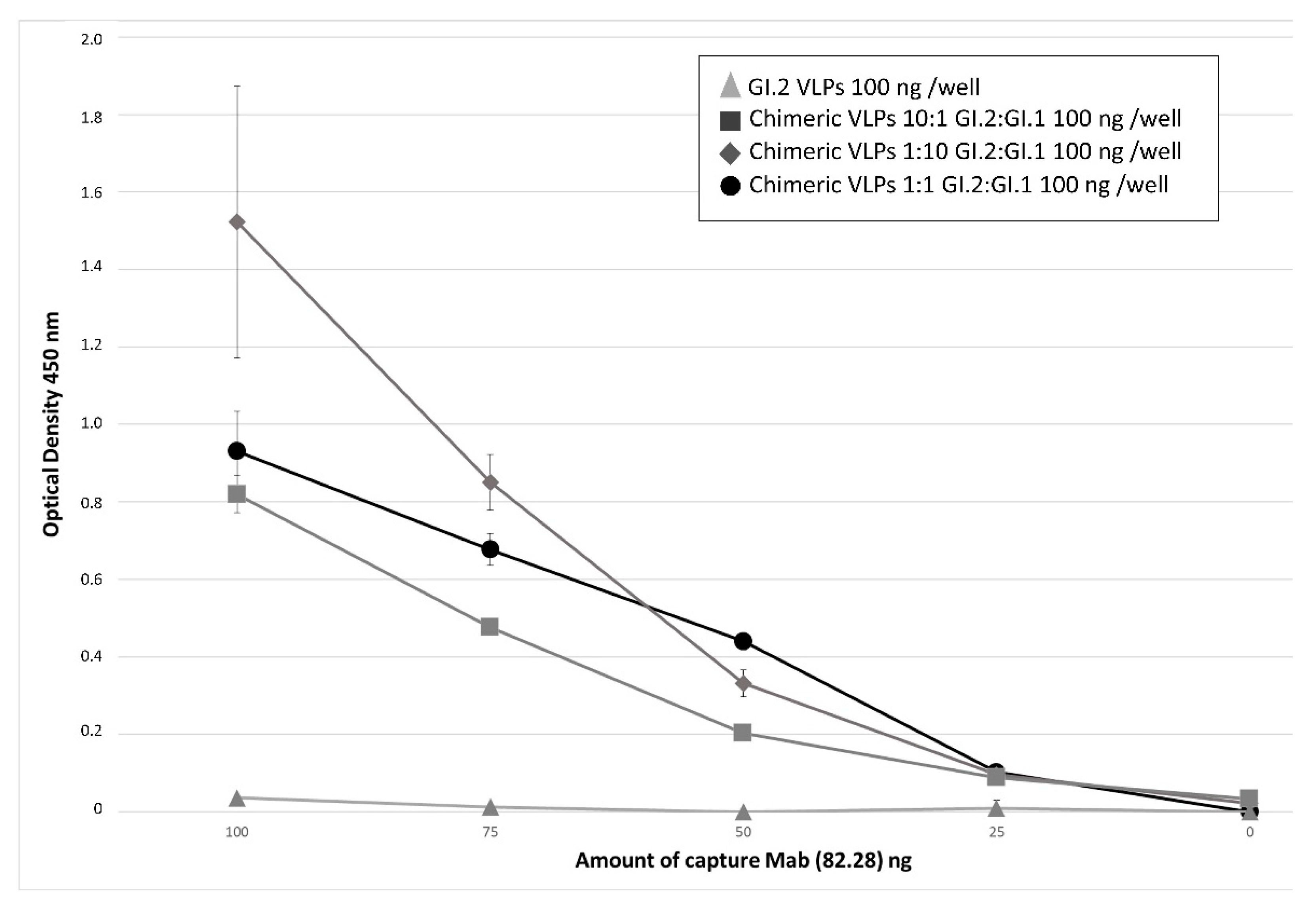
2.7. ELISAs for the Detection of Chimeric VLPs
2.8. Experimental Challenge and Ethical Considerations
- Group A: Non-vaccinated controls.
- Group B: 20 µg chimeric VLPs.
- Group C: 40 µg chimeric VLPs.
- Group D: 5 µg RHDV G1 VLPs + 5 µg RHDVb VLPs.
- Group E: Non-vaccinated controls.
- Group F: 40 µg chimeric VLPs.
2.9. Virus Isolate Used for Challenge
2.10. Detection of RHDV Specific Antibodies by ELISA
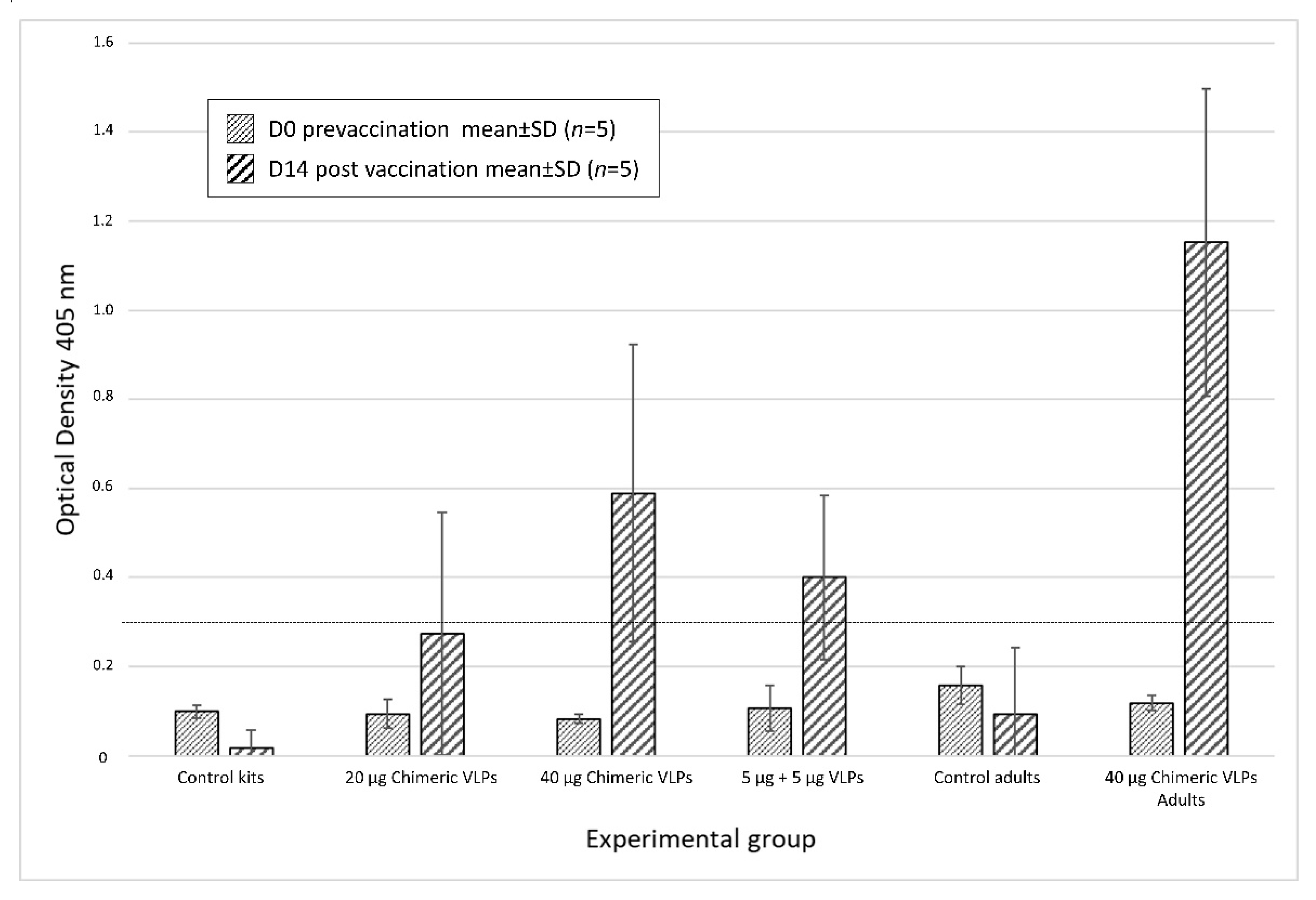
3. Results
3.1. Expression of VP60 Proteins and VLP Conformation
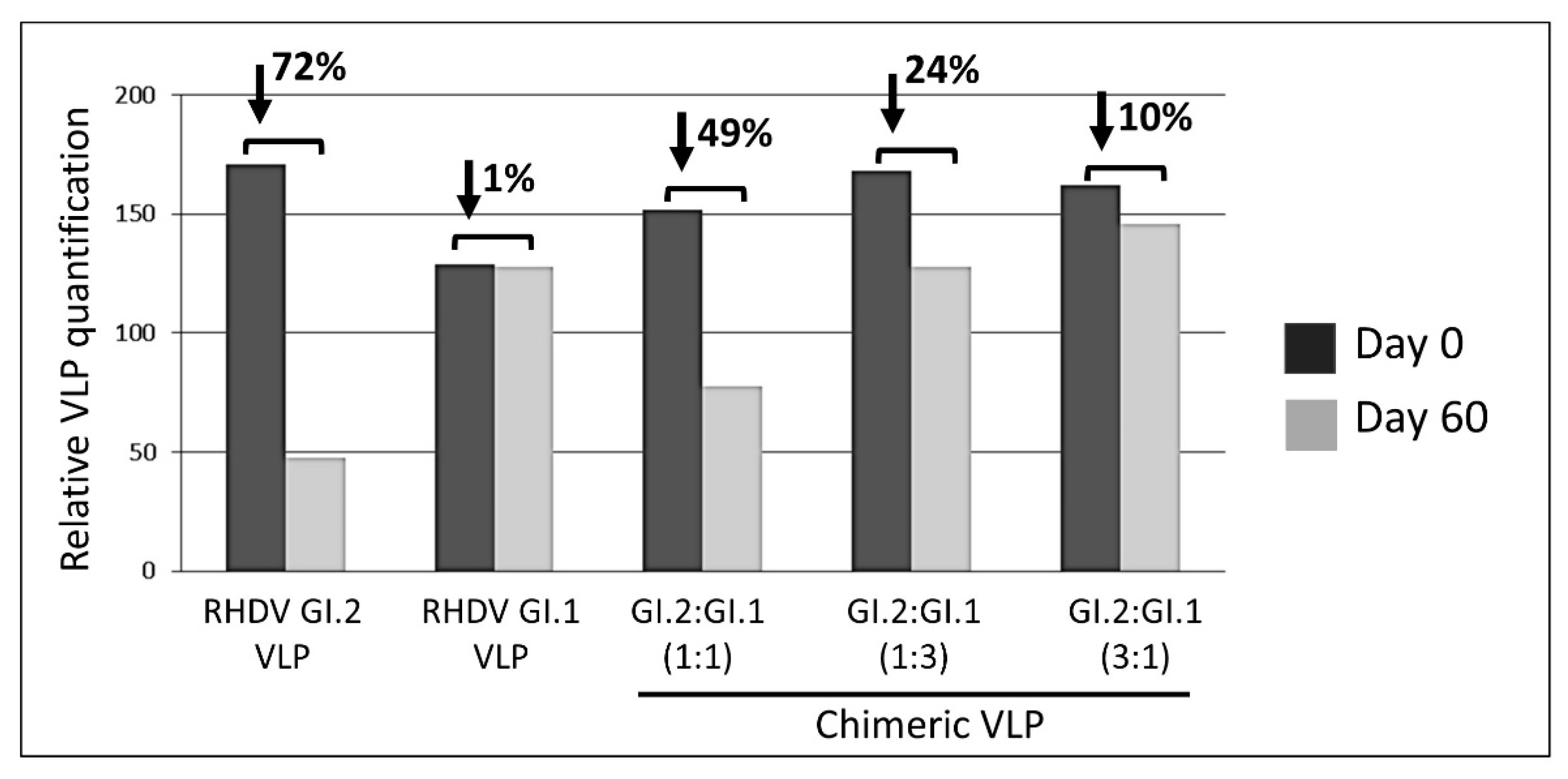
3.2. Relevance of Recombinant Baculovirus Ratios Used in Co-Infections on the Stability of the Chimeric VLP
3.3. Chimeric VLPs Protect Rabbits against a Lethal Challenge with RHDV GI.1 and RHDV GI.2 Viruses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooke, B.D. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease: Field epidemiology and the management of wild rabbit populations. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2002, 21, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moss, S.R.; Turner, S.L.; Trout, R.C.; White, P.J.; Hudson, P.; Desai, A.; Armesto, M.; Forrester, N.L.; Gould, E.A. Molecular epidemiology of Rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlinger, V.F.; Haas, B.; Meyers, G.; Weiland, F.; Thiel, H.J. Identification and characterization of the virus causing rabbit hemorrhagic disease. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3331–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Meng, C.; Wu, R.; Liu, G. Protective immune responses in rabbits induced by a suicidal DNA vaccine of the VP60 gene of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, F.; Prieto, M. Purification and characterization of a calicivirus as the causative agent of a lethal hemorrhagic disease in rabbits. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4013–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyers, G.; Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus-molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of a calicivirus genome. Virology 1991, 184, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, G.; Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H.J.; Thumfart, J.O. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: Genome organization and polyprotein processing of a calicivirus studied after transient expression of cDNA constructs. Virology 2000, 276, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boga, J.; Marín, M.; Casais, R.; Prieto, M.; Parra, F. In vitro translation of a subgenomic mRNA from purified virions of the Spanish field isolate AST/89 of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus (RHDV). Virus Res. 1992, 26, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, F.; Boga, J.A.; Marin, M.; Casais, R. The amino terminal sequence of VP60 from rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus supports its putative subgenomic origin. Virus Res. 1993, 27, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.V.V.; Matson, D.O.; Smith, A.W. Three-dimensional Structure of Calicivirus. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 240, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villares, J.A. Viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits: Vaccination and immune response. Rev. Sei. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 1991, 10, 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Filgueira, D.; Resino-Talavan, P.; Cubillos-Zapata, C.; Angulo, I.; Barderas, M.; Barcena, J.; Escribano, J. Development of a low-cost, insect larvae-derived recombinant subunit vaccine against RHDV. Virology 2007, 364, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushnir, N.; Streatfield, S.J.; Yusibov, V. Virus-like particles as a highly efficient vaccine platform: Diversity of targets and production systems and advances in clinical development. Vaccine 2012, 31, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgacic, E.V.L.; Anderson, D.A. Virus-like particles: Passport to immune recognition. Methods 2006, 40, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deml, L.; Speth, C.; Dierich, M.P.; Wolf, H.; Wagner, R. Recombinant HIV-1 Pr55gag virus-like particles: Potent stimulators of innate and acquired immune responses. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chackerian, B. Virus-like particles: Flexible platforms for vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2007, 6, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, P.J.; Kitchen, A.; Holmes, E.C. Origin and Phylodynamics of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12129–12138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, M.T.; Behan, S.C.; Mohamed, F.M.; Lu, Z.; Moran, E.K.; Burrage, T.G.; Neilan, J.G.; Ward, G.B.; Botti, G.; Capucci, L.; et al. A pandemic strain of calicivirus threatens rabbit industries in the Americas. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Pendu, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guitton, J.-S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lopes, A.; Marchandeau, S.; Alda, F.; Almeida, T.; Célio, A.P.; et al. Proposal for a unified classification system and nomenclature of lagoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.; Parra, F. Spread of new variant RHDV in domestic rabbits on the Iberian Peninsula. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Balseiro, A.; Muguerza, M.A.; Rosell, J.M.; Casais, R.; Álvarez, L.; Parra, F. Variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in young rabbits, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Boucher, S.; Le Normand, B.; Plassiart, G.; Portejoie, Y.; Decors, A.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guérin, J.-L.; Marchandeau, S. Detection of a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capucci, L.; Cavadini, P.; Schiavitto, M.; Lombardi, G.; Lavazza, A. Increased pathogenicity in rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus type 2 (RHDV2). Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boga, J.A.; Casais, R.; Marin, M.S.; Martin-Alonso, J.M.; Cármenes, R.S.; Prieto, M.; Parra, F. Molecular cloning, sequencing and expression in Escherichia coli of the capsid protein gene from rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (Spanish isolate AST/89). J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 2409–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boga, J.A.; Alonso, J.M.M.; Casais, R.; Parra, F. A single dose immunization with rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus major capsid protein produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae induces protection. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castañón, S.; Marín, M.S.; Martín-Alonso, J.M.; Boga, J.A.; Casais, R.; Humara, J.M.; Ordás, R.J.; Parra, F. Immunization with Potato Plants Expressing VP60 Protein Protects against Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4452–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Fernández, M.R.; Mouriño, M.; Rivera, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Plana-Durán, J.; García, J.A. Protection of Rabbits against Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus by Immunization with the VP60 Protein Expressed in Plants with a Potyvirus-Based Vector. Virology 2001, 280, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertagnoli, S.; Gelfi, J.; Le Gall, G.; Boilletot, E.; Vautherot, J.F.; Rasschaert, D.; Laurent, S.; Petit, F.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Milon, A. Protection against myxomatosis and rabbit viral hemorrhagic disease with recombinant myxoma viruses expressing rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus capsid protein. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5061–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertagnoli, S.; Gelfi, J.; Petit, F.; Vautherot, J.; Rasschaert, D.; Laurent, S.; Le Gall, G.; Boilletot, E.; Chantal, J.; Boucraut-Baralon, C. Protection of rabbits against rabbit viral haemorrhagic disease with a vaccinia-RHDV recombinant virus. Vaccine 1996, 14, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L. A recombinant canarypox virus protects rabbits against a lethal rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) challenge. Vaccine 1997, 15, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Vautherot, J.; Madelaine, O.; le Gall, G.; Rasschaertl, D. Recombinant Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Capsid Protein Expressed in Baculovirus Self-Assembles into Viruslike Particles and Induces Protection. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6794–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marín, M.S.; Alonso, J.M.; García, L.I.P.O.; Boga, J.A.; Argüello-Villares, J.; Casais, R.; Venugopal, K.; Jiang, W.; Gould, E.A.; Parra, F. Immunogenic properties of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus structural protein VP60 expressed by a recombinant baculovirus: An efficient vaccine. Virus Res. 1995, 39, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesha, H.S.; Wang, L.F.; Hyatt, A.D.; Morrissy, C.J.; Lenghaus, C.; Westbury, H.A. Self-assembly, antigenicity, and immunogenicity of the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (Czechoslovakian strain V-351) capsid protein expressed in baculovirus. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibilia, M.; Boniotti, M.B.; Angoscini, P.; Capucci, L.; Rossi, C. Two Independent Pathways of Expression Lead to Self-Assembly of the Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 5812–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escribano, J.M.; Cid, M.; Reytor, E.; Alvarado, C.; Nuñez, M.C.; Martínez-Pulgarín, S.; Dalton, R.M. Chrysalises as natural production units for recombinant subunit vaccines. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 324S, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Vidal, J.; Gómez-Sebastián, S.; Barcena, J.; Nuñez, M.D.C.; Martínez-Alonso, D.; Dudognon, B.; Guijarro, E.; Escribano, J.M. Improved production efficiency of virus-like particles by the baculovirus expression vector system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Sebastian, S.; López-Vidal, J.; Escribano, J.M. Significant productivity improvement of the baculovirus expression vector system by engineering a novel expression cassette. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96562. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, K.P.; Arnal, J.L.; Benito, A.A.; Chacón, G.; Alonso, J.M.M.; Parra, F. Conventional and real time RT-PCR assays for the detection and differentiation of variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDVb) and its recombinants. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 251, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, C.; Mendoza, M.; Alcaraz, A.; Sarto, M.P.; Jiménez-de-Bagüéss, M.P.; Calvo, A.J.; Monroy, F.; Calvo, J.H. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease: Cross-protection and comparative pathogenicity of GI.2/RHDV2/b and GI.1b/RHDV lagoviruses in a challenge trial. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahar, J.E.; Hall, R.N.; Peacock, D.; Kovaliski, J.; Piper, M.; Mourant, R.; Huang, N.; Campbell, S.; Gu, X.; Read, A.; et al. Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 (RHDV2; GI.2) Is Replacing Endemic Strains of RHDV in the Australian Landscape within 18 Months of Its Arrival. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01374-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, N.; Mena, I.; Angulo, I.; Gómez, Y.; Crisci, E.; Montoya, M.; Caston, J.; Blanco, E.; Bárcena, J. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus capsid, a versatile platform for foreign B-cell epitope display inducing protective humoral immune responses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debbink, K.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Swanstrom, J.; Baric, R.S. Chimeric GII.4 Norovirus Virus-Like-Particle-Based Vaccines Induce Broadly Blocking Immune Responses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7256–7266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzeyung, A.S.; Shadab; Bhattamisra, S.K.; Madheswaran, T.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Fabrication, Optimization, and Evaluation of Rotigotine-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for Nose-To-Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K.; Atmar, R.L. Prospects and Challenges in the Development of a Norovirus Vaccine. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Treanor, J.J.; Atmar, R.L.; Frey, S.E.; Gormley, R.; Chen, W.H.; Ferreira, J.; Goodwin, R.; Borkowski, A.; Clemens, R.; Mendelman, P.M. A Novel Intramuscular Bivalent Norovirus Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Candidate-Reactogenicity, Safety, and Immunogenicity in a Phase 1 Trial in Healthy Adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verardi, R.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Gorman, J.; Chuang, G.-Y.; Edwards, C.E.; Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Mallory, M.L.; Ou, L.; Schön, A.; et al. Disulfide stabilization of human norovirus GI.1 virus-like particles focuses immune response toward blockade epitopes. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Age | Vaccination | Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 30 d | PBS | RHDVGI.2 |
| B | 30 d | 20 µg Chimeric VLPs | RHDVGI.2 |
| C | 30 d | 40 µg Chimeric VLPs | RHDVGI.2 |
| D | 30 d | 5 µg RHDVGI.2 VLPs + 5 µg RHDVGI.1 VLPs | RHDVGI.2 |
| E | 60 d | PBS | RHDVGI.1 |
| F | 60 d | 40 µg Chimeric VLPs | RHDVGI.1 |
| Group | Vaccination | Virus Challenge | Mortality | Virus Genome Detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | PBS | RHDVGI.2 | 4/5 | 5/5 |
| B | 20 µg chimeric VLP | RHDVGI.2 | 1/5 | 1/5 |
| C | 40 µg chimeric VLP | RHDVGI.2 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| D | 5 µg RHDVGI.1 VLP +5 µg RHDVGI.2 VLP | RHDVGI.2 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| E | PBS | RHDVGI.1 | 4/5 | nd |
| F | 40 µg chimeric VLP | RHDVGI.1 | 0/5 | nd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalton, K.P.; Alvarado, C.; Reytor, E.; del Carmen Nuñez, M.; Podadera, A.; Martínez-Alonso, D.; Alonso, J.M.M.; Nicieza, I.; Gómez-Sebastián, S.; Dalton, R.M.; et al. Chimeric VLPs Bearing VP60 from Two Serotypes of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Are Protective against Both Viruses. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091005
Dalton KP, Alvarado C, Reytor E, del Carmen Nuñez M, Podadera A, Martínez-Alonso D, Alonso JMM, Nicieza I, Gómez-Sebastián S, Dalton RM, et al. Chimeric VLPs Bearing VP60 from Two Serotypes of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Are Protective against Both Viruses. Vaccines. 2021; 9(9):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091005
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalton, Kevin P., Carmen Alvarado, Edel Reytor, Maria del Carmen Nuñez, Ana Podadera, Diego Martínez-Alonso, Jose Manuel Martin Alonso, Ines Nicieza, Silvia Gómez-Sebastián, Romy M. Dalton, and et al. 2021. "Chimeric VLPs Bearing VP60 from Two Serotypes of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Are Protective against Both Viruses" Vaccines 9, no. 9: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091005
APA StyleDalton, K. P., Alvarado, C., Reytor, E., del Carmen Nuñez, M., Podadera, A., Martínez-Alonso, D., Alonso, J. M. M., Nicieza, I., Gómez-Sebastián, S., Dalton, R. M., Parra, F., & Escribano, J. M. (2021). Chimeric VLPs Bearing VP60 from Two Serotypes of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Are Protective against Both Viruses. Vaccines, 9(9), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091005






