Generation and Characterization of a Spike Glycoprotein Domain A-Specific Neutralizing Single-Chain Variable Fragment against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
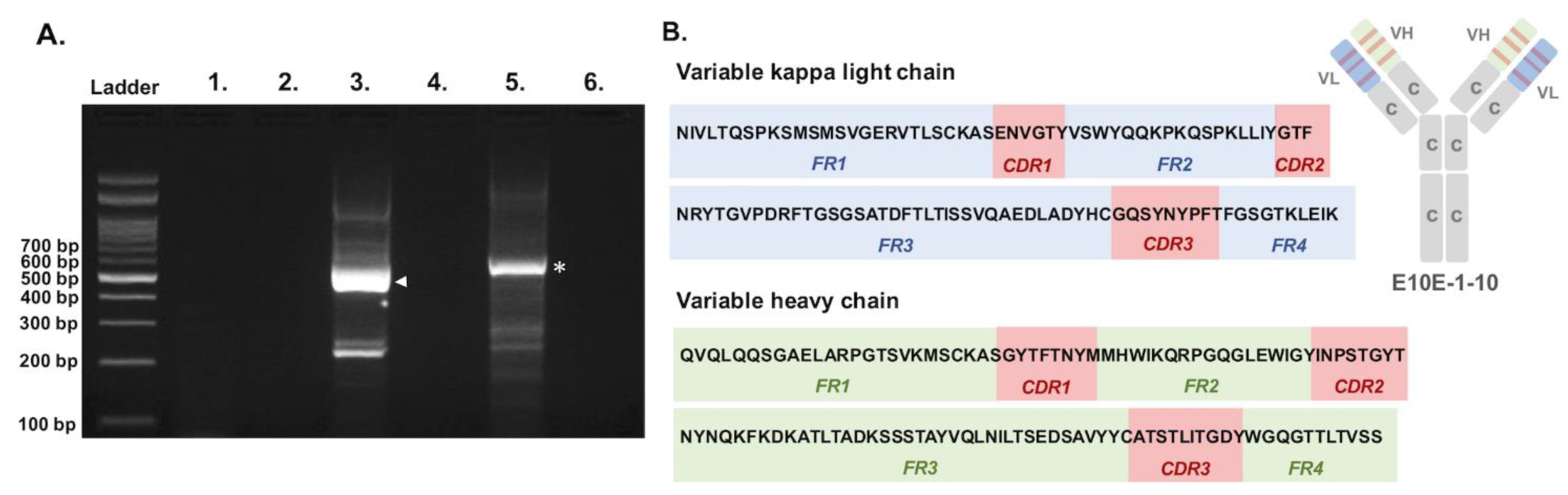
2.1. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription of the Variable Regions of PEDV S1A-Specific mAb
2.2. Touchdown PCR for Amplifying the Variable Regions of PEDV S1A-Specific NmAb
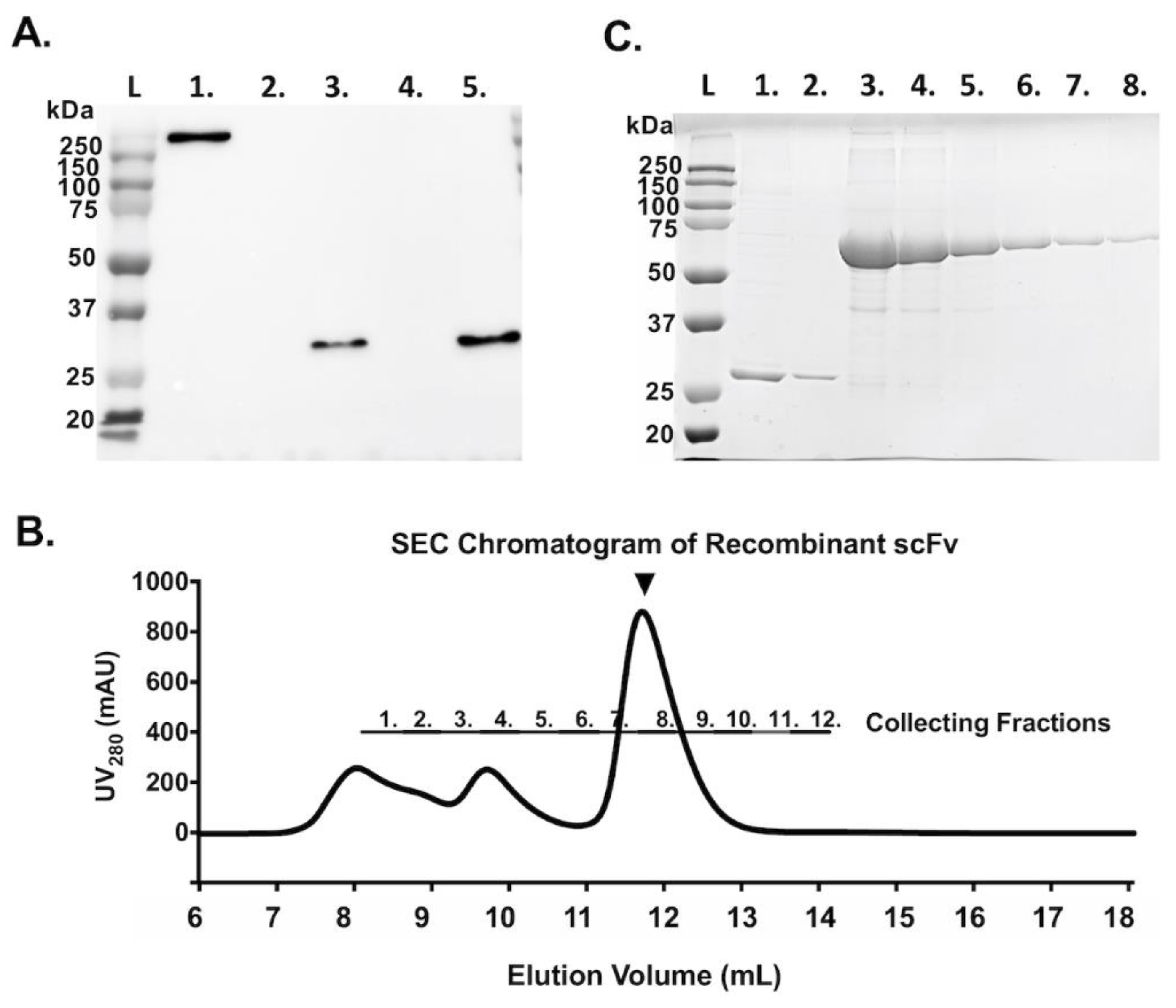
2.3. Construction and Expression of the Single-Chain Variable Fragment (scFv)
2.4. Purification of scFv by Using Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) and Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
2.5. Validation of the scFv by Immunocytochemical Staining (ICC) and Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.6. Binding Ability Estimation of scFv toward Homogenous and Heterogeneous PEDV Virions by Indirect ELISAs
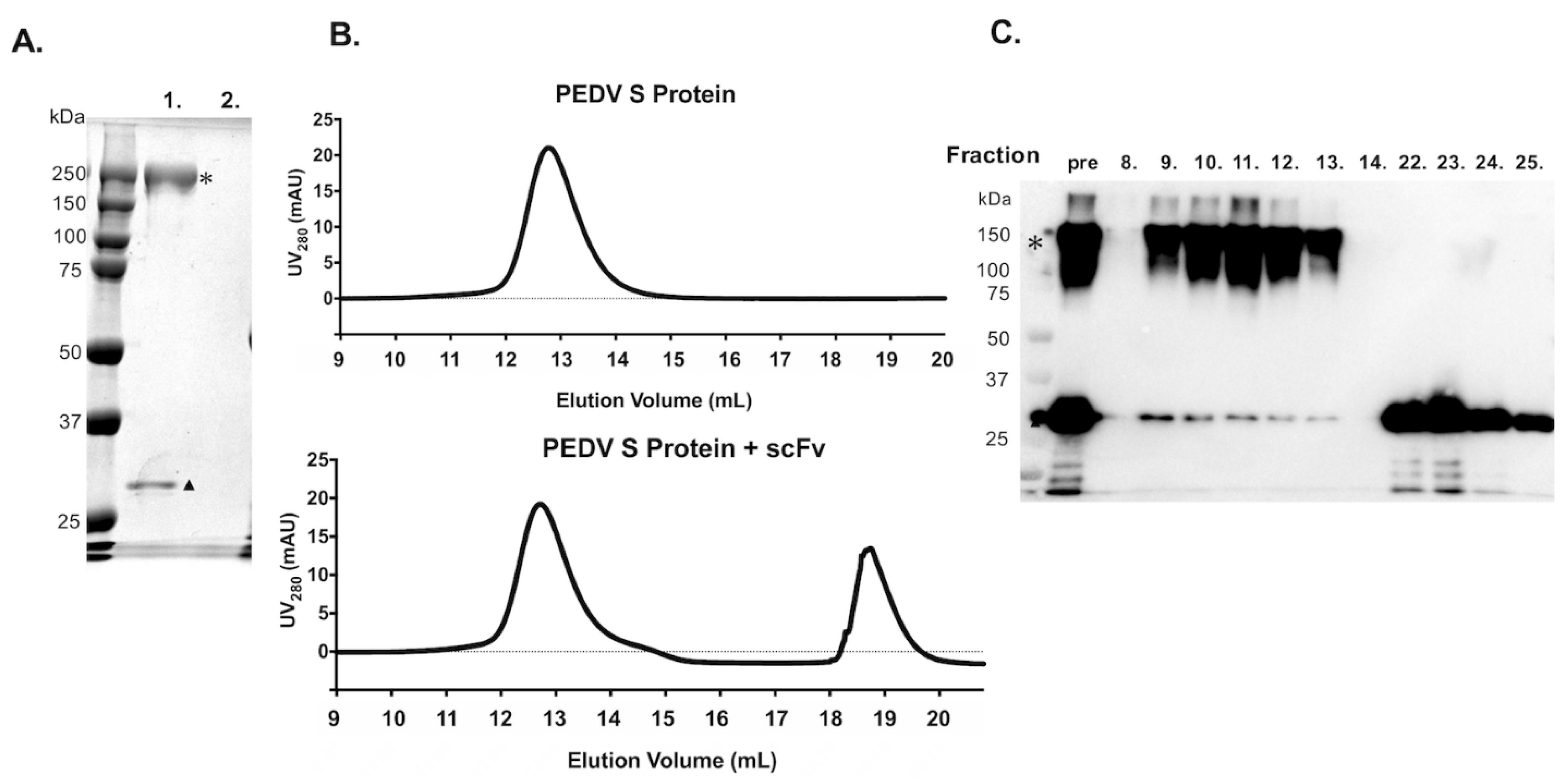
2.7. Binding Ability of scFv with Purified PEDV S Protein by Using Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.8. Estimation of Binding Ability between scFv and PEDV S Protein by SEC
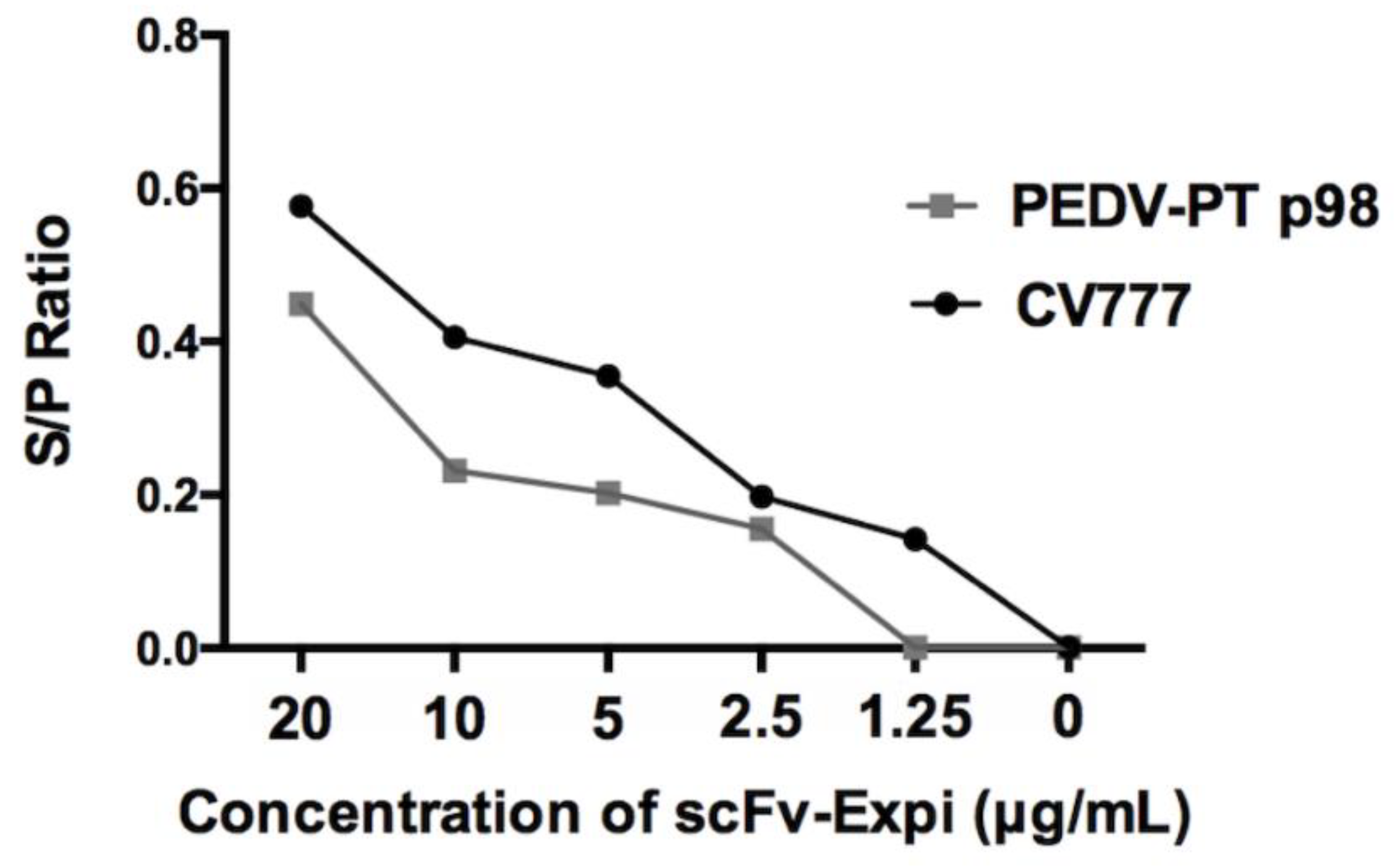
2.9. Neutralizing Test
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing of the Variable Regions of Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody
3.2. Construction, Expression, and Purification of scFv from Expi293F™ Cells
3.3. Binding Ability Estimation of scFv toward Homogenous and Heterogeneous PEDV Virions by Immunostainings and ELISA
3.4. Binding Ability of scFv with Purified PEDV S Protein by Using Pull-Down Assay and SEC
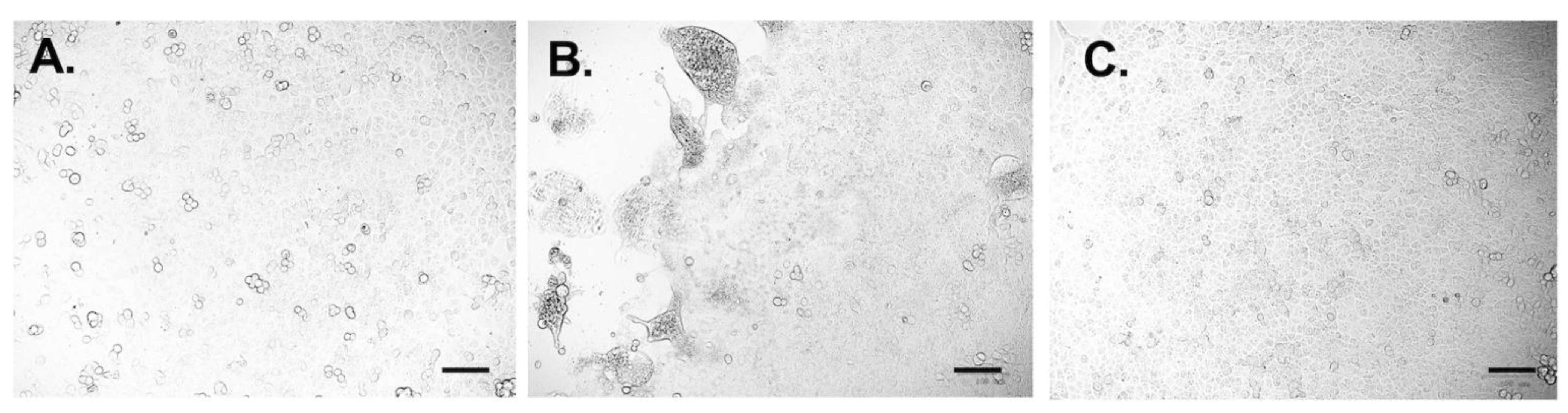
3.5. Neutralizing Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV): An Update on Etiology, Transmission, Pathogenesis, and Prevention and Control. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus: An Emerging and Re-emerging Epizootic Swine Virus. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pensaert, M.B.; de Bouck, P. A New Coronavirus-like Particle Associated with Diarrhea in Swine. Arch. Virol. 1978, 58, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection: Etiology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Immunoprophylaxis. Vet. J. 2015, 204, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karte, C.; Platje, N.; Bullermann, J.; Beer, M.; Höper, D.; Blome, S. Re-emergence of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in A Piglet-producing Farm in Northwestern Germany in 2019. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fang, L.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Zhu, X.; Miao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S. Evolutionary and Genotypic Analyses of Global Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Strains. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.-L.; Deng, M.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Jeng, C.-R.; Tsai, P.-S.; Yang, C.; Pang, V.F.; Chang, H.-W. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Spike (S) Gene of the New Variants of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus in Taiwan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-W.; Dickerman, A.W.; Piñeyro, P.; Li, L.; Fang, L.; Kiehne, R.; Opriessnig, T.; Meng, X.-J. Origin, Evolution, and Genotyping of Emergent Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Strains in the United States. mBio 2013, 4, e00737-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antas, M.; Woźniakowski, G. Current Status of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea (PED) in European Pigs. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and Re-emerging Coronaviruses in Pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederwerder, M.C.; Hesse, R.A. Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease: A Review of 4 Years with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus and Porcine Deltacoronavirus in the United States and Canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langel, S.N.; Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Host Factors Affecting Generation of Immunity Against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in Pregnant and Lactating Swine and Passive Protection of Neonates. Pathogens 2020, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chattha, K.S.; Roth, J.A.; Saif, L.J. Strategies for Design and Application of Enteric Viral Vaccines. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2015, 3, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Lim, J.; Noh, Y.H.; Yoon, I.; Yoo, H.S. Efficacy of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines 2020, 8, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, K.; Lager, K.M.; Kulshreshtha, V.; Miller, L.C.; Faaberg, K.S. Status of Vaccines for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in the United States and Canada. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.S. The 3.1 Å Cryo-electron Microscopy Structure of the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Spike Protein in the Prefusion Conformation. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00923-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; de Esesarte, E.L.; Guo, H.; van den Elzen, P.; Aarts, E.; van den Born, E.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Bosch, B.-J. Cell Attachment Domains of the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Spike Protein Are Key Targets of Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00273-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Cheng, I.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, P.-S.; Lai, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-L.; Jeng, C.-R.; Pang, V.F.; Chang, H.-W. Identification of Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Novel Conformational Epitopes of the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus Spike Protein. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Bae, J.L.; Kang, T.J.; Kim, J.; Chung, G.H.; Lim, C.W.; Laude, H.; Yang, M.S.; Jang, Y.S. Identification of the Epitope Region Capable of Inducing Neutralizing Antibodies against the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Mol. Cells 2002, 14, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.B.; Feng, L.; Shi, H.Y.; Chen, J.F.; Liu, S.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Y.F. Spike Protein Region (aa 636789) of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus is Essential for Induction of Neutralizing Antibodies. Acta Virol. 2007, 51, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okda, F.A.; Lawson, S.; Singrey, A.; Nelson, J.; Hain, K.S.; Joshi, L.R.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.A.; Diel, D.G. The S2 Glycoprotein Subunit of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Contains Immunodominant Neutralizing Epitopes. Virology 2017, 509, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-M.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Liu, I.J.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-Z.; Li, H.-J.; Wu, H.-C. Development of Therapeutic Antibodies for the Treatment of Diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, E.; Friede, M.; Sheikh, M.; Torvaldsen, S. Therapeutic Antibodies for Infectious Diseases. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, G.; Zhang, N.; Fu, T.-M.; An, Z. Antibody Therapies for the Prevention and Treatment of Viral Infections. Npj Vaccines 2017, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, J.G.H.; Ooi, E.E.; Vasudevan, S.G. Current Status of Dengue Therapeutics Research and Development. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S96–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachbagauer, R.; Krammer, F. Universal Influenza Virus Vaccines and Therapeutic Antibodies. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudinski, M.R.; Coates, E.E.; Novik, L.; Widge, A.; Houser, K.V.; Burch, E.; Holman, L.A.; Gordon, I.J.; Chen, G.L.; Carter, C.; et al. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Immunogenicity of the Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibody mAb114 Targeting Ebola Virus Glycoprotein (VRC 608): An Open-label Phase 1 Study. Lancet 2019, 393, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, Y.-F.; Chien, C.-S.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Luo, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Lai, W.-Y.; Yang, D.-M.; Chou, S.-J.; Yang, Y.-P.; et al. A Review of SARS-CoV-2 and the Ongoing Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bustamante-Córdova, L.; Melgoza-González, E.A.; Hernández, J. Recombinant Antibodies in Veterinary Medicine: An Update. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.P.V.; van Tilburg, M.F.; Florean, E.O.P.T.; Guedes, M.I.F. Egg Yolk Antibodies (IgY) and Their Applications in Human and Veterinary Health: A Review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.L.; Lindblad, P. A Guide for In-house Design of Template-switch-based 5′ Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends Systems. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 397, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; López, T.; Espinosa, R.; Arias, C.F.; Vollmers, C.; DuBois, R.M. A Simplified Workflow for Monoclonal Antibody Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.-C. Fusion Protein Linkers: Property, Design and Functionality. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Tsai, P.S.; Chiou, H.Y.; Jeng, C.R.; Pang, V.F.; Chang, H.W. Efficacy of Heat-labile Enterotoxin B Subunit-adjuvanted Parenteral Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Trimeric Spike Subunit Vaccine in Piglets. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7499–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langel, S.N.; Paim, F.C.; Alhamo, M.A.; Buckley, A.; Van Geelen, A.; Lager, K.M.; Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Stage of Gestation at Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection of Pregnant Swine Impacts Maternal Immunity and Lactogenic Immune Protection of Neonatal Suckling Piglets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel-Clopés, A.; Bentley, E.G.; Stewart, J.P.; Carding, S.R. Mucosal Vaccines and Technology. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L.; Zhu, J. Single Chain Fragment Variable (scFv) Antibodies Targeting the Spike Protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Provide Protection against Viral Infection in Piglets. Viruses 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beirão, B.C.B.; Raposo, T.; Jain, S.; Hupp, T.; Argyle, D.J. Challenges and Opportunities for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in Veterinary Oncology. Vet. J. 2016, 218, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michels, G.M.; Ramsey, D.S.; Walsh, K.F.; Martinon, O.M.; Mahabir, S.P.; Hoevers, J.D.; Walters, R.R.; Dunham, S.A. A Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Dose Determination Trial of Lokivetmab (ZTS-00103289), a Caninized, Anti-canine IL-31 Monoclonal Antibody in Client Owned Dogs with Atopic Dermatitis. Vet. Dermatol. 2016, 27, 478-e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Construction of ScFv that Bind Both Fibronectin-binding Protein A and Clumping Factor A of Stapylococcus Aureus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 100, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, P.; Singh, A. Staphylococcus Aureus β-hemolysin-neutralizing Single-domain Antibody Isolated from Phage Display Library of Indian Desert Camel. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2010, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Z.; Fu, F.; Jiang, F.; Tian, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Development of a Neutralizing Mouse-pig Chimeric Antibody with Therapeutic Potential Against Haemophilus Parasuis in Pichia pastoris. Fed. Eur. Microbiol. Soc. Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 354, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmsen, M.M.; Fijten, H.P.; Dekker, A.; Eblé, P.L. Passive Immunization of Pigs with Bispecific Llama Single-domain Antibody Fragments Against Foot-and-mouth Disease and Porcine Immunoglobulin. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, J.O.; Fathe, K.R.; Brunaugh, A.; Ferrati, S.; Li, S.; Montenegro-Nicolini, M.; Mousavikhamene, Z.; McConville, J.T.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Smyth, H.D.C. Challenges and Future Prospects for the Delivery of Biologics: Oral Mucosal, Pulmonary, and Transdermal Routes. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. J. 2017, 19, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahagun-Ruiz, A.; Velazquez, L.V.; Bhaskaran, S.; Jay, C.M.; Morales-Salinas, E.; Rathore, K.; Wagner, G.G.; Waghela, S.D. Reduction of Enterotoxin Induced Fluid Accumulation in Ileal Loops of Neonatal Calves with Anti-F5 Fimbriae Recombinant Antibody. Vet. Res. Commun. 2015, 39, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalafalla, R.E.; Daugschies, A. In Vivo Evaluation of Anticoccidial Effect of Antibody Fragments Expressed in Pea (Pasum sativum) on Eimeria Tenella Sporozoites. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Park, K. Oral Protein Delivery: Current Status and Future Prospect. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Template-switch oligonucleotide (TSO) | 5′-AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTACATGrGRrGr *-3′ |
| mIgK RT | 5′-TTGTCGTTCACTGCCATCAATC-3′ |
| mIgL RT | 5′-GGGGTACCATCTACCTTCCAG-3′ |
| mIgHG RT | 5′-AGCTGGGAAGGTGTGCACAC-3′ |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| ISPCR | 5′-AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAG-3′ |
| mIgKpcr | 5′-ACATTGATGTCTTTGGGGTAGAAG-3′ |
| mIgLpcr | 5′-ATCGTACACACCAGTGTGGC-3′ |
| mIgHGpcr | 5′-GGGATCCAGAGTTCCAGGTC-3′ |
| Time Post-Challenge (hr) | Concentration of scFv (µg/mL) | Protection |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 6.25 | No CPE |
| 12.5 | No CPE | |
| 25 | No CPE | |
| 48 | 6.25 | Few CPE |
| 12.5 | No CPE | |
| 25 | No CPE | |
| 72 | 6.25 | CPE |
| 12.5 | Few CPE | |
| 25 | No CPE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wu, J.-F.; Yang, T.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chae, C.; Chang, H.-W.; Hsu, S.-T.D. Generation and Characterization of a Spike Glycoprotein Domain A-Specific Neutralizing Single-Chain Variable Fragment against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Vaccines 2021, 9, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080833
Chang C-Y, Wang Y-S, Wu J-F, Yang T-J, Chang Y-C, Chae C, Chang H-W, Hsu S-TD. Generation and Characterization of a Spike Glycoprotein Domain A-Specific Neutralizing Single-Chain Variable Fragment against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Vaccines. 2021; 9(8):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080833
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chia-Yu, Yong-Sheng Wang, Jou-Fei Wu, Tzu-Jing Yang, Yen-Chen Chang, Chanhee Chae, Hui-Wen Chang, and Shang-Te Danny Hsu. 2021. "Generation and Characterization of a Spike Glycoprotein Domain A-Specific Neutralizing Single-Chain Variable Fragment against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus" Vaccines 9, no. 8: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080833
APA StyleChang, C.-Y., Wang, Y.-S., Wu, J.-F., Yang, T.-J., Chang, Y.-C., Chae, C., Chang, H.-W., & Hsu, S.-T. D. (2021). Generation and Characterization of a Spike Glycoprotein Domain A-Specific Neutralizing Single-Chain Variable Fragment against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Vaccines, 9(8), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080833







