The Beauty of Simplicity: Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reaction to Measure Cellular Immune Responses in RNA-SARS-Cov-2 Vaccinated Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Serology
2.3. Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Skin Test
3. Results
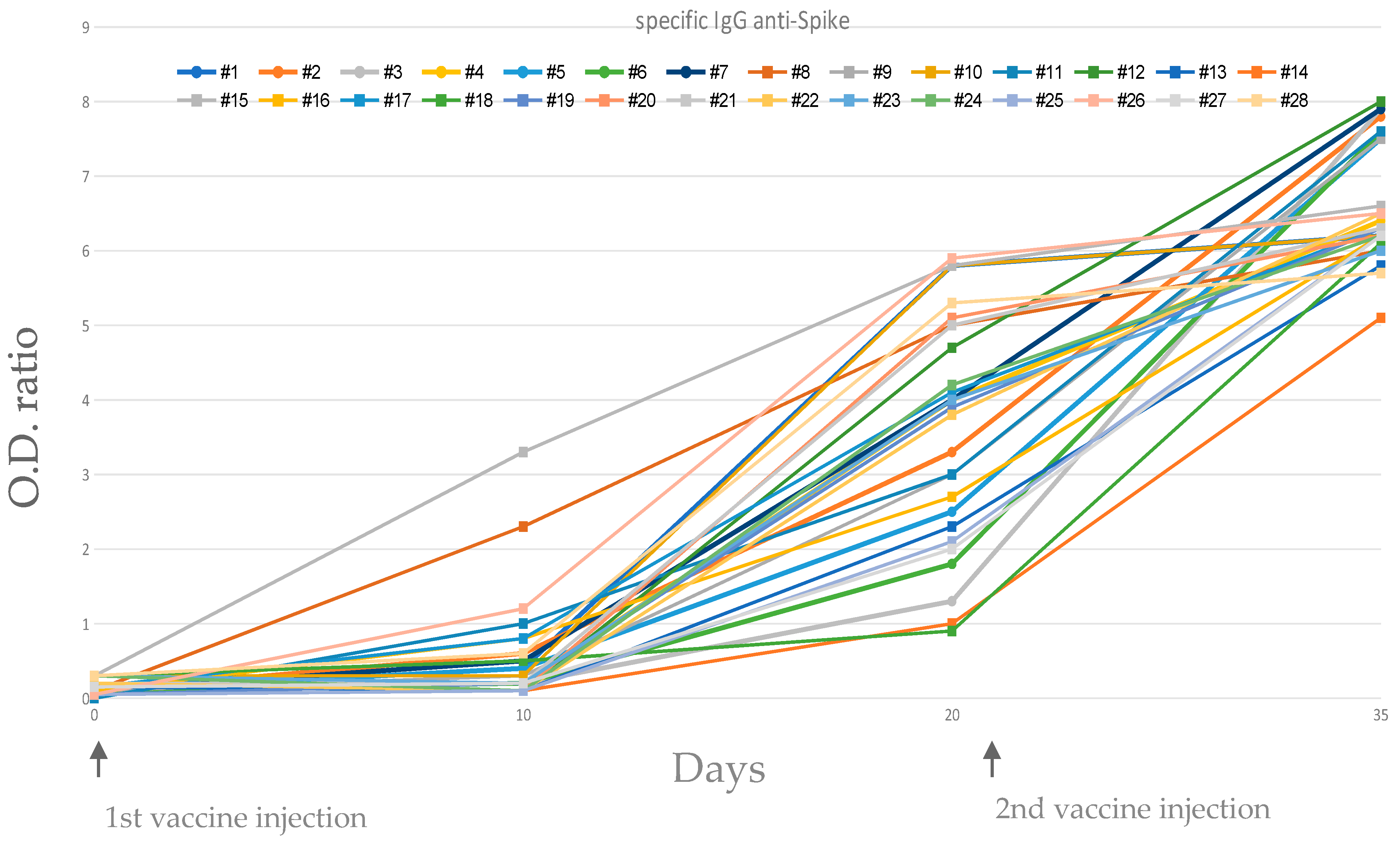
3.1. Specific IgG anti Spike
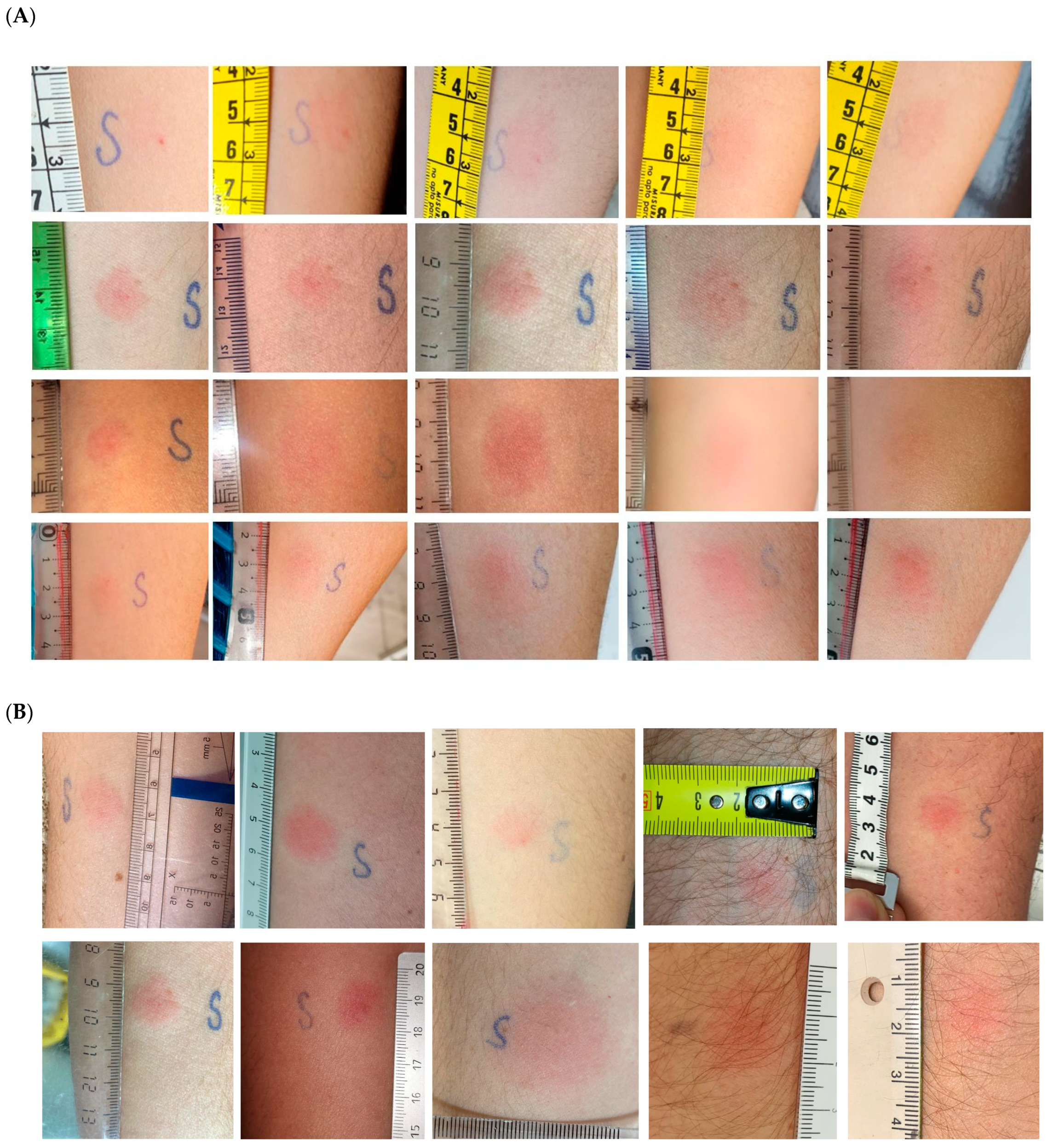
3.2. Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarzkopf, S.; Krawczyk, A.; Knop, D.; Klump, H.; Heinold, A.; Heinemann, F.M.; Thümmler, L.; Temme, C.; Breyer, M.; Witzke, O.; et al. Cellular Immunity in COVID-19 Convalescents with PCR-Confirmed Infection but with Undetectable SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgG. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Dowell, A.C.; Pearce, H.; Verma, K.; Long, H.M.; Begum, J.; Aiano, F.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Hoschler, K.; Brooks, T.; et al. Robust SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity is maintained at 6 months following primary infection. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meo, S.A.; Bukhari, I.A.; Akram, J.; Meo, A.S.; Klonoff, D.C. COVID-19 vaccines: Comparison of biological, pharmacological charac-teristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals following mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, Y.; Franco, A.; Sanchez-Machin, I.; Poza-Guedes, P.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.; Matheu, V. A novel application of delayed-type hipersensitivity reaction to measure cellular immune response in SARS-CoV-2 exposed individuals. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 226, 108730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.; Torriani, G.; Yerly, S.; Mazza, L.; Calame, A.; Arm-Vernez, I.; Zimmer, G.; Agoritsas, T.; Stirnemann, J.; Spechbach, H.; et al. Validation of a commercially available SARS-CoV-2 serological immunoassay. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, C.; Antolín, D.; Reano, M.; Valero, A.; Sastre, J. Safety and Quality Recommendations in Allergy Medicine (Spanish acronym, RESCAL). J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 28, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaro, R.; Machado, B.A.S.; Duthie, M.S.; Araujo-Neto, C.A.; Pedral-Sampaio, D.; Nakatani, M.; Reed, S.G. The single recombinant M. tuberculosis protein DPPD provides enhanced performance of skin testing among HIV-infected tuberculosis patients. Amb Express 2020, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, P.; Deb, P.K.; Al-Shar’I, N.A.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Venugopala, K.N.; Singh, V.; Shinu, P.; Hussain, S.; Deka, S.; Chandrasekaran, B.; et al. Perspectives on RNA Vaccine Candidates for COVID-19. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulter, L.; Seymour, G.; Duke, O.; Janossy, G.; Panayi, G. Immunohistological analysis of delayed-type hypersensitivity in man. Cell. Immunol. 1982, 74, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, R.; Pande, S.; Khopkar, U. Intradermal tests in dermatology-I: Tests for infectious diseases. Indian J. Derm. Venereol. Leprol. 2006, 72, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavia, C.S.; Wormser, G.P. COVID-19: Is there a role for Western blots and skin testing for determining immunity and development of a vaccine? Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 115148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sariol, A.; Perlman, S. Lessons for COVID-19 Immunity from Other Coronavirus Infections. J. Immun. 2020, 53, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; Macary, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, K.; E McElhaney, J. Immunosenescence: Influenza vaccination and the elderly. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 29, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.; Mateus, J.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Rawlings, S.A.; Sutherland, A.; Premkumar, L.; Jadi, R.S.; et al. Targets of T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus in Humans with COVID-19 Disease and Unexposed Individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hour | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 6 | 14 | 14 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 11 | 7 | 12 | 14 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 8 |
| 12 | 12 | 12 | 30 | 6 | 22 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 20 | 22 | 16 | 24 | 4 | 16 | 12 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 16 | 14 | 22 | 12 | 12 | 9 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 16 |
| 24 | 20 | 13 | 15 | 7 | 30 | 6 | 12 | 13 | 22 | 30 | 17 | 29 | 10 | 22 | 26 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 20 | 19 | 27 | 14 | 14 | 22 | 22 | 15 | 12 | 18 |
| 48 | 8 | 14 | 15 | 14 | 8 | 2 | 18 | 9 | 22 | 20 | 20 | 11 | 12 | 20 | 10 | 16 | 34 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrios, Y.; Franco, A.; Sánchez-Machín, I.; Poza-Guedes, P.; González-Pérez, R.; Matheu, V. The Beauty of Simplicity: Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reaction to Measure Cellular Immune Responses in RNA-SARS-Cov-2 Vaccinated Individuals. Vaccines 2021, 9, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060575
Barrios Y, Franco A, Sánchez-Machín I, Poza-Guedes P, González-Pérez R, Matheu V. The Beauty of Simplicity: Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reaction to Measure Cellular Immune Responses in RNA-SARS-Cov-2 Vaccinated Individuals. Vaccines. 2021; 9(6):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060575
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrios, Yvelise, Andres Franco, Inmaculada Sánchez-Machín, Paloma Poza-Guedes, Ruperto González-Pérez, and Victor Matheu. 2021. "The Beauty of Simplicity: Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reaction to Measure Cellular Immune Responses in RNA-SARS-Cov-2 Vaccinated Individuals" Vaccines 9, no. 6: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060575
APA StyleBarrios, Y., Franco, A., Sánchez-Machín, I., Poza-Guedes, P., González-Pérez, R., & Matheu, V. (2021). The Beauty of Simplicity: Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Reaction to Measure Cellular Immune Responses in RNA-SARS-Cov-2 Vaccinated Individuals. Vaccines, 9(6), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060575






