SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Anaphylaxis: Recommendations of the French Allergy Community and the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center
Abstract
1. The Scope of the Problem
1.1. The SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: Essential to Control the COVID-19 Pandemic
1.2. The Allergy Epidemic
2. Current Status: What Do We Know?
2.1. Impact of Vaccine Safety in Immunization Programs
2.2. Vaccine Safety Surveillance Programs
2.3. Anaphylaxis
2.4. Immediate Allergic Side Effects of Vaccines
3. Recommendations of the French Allergy Community and the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center
3.1. The Montpellier WHO Collaborating Center
3.2. Recommendations of the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center
3.3. First Nation-Wide Post-Marketing Pharmacovigilant Data
4. Let’s Keep Fighting COVID-19!
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANSM | National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EUA | Emergency Use Authorization |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
| Moderna vaccine | Moderna mRNA vaccine |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycols |
| Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine | Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WHO CC | WHO Collaborating Center |
References
- World Health Organization Website. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---13-april-2021 (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Centers of Disease Control Website. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7002e1.htm (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Pfizer and BioNTech Achieve First Authorization in the World for a Vaccine to Combat COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-and-biontech-achieve-first-authorization-world (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- U.S. FDA Takes Additional Action in Fight Against COVID-19 by Issuing Emergency Use Authorization for Second COVID-19 Vaccine. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-takes-additional-action-fight-against-covid-19-issuing-emergency-use-authorization-second-covid (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Moderna. Press Release. 2021. Available online: https://investors.modernatx.com/news-releases (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- AstraZeneca’s COVID-19 Vaccine Authorized for Emergency Supply in the UK. 2020. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2020/astrazenecas-covid-19-vaccine-authorised-in-uk.html (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Raine, J.; Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). Confirmation of Guidance to Vaccination Centres on Managing Allergic Reactions Following COVID-19 Vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech Vaccine. 9 December 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/confirmation-of-guidance-to-vaccination-centres-on-managing-allergic-reactions-following-covid-19-vaccination-with-the-pfizer-biontech-vaccine press release (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Cardona, V.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Ebisawa, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Fernandez Rivas, M.; Fineman, S.; Geller, M.; Gonzalez-Estrada, A.; Greenberger, P.A.; Sanchez Borges, M.; et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, S.S.; Javad, S.; de Silva, D.; Nwaru, B.I.; Hickstein, L.; Muraro, A.; Roberts, G.; Worm, M.; Bilò, M.B.; Cardona, V.; et al. The epidemiology of anaphylaxis in Europe: A systematic review. Allergy 2013, 68, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanno, L.K.; Molinari, N.; Bruel, S.; Bourrain, J.L.; Calderon, M.A.; Aubas, P.; Demoly, P.; Joint Allergy Academies. Field-testing the new anaphylaxis’ classification for the WHO International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-11 revision. Allergy 2017, 72, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanno, L.K.; Chalmers, R.; Bierrenbach, A.L.; Simons, F.E.R.; Martin, B.; Molinari, N.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Worm, M.; Cardona, V.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; et al. Changing the history of anaphylaxis mortality statistics through the World Health Organization’s International Classification of Diseases-11. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoly, P.; Tanno, L. Le modèle de l’anaphylaxie: Une nouvelle version de la Classification internationale des maladies de l’Organisation mondiale de la santé pour 2019. The model of anaphylaxis: A new version of the International Classification of Diseases from the World Health Organization. Bull. Acad. Natl. Med. 2020, 1, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.T.; Rastogi, S.C.; Mullen, J.R.; Hayes, S.W.; Cochi, S.L.; Donlon, J.A.; Wassilak, S.G. The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Vaccine 1994, 12, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://fr.vaccine-safety-training.org/securite-des-vaccins-dans-les-programmes-de-vaccination.html (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Demoly, P.; Adkinson, N.F.; Brockow, K.; Castells, M.; Chiriac, A.M.; Greenberger, P.A.; Khan, D.A.; Lang, D.M.; Park, H.-S.; Pichler, W.; et al. International Consensus (ICON) on Drug Allergy. Allergy 2014, 69, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halsey, N.A. The science of evaluation of adverse events associated with vaccination. Semin. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2002, 13, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products Website. Available online: https://ansm.sante.fr/uploads/2021/04/16/20210412-vaccins-covid-19-fiche-de-synhtese-vf.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Dreskin, S.C.; Halsey, N.A.; Kelso, J.M.; Wood, R.A.; Hummell, D.S.; Edwards, K.M.; Caubet, J.C.; Engler, R.J.; Gold, M.S.; Ponvert, C.; et al. International Consensus (ICON): Allergic reactions to vaccines. World Allergy Organ. J. 2016, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, C.A., Jr.; Rukasin, C.R.F.; Beachkofsky, T.M.; Phillips, E.J. Immune-mediated adverse reactions to vaccines. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 2694–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenande, E.; Garvey, L.H. Immediate-type hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycols: A review. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Stone, C.A., Jr.; Jakubovic, B.; Phillips, E.J.; Sussman, G.; Park, J.; Hoang, U.; Kirshner, S.L.; Levin, R.; Kozlowski, S. Anti-PEG IgE in anaphylaxis associated with polyethylene glycol. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 17, S2198–S2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, C.A., Jr.; Liu, Y.; Relling, M.V.; Krantz, M.S.; Pratt, A.L.; Abreo, A.; Hemler, J.A.; Phillips, E.J. Immediate hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycols and polysorbates: More common than we have recognized. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juniper, E.F.; Roberts, R.S.; Kennedy, L.K.; O’Connor, J.; Syty-Golda, M.; Dolovich, J.; Hargreave, F.E. Polyethylene glycol-modified ragweed pollen extract in rhinoconjunctivitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1985, 75, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbech, H.; Dirksen, A.; Dreborg, S.; Frolund, L.; Heinig, J.H.; Svendsen, U.G.; Søborg, M.; Taudore, E.; Weeke, B. Hyposensitization in asthmatics with mPEG-modified and unmodified house dust mite extract. IV. Occurrence and prediction of side effects. Allergy 1990, 45, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreborg, S.; Akerblom, E.B. Immunotherapy with monomethoxypolyethylene glycol modified allergens. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1990, 6, 315–365. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://professionnels.vaccination-info-service.fr/Aspects-pratiques/Allergies-et-autres-contre-indications/Personnes-allergiques (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Sellaturay, P.; Nasser, S.; Islam, S.; Gurugama, P.; Ewan, P.W. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a cause of anaphylaxis to the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M.C.; Phillips, E.J. Maintaining Safety with SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.allergicliving.com/2021/01/03/likely-more-than-one-cause-for-covid-19-vaccine-reactions/ (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- World Health Organization, Collaborating Centres List Website. Available online: http://apps.who.int/whocc/Detail.aspx?cc_ref=FRA-133&designation_date1=1/6/2018&designation_date2=18/7/2018& (accessed on 26 December 2019).
- Tanno, L.K.; Ganem, F.; Demoly, P.; Toscano, C.M.; Bierrenbach, A.L. Undernotification of anaphylaxis deaths in Brazil due to difficult coding under the ICD-10. Allergy 2012, 67, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoly, P.; Tanno, L.K.; Akdis, C.A.; Lau, S.; Calderon, M.A.; Santos, A.F.; Sanchez-Borges, M.; Rosenwasser, L.J.; Pawankar, R.; Papadopoulos, N.G. Global classification and coding of hypersensitivity diseases—An EAACI—WAO survey, strategic paper and review. Allergy 2014, 69, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, L.K.; Calderon, M.A.; Goldberg, B.J.; Gayraud, J.; Bircher, A.J.; Casale, T.; Li, J.; Sanchez-Borges, M.; Rosenwasser, L.J.; Demoly, P.; et al. Constructing a classification of hypersensitivity/allergic diseases for ICD-11 by crowdsourcing the allergist community. Allergy 2015, 70, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, L.K.; Calderon, M.A.; Demoly, P.; on behalf the Joint Allergy Academies. New Allergic and Hypersensitivity Conditions Section in the International Classification of Diseases-11. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2016, 8, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, L.K.; Casale, T.; Demoly, P. Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19: World Health Organization Definitions and Coding to Support the Allergy Community and Health Professionals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.J.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Campbell, D.E.; Cardona, V.; Ebisawa, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Fineman, S.; Geller, M.; Gonzalez-Estrada, A.; Greenberger, P.A.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine-associated anaphylaxis: A statement of the World Allergy Organization Anaphylaxis Committee. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonadonna, P.; Brockow, K.; Niedoszytko, M.; Elberink, H.O.; Akin, C.; Nedoszytko, B.; Butterfield, J.H.; Alvarez-Twose, I.; Sotlar, K.; Schwaab, J.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination in mastocytosis: Recommendations of the European Competence Network on Mastocytosis (ECNM) and American Initiative in Mast Cell Diseases (AIM). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 5, S2198–S2213. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath, V.; Rabinowitz, G.; Shah, M.; Jain, S.; Diamant, Z.; Jesenak, M.; Rabin, R.; Vieths, S.; Agache, I.; Akdis, M.; et al. Vaccines and Allergic reactions: The past, the current COVID-19 pandemic, and future perspectives. Allergy 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro, T.T.; Cole, M.; Su, J.R. Reports of anaphylaxis after receipt of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in the US—December 14, 2020–January 18, 2021. JAMA 2021, 325, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, K.G.; Robinson, L.B.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Shenoy, E.S.; Banerji, A.; Landman, A.B.; Wickner, P. Acute Allergic Reactions to mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines. JAMA 2021, 325, 1562–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
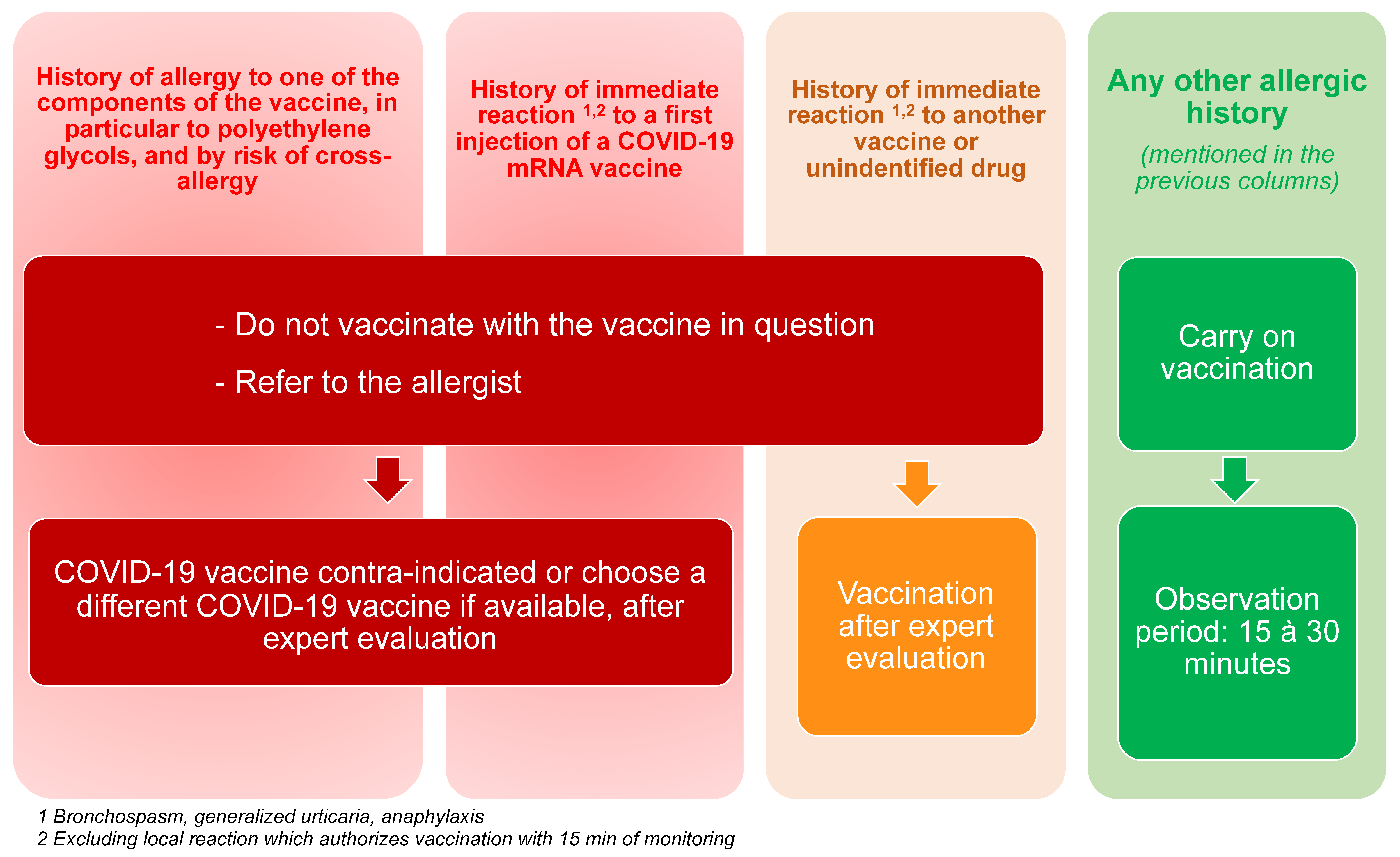
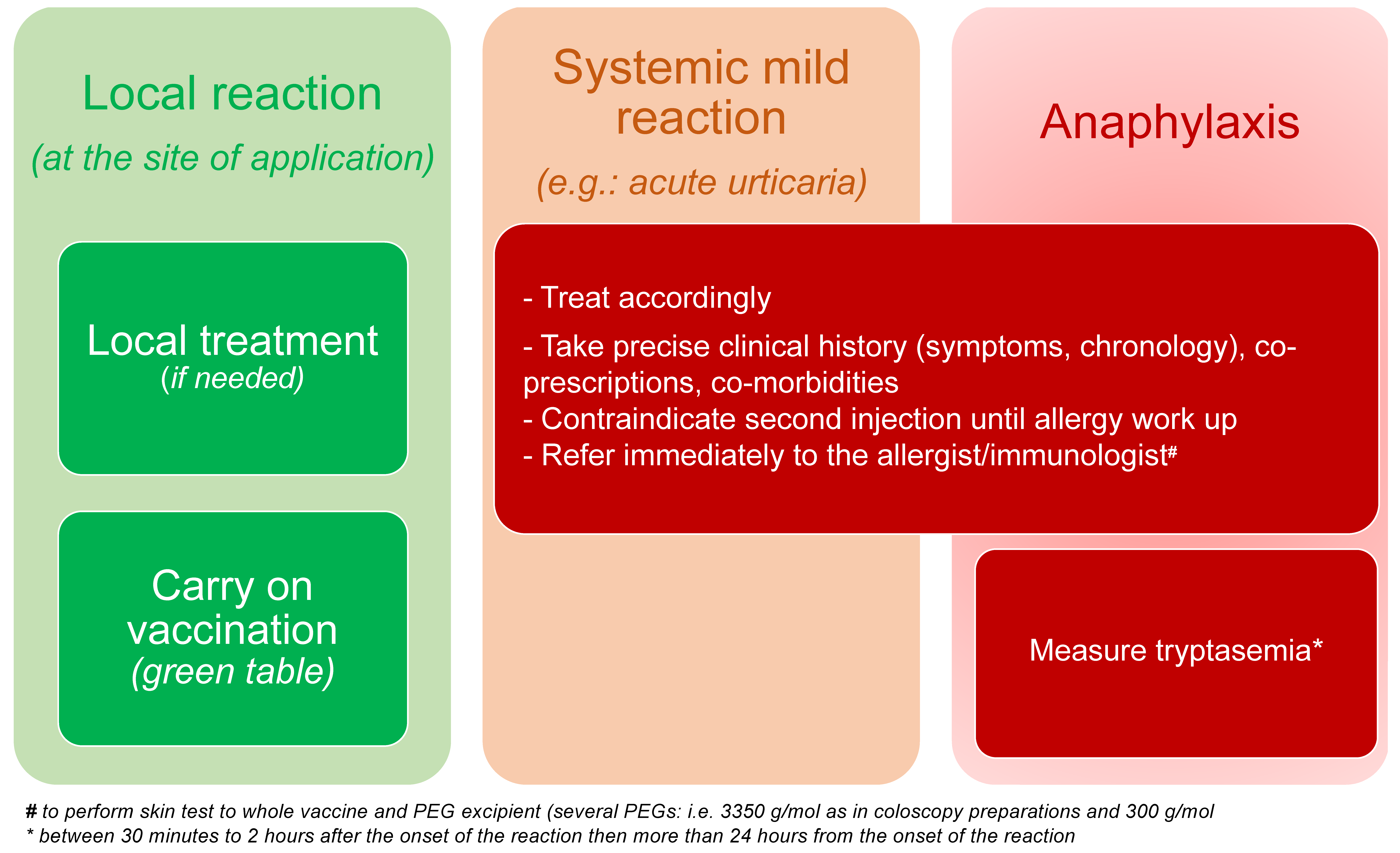
| Proceed with Vaccination | Special Precautions | Vaccination Contra-Indicated or Needing High Precaution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients’ Personal History |
|
|
|
| Recommendations |
|
|
|
| Vaccine & Manufacturer | Vaccine Type | Excipients |
|---|---|---|
| CoronaVac (Sinovac, China) | Inactivated vaccine (formalin with aluminum adjuvant) | Aluminum hydroxide, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride |
| Convidicea Ad5-nCoV (CanSino Biologics, Beijing Inst. Biotech., NPO Petrovax) | Recombinant adenovirus type 5 vector against spike RBD protein | N/A |
| BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm, Beijing Institute & Wuhan Inst. of Biological Products) | Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 (vero cells) + aluminum hydroxide adjuvant | Aluminum hydroxide, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, M199 |
| Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 | mRNA-based vaccine (encoding the viral spike (S) glycoprotein) | (4-hydroxybutyl) azanediyl)bis (hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate)] (ALC-0315), 2-[(polyethylene glycol)-2000]-N,N-ditetradecylacetamide (ALC-0159), 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine cholesterol, potassium chloride, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride, disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sucrose, water for injection |
| Moderna mRNA-1273 | mRNA-based vaccine (encoding the pre-fusion stabilized spike (S) glycoprotein) | Lipids (SM-102, 1,2-dimyristoyl-rac-glycero3-methoxypolyethylene glycol-2000 [PEG2000-DMG], cholesterol, and 1,2-distearoyl-snglycero-3-phosphocholine [DSPC]), tromethamine, tromethamine hydrochloride, acetic acid, sodium acetate, and sucrose. |
| ChAdOx1 (Oxford/AstraZeneca; Covishield in India) | Replication-deficient viral vector vaccine (adenovirus from chimpanzees) | L-Histidine, L-Histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, Magnesium chloride hexahydrate, polysorbate 80, Ethanol, Sucrose, Sodium chloride, Disodium edetate dihydrate, Water for injection |
| Covaxin (BBV152) (Bharat Biotech, India) | Inactivated vaccine | N/A |
| Sputnik V (Gamaleya Research Inst) | Non-replicating, two-component vector (adenovirus) against spike (S) glycoprotein | Tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane, sodium chloride, sucrose, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, Sodium EDTA, polysorbate 80, ethanol, water for injection |
| EpiVacCorona (Federal Budgetary Research Institution State Research Ctr, Russia) | Peptide vaccine with aluminum adjuvant | Aluminum hydroxide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium chloride, sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, sodium chloride, water for injection |
| Ad26.COV2.S (Jansen) | Adenovirus 26 vectored vaccine using AdVac and PER.C6 technology | Sodium chloride, citric acid monohydrate, polysorbate 80, 2 hydroxypropyl-B-cyclodextrin (HBCD), ethanol (absolute), sodium hydroxide |
| SARS-CoV-2 vaccine formulation with adjuvant (Sanofi Pasteur and GSK) | SARS-CoV-2 vaccine formulation with adjuvant (S-protein) (Baculovirus production) Spike protein | Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, sodium phosphate dibasic, sodium chloride polysorbate 20, disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium chloride |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanno, L.K.; Berard, F.; Beaudoin, E.; Didier, A.; Demoly, P., on behalf of the Montpellier WHO Collaborating Center. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Anaphylaxis: Recommendations of the French Allergy Community and the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center. Vaccines 2021, 9, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060560
Tanno LK, Berard F, Beaudoin E, Didier A, Demoly P on behalf of the Montpellier WHO Collaborating Center. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Anaphylaxis: Recommendations of the French Allergy Community and the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center. Vaccines. 2021; 9(6):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060560
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanno, Luciana Kase, Frédéric Berard, Etienne Beaudoin, Alain Didier, and Pascal Demoly on behalf of the Montpellier WHO Collaborating Center. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Anaphylaxis: Recommendations of the French Allergy Community and the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center" Vaccines 9, no. 6: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060560
APA StyleTanno, L. K., Berard, F., Beaudoin, E., Didier, A., & Demoly, P., on behalf of the Montpellier WHO Collaborating Center. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Anaphylaxis: Recommendations of the French Allergy Community and the Montpellier World Health Organization Collaborating Center. Vaccines, 9(6), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060560






