Epitope Mapping of the Diphtheria Toxin and Development of an ELISA-Specific Diagnostic Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Antibodies
2.2. Human, Horse, and Mice Sera
2.3. Synthesis of the Cellulose Membrane-Bound Peptide Array
2.4. Screening of SPOT Membranes
2.5. Scanning and Quantification of Spot Signal Intensities
2.6. Preparation of the Bi-Specific-Antigen Peptides
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Bioinformatics Tools
2.9. Structural Localization of the IgG Epitopes
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
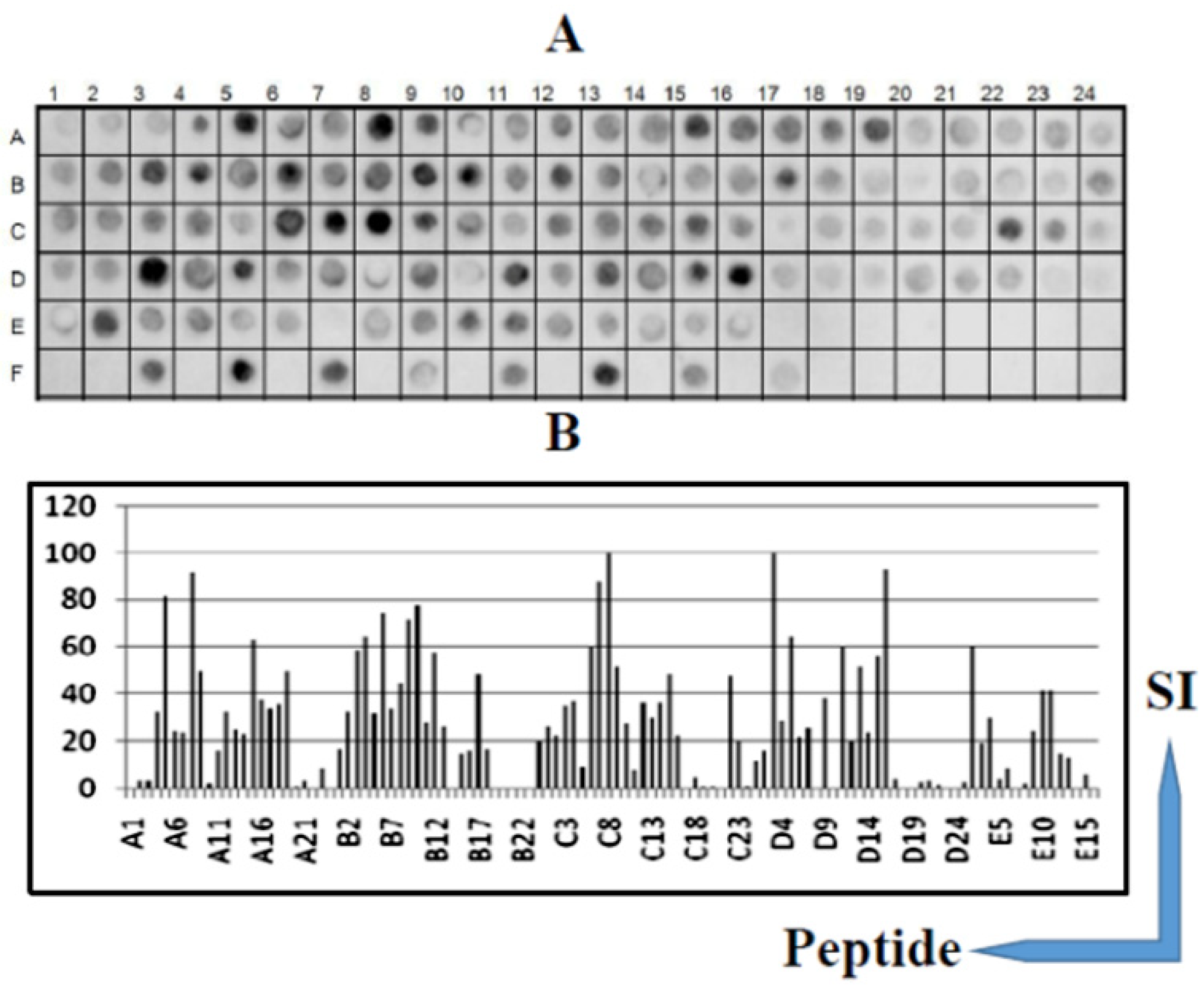
3.1. Identification of the Immunodominant IgG Epitopes in Diphtheria Toxin
3.2. Identification of the IgG Epitopes in SF23 Peptide Sequence
3.3. Cross-Immune IgG Epitopes
3.4. Epitope Reactivity by ELISA
3.5. The Spatial Location of Enterotoxins A, B, and P IgG Reactive Epitopes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sing, A.; Bierschenk, S.; Heesemann, J. Classical diphtheria caused by Corynebacterium ulcerans in Germany: Amino acid sequence differences between diphtheria toxins from Corynebacterium diphtheriae and C. ulcerans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, J.; Biggs, B.A. The impact of conflict on immunisation coverage in 16 countries. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2019, 8, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.E.N.; MacNeil, A.; Hadler, S.; Scott, C.; Tiwari, T.S.P.; Cherian, T. Global epidemiology of diphtheria, 2000–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 2, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, D.M.; Kuehl, R.; Zbinden, R.; Boskova, V.; Garzoni, C.; Fadini, D.; Dolina, M.; Blümel, B.; Weibel, T.; Tschudin-Sutter, S.; et al. Outbreak investigation for toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae wound infections in refugees from Northeast Africa and Syria in Switzerland and Germany by whole genome sequencing. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 1003.e1–1003.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniz-Mondolfi, A.E.; Tami, A.; Grillet, M.E.; Márquez, M.; Hernández-Villena, J.; Escalona-Rodríguez, M.A.; Blohm, G.M.; Mejías, I.; Urbina-Medina, H.; Rísquez, A.; et al. Resurgence of vaccine-preventable diseases in Venezuela as a regional public health threat in the Americas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giovine, P.; Kafatos, G.; Nardone, A.; Andrews, N.; Olander, R.M.; Alfarone, G.; Broughton, K.; Cohen, D.; Kriz, B.; Mikova, I.; et al. Comparative seroepidemiology of diphtheria in six European countries and Israel. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, J.; Sorvari, T.; Widerström, M.; Kauma, H.; Kaukoniemi, U.; Tarkka, E.; Puumalainen, T.; Kuusi, M.; Salminen, M.; Lyytikäinen, O. Respiratory diphtheria in an asylum seeker from Afghanistan arriving to Finland via Sweden, December 2015. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention Control. Cutaneous Diphtheria among Recently Arrived Refugees and Asylum Seekers in the EU, 30 July 2015; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015; Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/Diphtheria-cutaneous-EU-July-2015.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2019).
- Scheifer, C.; Rolland-Debord, C.; Badell, E.; Reibel, F.; Aubry, A.; Perignon, A.; Patey, O.; Brisse, S.; Caumes, E. Re-emergence of Corynebacterium diphtheria. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 49, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffit, J.; Bozio, C.H.; Poel, A.J.; Fitzpatrick, K.; DeBolt, C.A.; Cassiday, P.; Kenyon, C.; Smelser, C.; Vagnone, P.S.; Culbreath, K.; et al. Imported toxin-producing cutaneous diphtheria-Minnesota, Washington, and New Mexico, 2015–2018. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstratiou, A.; George, R.C. Laboratory guidelines for the diagnosis of infections caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae and C. ulcerans. World Health Organization. Commun. Dis. Public. Health 1999, 2, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.C.; Efstratiou, A.; Mokrousov, I.; Mutreja, A.; Das, B.; Ramamurthy, T. Diphtheria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodnin, M.V.; Kashipathy, M.M.; Kyrychenko, A.; Battaile, K.P.; Lovell, S.; Ladokhin, A.S. Structure of the diphtheria toxin at acidic pH: Implications for the conformational switching of the translocation domain. Toxins 2020, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, R.; Cole, H.A. Diphtheria toxin subunit active in vitro. Science 1969, 164, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S.; Bennett, M.J.; Fujii, G.; Curmi, P.M.; Kantardjieff, K.A.; Collier, R.J.; Eisenberg, D. The crystal structure of diphtheria toxin. Nature 1992, 357, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.E.; Eisenberg, D. Crystal structure of nucleotide-free diphtheria toxin. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubler, J.; Huber-Schneider, C.; Gruner, E.; Altwegg, M. An outbreak of non-toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae infection: Single bacterial clone causing invasive infection among Swiss drug users. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patey, O.; Bimet, F.; Riegel, P.; Halioua, B.; Emond, J.P.; Estrangin, E.; Dellion, S.; Alonso, J.M.; Kiredijan, M.; Dublanchet, A.; et al. Clinical and molecular study of Corynebacterium diphtheriae systemic infections in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, G.; Altwegg, M.; Frommel, L.; von Graevenitz, A.A. Emergence of related nontoxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae biotype mitis strains in Western Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hunolstein, C.; Alfarone, G.; Mascioli, M.; Franchi, F.; Errera, G.; Crostato, I. A diphtheria case due to Corynebacterium ulcerans. G. Ital. Mal. Infect. 1999, 5, 299–300. [Google Scholar]
- Reacher, M.; Romsay, M.; White, J.; de Zoysa, A.; Efstratiou, A.; Mann, G.; Mackay, A.; George, R.C. Nontoxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae: An emerging pathogen in England and Wales? Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 477–480. [Google Scholar]
- Von Hunolstein, C.; Alfarone, G.; Scopetti, F.; Pataracchia, M.; La Valle, R.; Franchi, F.; Pacciani, L.; Manera, A.; Giammanco, A.; Farinelli, S.; et al. Molecular epidemiology and characteristics of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans strains isolated in Italy during the 1990s. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Winter, L.M.; Bernard, K.A.; Romney, M.G. Human clinical isolates of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans collected in Canada from 1999 to 2003 but not fitting reporting criteria for cases of diphtheria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3447–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliti, M.; von Hunolstein, C.; Marangi, M.; Bistoni, F.; Tissi, L. Experimental model of infection with non-toxigenic strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and development of septic arthritis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romney, M.G.; Roscoe, D.L.; Bernard, K.; Lai, S.; Efstratiou, A.; Clarke, A.M. Emergence of an invasive clone of non-toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae in the urban poor population of Vancouver, Canada. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elden, S.; Coole, L.; Efstratiou, A.; Doshi, N. Laboratory-confirmed case of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. Euro. Surveill. 2007, 29, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, T.S.P.; Golaz, A.; Yu, D.T.; Ehresmann, K.R.; Jones, T.F.; Hill, H.E.; Cassiday, P.K.; Pawloski, L.C.; Moran, J.S.; Popovic, T.; et al. Investigations of 2 cases of diphtheria-like illness due to toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonmarin, I.; Guiso, N.; Le Flèche-Matéos, A.; Patey, O.; Patrick, A.D.; Levy-Bruhl, D. Diphtheria: A zoonotic disease in France? Vaccine 2009, 27, 4196–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, H.; Mazurova, I.K.; Glushkevich, T.; Popovic, T. Analysis of heterogeneity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae toxin gene, tox, and its regulatory element, dtxR, by direct sequencing. Res. Microbiol. 1997, 148, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, A.; Hogardt, M.; Bierschenk, S.; Heesemann, J. Detection of differences in the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of diphtheria toxin from Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans causing extrapharyngeal infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4848–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, A.; Berger, A.; Schneider-Brachert, W.; Holzmann, T.; Reischl, A. Rapid detection and molecular differentiation of toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium m ulcerans strains by LightCycler PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2485–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhegger, R.; Kugler, R.; Sing, A. Pitfalls with toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans causing diphtheria-like illness. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, K.H.; Glushkevich, T.; Mazurova, I.; George, R.; Efstratiou, A. A modified Elek test for detection of toxigenic corynebacteria in the diagnostic laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, S.; Efstratiou, A. On behalf of DIPNET and International Diphtheria Reference Laboratories. International external quality assurance for laboratory diagnosis of diphtheria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 4037–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L.G.C.; Pena, R.R.; Castro, T.L.P.; Dorella, F.A.; Bahia, R.C.; Carminati, R.; Frota, M.N.L.; Oliveira, S.C.; Meyer, R.; Alves, F.S.F.; et al. Multiplex PCR assay for identification of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis from pure cultures and for rapid detection of this pathogen in clinical samples. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassiday, P.K.; Pawloski, L.C.; Tiwari, T.; Sanden, G.N.; Wilkins, P.P. Analysis of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans strains revealing the potential for false negative real-time PCR results. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, F.P.; Matias, G.A.; Pereira, G.A.; Camello, T.C.; Alves, G.B.; Rosa, A.C.; Hirata, R.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L. A PCR for dtxR gene: Application to diagnosis of non-toxigenic and toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Mol. Cell. Probes 2008, 22, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, R.; Berger, A.; Huber, I.; Boschert, V.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Busch, U.; Hogardt, M.; Schubert, S.; Sing, A. Matrixassisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry as a tool for rapid diagnosis of potentially toxigenic Corynebacterium species in the laboratory management of diphtheria-associated bacteria. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, K.; Nishio, S.; Ito, A.; Murata, R.; Kono, R. Micro cell culture method for the determination of diphtheria toxin and antitoxin titre using VERO cells DI. Studies of factors affecting the toxin and antitoxin titration. J. Biol. Stand. 1974, 2, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggerbeck, H.; Norgaard-Pedersen, B.; Heron, I. Simultaneous quantization of diphtheria and tetanus antibodies by double antigen, time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay. J. Immunol. Meth. 1996, 190, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, M.; Aggerbeck, H.; Heron, I. Improved ELISA for determination of anti-diphtheria and/or anti-tetanus antitoxin antibodies in sera. APMIS 1997, 105, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.; Wi, J.; Chae, H.; Jo, G.; Yoon, J.-Y.; Chankyu, L.; Hyo Jeong, H.; Heeyoun, K.; et al. Generation of a human monoclonal antibody to cross-reactive material 197 (CR M197) and development of a sandwich ELISA for CRM conjugate vaccines. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Liuni, P.; Ettorre, L.; Chen, T.; Szeto, J.; Carpick, B.; James, D.A.; Wilson, D.J. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange epitope mapping reveals distinct neutralizing mechanisms for two monoclonal antibodies against diphtheria toxin. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakzaei, M.; Rasaee, M.J.; Fazaeli, A.A.; Aminian, M. A comparison of three strategies for biopanning of phage-scFv library against diphtheria toxin. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 9486–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, E.V.; Bosnak, M.; Tierney, R.; Schubert, M.; Brown, J.; Dübel, S.; Efstratiou, A.; Sesardic, D.; Stickings, P.; Hust, M. Human antibodies neutralizing diphtheria toxin in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesardic, D.; Khan, V.; Corbel, M.J. Targeting of specific domains of diphtheria toxin by site-directed antibodies. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1992, 138, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, L.M.; Booth, B.J.; Rowley, K.J.; Leav, B.A.; Cheslock, P.S.; Garrity, K.A.; Sloan, S.E.; Thomas, W.D.; Babcock, G.J.; Wang, Y. Identification of a human monoclonal antibody to replace equine diphtheria antitoxin for treatment of diphtheria intoxication. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3992–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi, S.; Bozorgmehr, M.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Tarahomjoo, S. Identification of conformational B-cell epitopes in diphtheria toxin at varying temperatures using molecular dynamics simulations. Arch. Razi Inst. 2020, 75, 427–437. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, D.F.H. SPOT Synthesis: The solid-phase peptide synthesis on planar surfaces. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2103, 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F.R.; Napoleão-Pego, P.; De-Simone, S.G. Identification of linear B epitopes of pertactin of Bordetella pertussis induced by immunization with whole and acellular vaccine. Vaccine. 2014, 32, 6251–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; De-Simone, T.S. Spot synthesis: A healthy and sensitive peptide microarray assay to detect IgE antibodies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1352, 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Souza, A.L.A.; Melgarejo, A.R.; Aguiar, A.S.; Provance, D.W., Jr. Development of elisa assay to detect specific human IgE anti-therapeutic horse sera. Toxicon 2017, 138, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrustaleva, T.A.; Khrustalev, V.V.; Barkovsky, E.V.; Kolodkina, V.L.; Astapov, A.A. Structural and antigenic features of the synthetic SF23 peptide corresponding to the receptor-binding fragment of diphtheria toxin. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobeck, K.; Drevet, P.; Léonetti, M.; Fromen-Romano, C.; Ducancel, F.; Lajeunesse, E.; Lemaire, C.; Ménez, A. Towards a recombinant vaccine against diphtheria toxin. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.V.; Lemes, E.M.; Queiroz, J.L.; Silva, J.G., Jr.; Nascimento, H.J.; Silva, E.D.; Hirata, R., Jr.; Dias, A.A.; Santos, C.S.; Pereira, G.M.B.; et al. Expression and purification of the immunogenically active fragment B of the Corynebacterium diphtheria strain toxin. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lechuga, G.C.; Bottino, C.C.G.; Pinho, R.T.; Souza, A.L.A.; Provance, D.W., Jr.; De-Simone, S.G. Trypanosoma cruzi presenilin-like transmembrane aspartyl protease: Characterization and cellular localization. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, G.V.; Yang, W.; Bowman, M.E.; Choe, S. Crystal structure of the complex of the diphteriae toxin with an extracellular fragment of its receptor. Mol. Cell 1997, 1, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, H.; Dedic, E.; Bjerrum, M.J.; Østergaard, O.; Kristensen, M.P.; Petersen, J.W.; Jørgensen, R. Biophysical comparison of diphtheria and tetanus toxins with the formaldehyde-detoxified toxoids, the main components of diphtheria and tetanus vaccines. Virulence 2017, 8, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Metz, B.; Michiels, T.; Uittenbogaard, J.; Danial, M.; Tilstra, W.; Meiring, H.D.; Hennink, W.E.; Crommelin, D.J.; Kersten, G.F.; Jiskoot, W. Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in diphtheria toxin. J. Pharm. Sci 2020, 109, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usuwanthim, K.; Pootong, A.; Chaisri, U.; Tongtawe, P.; Tapchaisri, P.; Chongsanguan, M.; Chaicumpa, W. Murine monoclonal antibodies neutral-izing the cytotoxic activity of diphtheria toxin. Asian Pac. J. Aller. Immun. 2008, 26, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Both, L.; White, J.; Mandal, S.; Efstratiou, A. Access to diphtheria antitoxin for therapy and diagnostics. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenny, A.T.; Hopkins, B.E. Diphtheria toxoid as an immunizing agent. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1923, 4, 283. [Google Scholar]
- Colli, A.; Fraquelli, M.; Casazza, G.; Conte, D.; Nikolova, D.; Duca, P.; Thorlund, K.; Gluud, C. The Architecture of diagnostic research: From bench to bedside-research guidelines using liver stiffness as an example. Hepatology 2014, 60, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Carneiro, F.R.G.; Durans, A.M.; Morel, C.M.; Provance, D.W., Jr.; De-Simone, S.G. Performance assessment of a multi-epitope chimeric antigen for the serological diagnosis of acute Mayaro fever. Sci. Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar]


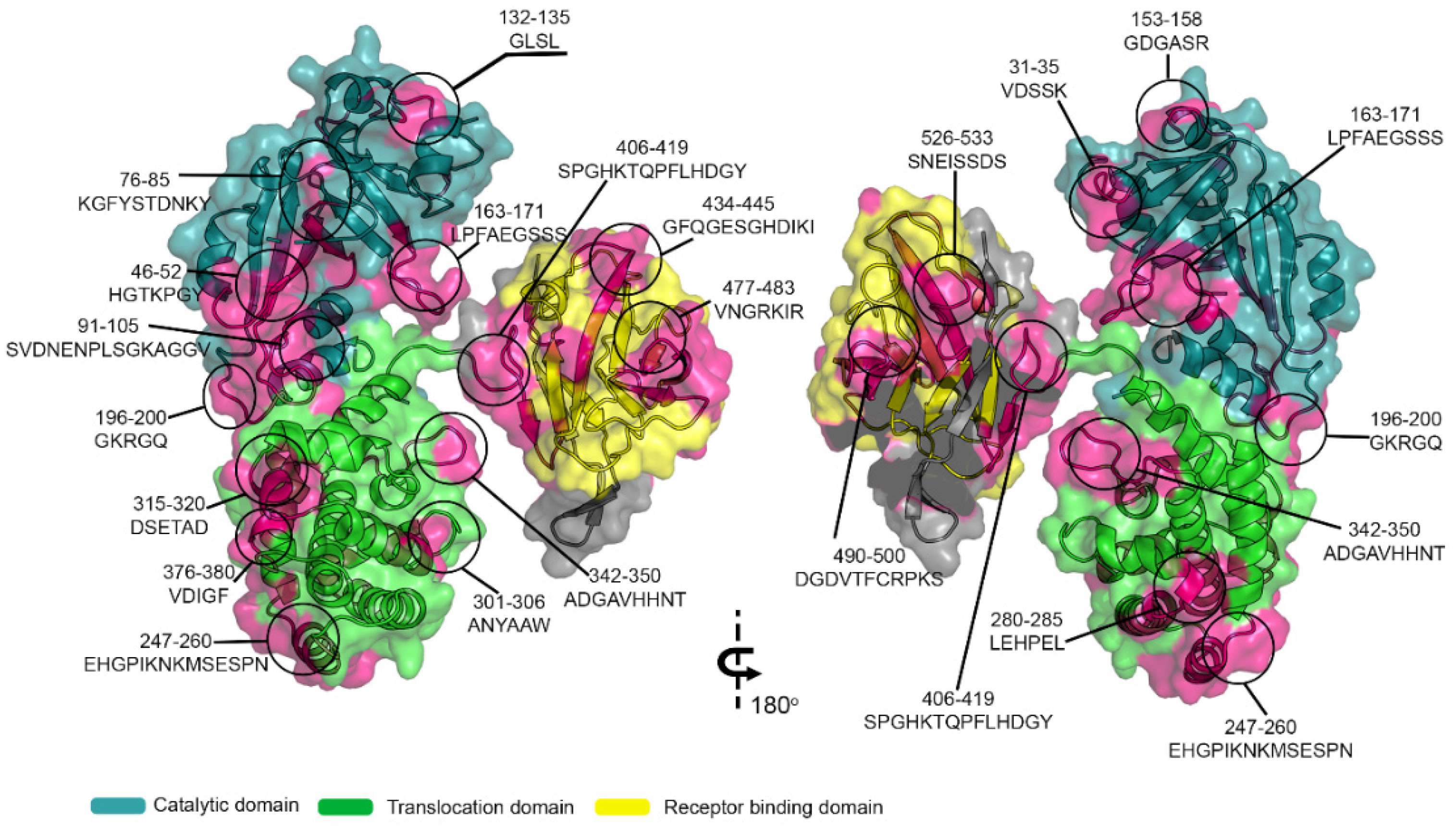
| Name of Epitope | Sequence | Secondary Structure | Name of Epitope | Sequence | Secondary Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB/DTX-1 | 16GIGAPPSAHA25 | C | CB/DTx-11 | 280LEHPEL285 | C |
| CB/DTx-2 | 31VDSSK35 | C+H | CB/DTx-12 | 301ANYAAW306 | C |
| CB/DTx-3 | 46HGTKPGY52 | C | CB/DTx-13 | 315DSETAD320 | C+H |
| CB/DTx-4 | 76KGFYSTDNKY85 | C | CB/DTx-14 | 342ADGAVHHNT350 | C |
| CB/DTx-5 | 91SVDNENPLSGKAGGV105 | C | CB/DTx-15 | 376VDIGF380 | C+H |
| CB/DTx-6 | 132GLSL135 | C | CB/DTx-16 | 406SPGHKTQPFLHDGY419 | C |
| CB/DTx-7 | 153GDGASR158 | C | CB/DTX-17 | 434GFQGESGHDIKI445 | C+S |
| CB/DTx-8 | 163LPFAEGSSS171 | C | CB/DTx-18 | 477VNGRKIR483 | C+S |
| CB/DTx-9 | 196GKRGQ200 | C | CB/DTx-19 | 490DGDVTFCRPKS500 | C+S |
| CB/DTx-10 | 247EHGPIKNKMSESPN260 | C | CB/DTx-20 | 526 SNEISSDS533 | C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De-Simone, S.G.; Gomes, L.R.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Lechuga, G.C.; de Pina, J.S.; da Silva, F.R. Epitope Mapping of the Diphtheria Toxin and Development of an ELISA-Specific Diagnostic Assay. Vaccines 2021, 9, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040313
De-Simone SG, Gomes LR, Napoleão-Pêgo P, Lechuga GC, de Pina JS, da Silva FR. Epitope Mapping of the Diphtheria Toxin and Development of an ELISA-Specific Diagnostic Assay. Vaccines. 2021; 9(4):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040313
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe-Simone, Salvatore Giovanni, Larissa Rodrigues Gomes, Paloma Napoleão-Pêgo, Guilherme Curty Lechuga, Jorge Soares de Pina, and Flavio Rocha da Silva. 2021. "Epitope Mapping of the Diphtheria Toxin and Development of an ELISA-Specific Diagnostic Assay" Vaccines 9, no. 4: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040313
APA StyleDe-Simone, S. G., Gomes, L. R., Napoleão-Pêgo, P., Lechuga, G. C., de Pina, J. S., & da Silva, F. R. (2021). Epitope Mapping of the Diphtheria Toxin and Development of an ELISA-Specific Diagnostic Assay. Vaccines, 9(4), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9040313







