Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adjuvants
2.2. Animals
2.3. Cells and Viruses
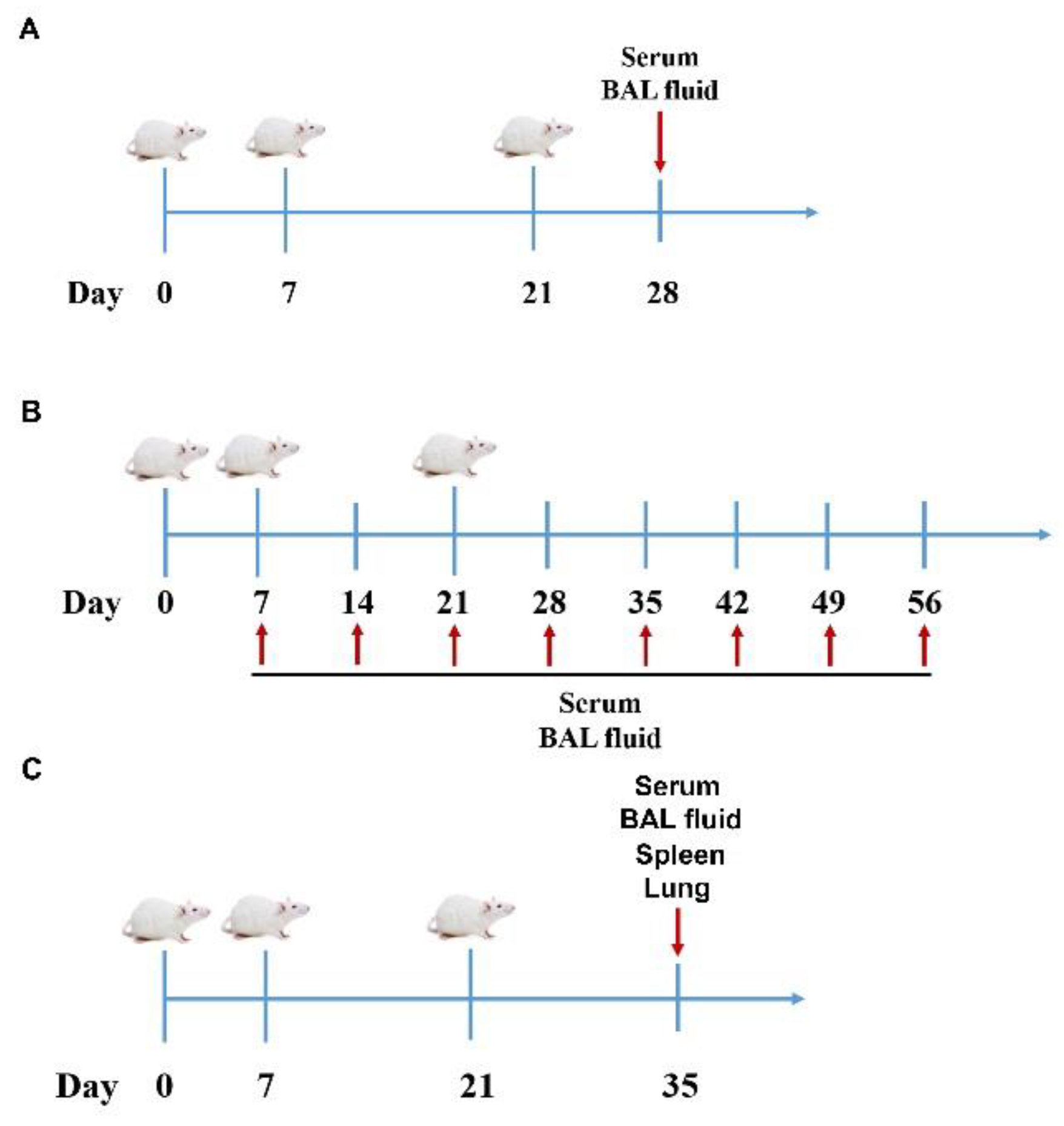
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Determination of PRRSV-Specific IgA, IgG, and Isotype Responses
2.6. Immunohistochemical Staining for IgA-Secreting Cells
2.7. Analysis of Neutralizing Antibodies
2.8. Test of Lymphocyte Proliferation
2.9. Cytokine Assay
2.10. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.12. Western Blot Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LTB and Rg1 Synergistically Enhance PRRSV-Specific Antibody Responses
3.2. LTB-Rg1 Induces Earlier and Prolonged Antibody Responses
3.3. LTB-Rg1 Increases Neutralizing Antibody Titers
3.4. LTB-Rg1 Induces Higher Lymphocyte Proliferation
3.5. LTB-Rg1 Selectively Expanded CD4+ T Cell Proliferation
3.6. LTB-Rg1 Enhances Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cellular Immunity
3.7. LTB-Rg1 Up-Regulates Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
References
- Evans, A.B.; Loyd, H.; Dunkelberger, J.R.; van Tol, S.; Bolton, M.J.; Dorman, K.S.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Carpenter, S. Antigenic and Biological Characterization of ORF2-6 Variants at Early Times Following PRRSV Infection. Viruses 2017, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwenhuis, N.; Duinhof, T.F.; van Nes, A. Economic analysis of outbreaks of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in nine sow herds. Vet. Rec. 2012, 170, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Du, L.; Liu, F.; Wei, Z.; Gao, L.; Feng, W.H. Highly Pathogenic Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Induces Interleukin-17 Production via Activation of the IRAK1-PI3K-p38MAPK-C/EBPbeta/CREB Pathways. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunney, J.K.; Fang, Y.; Ladinig, A.; Chen, N.; Li, Y.; Rowland, B.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV): Pathogenesis and Interaction with the Immune System. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhares, D.C.; Cano, J.P.; Wetzell, T.; Nerem, J.; Torremorell, M.; Dee, S.A. Effect of modified-live porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSv) vaccine on the shedding of wild-type virus from an infected population of growing pigs. Vaccine 2012, 30, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renukaradhya, G.J.; Meng, X.J.; Calvert, J.G.; Roof, M.; Lager, K.M. Live porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccines: Current status and future direction. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renukaradhya, G.J.; Meng, X.J.; Calvert, J.G.; Roof, M.; Lager, K.M. Inactivated and subunit vaccines against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome: Current status and future direction. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binjawadagi, B.; Dwivedi, V.; Manickam, C.; Ouyang, K.; Wu, Y.; Lee, L.J.; Torrelles, J.B.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Adjuvanted poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticle-entrapped inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccine elicits cross-protective immune response in pigs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshweiat, A.; Ambrus, R.; Csoka, I. Intranasal Nanoparticulate Systems as Alternative Route of Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6459–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Peng, X.; Shu, H.; Zhao, D. Intranasal immunization with live recombinant Lactococcus lactis combined with heat-labile toxin B subunit protects chickens from highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Recent advances in nontoxic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin and its derivative adjuvants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsted, D.; Fallahi, F.; Golshani, A.; Azizi, A. Advances and challenges in mucosal adjuvant technology. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, M. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) with Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Subunit VP1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioro, S.B.; Fisch, A.; Gomes, C.K.; Jorge, S.; Galli, V.; Haesebrouck, F.; Maes, D.; Dellagostin, O.; Conceicao, F.R. Local and systemic immune responses induced by a recombinant chimeric protein containing Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae antigens fused to the B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin LTB. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasarasakulpong, A.; Poolperm, P.; Tankaew, P.; Sawada, T.; Sthitmatee, N. Protectivity conferred by immunization with intranasal recombinant outer membrane protein H from Pasteurella multocida serovar A:1 in chickens. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duan, Q.; Xia, P.; Nandre, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Review of Newly Identified Functions Associated With the Heat-Labile Toxin of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, A.T.; Fraser, S.; Merritt, E.A.; Rodigherio, C.; Kenny, M.; Ahn, M.; Hol, W.G.; Williams, N.A.; Lencer, W.I.; Hirst, T.R. A mutant cholera toxin B subunit that binds GM1- ganglioside but lacks immunomodulatory or toxic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8536–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoeteweij, J.P.; Epperson, D.E.; Porter, J.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Frolova, O.Y.; Constantinides, A.P.; Fuhrmann, S.R.; El-Amine, M.; Tian, J.H.; Ellingsworth, L.R.; et al. GM1 binding-deficient exotoxin is a potent noninflammatory broad spectrum intradermal immunoadjuvant. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Xu, L.; Xue, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Yuan, X. Th1-biased immunoadjuvant effect of the recombinant B subunit of an Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin on an inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus antigen via intranasal immunization in mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Shen, L.H.; Zhang, J.T. Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, S. Ginsenosides Rg1 and Re act as adjuvant via TLR4 signaling pathway. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4106–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Hu, S. Protective effect of ginsenosides Rg1 and Re on lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis by competitive binding to Toll-like receptor 4. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5654–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.K.; Yin, B.; Liang, J.B.; Jiang, F.; Wu, W.X. Toll-Like Receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 Mediate the IgA Immune Response Induced by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 2019, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; Sung, B.; Ahn, K.S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Gambogic acid, a novel ligand for transferrin receptor, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Blood 2007, 110, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, X. Enhanced inducible costimulator ligand (ICOS-L) expression on dendritic cells in interleukin-10 deficiency and its impact on T-cell subsets in respiratory tract infection. Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Yuan, L.; Maqbool, B.; Xu, W.; He, S.; Guan, R.; Hu, S. A Solution with Ginseng Saponins and Selenium as Vaccine Diluent to Increase Th1/Th2 Immune Responses in Mice. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2714257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, T.; Serrano-Villar, S.; Diaz, L.; Gonzalez Tome, M.I.; Gurbindo, M.D.; de Jose, M.I.; Mellado, M.J.; Ramos, J.T.; Zamora, J.; Moreno, S.; et al. The CD4/CD8 ratio as a marker T-cell activation, senescence and activation/exhaustion in treated HIV-infected children and young adults. AIDS 2013, 27, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geffner, L.; Basile, J.I.; Yokobori, N.; Sabio, Y.G.C.; Musella, R.; Castagnino, J.; Sasiain, M.C.; de la Barrera, S. CD4(+) CD25(high) forkhead box protein 3(+) regulatory T lymphocytes suppress interferon-gamma and CD107 expression in CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells from tuberculous pleural effusions. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 175, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.T.; Goff, P.H.; Sun, R.J.; Ruge, M.J.; Ermler, M.E.; Sebring, A.; O'Konek, J.J.; Landers, J.J.; Janczak, K.W.; Sun, W.; et al. Combined Intranasal Nanoemulsion and RIG-I Activating RNA Adjuvants Enhance Mucosal, Humoral, and Cellular Immunity to Influenza Virus. Mol. Pharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Griffiths, K.L.; Milburn, P.J.; Hirst, T.R.; O’Neill, H.C. The B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin alters the development and antigen-presenting capacity of dendritic cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2019–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.J.; Haridas, S.; Ebenezer, M.; Raghupathy, R.; Khan, I. Immunization with a Double-Mutant (R192G/L211A) of the Heat-Labile Enterotoxin of Escherichia coli Offers Partial Protection against Campylobacter jejuni in an Adult Mouse Intestinal Colonization Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.J.; Huo, Z.; Barnett, S.; Kromann, I.; Giemza, R.; Galiza, E.; Woodrow, M.; Thierry-Carstensen, B.; Andersen, P.; Novicki, D.; et al. Transient facial nerve paralysis (Bell’s palsy) following intranasal delivery of a genetically detoxified mutant of Escherichia coli heat labile toxin. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwar, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Kadowaki, S.; Asanuma, H.; Chen, Z.; Komase, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Aizawa, C.; Kurata, T.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of mutant Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT H44A) as an adjuvant for nasal influenza vaccine. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Asanuma, H.; Sato, Y.; Sata, T.; Aizawa, C.; Kurata, T.; Tamura, S. Effects of intranasal administration of cholera toxin (or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin) B subunits supplemented with a trace amount of the holotoxin on the brain. Vaccine 2001, 19, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, W.I.; Bryden, W.L.; Husband, A.J. Evaluation of the efficacy of intraperitoneal immunization in reducing Salmonella typhimurium infection in chickens. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Galliher-Beckley, A.; Pappan, L.; Trible, B.; Kerrigan, M.; Beck, A.; Hesse, R.; Blecha, F.; Nietfeld, J.C.; Rowland, R.R.; et al. Comparison of host immune responses to homologous and heterologous type II porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) challenge in vaccinated and unvaccinated pigs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 416727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A.; Gilbert, P.B. Nomenclature for immune correlates of protection after vaccination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanella, E.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; de Castro, A.M.; Shen, H.; Halbur, P.G.; Opriessnig, T. An interferon inducing porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccine candidate elicits protection against challenge with the heterologous virulent type 2 strain VR-2385 in pigs. Vaccine 2017, 35, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, L.; Pijoan, C.; Dee, S.; Olin, M.; Molitor, T.; Joo, H.S.; Xiao, Z.; Murtaugh, M. Virological and immunological responses to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in a large population of gilts. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 68, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco, I.; Gomez-Laguna, J.; Rodriguez-Gomez, I.M.; Quereda, J.J.; Salguero, F.J.; Pallares, F.J.; Carrasco, L. Immunohistochemical expression of IL-12, IL-10, IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma in lymphoid organs of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-infected pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 149, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loving, C.L.; Osorio, F.A.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Zuckermann, F.A. Innate and adaptive immunity against Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 167, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, R.; Menz, B.; Dockrell, H.M.; Chiang, T.J. Recognition of Mycobacterium leprae recombinant 18,000 MW epitopes by IgG subclasses in leprosy. Immunology 1995, 84, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tangye, S.G.; Ferguson, A.; Avery, D.T.; Ma, C.S.; Hodgkin, P.D. Isotype switching by human B cells is division-associated and regulated by cytokines. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4298–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Bi, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhai, L.; Hu, S. Improved immune response to an attenuated pseudorabies virus vaccine by ginseng stem-leaf saponins (GSLS) in combination with thimerosal (TS). Antiviral. Res. 2016, 132, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.C.; Guo, X.; Ge, X.N.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H.C. Cytokine mRNA expression profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from piglets experimentally co-infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and porcine circovirus type 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Guo, X.; Han, J.; Yang, H. The Chinese highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection suppresses Th17 cells response in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 189, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Z.; Yang, J.Y.; Gu, M.; Wang, H.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhu, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. NIK signaling axis regulates dendritic cell function in intestinal immunity and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakam, A.K.; Brightbill, H.; Franci, C.; Kung, C.; Nunez, V.; Jones, C., 3rd; Peng, I.; Jeet, S.; Wu, L.C.; Mellman, I.; et al. Dendritic cells require NIK for CD40-dependent cross-priming of CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14664–14669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedantam, G.; Viswanathan, V.K. Unlocking the gates to inflammatory bowel disease: The role of Enterococcus faecalis gelatinase. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; He, H.; Du, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Increased Enterococcus faecalis infection is associated with clinically active Crohn disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cui, L.; Yao, S.; Lv, L.; Liu, J. Low-molecular-weight polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murrill modulate the Th1 response in cancer immunity. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3429–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Villar, S.; Sainz, T.; Lee, S.A.; Hunt, P.W.; Sinclair, E.; Shacklett, B.L.; Ferre, A.L.; Hayes, T.L.; Somsouk, M.; Hsue, P.Y.; et al. HIV-infected individuals with low CD4/CD8 ratio despite effective antiretroviral therapy exhibit altered T cell subsets, heightened CD8+ T cell activation, and increased risk of non-AIDS morbidity and mortality. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahe, M.C.; Murtaugh, M.P. Mechanisms of Adaptive Immunity to Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Viruses 2017, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashar, T.O.; Webb, H.M.; Eaglestone, S.; Williams, N.A.; Hirst, T.R. Potent immunogenicity of the B subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: Receptor binding is essential and induces differential modulation of lymphocyte subsets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terahara, K.; Ishii, H.; Nomura, T.; Takahashi, N.; Takeda, A.; Shiino, T.; Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Matano, T. Vaccine-induced CD107a+ CD4+ T cells are resistant to depletion following AIDS virus infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 14232–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soghoian, D.Z.; Jessen, H.; Flanders, M.; Sierra-Davidson, K.; Cutler, S.; Pertel, T.; Ranasinghe, S.; Lindqvist, M.; Davis, I.; Lane, K.; et al. HIV-specific cytolytic CD4 T cell responses during acute HIV infection predict disease outcome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 123ra125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Eller, M.; Teigler, J.E.; Maloveste, S.M.; Schultz, B.T.; Soghoian, D.Z.; Lu, R.; Oster, A.F.; Chenine, A.L.; Alter, G.; et al. Cooperativity of HIV-Specific Cytolytic CD4 T Cells and CD8 T Cells in Control of HIV Viremia. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7494–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laforge, M.; Silvestre, R.; Rodrigues, V.; Garibal, J.; Campillo-Gimenez, L.; Mouhamad, S.; Monceaux, V.; Cumont, M.C.; Rabezanahary, H.; Pruvost, A.; et al. The anti-caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPH prevents AIDS disease progression in SIV-infected rhesus macaques. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.J. Antagonizing cytokine-mediated JAK-STAT signaling by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 209, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, R.; Ma, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Nan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.J. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Antagonizes JAK/STAT3 Signaling via nsp5, Which Induces STAT3 Degradation. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.K.; Yu, Z.B.; Xu, A.T.; Tang, J.; Feng, W.H. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nonstructural protein 4 antagonizes beta interferon expression by targeting the NF-kappaB essential modulator. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10934–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beura, L.K.; Sarkar, S.N.; Kwon, B.; Subramaniam, S.; Jones, C.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Osorio, F.A. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nonstructural protein 1beta modulates host innate immune response by antagonizing IRF3 activation. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Ransburgh, R.; Snijder, E.J.; Fang, Y. Nonstructural protein 2 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus inhibits the antiviral function of interferon-stimulated gene 15. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ke, H.; Han, M.; Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Yoo, D. Nonstructural Protein 11 of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Suppresses Both MAVS and RIG-I Expression as One of the Mechanisms to Antagonize Type I Interferon Production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, F.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, L.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, C.; Yuan, X. Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice. Vaccines 2021, 9, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030266
Su F, Wu Y, Li J, Huang Y, Yu B, Xu L, Xue Y, Xiao C, Yuan X. Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice. Vaccines. 2021; 9(3):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Fei, Yige Wu, Junxing Li, Yee Huang, Bin Yu, Lihua Xu, Yin Xue, Chenwen Xiao, and Xiufang Yuan. 2021. "Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice" Vaccines 9, no. 3: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030266
APA StyleSu, F., Wu, Y., Li, J., Huang, Y., Yu, B., Xu, L., Xue, Y., Xiao, C., & Yuan, X. (2021). Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice. Vaccines, 9(3), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030266




