Mutagenic Distinction between the Receptor-Binding and Fusion Subunits of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Its Upshot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
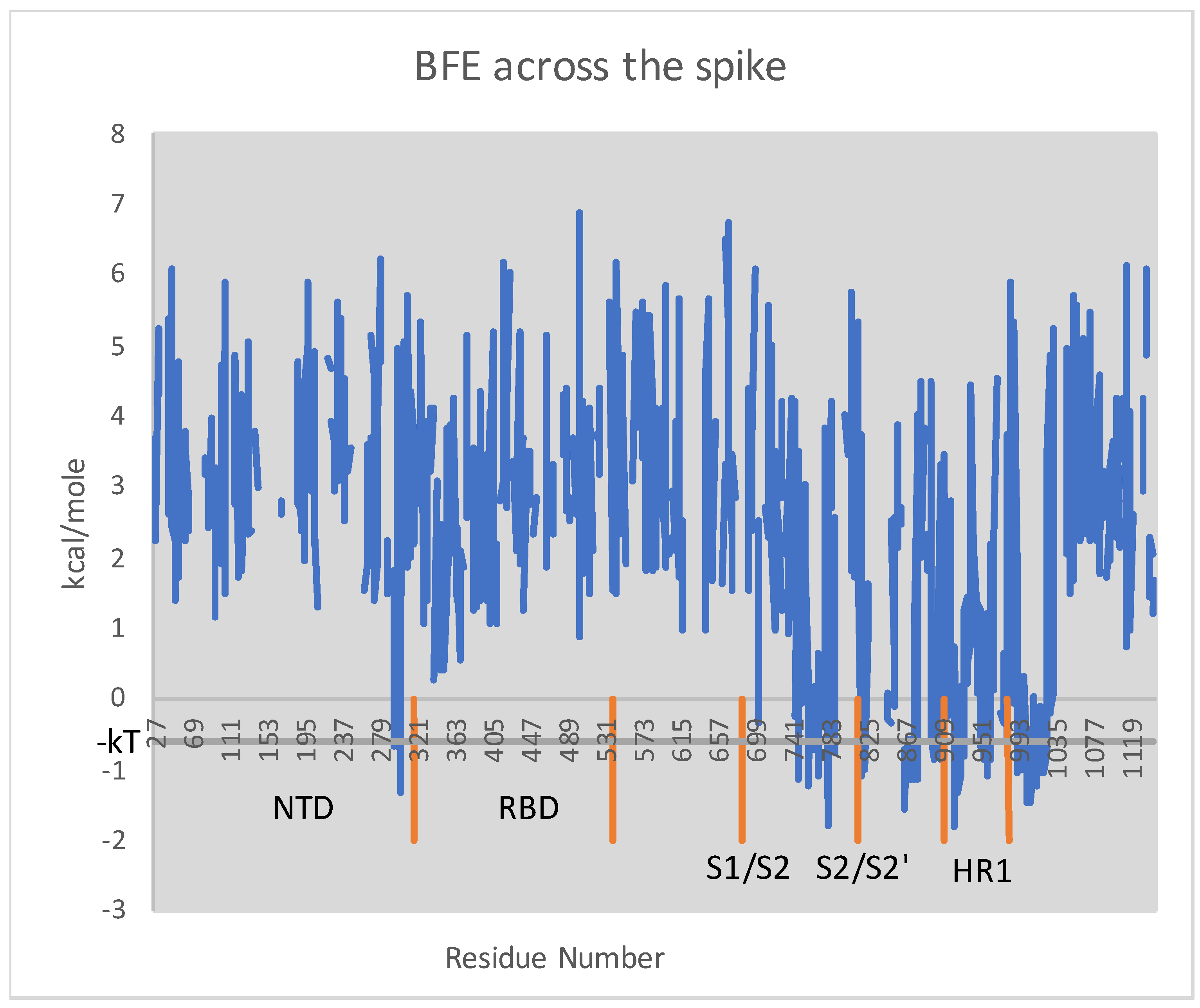
3.1. Wuhan-Hu-1 to Many Variants
- is more disorganized than (i.e., # missing is larger);
- there are more loops in than (i.e., # absent is larger);
- the BFE of is larger than ;
- the same three assertions above hold for compared to ; and
- a greater ratio of residues in are mutating in the variants under consideration than in .
3.2. Wuhan-Hu-1 to Delta to Omicron
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BFE | backbone free energy |
| BHB | backbone hydrogen bond |
| PDB | protein data bank |
| W | Wuhan-Hu-1 SARS-CoV-2 strain |
| , , O | Beta, Delta, and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant |
References
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gillil, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outbreak.info. Available online: https://outbreak.info/ (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Penner, R. Antiviral Resistance against Viral Mutation: Praxis and Policy for SARS-CoV-2. Comput. Math. Biophys. 2021, 9, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmock, N.J.; Easton, A.J.; Leppard, K.N. Introduction to Modern Virology, 6th ed.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, S.C. Viral membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.M.; Delos, S.E.; Brecher, M.; Schornberg, K. Structures and mechanisms of viral membrane fusion proteins: Multiple variations on a common theme. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 43, 189–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollavaram, K.; Leeman, T.H.; Lee, M.W.; Kulkarni, A.; Upshaw, S.G.; Yang, J.; Song, H.; Platt, M.O. Multiple sites on SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are susceptible to proteolysis by cathepsins B, K, L, S, and V. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, A.V.; Ptitsyn, O. Protein Physics, a Course of Lectures, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.; Edwards, R.J.; Mansouri, K.; Janowska, K.; Stalls, V.; Gobeil, S.M.; Kopp, M.; Li, D.; Parks, R.; Hsu, A.L.; et al. Controlling the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein conformation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraszek, J.; Rutten, L.; Blokl, S.; Bouchier, P.; Voorzaat, R.; Ritschel, T.; Bakkers, M.J.; Renault, L.L.; Langedijk, J.P. Stabilizing the closed SARS-CoV-2 spike trimer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, M.; Walls, A.C.; Bowen, J.E.; Corti, D.; Veesler, D. Structure-guided covalent stabilization of coronavirus spike glycoprotein trimers in the closed conformation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toelzer, C.; Gupta, K.; Yadav, S.K.; Borucu, U.; Davidson, A.D.; Williamson, M.K.; Shoemark, D.K.; Garzoni, F.; Staufer, O.; Milligan, R.; et al. Free fatty acid binding pocket in the locked structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science 2020, 370, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, A.G.; Benton, D.J.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S.R.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Gamblin, S.J. SARS-CoV-2 and bat RaTG13 spike glycoprotein structures inform on virus evolution and furin-cleavage effects. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Han, W.; Hong, X.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Conformational dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 trimeric spike glycoprotein in complex with receptor ACE2 revealed by cryo-EM. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, F.; Guo, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhong, X.; Chi, X.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the different states of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in complex with ACE2. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Gu, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; et al. Development and structural basis of a two-MAb cocktail for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Gorman, J.; Rapp, M.; Cerutti, G.; Chuang, G.Y.; Katsamba, P.S.; Sampson, J.M.; Schön, A.; Bimela, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Structures Delineate a pH-Dependent Switch that Mediates Endosomal Positioning of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domains. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, R. Backbone Free Energy Estimator Applied to Viral Glycoproteins. J. Comput. Biol. 2020, 27, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, R.C.; Andersen, E.S.; Jensen, J.L.; Kantcheva, A.K.; Bublitz, M.; Nissen, P.; Rasmussen, A.M.; Svane, K.L.; Hammer, B.; Rezazadegan, R.; et al. Hydrogen bond rotations as a uniform structural tool for analyzing protein architecture. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Finkelstein, A.V.; Gutin, A.M.; Badretdinov, A.Y. Boltzmann-like statistics of protein architectures: Origins and consequences. In Proteins: Structure Function, and Engineering; Biswas, B.B., Roy, S., Eds.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 24, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein, A.V.; Badretdinov, A.Y.; Gutin, A.M. Why do protein architectures have Boltzmann-like statistics? Proteins 1995, 23, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, F.M. Empirical protein energy maps. Nat. New Biol. 1971, 234, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, R. Conserved High Free Energy Sites in Human Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein Backbones. J. Comput. Biol. 2020, 27, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobeil, S.M.; Janowska, K.; McDowell, S.; Mansouri, K.; Parks, R.; Manne, K.; Stalls, V.; Kopp, M.F.; Henderson, R.; Edwards, R.J.; et al. D614G Mutation Alters SARS-CoV-2 Spike Conformation and Enhances Protease Cleavage at the S1/S2 Junction. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobeil, S.; Janowska, K.; McDowell, S.; Mansouri, K.; Parks, R.; Stalls, V.; Kopp, M.F.; Manne, K.; Saunders, K.O.; Edwards, R.J.; et al. Effect of natural mutations of SARS-CoV-2 on spike structure, conformation and antigenicity. Science 2021, 373, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugo, O. How large B-factors can be in protein crystal structures? BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mol | #Res | avg #Missing | avg #Absent | avg #Unbonded | avg BFE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 1121 | 1.39 | 4.91 | 0.35 | 2.41 |
| 56 | 4.71 | 5.34 | 0.61 | 2.47 | |
| S | 655 | 1.85 | 5.52 | 0.42 | 3.16 |
| 43 | 6.14 | 5.69 | 0.74 | 2.80 | |
| S | 466 | 0.73 | 4.05 | 0.25 | 1.60 |
| 13 | 0.00 | 4.15 | 0.15 | 2.14 |
| Mol | W to (*) | to | W to | W to |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 35 | 40 | 35 | 30 |
| 61 | 61 | 22 | 42 | |
| S | 42 | 46 | 42 | 32 |
| 74 | 67 | 27 | 43 | |
| S | 25 | 32 | 25 | 28 |
| 15 | 33 | 0 | 33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penner, R.C. Mutagenic Distinction between the Receptor-Binding and Fusion Subunits of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Its Upshot. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121509
Penner RC. Mutagenic Distinction between the Receptor-Binding and Fusion Subunits of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Its Upshot. Vaccines. 2021; 9(12):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121509
Chicago/Turabian StylePenner, Robert Clark. 2021. "Mutagenic Distinction between the Receptor-Binding and Fusion Subunits of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Its Upshot" Vaccines 9, no. 12: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121509
APA StylePenner, R. C. (2021). Mutagenic Distinction between the Receptor-Binding and Fusion Subunits of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Its Upshot. Vaccines, 9(12), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121509






