Mycoplasma suis Alpha-Enolase Subunit Vaccine Induces an Immune Response in Experimental Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
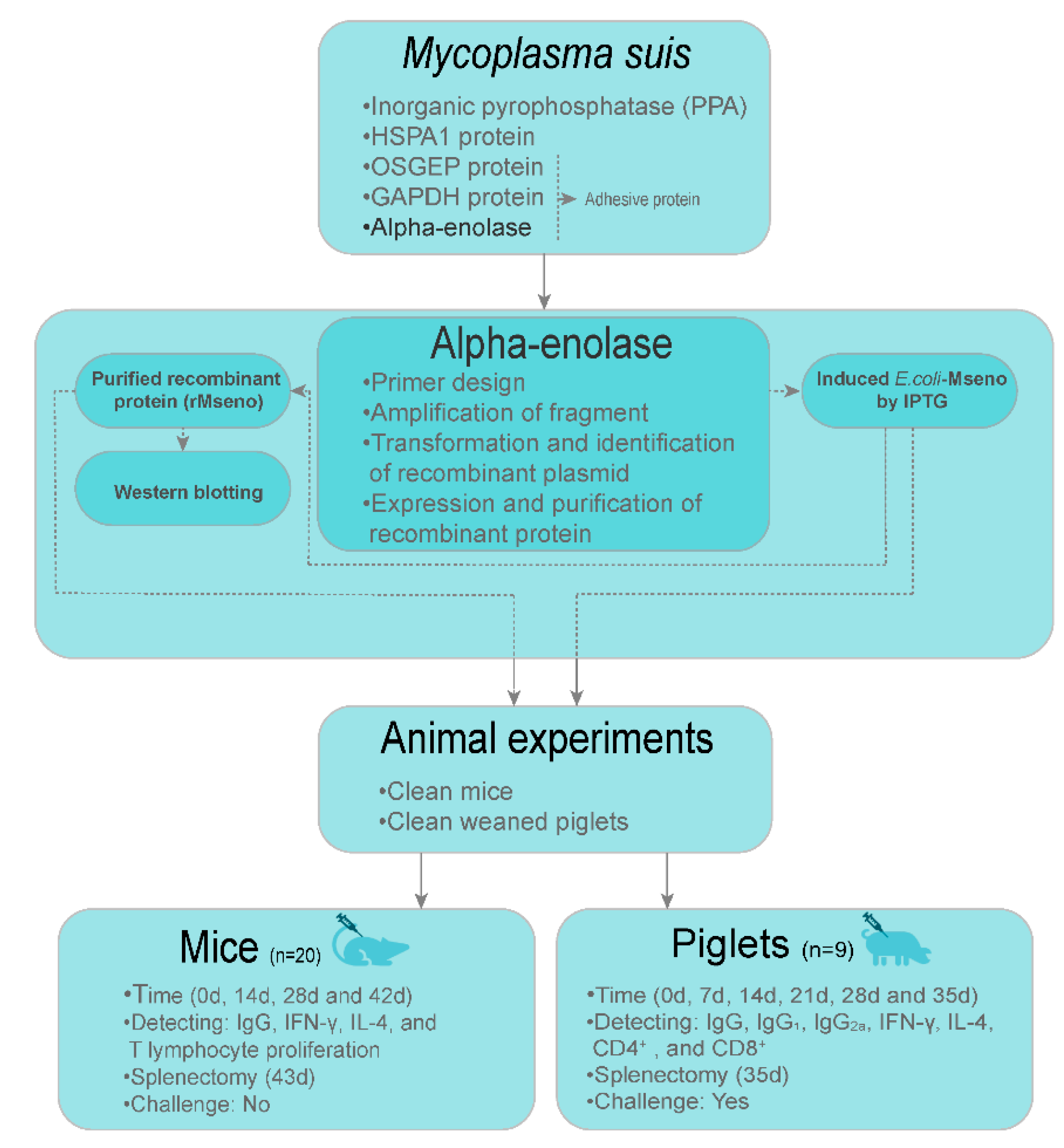
2.1. Design of Experiments
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Cells, Strains, Reagents, and Animals
2.4. Primer Design, Synthesis, and Amplification of Target Fragment
2.5. Construction, Transformation, and Identification of Recombinant pET-15b-ENO Plasmid
2.6. Expression, Purification, and Analysis of rMseno
2.7. Immunization of Mice
2.8. Evaluation of Anti-M.-suis Specific Antibody, IFN-γ, and IL-4 in Mouse Serum
2.9. T-lymphocyte Proliferation Experiment in Mice
2.10. Immunization of Piglets
2.11. Evaluation of Anti-M.-suis Specific Antibodies, IFN-γ, and IL-4 in the Porcine Serum
2.12. Detection of T lymphocytes in Piglets
2.13. Challenge Experiment
2.14. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Target Gene Amplification and Analysis
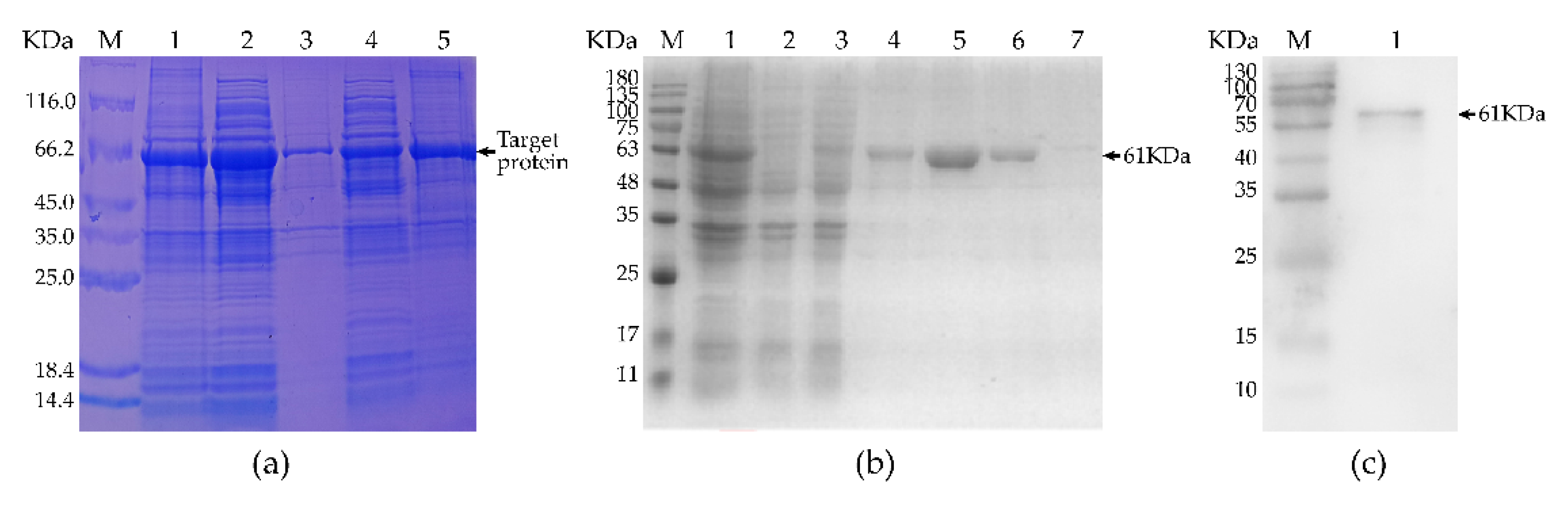
3.2. Expression, Purification, and Identification of Recombinant Protein
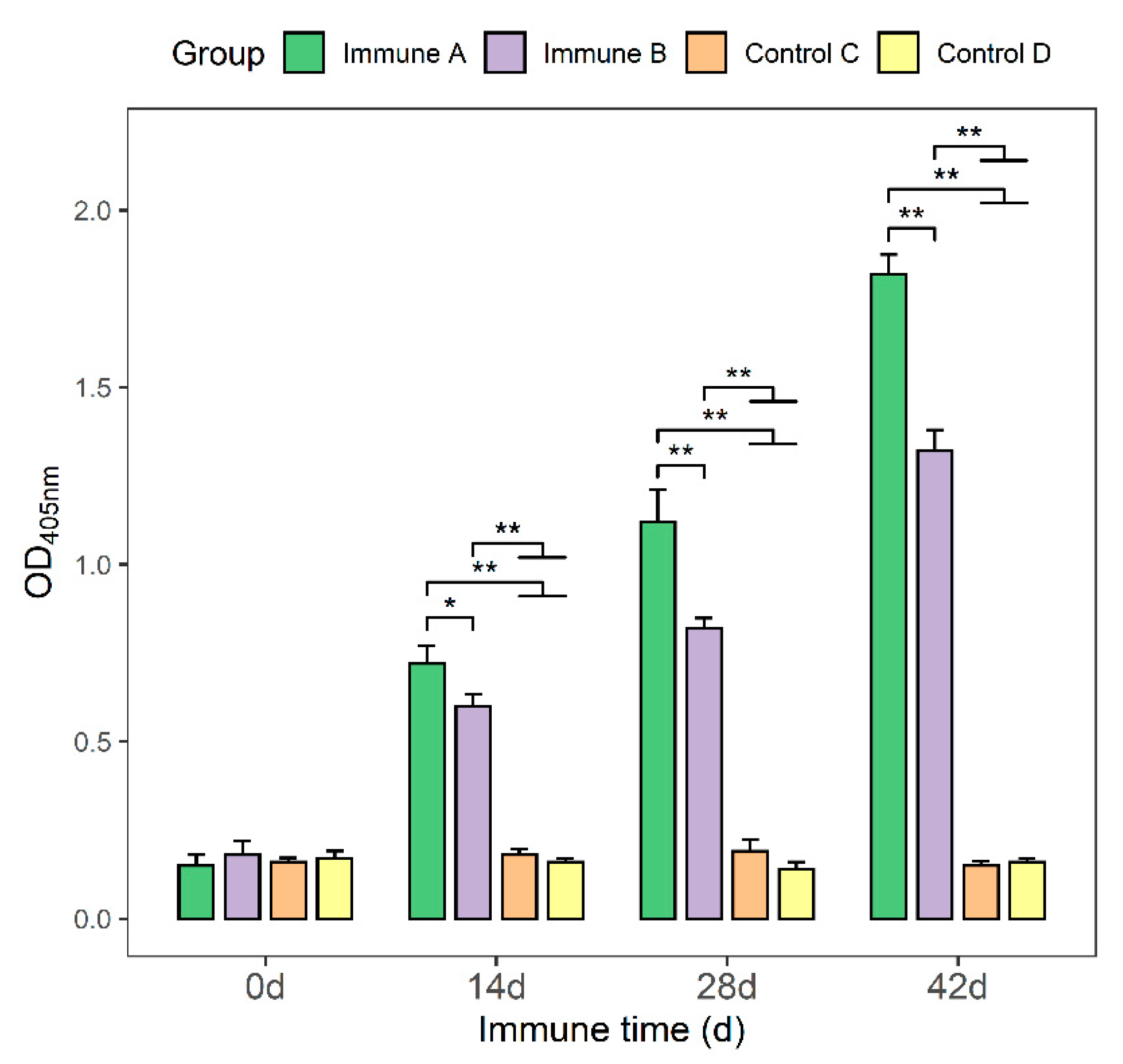
3.3. Detection of Anti-M. suis-Specific Antibodies in the Sera of Immunized Mice
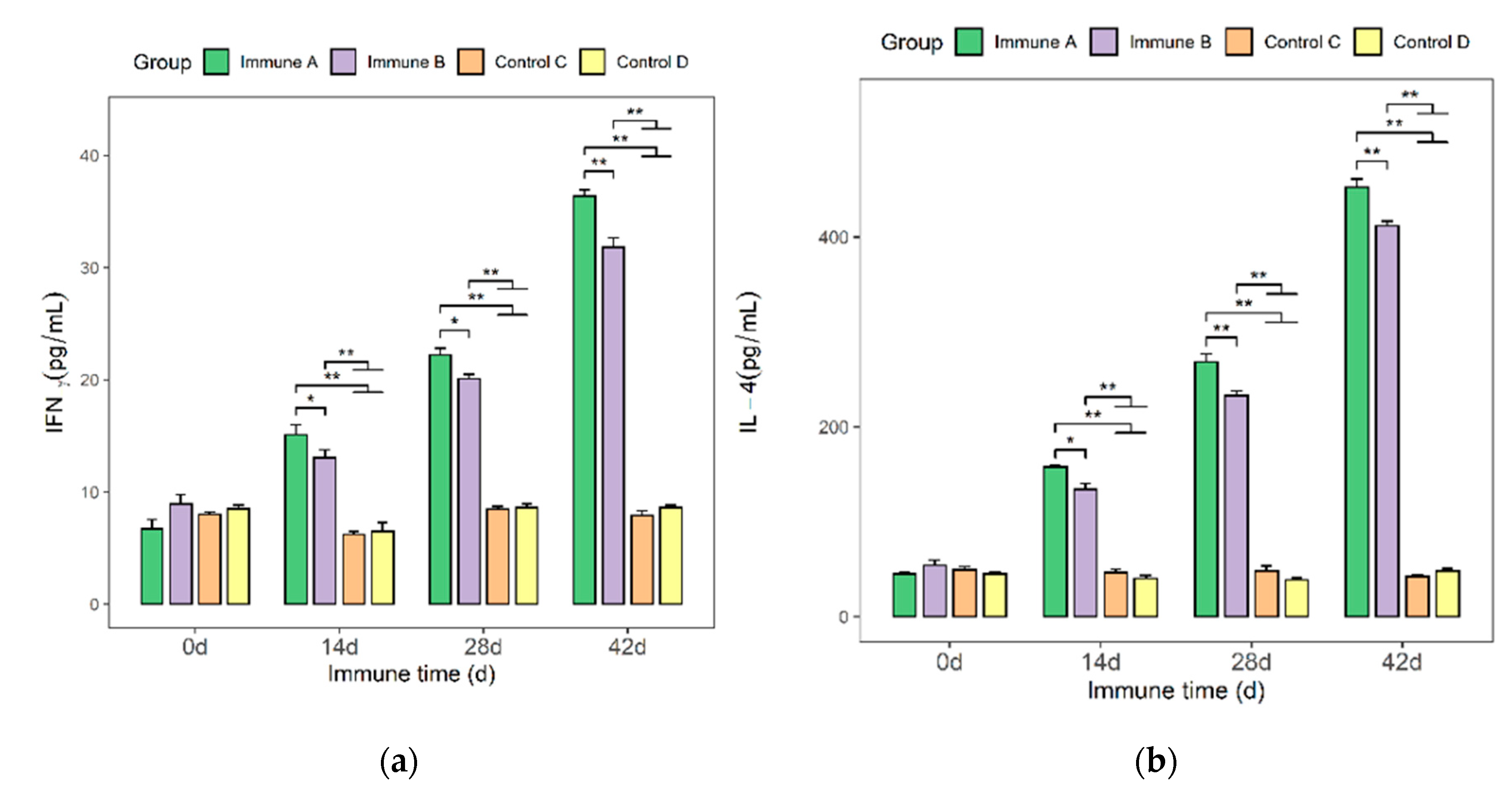
3.4. Detection of IFN-γ and IL-4 Cytokines in the Sera of Immunized Mice
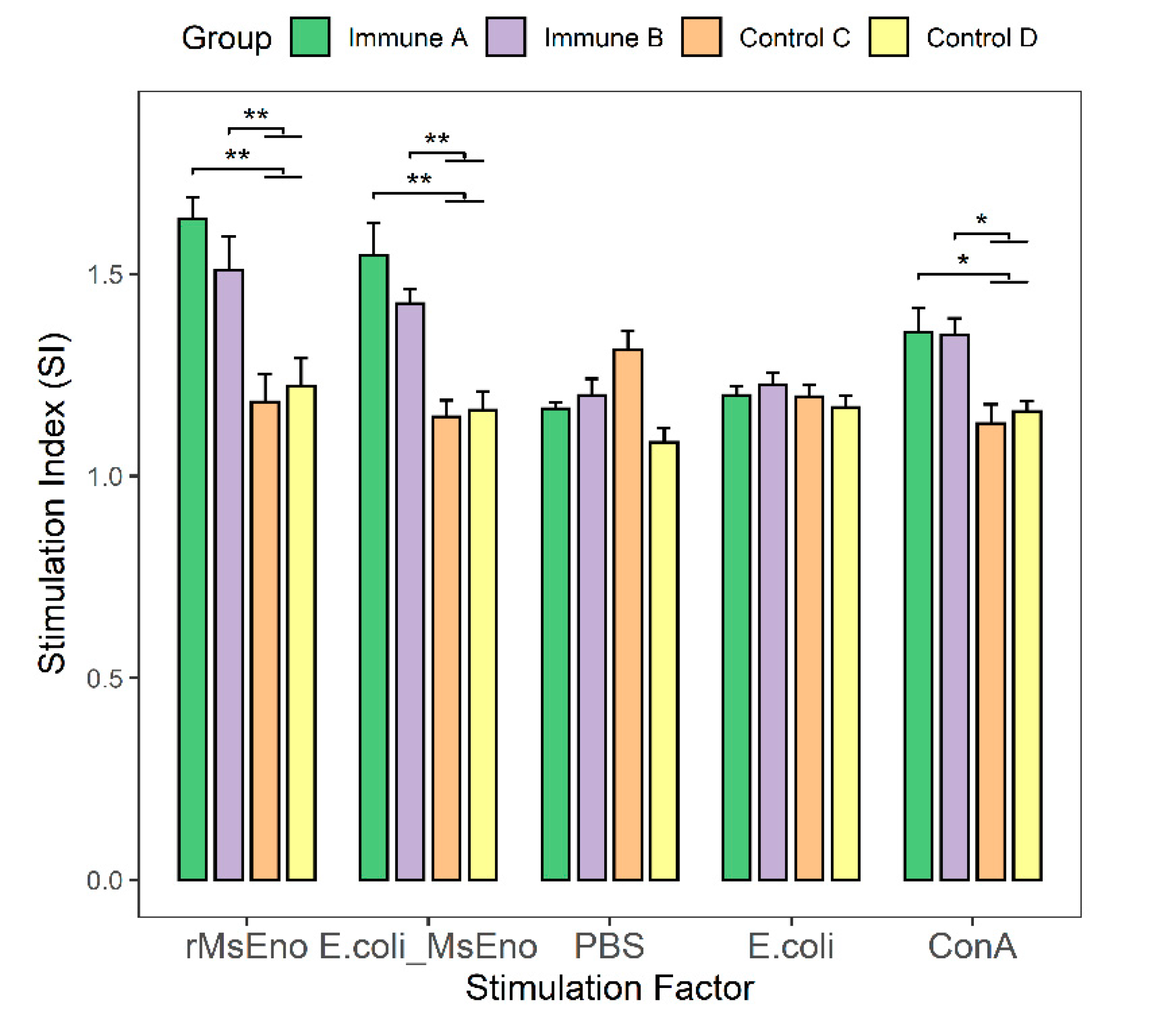
3.5. T-Lymphocyte Proliferation in Immunized Mice
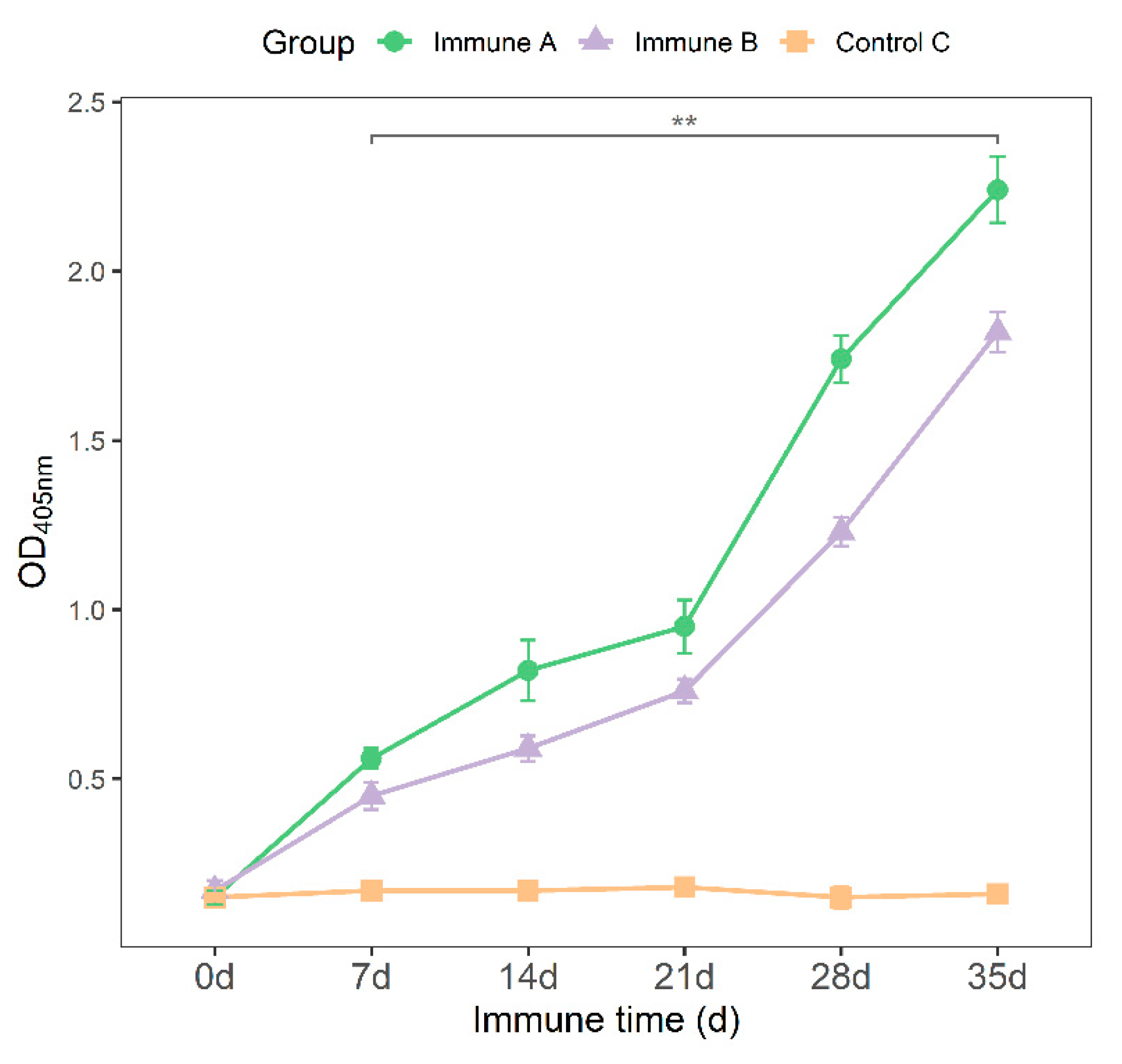
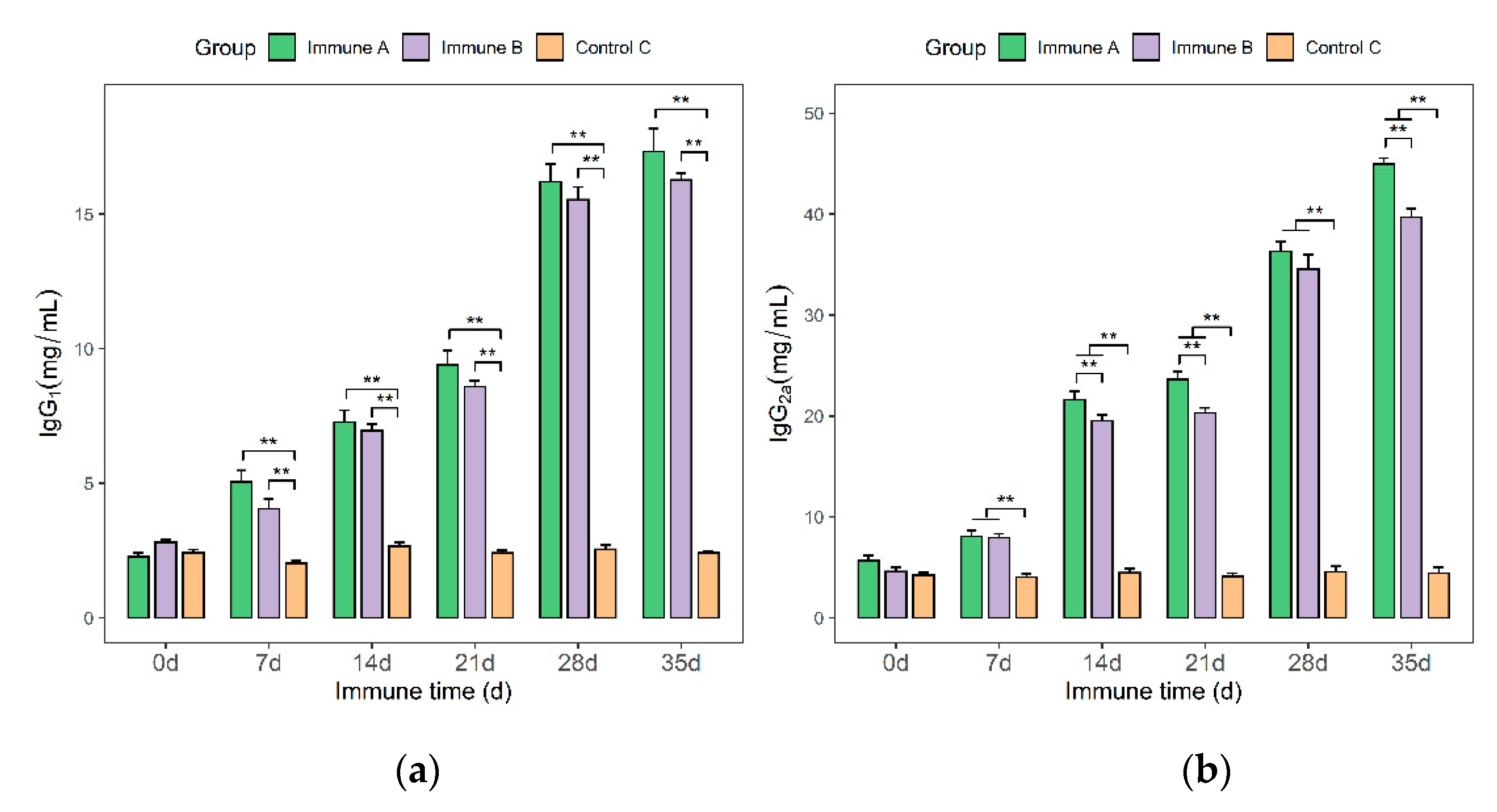
3.6. Detection of IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a Antibodies in Immunized Piglets
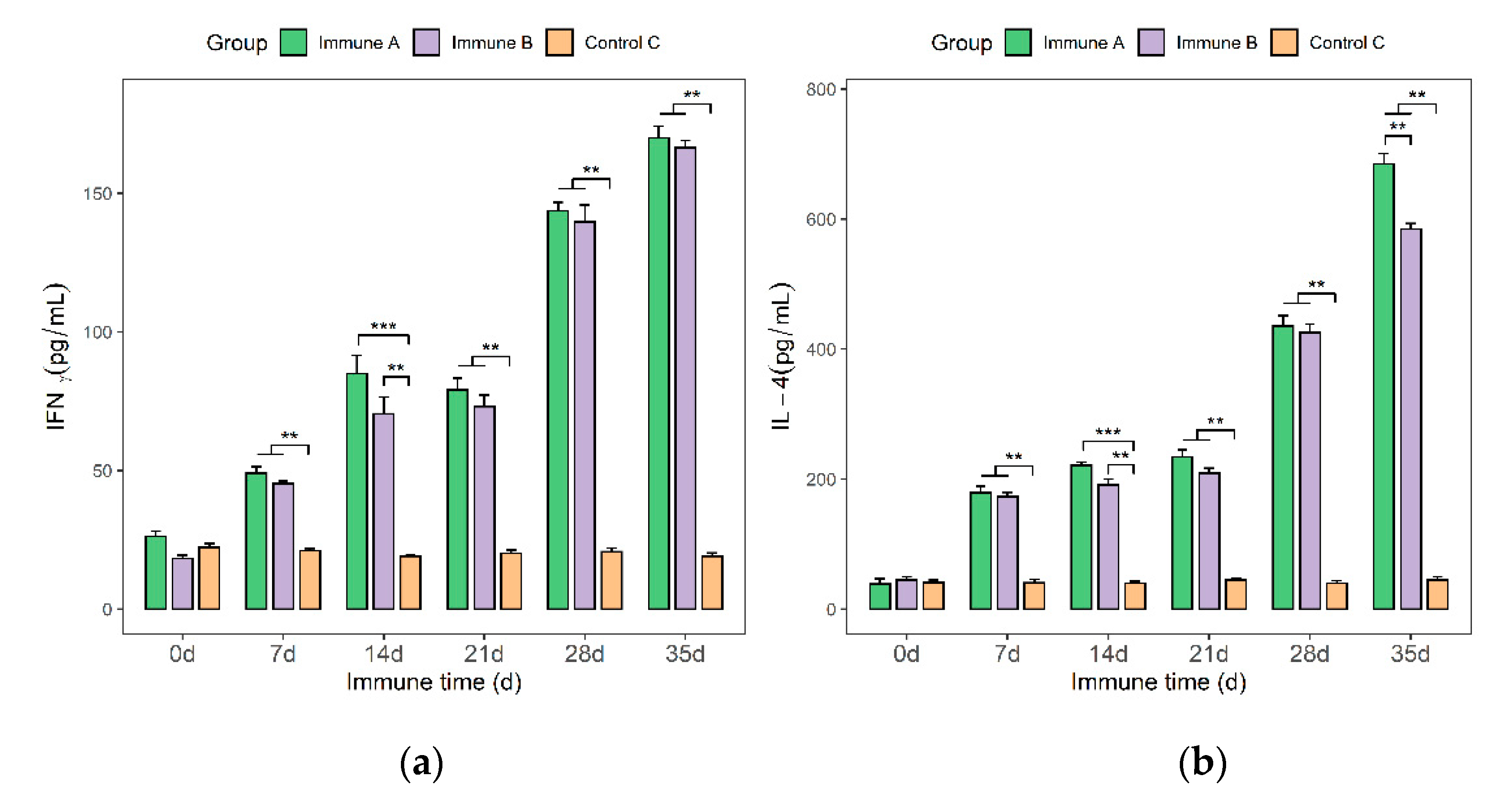
3.7. Detection of IFN-γ and IL-4 Cytokines in the Sera of Immunized Piglets
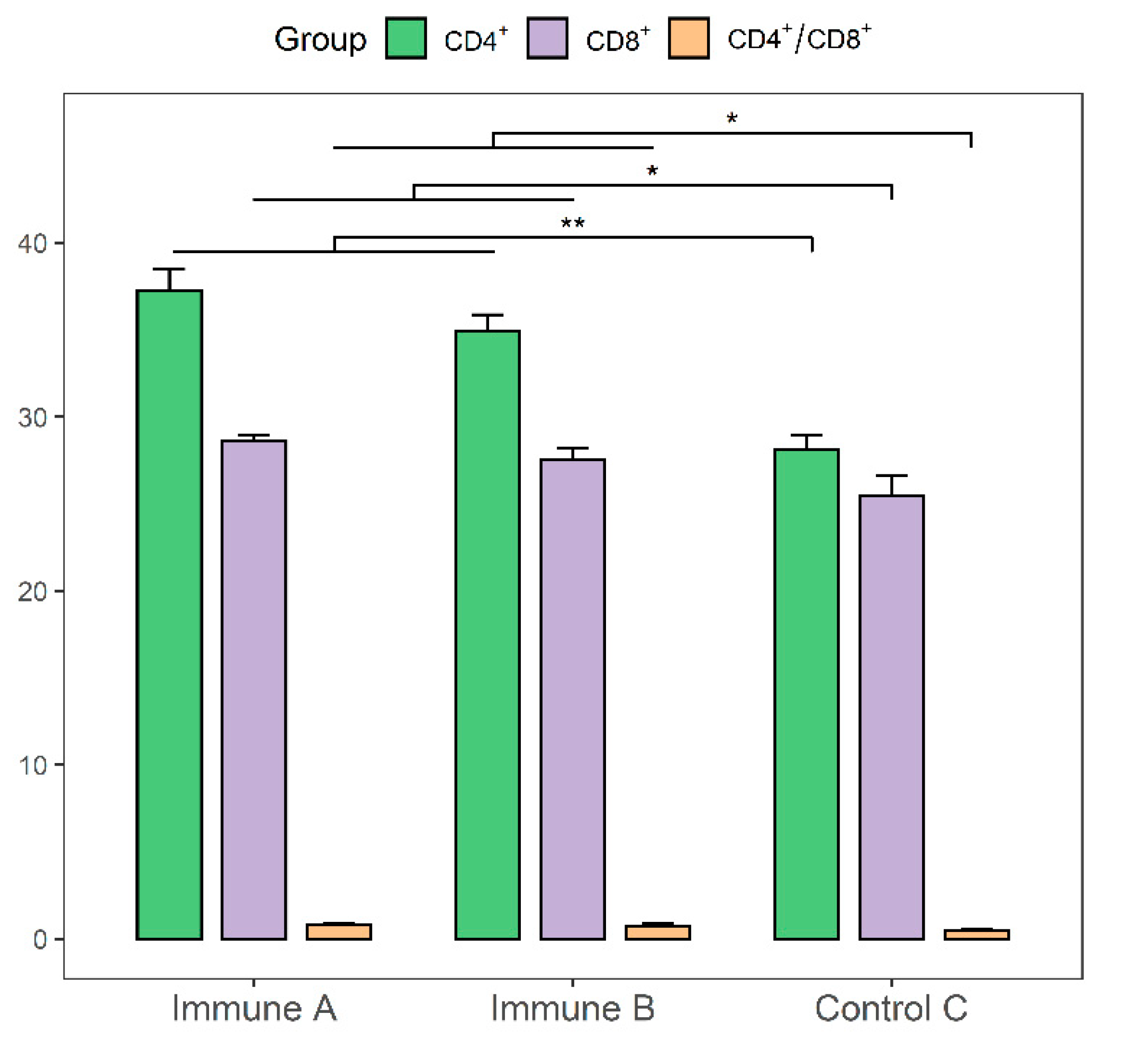
3.8. Evaluation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell Levels in the Immunized Piglets
3.9. The Outcome of Experimental Challenge
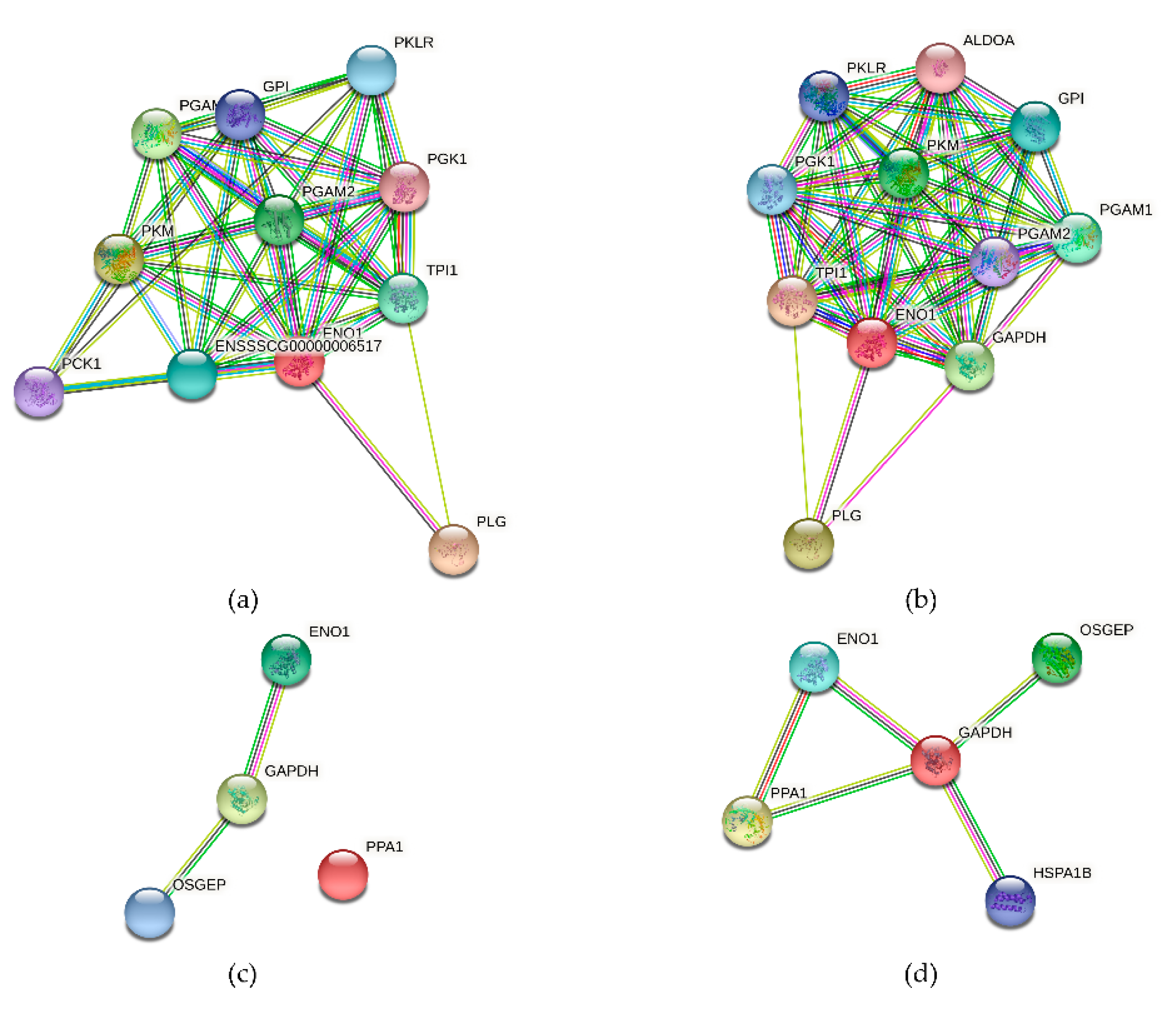
3.10. The Alpha-Enolase (ENO1) Protein Interaction Network
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoelzle, L.E.; Zeder, M.; Felder, K.M.; Hoelzle, K. Pathobiology of Mycoplasma suis. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neimark, H.; Johansson, K.-E.; Rikihisa, Y.; Tully, J.G. Revision of haemotrophic Mycoplasma species names. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messick, J.B. Hemotrophic mycoplasmas (hemoplasmas): A review and new insights into pathogenic potential. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 33, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z. Porcine Eperythrozoonosis in China. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1081, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, J.; Ade, J.; Hermanns, W.; Ritzmann, M.; Wentzel, S.; Hoelzle, K.; Hoelzle, L.E. Clinical, haematological and pathomorphological findings in Mycoplasma suis infected pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, S.; Lassek, C.; Mack, S.-L.; Ritzmann, M.; Stadler, J.; Becher, D.; Hoelzle, K.; Riedel, K.; Hoelzle, L.E. Updating the proteome of the uncultivable hemotrophic Mycoplasma suis in experimentally infected pigs. Proteomics 2016, 16, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neimark, H.; Johansson, K.E.; Rikihisa, Y.; Tully, J.G. Proposal to transfer some members of the Genera Haemobartonella and Eperythrozoon to the Genus Mycoplasma with Descriptions of ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma Haemofelis’, ‘Candidatus My-coplasma Haemomuris’, ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma Haemosuis’ and ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma Wenyonii’. Int. J. Syst Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 891–899. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Seroprevalence of Mycoplasma suis infection in pigs in Eastern China as estimated by a Blocking Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 81, 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, M.A.; Leite, A.I.; Goncalves, L.R.; Sousa, K.C.; Amaral, R.B.; Silva, G.C.; Machado, R.Z.; Andre, M.R. High occurrence of Mycoplasma suis infection in Swine Herds from non-technified farms in Mossoro, state of Rio Grande Do Norte, Northeastern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2016, 25, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritzmann, M.; Grimm, J.; Heinritzi, K.; Hoelzle, K.; Hoelzle, L.E. Prevalence of Mycoplasma suis in slaughter pigs, with correlation of PCR results to hematological findings. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 133, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, L.E. Significance of haemotrophic mycoplasmas in veterinary medicine with particular regard to the Mycoplasma suis infection in swine. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2007, 120, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strait, E.L.; Hawkins, P.A.; Wilson, W.D. Dysgalactia associated with Mycoplasma suis infection in a sow herd. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 241, 1666–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Sun, W.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, L.; Cai, D.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, S.; et al. Development of colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay for rapid detection of Mycoplasma suis in porcine plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, L. Haemotrophic mycoplasmas: Recent advances in Mycoplasma suis. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.B.; Amaral, R.B.D.; Gatto, I.R.H.; Lapera, I.M.; de Oliveira, L.G.; Hoppe, E.G.L.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Molecular detection of Mycoplasma suis in captive white-lipped peccaries (Tayassu pecari) and wild boars Wild Boars (Sus Scrofa) in Brazil. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 63, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, W.; Song, W.; Liu, Z.; Khan, M.K.; He, L.; Fang, R.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, M.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Mycoplasma suis infection in pig farms in central China. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 117, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, K.; Engels, M.; Kramer, M.M.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Dieckmann, S.M.; Hoelzle, L.E. Occurrence of Mycoplasma suis in wild boars (Sus scrofa L.). Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.L.; Liang, A.B.; Yao, C.B.; Yang, Z.B.; Zhu, J.G.; Cui, L.; Yu, F.; Zhu, N.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Hua, X.G. Prevalence of Mycoplasma suis (Eperythrozoon suis) infection in swine and swine-farm workers in Shanghai, China. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, D.B.; Ruiz, M.; Sanchez, J.P. First molecular detection of Mycoplasma suis in the pig louse Haematopinus suis (Phthiraptera: Anoplura) from Argentina. Acta Trop. 2019, 194, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntaric, V.; Borčić, D.; Vukelic, D.; Jeren, T.; Burek, V.; Wikerhauser, T.; Richter, B. Eperythrozoonosis in man. Lancet 1986, 328, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, S.A.; Sokoli, A.; Felder, K.M.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Schwarzenbach, S.; Guhl, B.; Hoelzle, K.; Hoelzle, L.E. The surface-localised alpha-enolase of Mycoplasma suis is an Adhesion protein. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, L.E.; Hoelzle, K.; Helbling, M.; Aupperle, H.; Schoon, H.A.; Ritzmann, M.; Heinritzi, K.; Felder, K.M.; Wittenbrink, M.M. MSG1, a surface-localised protein of Mycoplasma suis is involved in the adhesion to erythrocytes. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Fang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, B.; Hu, M.; Zhao, J. Identification of erythrocyte membrane proteins interacting with Mycoplasma suis GAPDH and OSGEP. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 119, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layh-Schmitt, G.; Podtelejnikov, A.; Mann, M. Proteins complexed to the P1 adhesin of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Microbiology 2000, 146, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Felder, K.M.; Carranza, P.M.; Gehrig, P.M.; Roschitzki, B.; Barkow-Oesterreicher, S.; Hoelzle, K.; Riedel, K.; Kube, M.; Hoelzle, L.E. Insights into the gene expression profile of uncultivable Hemotrophic Mycoplasma suis during acute infection, obtained using proteome analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, K.; Peter, S.; Sidler, M.; Kramer, M.M.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Felder, K.M.; Hoelzle, E.L. Inorganic pyrophosphatase in uncultivable hemotrophic mycoplasmas: Identification and properties of the enzyme from Mycoplasma suis. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, L.; Li, J.; Xue, S.; Gao, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, S. Interactive host cells related to Mycoplasma suis alpha-enolase by yeast two-hybrid analysis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, E.L.; Hoelzle, K.; Harder, A.; Ritzmann, M.; Aupperle, H.; Schoon, A.H.; Heinritzi, K.; Wittenbrink, M.M. First identification and functional characterization of an immunogenic protein in unculturable haemotrophic Mycoplasmas (Mycoplasma suis HspA1). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Chai, T. Synthesis, cloning, and expression of Mycoplasma suis inorganic pyrophosphatase gene using PCR-based accurate synthesis and overlap-extension PCR, and its immunogenicity analysis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 91, e100–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, N.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Chai, T. Development and evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant inorganic pyrophosphatase gene antigen for the detection of Mycoplasma suis antibodies. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 93, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzle, K.; Doser, S.; Ritzmann, M.; Heinritzi, K.; Palzer, A.; Elicker, S.; Kramer, M.; Felder, K.M.; Hoelzle, L.E. Vaccination with the Mycoplasma suis recombinant adhesion protein MSG1 elicits a strong immune response but fails to induce protection in pigs. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5376–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ju, Y.; Jia, L.; Kumagai, S.; Li, J.; Manabe, N. Establishment of an efficient enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Eperythrozoon sius antibody in Swine. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2008, 70, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Groebel, K.; Hoelzle, K.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Ziegler, U.; Hoelzle, L.E. Mycoplasma suis invades porcine Erythrocytes. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzle, E.L.; Felder, K.M.; Hoelzle, K. Porcine eperythrozoonosis: From Eperythrozoon suis to Mycoplasma suis. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. G Grosstiere Nutztiere 2011, 39, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sokoli, A.; Groebel, K.; Hoelzle, K.; Amselgruber, W.M.; Mateos, J.M.; Schneider, M.K.; Ziegler, U.; Felder, K.M.; Hoelzle, E.L. Mycoplasma suis infection results endothelial cell damage and activation: New insight into the cell tropism and pathogenicity of hemotrophic mycoplasma. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Q.; Rajadurai, P.; Abas, F.; Othman, I.; Naidu, R. Proteomic analysis on anti-proliferative and apoptosis effects of curcumin analog, 1,5-bis(4-Hydroxy-3-Methyoxyphenyl)-1,4-Pentadiene-3-One-treated human Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 645856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Casal, J.; Potter, A.A. Glyceradehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a suitable vaccine candidate for protection against bacterial and parasitic diseases. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furesz, E.S.; Wilkie, B.N.; Mallard, A.B.; Rosendal, S.; MacInnes, I.J. Anti-haemolysin IgG1 to IgG2 ratios correlate with haemolysin neutralization titres and lung lesion scores in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infected pigs. Vaccine 1998, 16, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, E.L.; Thacker, B.J.; Kuhn, M.; Hawkins, P.A.; Waters, W.R. Evaluation of local and systemic immune responses induced by intramuscular injection of a Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae bacterin to pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.L.; Bossie, A.; Sanders, V.M.; Fernandez-Botran, R.; Coffman, R.L.; Mosmann, T.R.; Vitetta, E.S. Regulation of antibody isotype secretion by subsets of antigen-specific helper T cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 1988, 334, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, F.J.; Pérez-Martin, E.J.; Carrón, A.; Navarrete, I. Comparison of IgM, IgG1 and IgG2 responses to Trichinella spiralis and Trichinella britoviin swine. Parasite 2001, 8, S133–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Okamba, F.R.; Moreau, E.; Bouh, K.C.S.; Gagnon, C.A.; Massie, B.; Arella, M. Immune responses induced by replication-defective adenovirus expressing the C-terminal portion of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae P97 Adhesin. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, S.; Seo, K.; Yang, M.; Cui, C.; Yang, M.; Xiang, S.; Yan, Z.; Wu, S.; Han, J.; Yu, X.; et al. Mycoplasma suis Alpha-Enolase Subunit Vaccine Induces an Immune Response in Experimental Animals. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121506
Xue S, Seo K, Yang M, Cui C, Yang M, Xiang S, Yan Z, Wu S, Han J, Yu X, et al. Mycoplasma suis Alpha-Enolase Subunit Vaccine Induces an Immune Response in Experimental Animals. Vaccines. 2021; 9(12):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121506
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Shujiang, Kangseok Seo, Miaosen Yang, Chengdu Cui, Meng Yang, Siyu Xiang, Zongbin Yan, Shengjun Wu, Jincheng Han, Xiaoyang Yu, and et al. 2021. "Mycoplasma suis Alpha-Enolase Subunit Vaccine Induces an Immune Response in Experimental Animals" Vaccines 9, no. 12: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121506
APA StyleXue, S., Seo, K., Yang, M., Cui, C., Yang, M., Xiang, S., Yan, Z., Wu, S., Han, J., Yu, X., Li, Y., & Jin, X. (2021). Mycoplasma suis Alpha-Enolase Subunit Vaccine Induces an Immune Response in Experimental Animals. Vaccines, 9(12), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121506




