Analyses of Safety Profile and Homologous Antibody Responses to a Mammalian Cell-Based, MF59-Adjuvanted, A/H5N1, Pandemic Influenza Vaccine across Four Phase II/III Clinical Trials in Healthy Children, Adults, and Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vaccines
2.2. Study Design and Objectives
2.3. Study Participants
2.4. Immunogenicity Assessment
2.5. Safety Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Immunogenicity
3.2. Safety
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saunders-Hastings, R.P.; Krewski, D. Reviewing the history of pandemic influenza: Understanding patterns of emergence and transmission. Pathogens 2016, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cumulative Number of Confirmed Human Cases of Avian Influenza a(h5n1) Reported to Who. Available online: https://www.Who.Int/influenza/human_animal_interface/h5n1_cumulative_table_archives/en/ (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Vaccines Licensed for Use in the United States. Available online: https://www.Fda.Gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines/vaccines-licensed-use-united-states (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- WHO Writing Group; Ampofo, W.K.; Baylor, N.; Cobey, S.; Cox, N.J.; Daves, S.; Edwards, S.; Ferguson, N.; Grohmann, G.; Hay, A.; et al. Improving influenza vaccine virus selection: Report of a who informal consultation held at who headquarters, geneva, switzerland, 14–16 June 2010. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2012, 6, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Zhou, H.; Ye, D.; Kemble, G.; Jin, H. Improvement of influenza a/fujian/411/02 (h3n2) virus growth in embryonated chicken eggs by balancing the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase activities, using reverse genetics. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6763–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.D.; Stewart, S.M.; Lee, J.; Ferdman, J.; Bajic, G.; Do, K.T.; Ernandes, M.J.; Suphaphiphat, P.; Settembre, E.C.; Dormitzer, P.R.; et al. Influenza immunization elicits antibodies specific for an egg-adapted vaccine strain. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.N.; Zost, S.J.; Thompson, A.J.; Oyen, D.; Nycholat, C.M.; McBride, R.; Paulson, J.C.; Hensley, S.E.; Wilson, I.A. A structural explanation for the low effectiveness of the seasonal influenza h3n2 vaccine. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zost, J.S.; Parkhouse, K.; Gumina, M.E.; Kim, K.; Perez, S.D.; Wilson, P.C.; Treanor, J.J.; Sant, A.J.; Cobey, S.; Hensley, S.E. Contemporary h3n2 influenza viruses have a glycosylation site that alters binding of antibodies elicited by egg-adapted vaccine strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12578–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormitzer, R.P.; Suphaphiphat, P.; Gibson, D.G.; Wentworth, D.E.; Stockwell, T.B.; Algire, M.A.; Alperovich, N.; Barro, M.; Brown, D.M.; Craig, S.; et al. Synthetic generation of influenza vaccine viruses for rapid response to pandemics. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 185ra68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doroshenko, A.; Halperin, S.A. Trivalent mdck cell culture-derived influenza vaccine optaflu (novartis vaccines). Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, P.J.; Schmitt, H.J.; Trusheim, H.; Broker, M. Safety of mdck cell culture-based influenza vaccines. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappuoli, R.; Dormitzer, P.R. Influenza: Options to improve pandemic preparation. Science 2012, 336, 1531–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohr, K. Perspective: Ill prepared for a pandemic. Nature 2014, 507, S20–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, B.J.; Valley, U.; Rappuoli, R. Vaccine manufacturing: Challenges and solutions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Available online: https://www.Fda.Gov/about-fda/fda-organization/center-biologics-evaluation-and-research-cber (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Available online: https://www.Ema.Europa.Eu/en/committees/committee-medicinal-products-human-use-chmp (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- World Health Organization. Pandemic (h1n1) 2009. Available online: https://www.Who.Int/csr/disease/swineflu/en/ (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Bart, A.S.; Hohenboken, M.; della Cioppa, G.; Narasimhan, V.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Kanesa-Thasan, N. A cell culture-derived mf59-adjuvanted pandemic a/h7n9 vaccine is immunogenic in adults. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 234ra55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beran, J.; Abdel-Messih, I.A.; Raupachova, J.; Hobzova, L.; Fragapane, E. A phase iii, randomized, open-label study to assess the tolerability and immunogenicity of an h5n1 influenza vaccine administered to healthy adults with a 1-, 2-, 3-, or 6-week interval between first and second doses. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 2186–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, L.S.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Guerrero, M.L.; Beygo, J.; Sales, V.; Holmes, S.J. Dose-range study of mf59-adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted monovalent a/h1n1 pandemic influenza vaccine in six- to less than thirty-six-month-old children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, e92–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajka, H.; Unal, S.; Ulusoy, S.; Usluer, G.; Strus, A.; Sennaroglu, E.; Guzik, J.; Iskit, A.T.; Dargiewicz, A.; Musial, D.; et al. A phase ii, randomised clinical trial to demonstrate the non-inferiority of low-dose mf59-adjuvanted pre-pandemic a/h5n1 influenza vaccine in adult and elderly subjects. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2012, 53, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, G.; Hancock, K.; Hoschler, K.; DeVos, J.; Praus, M.; Bardelli, M.; Malzone, C.; Castellino, F.; Gentile, C.; McNally, T.; et al. Fast rise of broadly cross-reactive antibodies after boosting long-lived human memory b cells primed by an mf59 adjuvanted prepandemic vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7962–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatz, C.; Cramer, J.P.; Vertruyen, A.; Schwarz, T.F.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Borkowski, A.; Lattanzi, M.; Hilbert, A.K.; Cioppa, G.D.; Leroux-Roels, G. A randomised, single-blind, dose-range study to assess the immunogenicity and safety of a cell-culture-derived a/h1n1 influenza vaccine in adult and elderly populations. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4820–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatz, C.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Casula, D.; Lattanzi, M.; Leroux-Roels, G. A randomized clinical trial to identify the optimal antigen and mf59((r)) adjuvant dose of a monovalent a/h1n1 pandemic influenza vaccine in healthy adult and elderly subjects. Vaccine 2012, 30, 3470–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Chearwae, W.; Castellino, F.; Manischewitz, J.; King, L.R.; Honorkiewicz, A.; Rock, M.T.; Edwards, K.M.; del Giudice, G.; Rappuoli, R.; et al. Vaccines with mf59 adjuvant expand the antibody repertoire to target protective sites of pandemic avian h5n1 influenza virus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 15ra5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Coyle, E.M.; Dimitrova, M.; Castellino, F.; Nicholson, K.; del Giudice, G.; Golding, H. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination with mf59-adjuvanted h5 vaccines promotes antibody affinity maturation towards the hemagglutinin ha1 domain and broad h5n1 cross-clade neutralization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.; Verma, N.; Yewdell, J.W.; Hilbert, A.K.; Castellino, F.; Lattanzi, M.; del Giudice, G.; Rappuoli, R.; Golding, H. Mf59 adjuvant enhances diversity and affinity of antibody-mediated immune response to pandemic influenza vaccines. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 85ra48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassim, C.; Christensen, S.; Henry, D.; Holmes, S.; Hohenboken, M.; Kanesa-Thasan, N. Identification of antigen and adjuvant doses resulting in optimal immunogenicity and antibody persistence up to 1 year after immunization with a pandemic a/h1n1 influenza vaccine in children 3 to <9 years of age. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesikari, T.; Forsten, A.; Herbinger, K.H.; Cioppa, G.D.; Beygo, J.; Borkowski, A.; Groth, N.; Bennati, M.; von Sonnenburg, F. Safety and immunogenicity of an mf59((r))-adjuvanted a/h5n1 pre-pandemic influenza vaccine in adults and the elderly. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuf, M.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Rumke, H.; Rivera, L.; Pedotti, P.; Arora, A.K.; Lattanzi, M.; Kieninger, D.; Cioppa, G.D. Immunogenicity and safety of cell-derived mf59(r)-adjuvanted a/h1n1 influenza vaccine for children. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2015, 11, 358–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Knuf, M.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Rumke, H.C.; Abarca, K.; Rivera, L.; Lattanzi, M.; Pedotti, P.; Arora, A.; Kieninger-Baum, D.; della Cioppa, G. Immunogenicity and tolerability of an mf59-adjuvanted, egg-derived, a/h1n1 pandemic influenza vaccine in children 6–35 months of age. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, e320–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knuf, M.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Rumke, H.C.; Abarca, K.; Rivera, L.; Lattanzi, M.; Pedotti, P.; Arora, A.; Kieninger-Baum, D.; della Cioppa, G. Safety and immunogenicity of an mf59-adjuvanted a/h1n1 pandemic influenza vaccine in children from three to seventeen years of age. Vaccine 2015, 33, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisinger, K.S.; Holmes, S.J.; Pedotti, P.; Arora, A.K.; Lattanzi, M. A dose-ranging study of mf59((r))-adjuvanted and non-adjuvanted a/h1n1 pandemic influenza vaccine in young to middle-aged and older adult populations to assess safety, immunogenicity, and antibody persistence one year after vaccination. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2014, 10, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.; Hohenboken, M.; Poling, T.; Jaehnig, P.; Kanesa-Thasan, N. Safety and immunogenicity of cell culture-derived a/h3n2 variant influenza vaccines: A phase i randomized, observer-blind, dose-ranging study. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Donis, R.O.; Working, G.I.C.C.; Davis, C.T.; Foust, A.; Hossain, M.J.; Johnson, A.; Klimov, A.; Loughlin, R.; Xu, X.; Tsai, T.; et al. Performance characteristics of qualified cell lines for isolation and propagation of influenza viruses for vaccine manufacturing. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6583–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanthavanich, P.; Anderson, E.; Kerdpanich, P.; Bulitta, M.; Kanesa-Thasan, N.; Hohenboken, M. Safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of an mf59-adjuvanted, cell culture-derived, a/h5n1, subunit influenza virus vaccine: Results from a dose-finding clinical trial in healthy pediatric subjects. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.E.; Shakib, S.; Chanthavanich, P.; Richmond, P.; Smith, T.; Tantawichien, T.; Kittel, C.; Jaehnig, P.; Mojares, Z.; Verma, B.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of mf59-adjuvanted cell culture-derived a/h5n1 subunit influenza virus vaccine: Dose-finding clinical trials in adults and the elderly. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Guideline for Good Clinical Practice e6(r2). Available online: https://www.Ema.Europa.Eu/en/ich-e6-r2-good-clinical-practice (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Available online: https://www.Wma.Net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/ (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Xu, J.; Murphy, S.L.; Kochanek, K.D.; Bastian, B.; Arias, E. Deaths: Final data for 2016. Natl. Vital. Stat. Rep. 2018, 67, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Department of Health and Human Services, U.S. Government. Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Available online: https://www.Phe.Gov/about/barda/pages/default.Aspx (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Fukase, H.; Furuie, H.; Yasuda, Y.; Komatsu, R.; Matsushita, K.; Minami, T.; Suehiro, Y.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Kusadokoro, H.; Sawata, H.; et al. Assessment of the immunogenicity and safety of varying doses of an mf59(r)-adjuvanted cell culture-derived a/h1n1 pandemic influenza vaccine in japanese paediatric, adult and elderly subjects. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5030–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, Y.; Komatsu, R.; Matsushita, K.; Minami, T.; Suehiro, Y.; Sawata, H.; Nakura, N.; Jaeger, R.K.; Lattanzi, M. Comparison of half and full doses of an mf59-adjuvanted cell culture-derived a/h1n1v vaccine in japanese children. Adv. Ther. 2010, 27, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihari, I.; Panczel, G.; Kovacs, J.; Beygo, J.; Fragapane, E. Assessment of antigen-specific and cross-reactive antibody responses to an mf59-adjuvanted a/h5n1 prepandemic influenza vaccine in adult and elderly subjects. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vesikari, T.; Forsten, A.; Borkowski, A.; Gaitatzis, N.; Banzhoff, A.; Clemens, R. Homologous and heterologous antibody responses to a one-year booster dose of an mf59((r)) adjuvanted a/h5n1 pre-pandemic influenza vaccine in pediatric subjects. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2012, 8, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keitel, W.; Groth, N.; Lattanzi, M.; Praus, M.; Hilbert, A.K.; Borkowski, A.; Tsai, T.F. Dose ranging of adjuvant and antigen in a cell culture h5n1 influenza vaccine: Safety and immunogenicity of a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Vaccine 2010, 28, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 6 Mo–17 y Half-Dose Study A (n = 288) | 6 Mo–17 y Full-Dose Study A (n = 289) | 18–64 y Half-Dose Study B (n = 440) | 18–64 y Full-Dose Study B (n = 451) | 18–64 y Full-Dose Study C (n = 1116) | ≥65 y Full-Dose Study C (n = 1133) | ≥65 y Half-Dose Study D (n = 664) | ≥65 y Full-Dose Study D (n = 673) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in Years (Mean ± SD) | 6.8 ± 4.5 | 6.6 ± 4.7 | 39 ± 14 | 39 ± 13 | 44 ± 13 | 72 ± 5.6 | 71 ± 4.8 | 71 ± 5.1 | |
| Male:Female (%) | 51:49 | 55:45 | 46:54 | 42:58 | 42:58 | 46:54 | 41:59 | 42:58 | |
| Race: | American Indian/Native Alaskan (%) | 0 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 0 | <1 |
| Asian (%) | 74 | 72 | 21 | 20 | 2 | <1 | 33 | 34 | |
| Black/African American (%) | 3 | 3 | 18 | 20 | 20 | 7 | 2 | <1 | |
| Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | <1 | 0 | 0 | |
| White (%) | 21 | 23 | 59 | 59 | 77 | 92 | 65 | 64 | |
| Other (%) | 2 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | |
| Ethnic Origin: | Hispanic/Latino (%) | 4 | 4 | 20 | 21 | 11 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Non-Hispanic/Non-Latino (%) | 96 | 96 | 80 | 79 | 88 | 96 | 98 | 98 | |
| Not Reported/Unknown (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Body Mass Index (Mean ± SD) | 18 ± 3.7 | 18 ± 3.5 | 26 ± 4.3 | 26 ± 4.3 | 27 ± 4.3 | 28 ± 4.0 | 27 ± 4.2 | 26 ± 4.0 | |
| Country: | USA (%) | 26 | 28 | 58 | 59 | 100 | 100 | 43 | 41 |
| Thailand (%) | 74 | 72 | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 34 | |
| Australia (%) | 0 | 0 | 23 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 13 | |
| New Zealand (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 | |
| Previous Influenza Vaccination * (%) | 16 | 15 | 20 | 21 | 36 | 71 | 55 | 56 | |
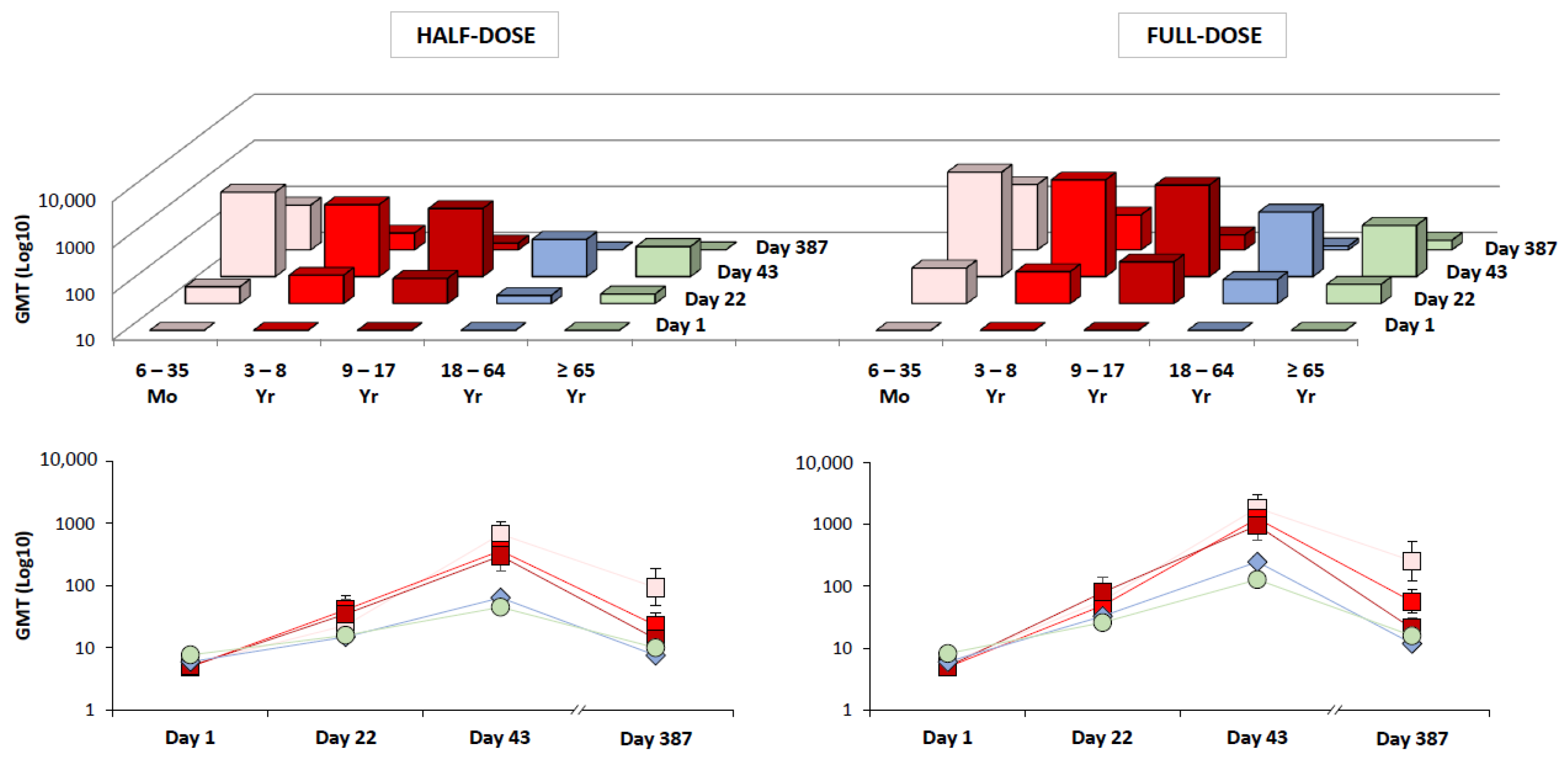
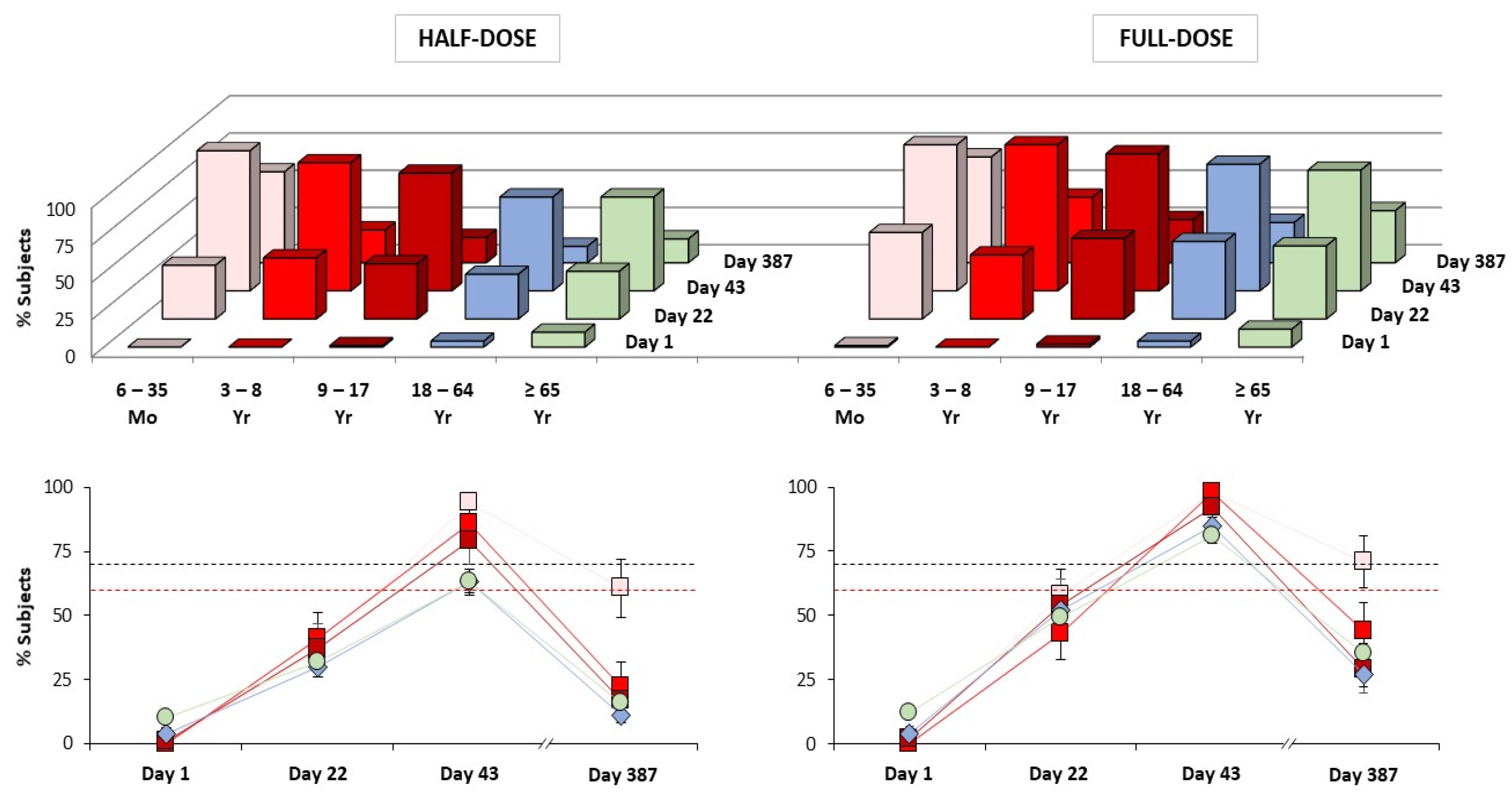
| Age Range | Day 22 | Day 43 |
|---|---|---|
| 6–35 Months (Study A) | 58% (46–69 †) n = 83 | 99% (93–100 †) n = 83 |
| 3–8 Years (Study A) | 43% (33–54 †) n = 95 | 98% (92–100 †) n = 93 |
| 9–17 Years (Study A) | 53% (43–63 †) n = 100 | 92% (85–96 †) n = 100 |
| 18–64 Years (Study B) | 48% (43–54 ‡) n = 464 | 83% (78–87 ‡) n = 451 |
| 18–64 Years (Study C) | 40% (38–43 †) n = 1115 | 80% (77–82 †) n = 1076 |
| ≥65 Years (Study C) | 24% (22–27 †) n = 1130 | 54% (51–57 †) n = 1080 |
| ≥65 Years (Study D) | 36% (32–40 ‡) n = 681 | 74% (70–77 ‡) n = 673 |
| Age Range | Day 22:Day 1 | Day 43:Day 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 6–35 Months (Study A) | 12 (7.3–19 †) n = 84 | 302 (192–476 †) n = 84 |
| 3–8 Years (Study A) | 9.8 (6.0–16 †) n = 95 | 249 (153–404 †) n = 93 |
| 9–17 Years (Study A) | 15 (8.8–27 †) n = 102 | 186 (105–328 †) n = 102 |
| 18–64 Years (Study B) | 5.4 (4.6–6.3 †) n = 464 | 41 (34–49 †) n = 451 |
| 18–64 Years (Study C) | 3.8 (3.6–4.1 †) n = 1115 | 13 (12–14 †) n = 1076 |
| ≥65 Years (Study C) | 2.1 (2.0–2.3 †) n = 1130 | 4.9 (4.6–5.2 †) n = 1080 |
| ≥65 Years (Study D) | 3.2 (2.8–3.7 ‡) n = 681 | 16 (13–19 ‡) n = 673 |
| Age Range | Clinical Trial | CBER (USA) | CHMP (Europe) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 22 | Day 43 | Day 22 | Day 43 | ||||||||
| ≥1:40 | SC | ≥1:40 | SC | ≥1:40 | SC | GMR | ≥1:40 | SC | GMR | ||
| 6–35 Mo | Study A | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 3–8 Yr | Study A | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 9–17 Yr | Study A | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 18–59 Yr | Study C | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 18–60 Yr | Study B | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 18–64 Yr | Study C | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 18–64 Yr | Study B | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ≥60 Yr | Study C | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ≥65 Yr | Study C | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Study D | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 6 Mo–5 y Full-Dose (n = 159) | 6–17 y Full-Dose (n = 163) | 18–64 y Full-Dose (n = 1636) | 18–64 y Placebo (n = 387) | ≥65 y Full-Dose (n = 1882) | ≥65 y Placebo (n = 397) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecchymosis: | Any (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | <1 |
| Grade I (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | <1 | |
| Grade II (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Induration: | Any (%) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Grade I (%) | 1 | 2 | <1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Grade II (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0 | |
| Grade III (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Erythema: | Any (%) | 3 | 1 | <1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Grade I (%) | 3 | 1 | <1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Grade II (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0 | |
| Grade III (%) | 0 | 0 | <1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Tenderness/Pain: | Any (%) | 56 | 68 | 65 | 20 | 39 | 10 |
| Mild (%) | 35 | 48 | 54 | 19 | 36 | 9 | |
| Moderate (%) | 20 | 19 | 11 | <1 | 3 | 1 | |
| Severe (%) | 1 | 2 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 0 | |
| 6 Mo–5 y Full-Dose (n = 160) | 6–17 y Full-Dose (n = 162) | 18–64 y Full-Dose (n = 1636) | 18–64 y Placebo (n = 387) | ≥65 y Full-Dose (n = 1882) | ≥65 y Placebo (n = 397) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea: | Any (%) | – | 13 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 6 |
| Severe (%) | – | 1 | <1 | 2 | <1 | <1 | |
| Fatigue: | Any (%) | – | 27 | 25 | 21 | 19 | 19 |
| Severe (%) | – | 1 | 1 | 2 | <1 | 1 | |
| Myalgia: | Any (%) | – | 30 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 8 |
| Severe (%) | – | 0 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | |
| Arthralgia: | Any (%) | – | 13 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 9 |
| Severe (%) | – | 0 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 0 | |
| Headache: | Any (%) | – | 22 | 25 | 23 | 15 | 16 |
| Severe (%) | – | 0 | 1 | 2 | <1 | 0 | |
| Malaise: | Any (%) | – | 25 | 23 | 12 | 16 | 12 |
| Severe (%) | – | 1 | 1 | 2 | <1 | <1 | |
| Loss of Appetite *: | Any (%) | 18 | 14 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| Severe (%) | 0 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 0 | |
| Fever: | ≥38.0 °C (%) | 16 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | <1 |
| ≥40.0 °C (%) | 1 | 0 | <1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 Mo–17 y Full-Dose (n = 326) | 18–64 y Full-Dose (n = 1683) | 18–64 y Placebo (n = 398) | ≥65 y Full-Dose (n = 1896) | ≥65 y Placebo (n = 398) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsolicited AEs: Day 1–43 (%) | 26 | 23 | 22 | 28 | 24 |
| Vaccine-Related Unsolicited AEs: Day 1–43 (%) | 4 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 7 |
| Serious AEs † (%) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 15 |
| Vaccine-Related Serious AEs † (%) | 0 | <1 | 0 | 0 | <1 |
| AEs of Special Interest † (%) | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | 2 |
| New Onset of Chronic Disease † (%) | 0 | 6 | 5 | 13 | 13 |
| AEs Leading to Withdrawal †,* (%) | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| AEs Leading to Death † (%) | 0 | <1 | 0 | <1 | <1 |
| AEs Requiring Medical Attention † (%) | 34 | 38 | 37 | 55 | 55 |
| MedDRA Preferred Term (%) | 6 Mo–17 y Full-Dose Study A (n = 329) | 18–64 y Full-Dose Study C (n = 1198) | 18–64 y Placebo Study C (n = 398) | ≥ 65 y Full-Dose Study C (n = 1197) | ≥ 65 y Placebo Study C (n = 398) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | V-R | All | V-R | All | V-R | All | V-R | All | V-R | |
| Any AE | 26 | 4 | 20 | 6 | 21 | 6 | 27 | 8 | 23 | 7 |
| Arthralgia | 1 | <1 | 1 | <1 | 2 | <1 | 2 | <1 | <1 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 2 | 0 | <1 | <1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Fatigue | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Headache | 1 | <1 | 2 | <1 | 3 | <1 | 2 | <1 | 2 | 1 |
| Injection Site Bruising | 0 | 0 | 1 | <1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 5 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 0 | 0 |
| URT Infection | 8 | <1 | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0 | 1 | <1 | <1 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 2 | 1 | <1 | <1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Versage, E.; van Twuijver, E.; Jansen, W.; Theeuwes, A.; Sawlwin, D.; Hohenboken, M. Analyses of Safety Profile and Homologous Antibody Responses to a Mammalian Cell-Based, MF59-Adjuvanted, A/H5N1, Pandemic Influenza Vaccine across Four Phase II/III Clinical Trials in Healthy Children, Adults, and Older Adults. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121468
Versage E, van Twuijver E, Jansen W, Theeuwes A, Sawlwin D, Hohenboken M. Analyses of Safety Profile and Homologous Antibody Responses to a Mammalian Cell-Based, MF59-Adjuvanted, A/H5N1, Pandemic Influenza Vaccine across Four Phase II/III Clinical Trials in Healthy Children, Adults, and Older Adults. Vaccines. 2021; 9(12):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121468
Chicago/Turabian StyleVersage, Eve, Esther van Twuijver, Wim Jansen, Ad Theeuwes, Daphne Sawlwin, and Matthew Hohenboken. 2021. "Analyses of Safety Profile and Homologous Antibody Responses to a Mammalian Cell-Based, MF59-Adjuvanted, A/H5N1, Pandemic Influenza Vaccine across Four Phase II/III Clinical Trials in Healthy Children, Adults, and Older Adults" Vaccines 9, no. 12: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121468
APA StyleVersage, E., van Twuijver, E., Jansen, W., Theeuwes, A., Sawlwin, D., & Hohenboken, M. (2021). Analyses of Safety Profile and Homologous Antibody Responses to a Mammalian Cell-Based, MF59-Adjuvanted, A/H5N1, Pandemic Influenza Vaccine across Four Phase II/III Clinical Trials in Healthy Children, Adults, and Older Adults. Vaccines, 9(12), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121468






