Abstract
The causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) is the bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which secretes toxins into the gastrointestinal tract of its host. Vibrio parahaemolyticus toxins A and B (PirAvp/PirBvp) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of this disease, and are, therefore, the focus of studies developing treatments for AHPND. We previously produced recombinant antibodies based on the hagfish variable lymphocyte receptor B (VLRB) capable of neutralizing some viruses, suggesting that this type of antibody may have a potential application for treatment of AHPND. Here, recombinant PirAvp/PirBvp, produced using a bacterial expression system, were used as antigens to screen a hagfish VLRB cDNA library to obtain PirAvp/PirBvp-specific antibodies. A cell line secreting these antibodies was established by screening and cloning the DNA extracted from hagfish B cells. Supernatants collected from cells secreting the PirAvp/PirBvp antibodies were collected and concentrated, and used to passively immunize shrimp to neutralize the toxins PirAvp or PirBvp associated with AHPND. Briefly, 10 μg of PirAvp and PirBvp antibodies, 7C12 and 9G10, respectively, were mixed with the shrimp feed, and fed to shrimp for three days consecutive days prior to experimentally infecting the shrimp with V. parahaemolyticus (containing toxins A and B), and resulting mortalities recorded for six days. Results showed significantly higher level of survival in shrimp fed with the PirBvp-9G10 antibody (60%) compared to the group fed the PirAvp-7C12 antibody (3%) and the control group (0%). This suggests that VLRB antibodies may be a suitable alternative to immunoglobulin-based antibodies, as passive immunization treatments for effective management of AHPND outbreaks within shrimp farms.
1. Introduction
Shrimp is an important aquatic food resource for human consumption worldwide, and are widely cultured to meet the growing demand for shrimp by consumers. This crustacean, as with other invertebrates, lacks adaptive immunity []. This is an important issue, especially since they are prone to acquiring infections and developing diseases when reared in aquaculture systems. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND), formerly known as early mortality syndrome, was first recognized as an emerging disease in China in 2009, and since being identified has spread to neighboring countries in Southeast Asia, including Vietnam in 2010, Malaysia in 2011, and Thailand in 2012. The disease has now reached as far as Mexico in early 2013 [,], the Philippines in 2015 [] and South America in 2016 []. Three shrimp species appear susceptible to this disease, namely whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeaus/Penaeus vannamei), black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon), and Chinese white shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) []. Affected shrimp have an empty gut and an atrophied pale hepatopancreas, which can be reduced in size by more than 50%. AHPND can cause up to 100% mortality within 20–30 days after the pond has been stocked with post-larvae shrimp []. The disease has resulted in huge economical losses for shrimp farmers globally. In Thailand alone, shrimp farmers experienced financial losses of $11.58 billion between 2010–2016, and total shrimp production fell by 54% between 2009 and 2014 due to AHPDH [].
A unique strain of Vibrio parahaemlyticus is responsible for causing AHPND. Vibrio parahaemlyticus is a Gram-negative, halophilic bacterium found ubiquitously in warm marine and estuarine environments around the world [,]. The strains responsible for causing AHPND possess a 63 to 70 kDa plasmid that encodes binary toxins PirAvp/PirBvp, which are actually homologs of the Photorhabdovirus insect-related (Pir) toxins PirAB. These two toxins are secreted by the bacterium, and have been associated with the pathogenesis of the disease; they are considered to be the primary virulence factors involved in causing AHPND [,].
The variable lymphocyte receptor (VLR), composed of leucine-rich repeats (LRRSs), is a mediator of the humoral immune response in lamprey and hagfish []. As the VLRs mature, a repertoire of antigen-binding receptors are produced through the somatic diversification of the LRRs [,]. These antigen-binding receptors have three distinct types, namely VLRA, VLRB, and VLRC, which have been observed in both lamprey and hagfish. The VLRB has similarities to the B-cell receptor (BCR) in mammals. It is expressed on the cell membrane and is then secreted into the serum acting as a humoral agglutinin, making it the main component of the humoral immune response of jawless vertebrates with regards to antigen recognition [,,]. Previous reports have shown that circulating antigen-specific VLRBs can be produced in response to an antigen (e.g., bacteriophages, Brucella abortus, human red blood cells and Bacillus antracis exosporium), with the VLRBs demonstrating both agglutinating and neutralizing activities [,].
A variety of methods have been investigated for controlling AHPND, including passive immunization. Here, we report on a VLRB antibody that we developed, which specifically recognizes and neutralizes the binary toxins produced by V. parahaemolyticus that are responsible for inducing the pathogenesis associated with AHPND in shrimp.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of Toxin Plasmids
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (D2 strain) cells were cultured in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth containing 3% NaCl at 30 °C for 16 h. DNA was extracted from this bacterial cell culture using a G-spin™ Total DNA extraction kit (iNtRon Biotechnology, Seong-Nam, Korea). PirAvp and PirBvp were amplified using respective primers shown in Table 1. Specifically, PirAvp was amplified with a 6× His tag added onto the C-terminal region of the sequence, then the amplified PirAvp was flanked with Nde I and Sac I and cloned into pet32a vector (Novagen, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). The PirBvp, on the other hand, was amplified to include three Strep tags on its C-terminal region and was cloned into a pet28b vector (Novagen, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) between the Nco I and Xba I region. The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) conditions used were as follows: initial denaturation: 95 °C, 5 min; denaturation: 95 °C, 20 s; annealing: 60 °C, 10 s; extension: 72 °C, 30 s; final extension: 72 °C, 5 min, for 30 cycles. The plasmids (pet32a-PirAvp and pet28b-PirBvp) were transformed using BL21 competent cells. To check the veracity of the cloned PirAvp/PirBvp plasmids, each plasmid was sequenced (Solgent, Korea) and the sequences aligned with the original PirAvp/PirBvp sequence.

Table 1.
Primer Sequences.
2.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Toxins
To induce the expression of PirAvp/PirBvp proteins, BL21 cells harboring the pet32a-PirAvp or pet28b-PirBvp plasmids were grown overnight in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth with ampicillin (LB amp) and kanamycin (LB kan), respectively. The respective bacterial cultures were placed in fresh LB amp or LB kan, and grown to an OD 500 nm of 0.3, before adding 0.1 mM isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) to the cultures for 4 h at 37 °C. The cells were collected by centrifugation at 3000× g for 5 min and resuspended in 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (with 200 mM NaCl) by vortexing. The cells were then subjected to three cycles of freeze-thawing to break the bacterial cell wall, sonicated with a 5 s pulse for 3 min on ice, and the soluble fractions collected by centrifuging the lysates at 3000× g for 10 min at 4 °C.
The soluble fractions were purified using affinity chromatography columns. The PirAvp fractions were added to propylene column containing Ni-NTA agarose (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), while the PirBvp fractions were added to a column containing Streptactin resin (Iba LifesciencesTM, Gottingen, Germany). To remove any non-specific proteins bound to the resin, the columns were first washed with 1× PBS (with 10 mM imidazole), then the specific protein (PirAvp/PirBvp) was eluted from the column using elution buffer, 1× PBS (with 500 mM imidazole). To verify the correct sizes of the purified PirAvp/PirBvp proteins, the eluted proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing condition (samples (1:20 dilution) were treated with β–mercaptoethanol, boiled at 100 °C for 5 min, and run at 80 V for 20 min, 120 V for 90 min), after which the gels were stained with Coomassie blue.
The purified recombinant toxins were also subjected to Western blotting to further check their specificity. Briefly, the collected proteins were separated on 12% (PirAvp) and 8% (PirBvp) SDS-PAGE gel under reducing condition, then the separated proteins were transferred onto methanol-activated polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes at 50 mA for 90 min. Blocking of the membrane was performed using 5% skimmed milk in 1× PBS mixed with 0.1% Tween 20. The membrane bearing the PirAvp protein was incubated with (1:4 dilution) anti-6× His antibody produced by the lab, followed by (1:3000 dilution) HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), while the membrane with the PirBvp protein was incubated with (1:4000 dilution) streptactin-HRP antibody (Iba LifesciencesTM, Gottingen, Germany). The expression of the recombinant toxins was visualized using SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Large scale preparations of the respective proteins were performed once the correct sizes were verified. The proteins were dialyzed against 1× PBS to remove resin impurities and were quantified using PierceTM BCA protein Assay kit (Thermo ScientificTM) following the protocol provided in the kit. Finally, the quantified proteins were stored at −70 °C. These proteins were used as antigens in subsequent experiments.
2.3. Screening of VLRB Library
The cell line bearing the VLRB cDNA library [] was seeded into twenty 96-well plates with 200 cells/well and grown to 100% cell confluency. The supernatants containing the recombinant VLRBs was collected and screened by ELISA, for which 96-well plates (Corning, Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA) were coated with 200ng/well of PirAvp or PirBvp overnight at 4 °C. Unbound antigen was removed with 1× Tris buffered saline with Tween 20 (TBST: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Tween 20, pH 8.0), and wells blocked with blocking buffer (5% skimmed milk in 1× TBST) for 1 h at room temperature, after which the plates were washed three times with 1× TBST. The collected recombinant VLRB supernatants were added to the plates for 1 h at room temperature. Binding of the recombinant VLRBs to their respective antigen was detected using mouse anti-VLRB IgG1 (11G5, produced in the lab) diluted (1:5) in blocking buffer, followed by a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Thermo Scientific, USA) (1:3000 dilution). After washing the plates again, 100 µL/well of substrate buffer containing 42 mM 3, 3′, 5, 5′-tetramethylbenzidine and 1% H2O2 was added for 20 min at room temperature, the reaction was stopped by adding 50 µL of stop solution (1 mM H2SO4) and the plate was then read at 450 nm using a microtiter plate reader. The ELISA was performed three times to ensure the specificity of the PirAvp or PirBvp-specific VLRBs, with PirAvp-7C12 and PirBvp-9G10 showing the highest levels of specificity and were subsequently used in for further experiments.
2.4. Establishment of Cell Line Secreting Anti-PirAvp/PirBvp Recombinant VLRBs
The cells secreting PirAvp/PirBvp-specific recombinant VLRBs, PirAvp-7C12, and PirBvp-9G10 were collected, then their respective DNA extracted using a DNA extraction kit (iNtRon Biotechnology) following the protocol provided with the kit. Amplification was performed using primer set LRRNT Sfi I/Stalk Sfi I (Table 1). The following PCR conditions used were initial denaturation: 95 °C, 5 min; denaturation: 95 °C, 20 s; annealing: 60 °C, 10 s; extension: 72 °C, 45 s; final extension: 72 °C, 5 min, for 30 cycles. The amplicons were purified using a DNA purification kit (iNtRon Biotechnology), digested with Sfi I enzymes for 1 h at 37 °C, and then were finally ligated into the Sfi I sites of the plasmid Δ514/VLR/kepta vector (developed in our lab). Colony PCR was performed to check the proper ligation of the DNA into the vector. The constructed plasmids, Δ514/VLR/kepta-PirAvp-7C12 and Δ514/VLR/kepta-PirBvp-9G10 were then transfected into human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293F cells in a 24-well plate using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen Life Technologies). After 4 h, the DNA-lipofectamine complexes were replaced with Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) containing 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Two days after transfection, the supernatants were collected to further check the specificity of the VLRs by ELISA (as described above). Once specificity was established, large scale preparation of the supernatants was performed. These supernatants were designated as PirAvp-7C12 and PirBvp-9G10 antibody from here on. The VLRB antibodies were purified by affinity chromatography column using Streptactin resin (Iba LifesciencesTM, Gottingen, Germany), and then were freeze-dried using a refrigerated vacuum. All the freeze-dried VLRB antibodies were stored in −70 °C until used.
2.5. Bacterial Challenge Test
Litopenaeus vannamei post-larvae (n = 100, 0.1 ± 0.03 g) were transferred into three 250-L tanks corresponding to the two experimental groups (PirAvp-7C12 and PirBvp-9G10 antibody) and one control group fed no antibody (negative control). The shrimp were fed with antibody added to the shrimp diet (10 µg of respective antibody per gram of feed (equivalent to 8% bodyweight/day)) every day for three days prior to the challenge test. After three days, the shrimp were challenged by immersion with an AHNPD-causing strain of V. parahaemolyticus. To be more specific, each treatment group containing 30 shrimp, were immersed in 1.5 water (25 ppm salinity) containing 107 colony forming units (cfu) mL−1 of V. parahaemolyticus for 15 min. Determination of colony forming unit (CFU) for V. parahaemolyticus was remunerated with a standard plate count technique using thiosulfate-citrate-bile salts-sucrose agar. The challenged shrimp and bacterial solution were poured into a new aquarium containing 100 volume of clean water. The final volume was 15 L, which contained 105 cfu/mL of V. parahaemolyticus. Shrimp were maintained under these conditions for another 24 h. After 24 h, 100% water was replaced with fresh clean water (25 ppm salinity). The shrimp (n = 30 per group) were then transferred into new15 L tanks, where they were monitored for six days. They were continuously fed with the respective experimental feed diet containing the antibody during this time. Mortality data were obtained from two separate trials.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Survival data were statistically analyzed via Kaplan-Meier with the Chi-square test using GraphPad Prism v.5 software. Differences between groups were considered significant when ** p < 0.001.
3. Results
3.1. Expression of Recombinant Toxins
Successful transformation of toxin plasmids produced a band corresponding to 336 bp for pet32a-PirAvp and 1317 bp for pet28b-PirBvp (Supplementary Figure S1), while the results of the Western blot and Coomassie blue staining showed distinct bands at appropriately 15 and 55 kDa for PirAvp and PirBvp, respectively (Figure 1).
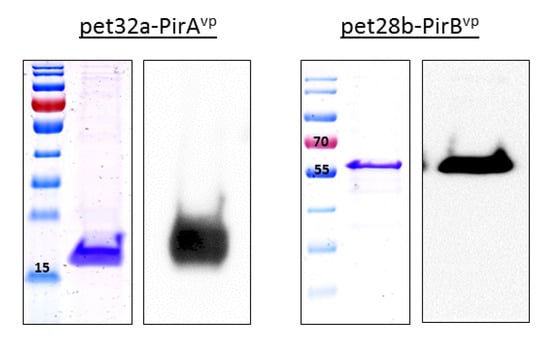
Figure 1.
The expression of PirAvp and PirBvp was verified through Coomassie staining and Western Blotting. After purification using His resin, PirAvp was evident as a band at ~15 kDa (using His Ab for detection), while PirBvp was purified using Streptactin resin and a band evident at ~55 kDa size (using Streptactin-HRP for Western blot detection).
3.2. Specificity of Established Toxin-Specific VLRBs
The capacity of the toxin-specific VLRBs to recognize their respective PirAvp and PirBvp antigens was verified by ELISA and Western blotting. Of the twenty 96-well plates that that were screened in the first round of ELISA screening, only 19 wells showed high binding with PirAvp and 24 wells with PirBvp (Figure 2a). Positive wells were serially diluted to obtain single cells, which were again screened by ELISA. In the second screening, eight cells from each of the PirAvp and PirBvp groups displayed a binding affinity to the antigen (Figure 2b). After the third round of screening, only one antibody for each group with the highest binding capacity was selected, namely PirAvp-7C12 and PirBvp-9G10 (Figure 2c). Western blot analysis of these two selected toxin-specific VLRBs showed specific binding to the respective toxin antigens, thereby, verifying the specificity of these antibodies for recognizing either PirAvp or PirBvp, respectively (Figure 2d).
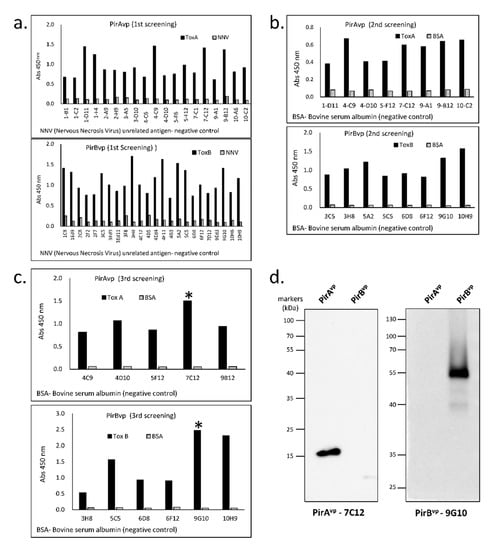
Figure 2.
ELISA screening and Western blotting of recombinant VLRBs to check specificity to PirAvp and PirBvp. (a) first screening, (b) second screening, (c) third screening, and (d) blotting results show specificity of the VLRBs, PirAvp-7C12, and PirBvp-9G10, with band size 15 kDa and 55 kDa, corresponding to PirAvp and PirBvp, respectively. The * corresponds to the respective VLRB-specific PirAvp and PirBvp used in succeeding experiments.
3.3. Protective Efficiency of Toxin-Specific VLRBs in Shrimp Infected with V. parahaemolyticus
Based on the results collected, the level of survival in the first experimental trial in which shrimp were fed with PirBvp-9G10 antibody was 26.7%, which was significantly higher than the group fed with PirAvp-7C12 antibody (3%) and the negative control (6%) (Figure 3a). In the replicate trial, results were even more pronounced, wherein the group fed with PirBvp-9G10 antibody demonstrated a 60% survival, in contrast to the group fed PirAvp-7C12 or the negative control group that exhibited 3% and 0% survival, respectively (Figure 3b). This particular dataset is statistically significant at ** p< 0.001, indicating the protective effect of the PirBvp-9G10 antibody.
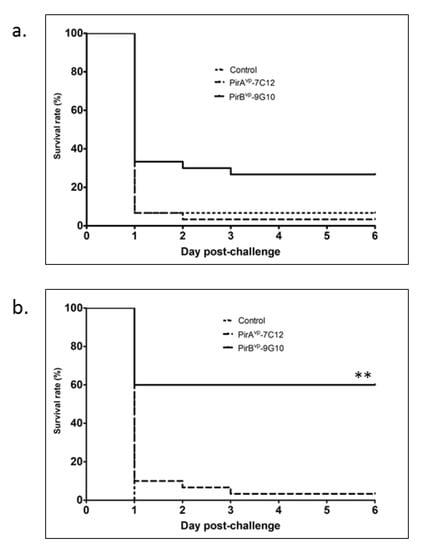
Figure 3.
Survival rate of shrimp after bacterial challenge. Shrimp fed with or without VLRB antibodies were challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus by immersion and mortality was recorded for six days. (a) first trial and (b) second trial. ** Statistically significant p < 0.001.
4. Discussions
The demand for farmed shrimp continues to grow faster than any other aquaculture species in the global setting, with most of the shrimp being produced coming from Asia. In the latest statistics presented by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), it was estimated that the global production of farmed shrimp is growing at an annual rate of 6% []. With this growing trend, one of the ways to address the increasing demand for shrimp is to use high density stocking within shrimp farms. As a result of this intensification, farmed shrimp are continually being plagued by disease, which has greatly affected shrimp production. Thus, the development of safe and efficacious treatment for diseases such as AHPND has been the subject of increased research in recent years. The use of antibiotics to treat bacterial infections in industrial aquaculture has been opposed despite their effectiveness, due to antibiotic usage giving rise to antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria. Vaccination is currently considered to be the most effective strategy for controlling infections in aquaculture; however, shrimp do not possess acquired immunity, necessary to induce a memory response to the vaccine. Also, they are too fragile to be vaccinated by intraperitoneal injection, the traditional route of vaccine delivery, which is both labor-intensive and stressful, so oral administration of antibodies to passively immunize shrimp is an attractive alternative.
The potential of using passive immunization to protect shrimp against infections has been explored previously, with varying degrees of success. Previous studies have used chicken antibodies (immunoglobulin Y–IgY) to develop passive vaccination protocols for shrimp; chickens are able to efficiently produce large amounts of IgY in their eggs []. Gao et al. (2016) showed egg yolk powder containing antibodies against V. harveyi and V. parahaemolyticus orally administered to white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei to be effective for reducing subsequent Vibrio infections. More specifically, the antibodies showed an inhibiting effect on both bacteria in vitro, and in vivo. When the anti-Vibrio antibodies, present in egg yolk were encapsulated in β-cyclodextrin, and fed to shrimp, lower mortality was observed in zoeae, mysis and post-larva, and lower bacterial load recorded in post-larva compared to shrimp fed with normal egg powder (i.e., from non-immunized chickens) []. Likewise, in another study Indian white shrimp were fed with an anti-V. harveyi IgY, obtained from eggs of chicken immunized with V. harveyi, for 30 and 60 days and subsequently challenged with a virulent strain of V. harveyi and their hematological and immunological parameters evaluated. The group fed with the edible IgY exhibited a significant increase in total hemocyte counts (THC), and increased levels of coagulase, oxyhemocyanin, prophenoloxidase, intracellular superoxide anion production, lysozyme activity, phagocytosis, and bacterial agglutinin. Furthermore, the group fed with the anti-V. harveyi IgY-coated feeds had a lowered Vibrio load compared to control shrimp and had an improved immune response against the V. harveyi challenge []. In another study of note, outer membrane proteins (OMPs) obtained from V. parahaemolyticus were used to immunize hens to produce V. parahaemolyticus OMP IgY antibodies. These were then incorporated into extruded pellet diets and fed to white pacific shrimp, experimentally infected with the bacterium. Lower bacterial loads were measured in the muscle of shrimp fed with the specific IgY incorporated into their diets, compared with the control group fed with non-specific IgY from non-immunized chickens. Along with those results, the superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the muscle of the IgY-fed shrimp was significantly higher than the control group []. In line with these studies, a potential way to treat Vibrio sp. causing AHPND is to target the toxins it secretes while infecting its host. In one such study, IgY from eggs of hens immunized with recombinant PirA- and PirB-like toxins (the virulent toxins released by AHPND-causing V. parahaemolyticus) was administered orally to shrimp by feeding them egg yolk powder containing the IgY; 87% survival was noted in shrimp fed with the anti-PirA-IgY-coated feed after challenging the shrimp with the bacterium [].
The results of the studies described above, indicate the potential of using an edible antibody as a means of passively immunizing shrimp to help them fight infection. In our current study, we developed VLRB antibodies that specifically recognized PirAvp and PirBvp, which could potentially “neutralize” the effect of these virulence toxins. Although the exact mechanism of action of these toxins is still unclear, the presence of the plasmid (pVA1) encoding these toxins in all AHPND-causing strains of V. parahaemolyticus indicates that they are causative factors involved in the disease process. The PirAvp/PirBvp toxins are known to be homologs of the insecticidal Photorhabdus insect-related (Pir) binary toxin PirAB that exhibits pore-forming activity in insects, thus suggesting that PirAvp and PirBvp might function similarly. In a previous report, both Pir A and Pir B are needed to be present in insect larvae to induce mortality []. Since these binary toxins have been discovered together in V. parahaemolyticus, it would seem reasonable that they are also both essential for the onset of symptoms associated with AHPND.
Structural analysis of the PirAvp/PirBvp binary toxins suggested strong similarity with Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins [,]. The N-terminal domain of PirBvp, as with the Cry domain I, contains a bundle of α-helices and in the center of this α-bundle, there are abundant hydrophobic residues. Specifically, the hydrophobic α-helix 8 is lodged within a bunch of amphipathic helices; this “inside-out membrane fold” is a typical characteristic of other pore-forming toxins, which can switch between soluble and transmembrane conformations []. Such characteristics strongly implicate that the N-terminal region of PirBvp has the capability to form a pore in the cell membrane that leads to cell death []. On the other hand, the C-terminal of PirBvp, similar to the Cry domain II, has three antiparallel β-sheets and contains an immunoglobulin-like folding domain that plays a role in protein-protein or protein-ligand interactions [], thereby indicating that the PirBvp C-terminal plays a similar functional role. Moreover, since this domain can interact with insect receptors in its insect homolog, the similarity in structure suggests that the PirBvp C-terminal is also a receptor binding domain [,,,,,,]. Understanding the structural conformation of PirBvp and its role in the pathogenicity of AHPND is very important, as this could help scientists in formulating potential treatments for the disease.
Several notable studies had demonstrated the potential role of VLRBs in neutralizing certain viruses such as avian influenza virus H9N2 [], viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus [] and nervous necrosis virus [], and results are compelling enough to promote their usage as a therapeutic agent against bacterial and viral infections. In the current study, the high level of survival in the group fed with the PirBvp-9G10 antibody after the AHPND-challenge, suggests that the VLRB antibody can provide protection against a V. parahaemolyticus infection in shrimp. The difference in the survival rate between the two in vivo feeding trials performed in the current study, might reflect a difference in the amount of feed consumption by the shrimp within the two feeding trials [,]. Our finding appears to be in contrast with the results of a previous study, wherein shrimp fed with diet containing anti-PirA-IgY demonstrated consistently higher levels of survival compared with anti-PirB-IgY-fed and control groups []. We speculate that the reason behind the effectiveness of the PirBvp-9G10 antibody in our study might be due to the abundant hydrophobic residues in the structure of PirBvp that our VLRB antibody readily recognizes and which the PirAvp noticeably lacks. VLRBs are known to have high binding capacity with hydrophobic structures such as carbohydrates and glycoproteins that form hydrophobic clusters [], thus contributing to the efficiency of PirBvp-9G10 antibody reaction with the PirBvp toxin. Although the use of the PirAvp-7C12 antibody may not be as effective as the PirBvp-9G10 antibody, we still consider its potency as a therapeutic agent, and we plan to do further studies focusing on its use. However, in general, our results clearly suggest that the PirBvp-9G10 VLRB antibody can improve shrimp survival against V. parahaemolyticus by simply targeting the virulent toxin PirBvp.
In summary, the results of a previous report showing that only the PirBvp toxin could induce histological signs of AHPDH [], and another stating that the virulence of AHPND relies heavily on the amount of toxins secreted by the bacterial cells [], greatly substantiates the aim of our study to develop new therapeutic agents for AHPND targeting the PirBvp toxin. Furthermore, the efficacy of VLRB antibodies as immunogenic agents to passively immunize shrimp reared at high stocking densities could significantly help the shrimp industry to combat outbreaks of AHPND.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/9/1/55/s1, Figure S1: Colony PCR to check proper cloning of pet32a-PirAvp and pet28b-PirBvp. Checking presence of inserts by amplifying the cloning site using gene-specific primers. Band size 336 bp and 1317 bp were observed, which correspond to PirAvp and PirBvp, respectively. One clone from each gene was sent for sequencing to further check the identity of the gene inserted in the plasmid.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.J.; Data curation, J.M.S.L., Y.R.K., J.H.C., J.S.L., S.W.K. and P.K.; Formal analysis, J.M.S.L. and J.W.J.; Methodology, J.M.S.L. and J.K.; Resources, H.K.; Writing—original draft, J.M.S.L.; Writing—review & editing, K.D.T. and T.S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Korea Research Foundation, grant number NRF-2018 R1A2B2005505 and National Institute of Fisheries Science, grant number R2020013.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to the use of an invertebrate sample (shrimp) which is exempted from the list of experimental animals for ethical review.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy reasons.
Acknowledgments
The genetic information of PirAvp and PirBvp was kindly provided by Ikuo Hirono (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology) and Han-Ching Wang (National Cheng Kung University).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, L.M.; Song, L.S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.M.; Wang, L.L.; Yu, Y.D.; Li, C.H.; Li, F.M.; Xing, K.Z.; et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel C-type lectin gene from shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gil, B.; Soto-Rodriguez, S.; Lozano, R.; Betancourt-Lozano, M. Draft genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain M0605, which causes severe mortalities of shrimps in Mexico. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00055-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, L.; Lightner, D.; Pantoja, C.; Gomez-Jimenez, S. Detection of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Mexico. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 111, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Peña, L.D.; Cabillon, N.A.; Catedral, D.D.; Amar, E.C.; Usero, R.C.; Monotilla, W.D.; Calpe, A.T.; Fernandez, D.D.; Saloma, C.P. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) outbreaks in Penaeus vannamei and P. monodon cultured in the Philippines. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 116, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, L.; Bayot, B.; Betancourt, I.; Pinzon, A. Draft genome sequence of pathogenic bacteria Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain Ba94C2, associated with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease isolate from South America. Genom. Data 2016, 9, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NACA. Report of the Asia Pacific Emergency Regional Consultation on the Emerging Shrimp Disease: Early Mortality Syndrome (EMS)/Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Syndrome (AHPNS); Network of Aquaculture Centres in Asia-Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 9–10 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- De Schryver, P.; Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P. Early mortality syndrome outbreaks: A microbial management issue in shrimp farming. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Ng, T.H.; Ando, M.; Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Chuang, J.C.; Mavichak, R.; Chang, S.H.; Yeh, M.D.; Chiang, Y.A.; et al. Pathogenesis of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, C.A.; Calder, T.J.; Orth, K. Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Orth, K. Virulence determinants for Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirikharin, R.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Sanguanrut, P.; Chi, T.D.; Mavichak, R.; Proespraiwong, P.; Nuangsaeng, B.; Thitamadee, S.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Characterization and PCR detection of binary, Pir-like toxins from Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, J.R.M.; Paganini, J.; Pontarotti, P. Convergent evolution of the adaptive immune response in jawed vertebrates and cyclostomes: An evolutionary biology approach based study. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 75, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, M.N.; Rogozin, I.B.; Iyer, L.M.; Glazko, G.V.; Cooper, M.D.; Pancer, Z. Diversity and function of adaptive immune receptors in a jawless vertebrate. Science 2005, 310, 1970–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrin, B.R.; Alder, M.N.; Roux, K.H.; Sina, C.; Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Boydston, J.A.; Turnbough, C.L., Jr.; Cooper, M.D. Structure and specificity of lamprey monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Das, S.; Herrin, B.R.; Hirano, M.; Cooper, M.D. Definition of a third VLR gene in hagfish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15013–15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Murakawa, S. Immunity in lamprey. I. Production of haemolytic and haemagglutinating antibody to sheep red blood cells in Japanese lampreys. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1979, 3, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, M.N.; Herrin, B.R.; Sadlonova, A.; Stockard, C.R.; Grizzle, W.E.; Gartland, L.A.; Gartland, G.L.; Boydston, J.A.; Turnbough, C.L., Jr.; Cooper, M.D. Antibody responses of variable lymphocyte receptors in the lamprey. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Im, S.P.; Kim, S.W.; Lazarte, J.M.; Jung, J.W.; Gong, T.W.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Generation and characterization of hagfish variable lymphocyte receptor B against glycoprotein of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV). Mol. Immunol. 2018, 99, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Im, S.P.; Kim, S.W.; Lazarte, J.; Kim, Y.R.; Chun, J.H.; Ha, M.W.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Characterization of Hagfish (Eptatretus burgeri) Variable Lymphocyte Receptor-Based Antibody and Its Potential Role in the Neutralization of Nervous Necrosis Virus. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: www.fao.org/in-action/globefish/market-reports/resource-detail/en/c/1261310 (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Gottstein, B.; Hemmeler, E. Egg yolk immunoglobulin Y as an alternative antibody in the serology of echinococcosis. Z. Parasitenkd. 1985, 71, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, D.; Sun, J.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y. Passive Immune-Protection of Litopenaeus vannamei against Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus Infections with Anti-Vibrio Egg Yolk (IgY)-Encapsulated Feed. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, T.; Thirumalaikumar, E.; Lelin, C.; Palanikumar, P.; Michaelbabu, M.; Citarasu, T. Physicochemical properties of anti Vibrio harveyi egg yolk antibody (IgY) and its immunological influence in Indian white shrimp Fenneropenaeus indicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.; Guo, E.; Zhou, P.; Xu, D.; Qi, Z.; Deng, L.J. The preparation and antibacterial effect of egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) against the outer membrane proteins of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Pedrosa-Gerasmio, I.R.; Alenton, R.R.R.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Anti-PirA-like toxin immunoglobulin (IgY) in feeds passively immunizes shrimp against acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.; Kamita, S.G.; Hammock, B.D.; Ffrench-Constant, R. The Photorhabdus Pir toxins are similar to a developmentally regulated insect protein but show no juvenile hormone esterase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 245, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.J.; Hsu, K.C.; Wang, H.C. Structural Insights into the Cytotoxic Mechanism of Vibrio parahaemolyticus PirAvp and PirBvp Toxins. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraro, M.D.; van der Goot, F.G. Pore-forming toxins: Ancient, but never really out of fashion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 14, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitami, M.; Kadotani, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Atsumi, S.; Higurashi, S.; Ishizaka, T.; Watanabe, A.; Sato, R. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry Toxins Bound Specifically to Various Proteins via Domain III, Which Had a Galactose-Binding Domain-Like Fold. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adang, M.; Crickmore, N.; Jurat-Fuentes, J. Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis Crystal Toxins and Mechanism of Action. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2014, 47, 39–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, A.; Gómez, I.; Porta, H.; García-Gómez, B.I.; Rodriguez-Almazan, C.; Pardo, L.; Soberón, M. Evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins insecticidal activity. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 6, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochulski, P.; Masson, L.; Borisova, S.; Pusztai-Carey, M.; Schwartz, J.L.; Brousseau, R.; Cygler, M. Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA(a) insecticidal toxin: Crystal structure and channel formation. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soberón, M.; Pardo, L.; Muñóz-Garay, C.; Sánchez, J.; Gómez, I.; Porta, H.; Bravo, A. Pore formation by Cry toxins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 677, 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Pigott, C.R.; Ellar, D.J. Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.P.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, J.W.; Lazarte, J.M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, J.H.; Chong, R.S.M.; et al. Potential use of genetically engineered variable lymphocyte receptor B specific to avian influenza virus H9N2. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc Tran, L.; Nunan, L.; Redman, R.; Mohney, L.; Pantoja, C.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Lightner, D. Determination of the infectious nature of the agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome affecting penaeid shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 105, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.; Srisala, J.; Truong, V.T.; Chen, I.-T.; Nuangsaeng, N.; Suthienkul, O.; Lo, C.L.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Thitamadee, S. Variation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from a single Thai shrimp farm experiencing an outbreak of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Aquaculture 2014, 428, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Im, S.P.; Lee, J.S.; Lazarte, J.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, S.; Kim, G.J.; et al. Globular-shaped variable lymphocyte receptors B antibody multimerized by a hydrophobic clustering in hagfish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinwongger, S.; Nochiri, Y.; Thawonsuwan, J.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Awasthi, S.; Hinenoya, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Hirono, I. Virulence of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease PirAB-like relies on secreted proteins not on gene copy number. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).