A Multi-Filovirus Vaccine Candidate: Co-Expression of Ebola, Sudan, and Marburg Antigens in a Single Vector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Antigens
2.3. Vector Construction
2.4. Virus Production and Expression Testing
2.5. Mouse Experiment Design
2.6. ELISpot
2.7. ELISA
2.8. Intracellular Cytokine Staining (ICS)
2.9. Neutralising Antibody Titres
2.10. Statistics
2.11. Guinea Pig Experiment Design
2.12. Viral Loads and Histology
3. Results
3.1. Vaccine Design
3.2. Cellular Immunogenicity
3.3. Humoral Immunogenicity
3.4. Prime-Boost Immune Profiling
3.5. Lethal EBOV Challenge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Ebola Virus Disease—Democratic Rebublic of the Congo—External Situation Report 85; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Situation Report—Ebola Virus Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hallam, H.J.; Hallam, S.; Rodriguez, S.E.; Barrett, A.D.T.; Beasley, D.W.C.; Chua, A.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Milligan, G.N.; Sathiyamoorthy, V.; Reece, L.M. Baseline mapping of Lassa fever virology, epidemiology and vaccine research and development. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, N.A.; Mukadi, P.; Doshi, R.H.; Bramble, M.S.; Lu, K.; Gadoth, A.; Sinai, C.; Spencer, D.A.; Nicholson, B.P.; Williams, R.; et al. Serologic markers for ebolavirus among healthcare workers in the democratic republic of the congo. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruibal, P.; Oestereich, L.; Ludtke, A.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Wozniak, D.M.; Kerber, R.; Korva, M.; Cabeza-Cabrerizo, M.; Bore, J.A.; Koundouno, F.R.; et al. Unique human immune signature of Ebola virus disease in Guinea. Nature 2016, 533, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Bailey, M.; Geisbert, J.B.; Asiedu, C.; Roederer, M.; Grazia-Pau, M.; Custers, J.; Jahrling, P.; Goudsmit, J.; Koup, R.; et al. Vector choice determines immunogenicity and potency of genetic vaccines against Angola Marburg virus in nonhuman primates. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10386–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, D.; Misasi, J.; Mulangu, S.; Stanley, D.A.; Kanekiyo, M.; Wollen, S.; Ploquin, A.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Staupe, R.P.; Bailey, M.; et al. Protective monotherapy against lethal Ebola virus infection by a potently neutralizing antibody. Science 2016, 351, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphire, E.O.; Schendel, S.L.; Fusco, M.L.; Gangavarapu, K.; Gunn, B.M.; Wec, A.Z.; Halfmann, P.J.; Brannan, J.M.; Herbert, A.S.; Qiu, X.; et al. Systematic analysis of monoclonal antibodies against ebola virus GP defines features that contribute to protection. Cell 2018, 174, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, T.; Fusco, M.L.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; Lee, J.E.; Flyak, A.I.; Matsuoka, R.; Kohda, D.; Yanagi, Y.; Hammel, M.; Crowe, J.E.; et al. Structural basis for Marburg virus neutralization by a cross-reactive human antibody. Cell 2015, 160, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyak, A.I.; Ilinykh, P.A.; Murin, C.D.; Garron, T.; Shen, X.; Fusco, M.L.; Hashiguchi, T.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; Slaughter, J.C.; Sapparapu, G.; et al. Mechanism of human antibody-mediated neutralization of Marburg virus. Cell 2015, 160, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Restrepo, A.M.; Camacho, A.; Longini, I.M.; Watson, C.H.; Edmunds, W.J.; Egger, M.; Carroll, M.W.; Dean, N.E.; Diatta, I.; Doumbia, M.; et al. Efficacy and effectiveness of an rVSV-vectored vaccine in preventing Ebola virus disease: Final results from the Guinea ring vaccination, open-label, cluster-randomised trial (Ebola Ca Suffit!). Lancet 2017, 389, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Restrepo, A.M.; Longini, I.M.; Egger, M.; Dean, N.E.; Edmunds, W.J.; Camacho, A.; Carroll, M.W.; Doumbia, M.; Draguez, B.; Duraffour, S.; et al. Efficacy and effectiveness of an rVSV-vectored vaccine expressing Ebola surface glycoprotein: Interim results from the Guinea ring vaccination cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewer, K.; Rampling, T.; Venkatraman, N.; Bowyer, G.; Wright, D.; Lambe, T.; Imoukhuede, E.B.; Payne, R.; Fehling, S.K.; Strecker, T.; et al. A monovalent chimpanzee adenovirus ebola vaccine boosted with mva. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winslow, R.L.; Milligan, I.D.; Voysey, M. Immune responses to novel adenovirus type 26 and modified vaccinia virus ankara–vectored ebola vaccines at 1 year. JAMA 2017, 317, 1075–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, I.D.; Gibani, M.M.; Sewell, R.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Campbell, D.; Plested, E.; Nuthall, E.; Voysey, M.; Silva-Reyes, L.; McElrath, M.J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of novel adenovirus type 26- and modified vaccinia ankara-vectored ebola vaccines: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1610–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, N.; Ndiaye, B.P.; Bowyer, G.; Wade, D.; Sridhar, S.; Wright, D.; Powlson, J.; Ndiaye, I.; Dieye, S.; Thompson, C.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a heterologous prime-boost ebola virus vaccine regimen in healthy adults in the United Kingdom and senegal. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutua, G.; Anzala, O.; Luhn, K.; Robinson, C.; Bockstal, V.; Anumendem, D.; Douoguih, M. Safety and immunogenicity of a 2-dose heterologous vaccine regimen with Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-filo ebola vaccines: 12-month data from a phase 1 randomized clinical trial in Nairobi, Kenya. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anywaine, Z.; Whitworth, H.; Kaleebu, P.; Praygod, G.; Shukarev, G.; Manno, D.; Kapiga, S.; Grosskurth, H.; Kalluvya, S.; Bockstal, V.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a 2-dose heterologous vaccination regimen with Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-filo ebola vaccines: 12-month data from a phase 1 randomized clinical trial in uganda and tanzania. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matassov, D.; Mire, C.E.; Latham, T.; Geisbert, J.B.; Xu, R.; Ota-Setlik, A.; Agans, K.N.; Kobs, D.J.; Wendling, M.Q.S.; Burnaugh, A.; et al. Single-dose trivalent vesiculovax vaccine protects macaques from lethal ebolavirus and marburgvirus challenge. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01190-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledgerwood, J.E.; DeZure, A.D.; Stanley, D.A.; Coates, E.E.; Novik, L.; Enama, M.E.; Berkowitz, N.M.; Hu, Z.; Joshi, G.; Ploquin, A.; et al. Chimpanzee adenovirus vector Ebola vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mire, C.E.; Geisbert, J.B.; Versteeg, K.M.; Mamaeva, N.; Agans, K.N.; Geisbert, T.W.; Connor, J.H. A single-vector, single-injection trivalent filovirus vaccine: Proof of concept study in outbred guinea pigs. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S384–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callendret, B.; Vellinga, J.; Wunderlich, K.; Rodriguez, A.; Steigerwald, R.; Dirmeier, U.; Cheminay, C.; Volkmann, A.; Brasel, T.; Carrion, R.; et al. A prophylactic multivalent vaccine against different filovirus species is immunogenic and provides protection from lethal infections with Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus species in non-human primates. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0192312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnandji, S.T.; Huttner, A.; Zinser, M.E.; Njuguna, P.; Dahlke, C.; Fernandes, J.F.; Yerly, S.; Dayer, J.A.; Kraehling, V.; Kasonta, R.; et al. Phase 1 trials of rVSV Ebola vaccine in Africa and Europe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1647–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, S.A.; Arribas, J.R.; Rupp, R.; Andrews, C.P.; Chu, L.; Das, R.; Simon, J.K.; Onorato, M.T.; Liu, K.; Martin, J.; et al. Six-month safety data of recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-zaire ebola virus envelope glycoprotein vaccine in a phase 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized study in healthy adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, A.; Dayer, J.A.; Yerly, S.; Combescure, C.; Auderset, F.; Desmeules, J.; Eickmann, M.; Finckh, A.; Goncalves, A.R.; Hooper, J.W.; et al. The effect of dose on the safety and immunogenicity of the VSV Ebola candidate vaccine: A randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medaglini, D.; Santoro, F.; Siegrist, C.-A. Correlates of vaccine-induced protective immunity against Ebola virus disease. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 39, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewer, K.; Sebastian, S.; Spencer, A.J.; Gilbert, S.; Hill, A.V.S.; Lambe, T. Chimpanzee adenoviral vectors as vaccines for outbreak pathogens. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 3020–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, M.D.; Spencer, A.J.; Edwards, N.J.; Wadell, G.; Bojang, K.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hill, A.V.; Cottingham, M.G. A novel chimpanzee adenovirus vector with low human seroprevalence: Improved systems for vector derivation and comparative immunogenicity. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, J.; Wang, T.; Nian, R.; Lau, A.; Hoi, K.M.; Ho, S.C.; Gagnon, P.; Bi, X.; Yang, Y. Cleavage efficient 2A peptides for high level monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells. MAbs 2015, 7, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, M.G.; Andersen, R.F.; Spencer, A.J.; Saurya, S.; Furze, J.; Hill, A.V.; Gilbert, S.C. Recombination-mediated genetic engineering of a bacterial artificial chromosome clone of modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA). PLoS One 2008, 3, e1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavot, V.; Sebastian, S.; Turner, A.V.; Matthews, J.; Gilbert, S.C. Generation and production of modified vaccinia virus ankara (MVA) as a vaccine vector. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1581, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cassan, S.C.; Forbes, E.K.; Douglas, A.D.; Milicic, A.; Singh, B.; Gupta, P.; Chauhan, V.S.; Chitnis, C.E.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hill, A.V.; et al. The requirement for potent adjuvants to enhance the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of protein vaccines can be overcome by prior immunization with a recombinant adenovirus. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambe, T.; Carey, J.B.; Li, Y.; Spencer, A.J.; van Laarhoven, A.; Mullarkey, C.E.; Vrdoljak, A.; Moore, A.C.; Gilbert, S.C. Immunity against heterosubtypic influenza virus induced by adenovirus and MVA expressing nucleoprotein and matrix protein-1. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Wright, E.; Molesti, E.; Temperton, N.; Barclay, W. Antiviral therapies against Ebola and other emerging viral diseases using existing medicines that block virus entry. F1000Research 2015, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Lofts, L.L.; Kugelman, J.R.; Smither, S.J.; Lever, M.S.; van der Groen, G.; Johnson, K.M.; Radoshitzky, S.R.; Bavari, S.; Jahrling, P.B.; et al. Reidentification of ebola virus E718 and ME as Ebola Virus/H.sapiens-tc/COD/1976/Yambuku-Ecran. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01178-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowall, S.D.; Matthews, D.A.; Garcia-Dorival, I.; Taylor, I.; Kenny, J.; Hertz-Fowler, C.; Hall, N.; Corbin-Lickfett, K.; Empig, C.; Schlunegger, K.; et al. Elucidating variations in the nucleotide sequence of Ebola virus associated with increasing pathogenicity. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombley, A.R.; Wachter, L.; Garrison, J.; Buckley-Beason, V.A.; Jahrling, J.; Hensley, L.E.; Schoepp, R.J.; Norwood, D.A.; Goba, A.; Fair, J.N.; et al. Comprehensive panel of real-time TaqMan polymerase chain reaction assays for detection and absolute quantification of filoviruses, arenaviruses, and New World hantaviruses. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, J.C.; Kurupati, R.K.; Zhou, X.; Bian, A.; Chi, E.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Ertl, H.C. Construction and characterization of E1- and E3-deleted adenovirus vectors expressing two antigens from two separate expression cassettes. Hum. Gene Ther. 2014, 25, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, E.K.; Biswas, S.; Collins, K.A.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hill, A.V.; Draper, S.J. Combining liver- and blood-stage malaria viral-vectored vaccines: Investigating mechanisms of CD8+ T cell interference. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3738–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coller, B.G.; Blue, J.; Das, R.; Dubey, S.; Finelli, L.; Gupta, S.; Helmond, F.; Grant-Klein, R.J.; Liu, K.; Simon, J.; et al. Novel bivalent viral-vectored vaccines induce potent humoral and cellular immune responses conferring protection against stringent influenza a virus challenge. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coller, B.G.; Blue, J.; Das, R.; Dubey, S.; Finelli, L.; Gupta, S.; Helmond, F.; Grant-Klein, R.J.; Liu, K.; Simon, J.; et al. Clinical development of a recombinant Ebola vaccine in the midst of an unprecedented epidemic. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4465–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambe, T.; Bowyer, G.; Ewer, K.J. A review of Phase I trials of ebola virus vaccines: What can we learn from the race to develop novel vaccines? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.C. Clinical development of modified vaccinia virus ankara vaccines. Vaccine 2013, 31, 4241–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; Richardson, J.S.; Pillet, S.; Patel, A.; Qiu, X.; Alimonti, J.; Hogan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Takada, A.; Feldmann, H.; et al. Immune parameters correlate with protection against ebola virus infection in rodents and nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 158ra146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, N.J.; Geisbert, T.W.; Geisbert, J.B.; Shedlock, D.J.; Xu, L.; Lamoreaux, L.; Custers, J.H.; Popernack, P.M.; Yang, Z.Y.; Pau, M.G.; et al. Immune protection of nonhuman primates against Ebola virus with single low-dose adenovirus vectors encoding modified GPs. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regules, J.A.; Beigel, J.H.; Paolino, K.M.; Voell, J.; Castellano, A.R.; Hu, Z.; Munoz, P.; Moon, J.E.; Ruck, R.C.; Bennett, J.W.; et al. A recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus ebola vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, L.; Sridhar, S.; Payne, R.; Edmans, M.; Milicic, A.; Venkatraman, N.; Lugonja, B.; Clifton, L.; Qi, C.; Folegatti, P.M.; et al. Heterologous two-dose vaccination with simian adenovirus and poxvirus vectors elicits long-lasting cellular immunity to influenza virus a in healthy adults. EBioMedicine 2018, 29, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramble, M.S.; Hoff, N.; Gilchuk, P.; Mukadi, P.; Lu, K.; Doshi, R.H.; Steffen, I.; Nicholson, B.P.; Lipson, A.; Vashist, N.; et al. Pan-filovirus serum neutralizing antibodies in a subset of congolese ebolavirus infection survivors. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, S.; Sullivan, B.M.; Hartnett, J.N.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Gangavarapu, K.; Cubitt, B.; Ware, B.C.; Kotliar, D.; Branco, L.M.; Goba, A.; et al. Analysis of CD8(+) T cell response during the 2013-2016 Ebola epidemic in West Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7578–E7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploquin, A.; Zhou, Y.; Sullivan, N.J. Ebola immunity: Gaining a winning position in lightning chess. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyak, A.I.; Shen, X.; Murin, C.D.; Turner, H.L.; David, J.A.; Fusco, M.L.; Lampley, R.; Kose, N.; Ilinykh, P.A.; Kuzmina, N.; et al. Cross-reactive and potent neutralizing antibody responses in human survivors of natural ebolavirus infection. Cell 2016, 164, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
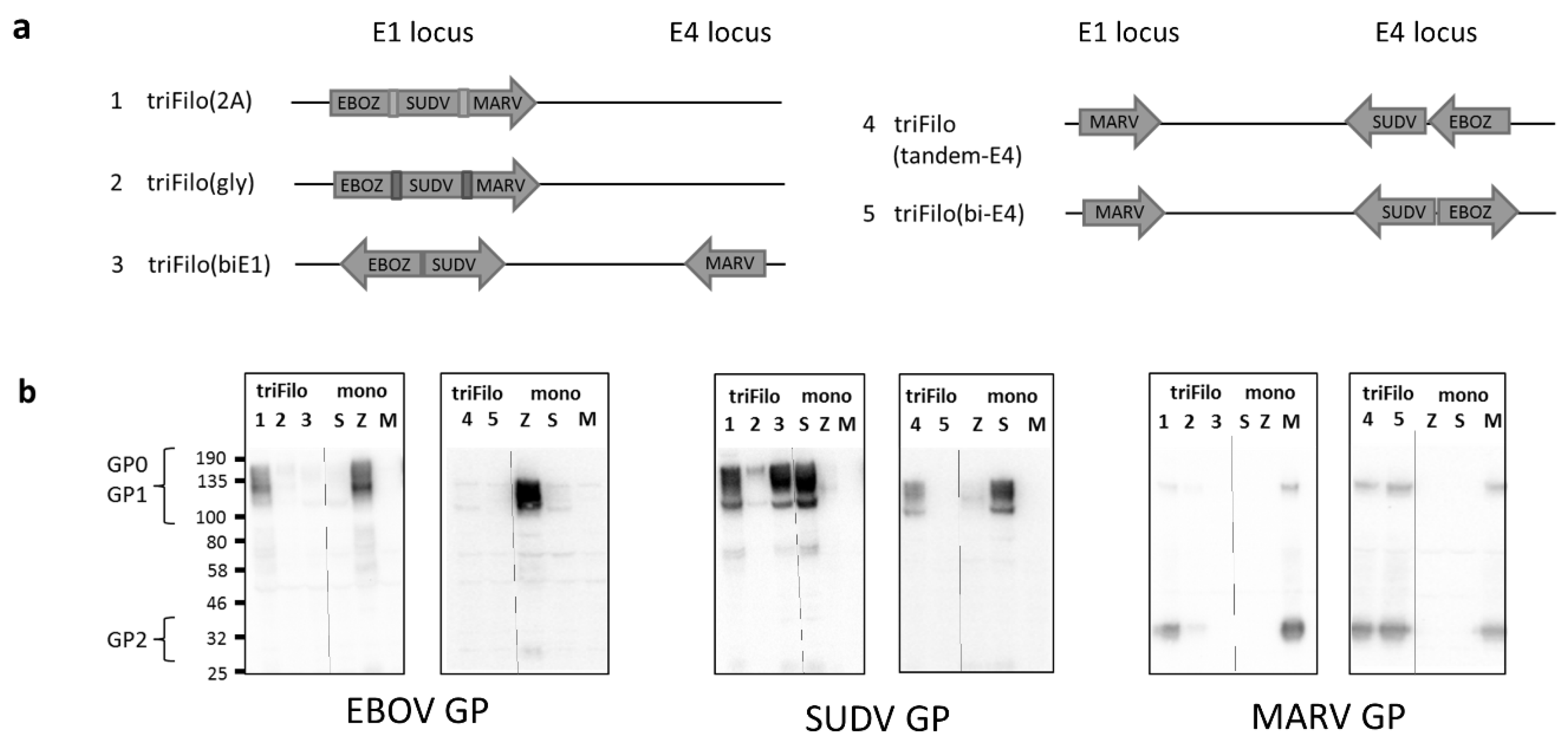


| Vector # | Vector Name | Expression by Western Blot # | Antibody Immunogenicity * (BALB/c /CD-1) | T-Cell Immunogenicity * (BALB/c) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | triFilo(2A) | EBOV | ++ | ++/+++ | +++ |
| SUDV | +++ | +++/+++ | ++ | ||
| MARV | ++ | +++/++ | +++ | ||
| 2 | triFilo(gly) | EBOV | + | +/++ | +++ |
| SUDV | ++ | ++/++ | ++ | ||
| MARV | + | +++/+++ | +++ | ||
| 3 | triFilo (biE1) | EBOV | − | n/a | + |
| SUDV | +++ | n/a | +++ | ||
| MARV | − | n/a | + | ||
| 4 | triFilo (tandem-E4) | EBOV | + | n/a | + |
| SUDV | ++ | n/a | +++ | ||
| MARV | +++ | n/a | +++ | ||
| 5 | triFilo(bi-E4) | EBOV | − | n/a | n/a |
| SUDV | − | n/a | n/a | ||
| MARV | +++ | n/a | n/a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sebastian, S.; Flaxman, A.; Cha, K.M.; Ulaszewska, M.; Gilbride, C.; Sharpe, H.; Wright, E.; Spencer, A.J.; Dowall, S.; Hewson, R.; et al. A Multi-Filovirus Vaccine Candidate: Co-Expression of Ebola, Sudan, and Marburg Antigens in a Single Vector. Vaccines 2020, 8, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020241
Sebastian S, Flaxman A, Cha KM, Ulaszewska M, Gilbride C, Sharpe H, Wright E, Spencer AJ, Dowall S, Hewson R, et al. A Multi-Filovirus Vaccine Candidate: Co-Expression of Ebola, Sudan, and Marburg Antigens in a Single Vector. Vaccines. 2020; 8(2):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020241
Chicago/Turabian StyleSebastian, Sarah, Amy Flaxman, Kuan M. Cha, Marta Ulaszewska, Ciaran Gilbride, Hannah Sharpe, Edward Wright, Alexandra J. Spencer, Stuart Dowall, Roger Hewson, and et al. 2020. "A Multi-Filovirus Vaccine Candidate: Co-Expression of Ebola, Sudan, and Marburg Antigens in a Single Vector" Vaccines 8, no. 2: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020241
APA StyleSebastian, S., Flaxman, A., Cha, K. M., Ulaszewska, M., Gilbride, C., Sharpe, H., Wright, E., Spencer, A. J., Dowall, S., Hewson, R., Gilbert, S., & Lambe, T. (2020). A Multi-Filovirus Vaccine Candidate: Co-Expression of Ebola, Sudan, and Marburg Antigens in a Single Vector. Vaccines, 8(2), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020241





