Influenza Anti-Stalk Antibodies: Development of a New Method for the Evaluation of the Immune Responses to Universal Vaccine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Antigen
2.2. Pseudotype Production
2.3. Serum Samples
2.4. Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay
2.5. Single Radial Hemolysis Assay
2.6. Micro-Neutralization Assay
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Lectin Assay
2.8. Competitive ELISA for Anti-HA2 Antibody Detection
2.9. Statistical Analysis
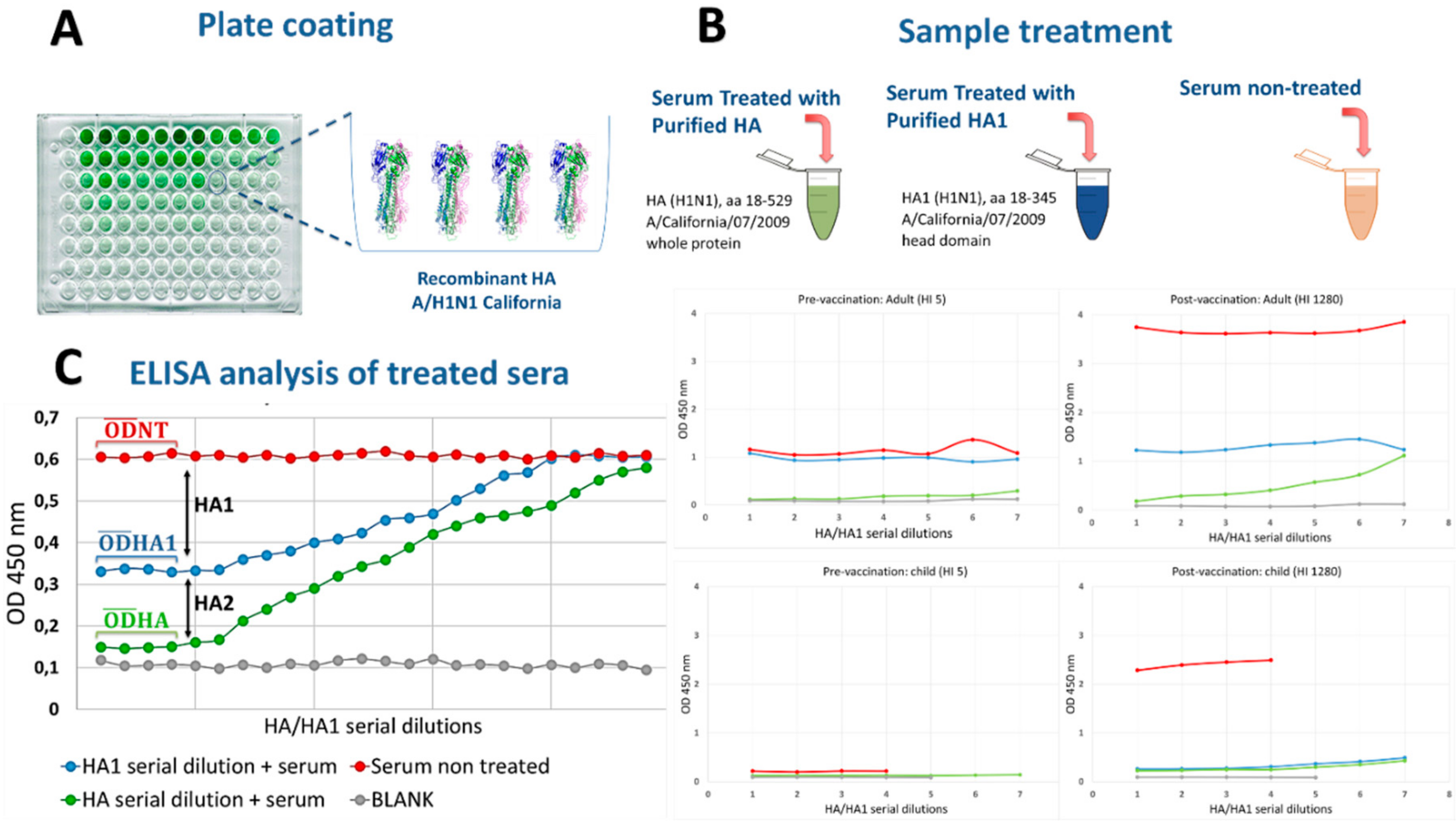
3. Results
3.1. Serum Samples Were Selected Based on HI Titers
3.2. Different Levels of Anti-HA2-specific Antibody Responses Were Found in Pre-Vaccination Samples from Adults, but Not in Children
3.3. Correlation between Anti-HA1 ELISA and SRH- and MN-Antibody Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernelin-Cottet, C.; Deloizy, C.; Staněk, O.; Barc, C.; Bouguyon, E.; Urien, C.; Boulesteix, O.; Pezant, J.; Richard, C.-A.; Moudjou, M.; et al. A Universal Influenza Vaccine Can Lead to Disease Exacerbation or Viral Control Depending on Delivery Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, A.E.; Shay, D.K.; Haber, P.; Iskander, J.K.; Uyeki, T.M.; Mootrey, G.; Bresee, J.S.; Cox, N.J.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Advisory Committee on Immunization. Practices, and Prevention, Prevention and control of influenza. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2007. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2007, 56, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, K.; Viboud, C.; Simonsen, L. Antibody response to influenza vaccination in the elderly: A quantitative review. Vaccine 2006, 24, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Mendez, N.V.; Landin, A.M.; Blomberg, B.B. Effects of age on H1N1-specific serum IgG1 and IgG3 levels evaluated during the 2011–2012 influenza vaccine season. Immun. Ageing 2013, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.M.; Hancock, K.; Xu, X. Serologic assays for influenza surveillance, diagnosis and vaccine evaluation. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2011, 9, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkenstädt, B.F.; Morton, A.; Rand, D.A. Modelling antigenic drift in weekly flu incidence. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghendon, Y. Influenza surveillance. Bull. World Heal. Organ. 1991, 69, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological record. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2000, 75, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Degoot, A.M.; Adabor, E.S.; Chirove, F.; Ndifon, W. Predicting Antigenicity of Influenza A Viruses Using biophysical ideas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, J.C.; Beyer, W.E.; Palache, A.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D. Mismatch between the 1997/1998 influenza vaccine and the major epidemic A(H3N2) virus strain as the cause of an inadequate vaccine-induced antibody response to this strain in the elderly. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 61, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapshak, P.; Chiappelli, F.; Somboonwit, C.; Sinnott, J. The Influenza Pandemic of 2009. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2011, 15, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Hai, R.; Yondola, M.; Tan, G.S.; Leyva-Grado, V.H.; Ryder, A.B.; Miller, M.S.; Rose, J.K.; Palese, P.; García-Sastre, A.; et al. Assessment of Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin Stalk-Based Immunity in Ferrets. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3432–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; Manini, I.; Lazzeri, G.; Montomoli, E. Challenges in the development of egg-independent vaccines for influenza. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neirynck, S.; DeRoo, T.; Saelens, X.; Vanlandschoot, P.; Jou, W.M.; Fiers, W. A universal influenza A vaccine based on the extracellular domain of the M2 protein. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monto, A.S.; Petrie, J.G.; Cross, R.T.; Johnson, E.; Liu, M.; Zhong, W.; Levine, M.; Katz, J.M.; Ohmit, S.E. Antibody to Influenza Virus Neuraminidase: An Independent Correlate of Protection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.P.; Lourenço, J.; Walters, A.A.; Obolski, U.; Edmans, M.; Palmer, D.S.; Kooblall, K.; Carnell, G.W.; O’Connor, D.; Bowden, T.A.; et al. A naturally protective epitope of limited variability as an influenza vaccine target. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Palese, P. Influenza virus hemagglutinin stalk-based antibodies and vaccines. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palese, P.; Shaw, A.R. Orthomyxoviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Perini, D.; Mather, S.; Temperton, N.; Montomoli, E. Overview of Serological Techniques for Influenza Vaccine Evaluation: Past, Present and Future. Vaccines 2014, 2, 707–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Remarque, E.J.; Mortier, D.; Montomoli, E. Comparison of hemagglutination inhibition, single radial hemolysis, virus neutralization assays, and ELISA to detect antibody levels against seasonal influenza viruses. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2018, 12, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.; Nicolay, U.; Vesikari, T.; Knuf, M.; Del Giudice, G.; Della Cioppa, G.; Tsai, T.; Clemens, R.; Rappuoli, R. Hemagglutination Inhibition Antibody Titers as a Correlate of Protection for Inactivated Influenza Vaccines in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, Z.; Kleppinger, A.; Gentleman, B.; Falsey, A.R.; McElhaney, J.E. Clinical and immunologic predictors of influenza illness among vaccinated older adults. Vaccine 2010, 28, 6145–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidich, S.D.; Green, W.D.; Rebeles, J.; Karlsson, E.A.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Noah, T.L.; Chakladar, S.; Hudgens, M.G.; Weir, S.S.; Beck, M.A. Increased risk of influenza among vaccinated adults who are obese. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Manenti, A.; Kistner, O.; Trombetta, C.; Manini, I.; Montomoli, E. How to assess the effectiveness of nasal influenza vaccines? Role and measurement of sIgA in mucosal secretions. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-C.; Nachbagauer, R.; Stadlbauer, D.; Solórzano, A.; Berlanda-Scorza, F.; García-Sastre, A.; Palese, P.; Krammer, F.; Albrecht, R.A. Sequential Immunization With Live-Attenuated Chimeric Hemagglutinin-Based Vaccines Confers Heterosubtypic Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses in a Preclinical Ferret Model. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, H.; Rajendran, M.; Choi, A.; Sjursen, H.; Brokstad, K.A.; Cox, R.J.; Palese, P.; Krammer, F.; Nachbagauer, R. Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin Stalk-Specific Antibodies in Human Serum are a Surrogate Marker for In Vivo Protection in a Serum Transfer Mouse Challenge Model. mBio 2017, 8, e01463-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, P.; Schulman, J.; Young, J.; Palese, P. Preparation of influenza virus subviral particles lacking the HA1 subunit of hemagglutinin: Unmasking of cross-reactive HA2 determinants. Virology 1983, 126, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, H.; Ohshima, A.; Kato, I.; Okuno, Y.; Isegawa, Y. The immunological activity of a deletion mutant of influenza virus haemagglutinin lacking the globular region. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlbold, T.J.; Nachbagauer, R.; Margine, I.; Tan, G.S.; Hirsh, A.; Krammer, F. Vaccination with soluble headless hemagglutinin protects mice from challenge with divergent influenza viruses. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biuso, F.; Carnell, G.W.; Montomoli, E.; Temperton, N. A Lentiviral Pseudotype ELLA for the Measurement of Antibodies Against Influenza Neuraminidase. Bio-101 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Manual for the Laboratory Diagnosis and Virological Surveillance of Influenza; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; 153p. [Google Scholar]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Perini, D.; Vitale, L.; Cox, R.J.; Stanzani, V.; Piccirella, S.; Montomoli, E. Validation of Single Radial Hemolysis assay: A reliable method to measure antibodies against influenza viruses. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 422, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainai, A.; Tamura, S.-I.; Suzuki, T.; Van Riet, E.; Ito, R.; Odagiri, T.; Tashiro, M.; Kurata, T.; Hasegawa, H. Intranasal vaccination with an inactivated whole influenza virus vaccine induces strong antibody responses in serum and nasal mucus of healthy adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couzens, L.; Gao, J.; Westgeest, K.; Sandbulte, M.; Lugovtsev, V.; Fouchier, R.; Eichelberger, M. An optimized enzyme-linked lectin assay to measure influenza A virus neuraminidase inhibition antibody titers in human sera. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 210, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim results: State-specific influenza vaccination coverage—United States, August 2010–February 2011. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2011, 60, 737–743. [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee, S.L.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: Monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treanor, J.J.; Tierney, E.L.; Zebedee, S.L.; Lamb, R.A.; Murphy, B.R. Passively transferred monoclonal antibody to the M2 protein inhibits influenza A virus replication in mice. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-N.; Lee, Y.-T.; Kim, M.-C.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kang, S.-M. Fc receptor is not required for inducing antibodies but plays a critical role in conferring protection after influenza M2 vaccination. Immunol. 2014, 143, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, F.-S.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, B.-J.; Song, J.-M.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.-M. Influenza M1 VLPs containing neuraminidase induce heterosubtypic cross-protection. Virol. 2012, 430, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Isegawa, Y.; Sasao, F.; Ueda, S. A common neutralizing epitope conserved between the hemagglutinins of influenza A virus H1 and H2 strains. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Palese, P. Universal influenza virus vaccines: Need for clinical trials. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommakanti, G.; Citron, M.P.; Hepler, R.W.; Callahan, C.; Heidecker, G.J.; Najar, T.A.; Lu, X.; Joyce, J.G.; Shiver, J.W.; Casimiro, D.R.; et al. Design of an HA2-based Escherichia coli expressed influenza immunogen that protects mice from pathogenic challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13701–13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, R.; Krammer, F.; Tan, G.S.; Pica, N.; Eggink, D.; Maamary, J.; Margine, I.; Albrecht, R.A.; Palese, P. Influenza Viruses Expressing Chimeric Hemagglutinins: Globular Head and Stalk Domains Derived from Different Subtypes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5774–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Clinical Data Needed to Support the Licensure of Seasonal Inactivated Influenza Vaccines. 2007. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/clinical-data-needed-support-licensure-seasonal-inactivated-influenza-vaccines (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- European Medicine Agency. Guideline on Influenza Vaccines. Guideline on Influenza Vaccines; European Medicine Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; 31p. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, J.; Gaines-Das, R.; Taylor, J.; Chakraverty, P. Comparison of influenza serological techniques by international collaborative study. Vaccine 1994, 12, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, P.; Arnou, R.; Kafeja, F.; Fiquet, A.; Richard, P.; Thomas, S.; Meghlaoui, G.; Samson, S.I.; Ledesma, E. Evaluation of non-inferiority of intradermal versus adjuvanted seasonal influenza vaccine using two serological techniques: A randomised comparative study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Russell, M.L.; Brewer, A.; Newton, J.; Singh, P.; Ward, B.J.; Loeb, M. Single radial hemolysis compared to haemagglutinin inhibition and microneutralization as a correlate of protection against influenza A H3N2 in children and adolescents. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2017, 11, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auladell, M.; Jia, X.; Hensen, L.; Chua, B.; Fox, A.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Doherty, P.C.; Kedzierska, K. Recalling the Future: Immunological Memory Toward Unpredictable Influenza Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, M.A.; Zhang, R.; Walter, E.B.; Woods, C.W.; Ginsburg, G.S.; McClain, M.T.; Denny, T.N.; Chen, X.; Munshaw, S.; Marshall, D.J.; et al. H3N2 Influenza Infection Elicits More Cross-Reactive and Less Clonally Expanded Anti-Hemagglutinin Antibodies Than Influenza Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, J.; Hoy, G.; Gordon, A. Influenza in Children. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Myers, J.L.; Bostick, D.L.; Sullivan, C.B.; Madara, J.; Linderman, S.L.; Liu, Q.; Carter, D.M.; Wrammert, J.; Esposito, S.; et al. Immune history shapes specificity of pandemic H1N1 influenza antibody responses. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, P.E.; He, W.; Mullarkey, C.E.; Bailey, M.J.; Miller, M.S.; Krammer, F.; Palese, P.; Tan, G.S. Optimal activation of Fc-mediated effector functions by influenza virus hemagglutinin antibodies requires two points of contact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, E5944–E5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.; Kwaks, T.; Brandenburg, B.; Koldijk, M.H.; Klaren, V.; Smal, B.; Korse, H.J.; Geelen, E.; Tettero, L.; Zuijdgeest, D.; et al. HA Antibody-Mediated FcgammaRIIIa Activity Is Both Dependent on FcR Engagement and Interactions between HA and Sialic Acids. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
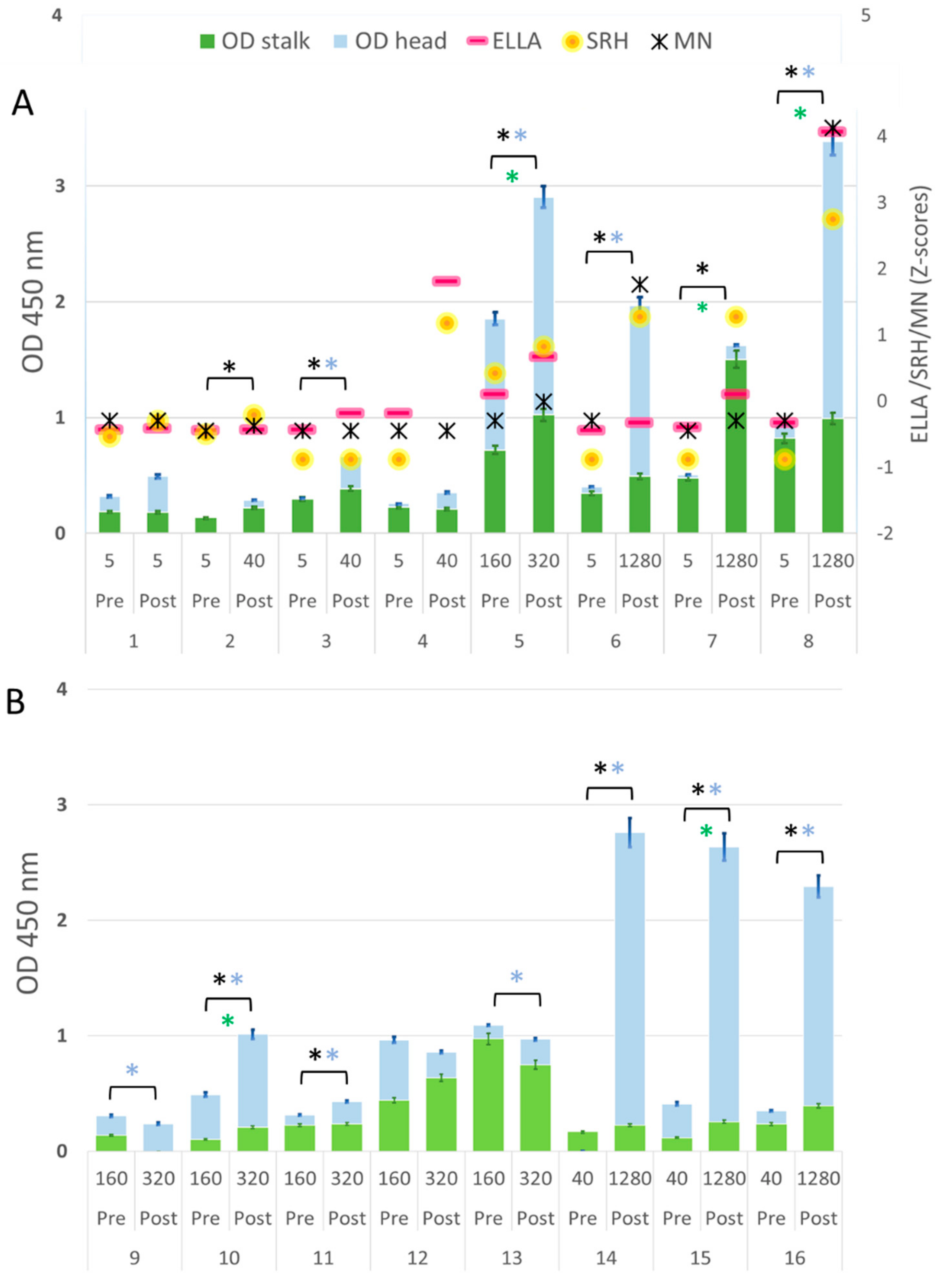

| Subject | Dose | HI Titer | Competitive ELISA | ELLA Titer | SRH Area [mm2] | MN Titer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD Stalk (HA2) | OD Head (HA1) | OD HA | ||||||
| 1 | Pre | 5 | 0.187 | 0.133 | 0.320 | 10 | 10.2 | 40 |
| Post | 5 | 0.182 | 0.295 | 0.477 | 15 | 17.3 | 40 | |
| 2 | Pre | 5 | 0.133 | −0.018 | 0.116 | 5 | 11.3 | 20 |
| Post | 40 | 0.220 | 0.069 | * 0.289 | 10 | 19.6 | 30 | |
| 3 | Pre | 5 | 0.281 | 0.022 | 0.303 | 10 | 2.256 | 20 |
| Post | 40 | 0.391 | * 0.255 | * 0.647 | 80 | 2.256 | 20 | |
| 4 | Pre | 5 | 0.238 | 0.032 | 0.269 | 80 | 2.256 | 20 |
| Post | 40 | 0.211 | 0.159 | 0.370 | 640 | 60.8 | 20 | |
| 5 | Pre | 160 | 0.723 | 1.164 | 1.887 | 160 | 38.5 | 40 |
| Post | 320 | * 1.041 | * 1.834 | * 2.875 | 320 | 50.2 | 80 | |
| 6 | Pre | 5 | 0.341 | 0.059 | 0.400 | 5 | 2.256 | 40 |
| Post | 1280 | 0.485 | * 1.464 | * 1.949 | 40 | 63.6 | 320 | |
| 7 | Pre | 5 | 0.452 | 0.039 | 0.491 | 20 | 2.256 | 20 |
| Post | 1280 | * 1.499 | 0.113 | *1.612 | 160 | 63.6 | 40 | |
| 8 | Pre | 5 | 0.816 | 0.131 | 0.947 | 40 | 2.256 | 40 |
| Post | 1280 | * 0.987 | * 2.371 | * 3.359 | 1280 | 107.5 | 640 | |
| Subject | Dose | HI Titer | Competitive ELISA | ELLA Titer | SRH Area [mm2] | MN Titer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD Stalk (HA2) | OD Head (HA1) | OD HA | ||||||
| 1 | Pre | 5 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 5 | 2.256 | 40 |
| Post | 80 | 0.039 | * 0.179 | * 0.219 | 120 | 21.2 | 80 | |
| 2 | Pre | 5 | −0.016 | 0.023 | 0.007 | 5 | 2.256 | 20 |
| Post | 226.3 | * 0.040 | * 0.461 | * 0.501 | 10 | 38.5 | 80 | |
| 3 | Pre | 5 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.051 | 5 | 12.6 | 10 |
| Post | 320 | 0.009 | * 0.521 | * 0.530 | 160 | 59.4 | 80 | |
| 4 | Pre | 5 | 0.016 | 0.044 | 0.060 | 5 | 2.256 | 40 |
| Post | 380 | * 0.251 | * 0.824 | * 1.075 | 20 | 50.2 | 160 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manenti, A.; Maciola, A.K.; Trombetta, C.M.; Kistner, O.; Casa, E.; Hyseni, I.; Razzano, I.; Torelli, A.; Montomoli, E. Influenza Anti-Stalk Antibodies: Development of a New Method for the Evaluation of the Immune Responses to Universal Vaccine. Vaccines 2020, 8, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010043
Manenti A, Maciola AK, Trombetta CM, Kistner O, Casa E, Hyseni I, Razzano I, Torelli A, Montomoli E. Influenza Anti-Stalk Antibodies: Development of a New Method for the Evaluation of the Immune Responses to Universal Vaccine. Vaccines. 2020; 8(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010043
Chicago/Turabian StyleManenti, Alessandro, Agnieszka Katarzyna Maciola, Claudia Maria Trombetta, Otfried Kistner, Elisa Casa, Inesa Hyseni, Ilaria Razzano, Alessandro Torelli, and Emanuele Montomoli. 2020. "Influenza Anti-Stalk Antibodies: Development of a New Method for the Evaluation of the Immune Responses to Universal Vaccine" Vaccines 8, no. 1: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010043
APA StyleManenti, A., Maciola, A. K., Trombetta, C. M., Kistner, O., Casa, E., Hyseni, I., Razzano, I., Torelli, A., & Montomoli, E. (2020). Influenza Anti-Stalk Antibodies: Development of a New Method for the Evaluation of the Immune Responses to Universal Vaccine. Vaccines, 8(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010043





