Parenteral–Oral Immunization with Plant-Derived HBcAg as a Potential Therapeutic Vaccine against Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transient Expression in Nicotiana benthamiana
2.2. Lettuce Stable Transformation
2.3. Microscopic Observations of Plant-Expressed HBcAg
2.4. Lyophilization
2.5. Mouse Immunization
2.6. ELISA Tests
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transient Expression of HBcAg in Nicotiana benthamiana
3.2. HBcAg Expression in Transgenic Lettuce
3.3. Observation of HBcAg CLPs in Plant Tissue
3.4. Lyophilization and Material Stability
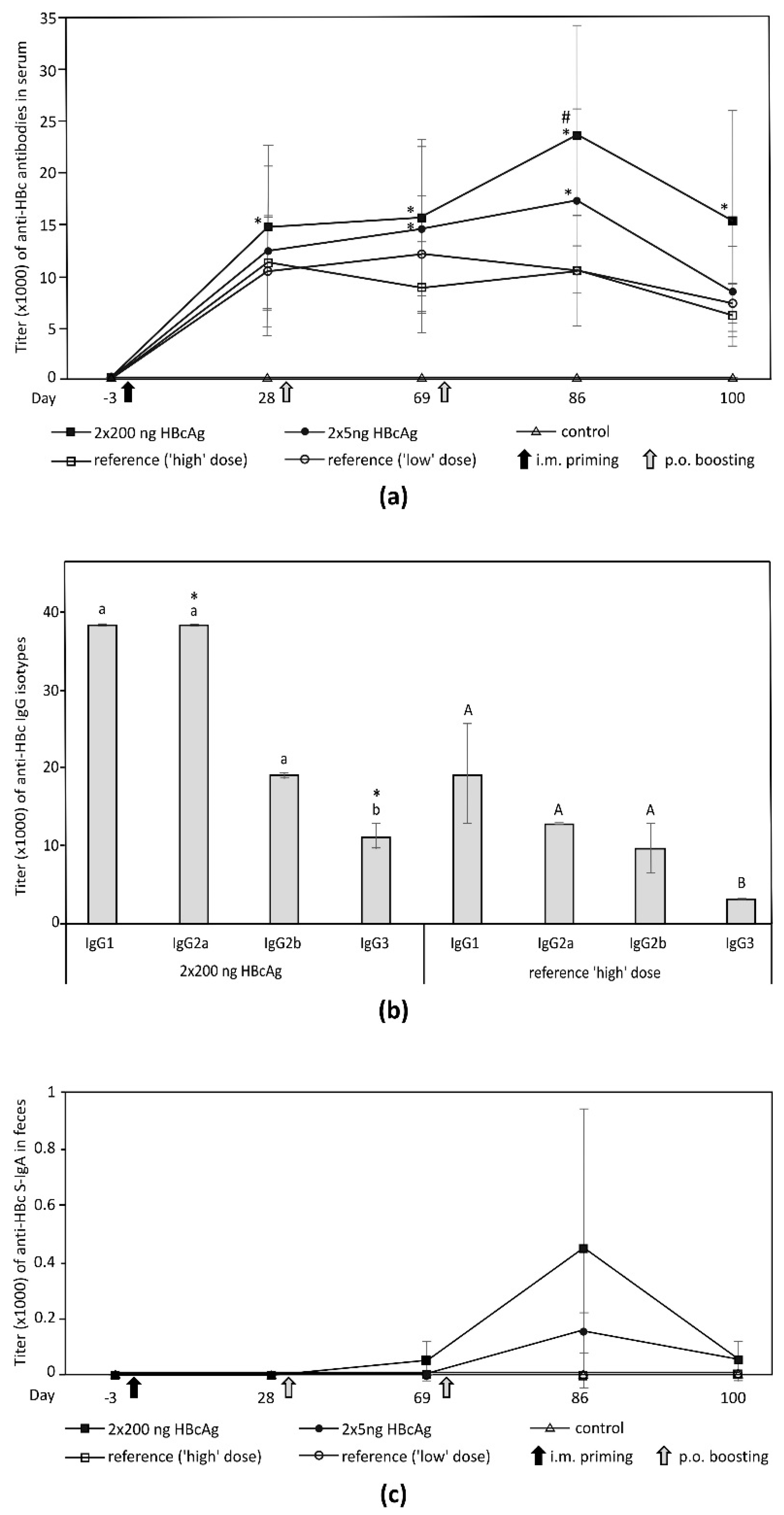
3.5. Immunogenicity of Plant-Derived HBcAg
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stasi, C.; Silvestri, C.; Voller, F. Emerging trends in epidemiology of Hepatitis B virus infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, L.A.; Orsi, A.; Tatarelli, P.; Viscoli, C.; Icardi, G.; Sticchi, L. A global view to HBV chronic infection: Evolving strategies for diagnosis, treatment and prevention in immunocompetent individuals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, W.-K.; Lo, Y.-R.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Yuen, M.-F. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2018, 392, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.S.Y.; Covert, E.; Wilson, E.; Kottilil, S. Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. JAMA 2018, 319, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.M.F.; Al-Mahtab, M.; Uddin, M.H.; Khan, M.S.I. HBsAg, HBcAg, and combined HBsAg/HBcAg-based therapeutic vaccines in treating chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2013, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Le Bert, N. Immunotherapy for chronic Hepatitis B virus infection. Gut Liver 2018, 12, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gish, R.G.; Given, B.D.; Lai, C.-L.; Locarnini, S.A.; Lau, J.Y.N.; Lewis, D.L.; Schluep, T. Chronic hepatitis B: Virology, natural history, current management and a glimpse at future opportunities. Antiviral Res. 2015, 121, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, P.; Dembek, C.; Kuklick, L.; Jäger, C.; Tedjokusumo, R.; von Freyend, M.J.; Drebber, U.; Janowicz, Z.; Melber, K.; Protzer, U. A novel therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine induces cellular and humoral immune responses and breaks tolerance in hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Santi, L.; LePore, K.; Kilbourne, J.; Arntzen, C.J.; Mason, H.S. Rapid, high-level production of hepatitis B core antigen in plant leaf and its immunogenicity in mice. Vaccine 2006, 24, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, N.; Streatfield, S.J.; Yusibov, V. Virus-like particles as a highly efficient vaccine platform: Diversity of targets and production systems and advances in clinical development. Vaccine 2012, 31, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainsbury, F.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Extremely high-level and rapid transient protein production in plants without the use of viral replication. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrski, M.; Rugowska, A.; Wierzbiński, K.R.; Kasprzyk, A.; Bogusiewicz, M.; Bociąg, P.; Samardakiewicz, S.; Czyż, M.; Kurpisz, M.; Pniewski, T. HBcAg produced in transgenic tobacco triggers Th1 and Th2 response when intramuscularly delivered. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5714–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Moon, K.-B.; Jeon, J.-H.; Cho, H.-S.; Kim, H.-S. The last ten years of advancements in plant-derived recombinant vaccines against Hepatitis B. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela Ramirez, J.E.; Sharpe, L.A.; Peppas, N.A. Current state and challenges in developing oral vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 114, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pniewski, T.; Milczarek, M.; Wojas-Turek, J.; Pajtasz-Piasecka, E.; Wietrzyk, J.; Czyż, M. Plant lyophilisate carrying S-HBsAg as an oral booster vaccine against HBV. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybka, J.; Mieloch, A.; Plis, A.; Pyrski, M.; Pniewski, T.; Giersig, M. Assembly and characterization of HBc derived virus-like particles with magnetic core. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pniewski, T.; Kapusta, J.; Bociąg, P.; Wojciechowicz, J.; Kostrzak, A.; Gdula, M.; Fedorowicz-Strońska, O.; Wójcik, P.; Otta, H.; Samardakiewicz, S.; et al. Low-dose oral immunization with lyophilized tissue of herbicide-resistant lettuce expressing hepatitis B surface antigen for prototype plant-derived vaccine tablet formulation. J. Appl. Genet. 2011, 52, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.C.; Wheeler, R.M.; Grim, E. The gravimetric method for the determination of residual moisture in freeze-dried biological products. Cryobiology 1989, 26, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghag, S.B.; Adki, V.S.; Ganapathi, T.R.; Bapat, V.A. Heterologous protein production in plant systems. GM Crops Food 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; Penney, C.A.; Majumder, A.; Walmsley, A.M. Evolution of plant-made pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3220–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Hjelm, B.; Arntzen, C.; Mason, H. A DNA replicon system for rapid high-level production of virus-like particles in plants. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pniewski, T.; Czyż, M.; Wyrwa, K.; Bociąg, P.; Krajewski, P.; Kapusta, J. Micropropagation of transgenic lettuce containing HBsAg as a method of mass-scale production of standardised plant material for biofarming purposes. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyż, M.; Dembczyński, R.; Marecik, R.; Pniewski, T. Stability of S-HBsAg in long-term stored lyophilised plant tissue. Biologicals 2016, 44, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, A.; Lomonossoff, G.P.; Evans, D.J.; Barker, S.A. Plant-expressed Hepatitis B core antigen virus-like particles: Characterization and investigation of their stability in simulated and pig gastro-intestinal fluids. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 522, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowat, A.M. Anatomical basis of tolerance and immunity to intestinal antigens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, R.; Allais, L.; Cuvelier, C.A. Recent advances in oral vaccine development: Yeast-derived β-glucan particles. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.; Lobaina, Y.; Muzio, V.; García, D.; Pentón, E.; Iglesias, E.; Pichardo, D.; Urquiza, D.; Rodríguez, D.; Silva, D.; et al. Development of a nasal vaccine for chronic hepatitis B infection that uses the ability of hepatitis B core antigen to stimulate a strong Th1 response against hepatitis B surface antigen. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schödel, F.; Peterson, D.; Hughes, J.; Wirtz, R.; Milich, D. Hybrid hepatitis B virus core antigen as a vaccine carrier moiety: I. Presentation of foreign epitopes. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 44, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donin, M.V.; Boĭchenko, M.N.; Vorob’ev, A.A. The possibility of using the attenuated recombinant strain of Salmonella enteritidis producing the HBc-antigen as a rectal vaccine in an experiment. Vestn. Ross. Akad. Meditsinskikh Nauk 2004, 6, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, R.M.; Weiner, H.L. History and mechanisms of oral tolerance. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 30, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, R.M.; Tetland, S.; Wilson, H.L. Low dose antigen exposure for a finite period in newborn rats prevents induction of mucosal tolerance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 0051437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oliveira, R.P.; Santiago, A.F.; Ficker, S.M.; Gomes-Santos, A.C.; Faria, A.M.C. Antigen administration by continuous feeding enhances oral tolerance and leads to long-lasting effects. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 421, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balke, I.; Zeltins, A. Use of plant viruses and virus-like particles for the creation of novel vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 145, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehermann, B.; Nascimbeni, M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, C.A.; Fischer, M.E.; Andrews, B.L.; Chilton, H.C.; Turner, D.D.; Walker, J.H.; Tizard, I.R.; Howard, J.A. Oral delivery of wafers made from HBsAg-expressing maize germ induces long-term immunological systemic and mucosal responses. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.L.; Paruch, L.; Dobrica, M.O.; Caras, I.; Tucureanu, C.; Onu, A.; Ciulean, S.; Stavaru, C.; Eerde, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Lettuce-produced hepatitis C virus E1E2 heterodimer triggers immune responses in mice and antibody production after oral vaccination. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsted, D.; Fallahi, F.; Golshani, A.; Azizi, A. Advances and challenges in mucosal adjuvant technology. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshi, T. Modes of Action for Mucosal Vaccine Adjuvants. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, M.; Pezzotti, M.; Avesani, L. Edible plants for oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, M.T.; Sameeullah, M.; Khan, F.A.; Syed, T.; Ilahi, M.; Gottschamel, J.; Lössl, A.G. Need of cost-effective vaccines in developing countries: What plant biotechnology can offer? SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyrski, M.; Mieloch, A.A.; Plewiński, A.; Basińska-Barczak, A.; Gryciuk, A.; Bociąg, P.; Murias, M.; Rybka, J.D.; Pniewski, T. Parenteral–Oral Immunization with Plant-Derived HBcAg as a Potential Therapeutic Vaccine against Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines 2019, 7, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040211
Pyrski M, Mieloch AA, Plewiński A, Basińska-Barczak A, Gryciuk A, Bociąg P, Murias M, Rybka JD, Pniewski T. Parenteral–Oral Immunization with Plant-Derived HBcAg as a Potential Therapeutic Vaccine against Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines. 2019; 7(4):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040211
Chicago/Turabian StylePyrski, Marcin, Adam Aron Mieloch, Adam Plewiński, Aneta Basińska-Barczak, Aleksandra Gryciuk, Piotr Bociąg, Marek Murias, Jakub Dalibor Rybka, and Tomasz Pniewski. 2019. "Parenteral–Oral Immunization with Plant-Derived HBcAg as a Potential Therapeutic Vaccine against Chronic Hepatitis B" Vaccines 7, no. 4: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040211
APA StylePyrski, M., Mieloch, A. A., Plewiński, A., Basińska-Barczak, A., Gryciuk, A., Bociąg, P., Murias, M., Rybka, J. D., & Pniewski, T. (2019). Parenteral–Oral Immunization with Plant-Derived HBcAg as a Potential Therapeutic Vaccine against Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines, 7(4), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040211







