Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Vaccination against Shigellosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Outer Membrane Vesicle Obtention
2.2. Polymeric MN Arrays Formulation
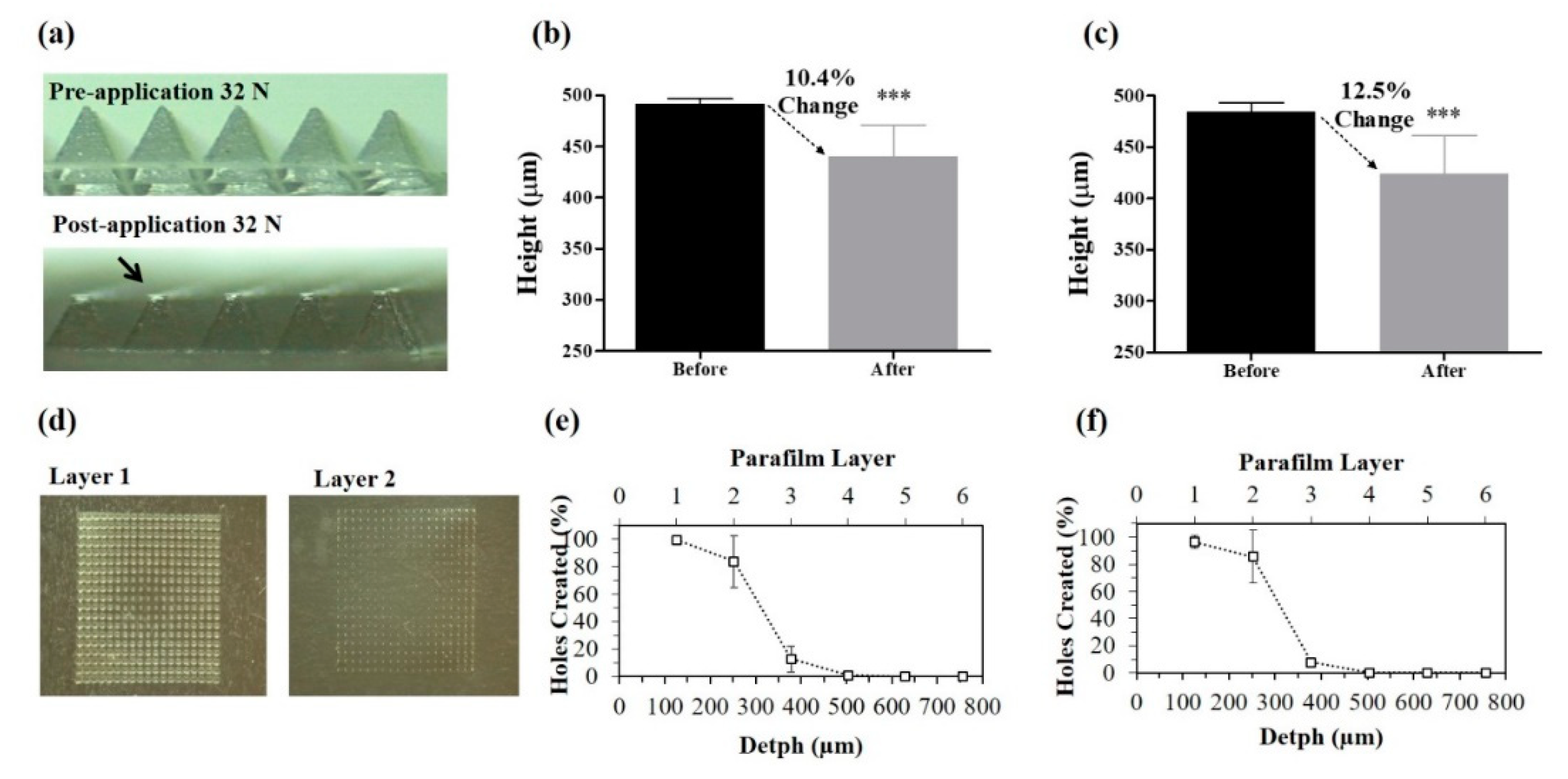
2.3. Mechanical Characterization of MNs
2.3.1. Compression Test
2.3.2. Insertion Test
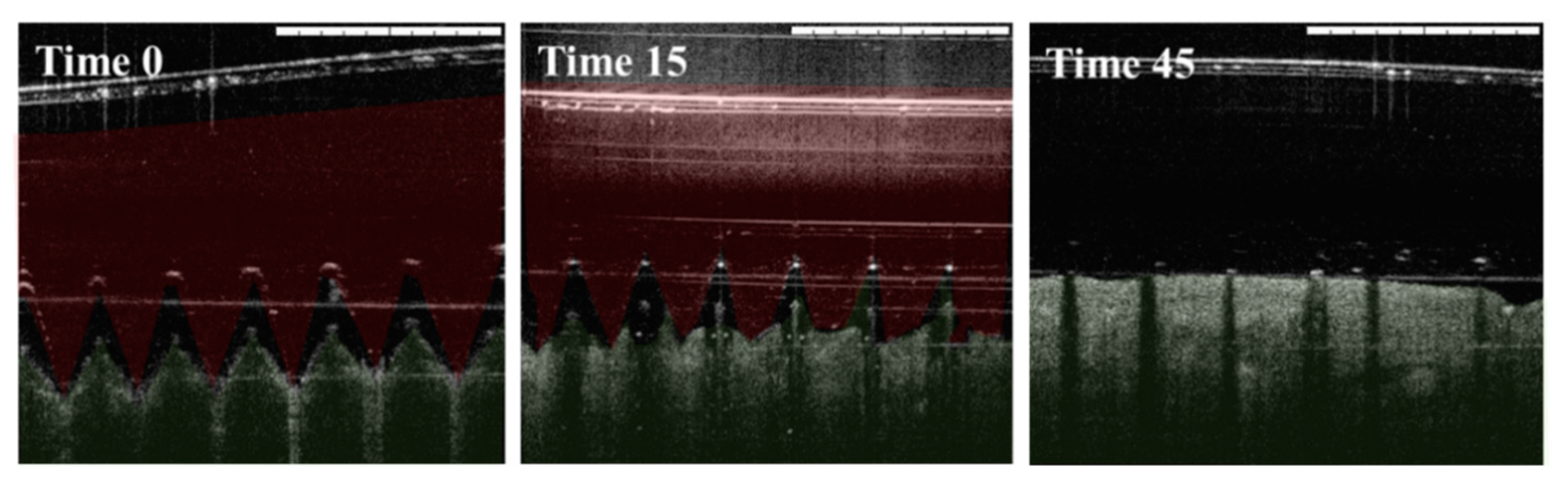
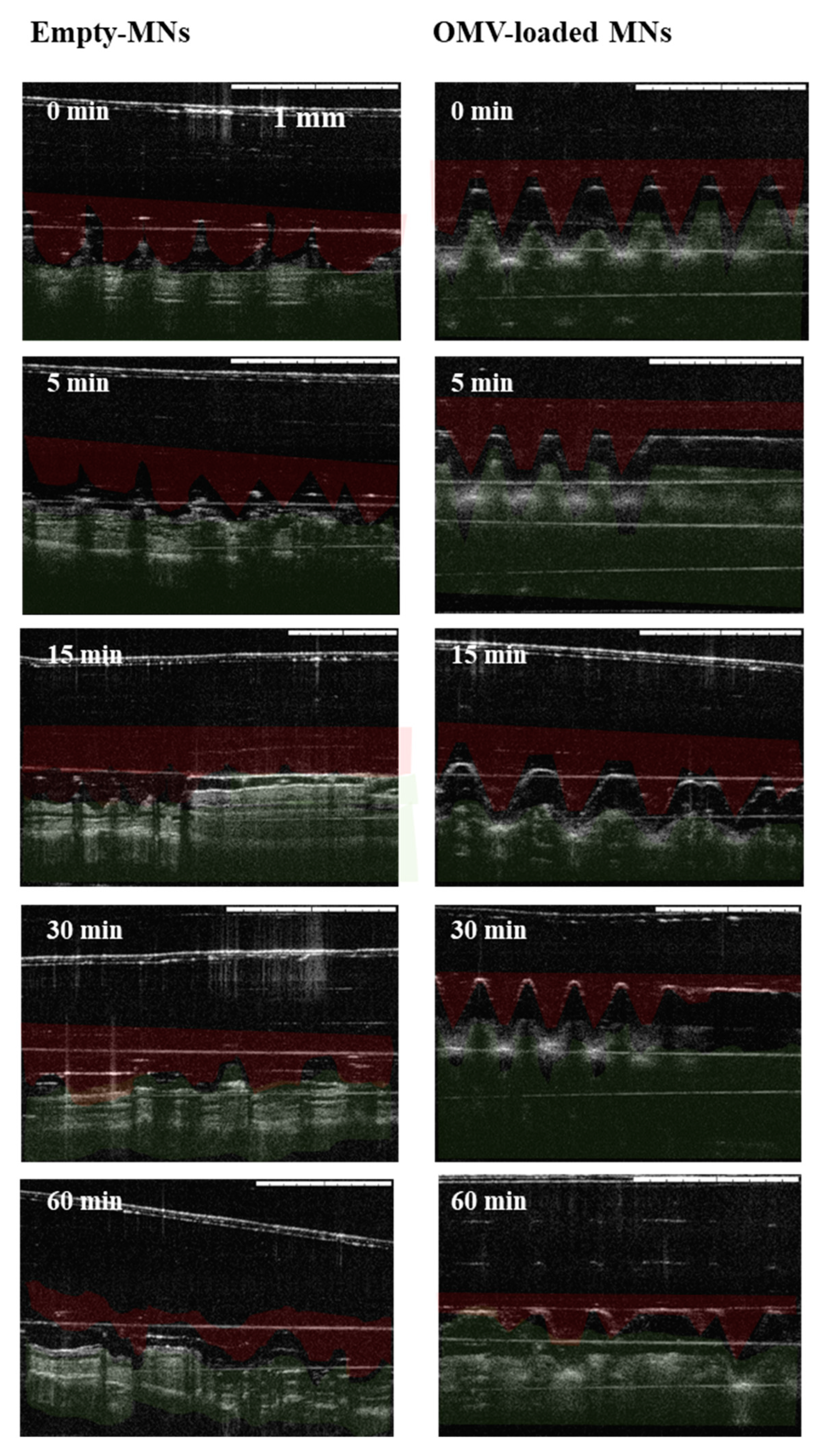
2.4. Skin Insertion Studies
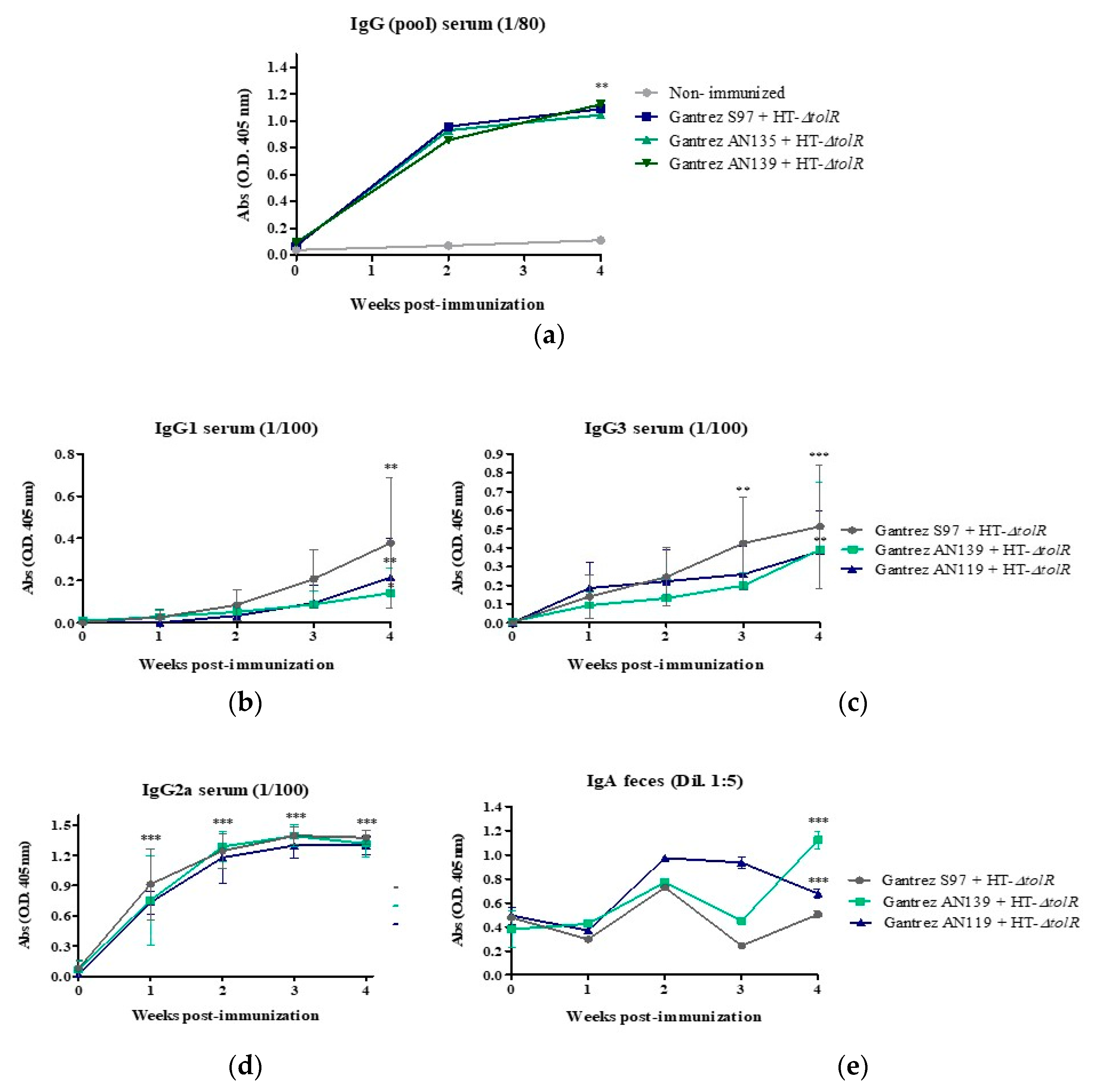
2.5. Immunization and Protection In Vivo Studies
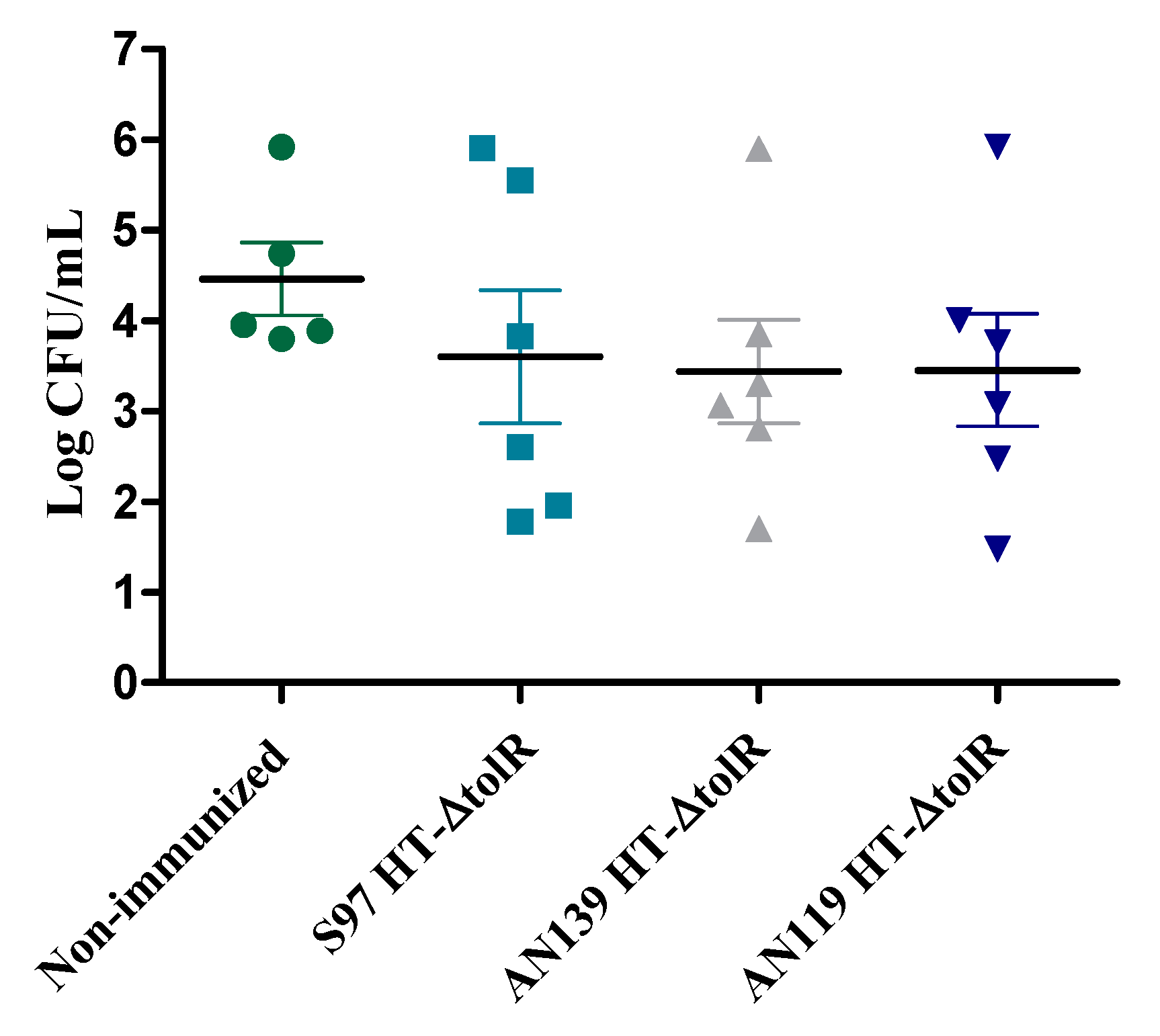
2.5.1. Comparative Study between Gantrez® Polymers
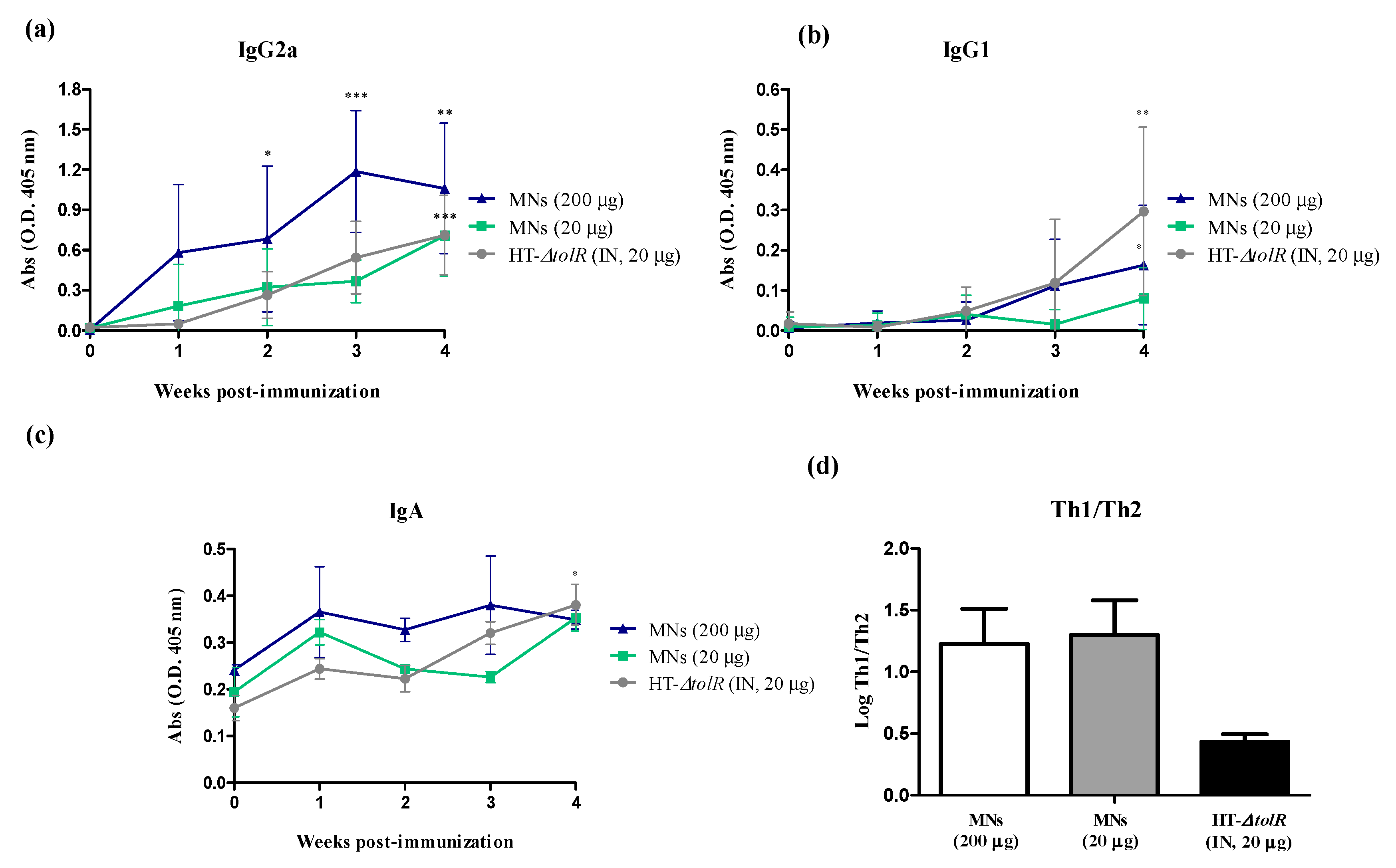
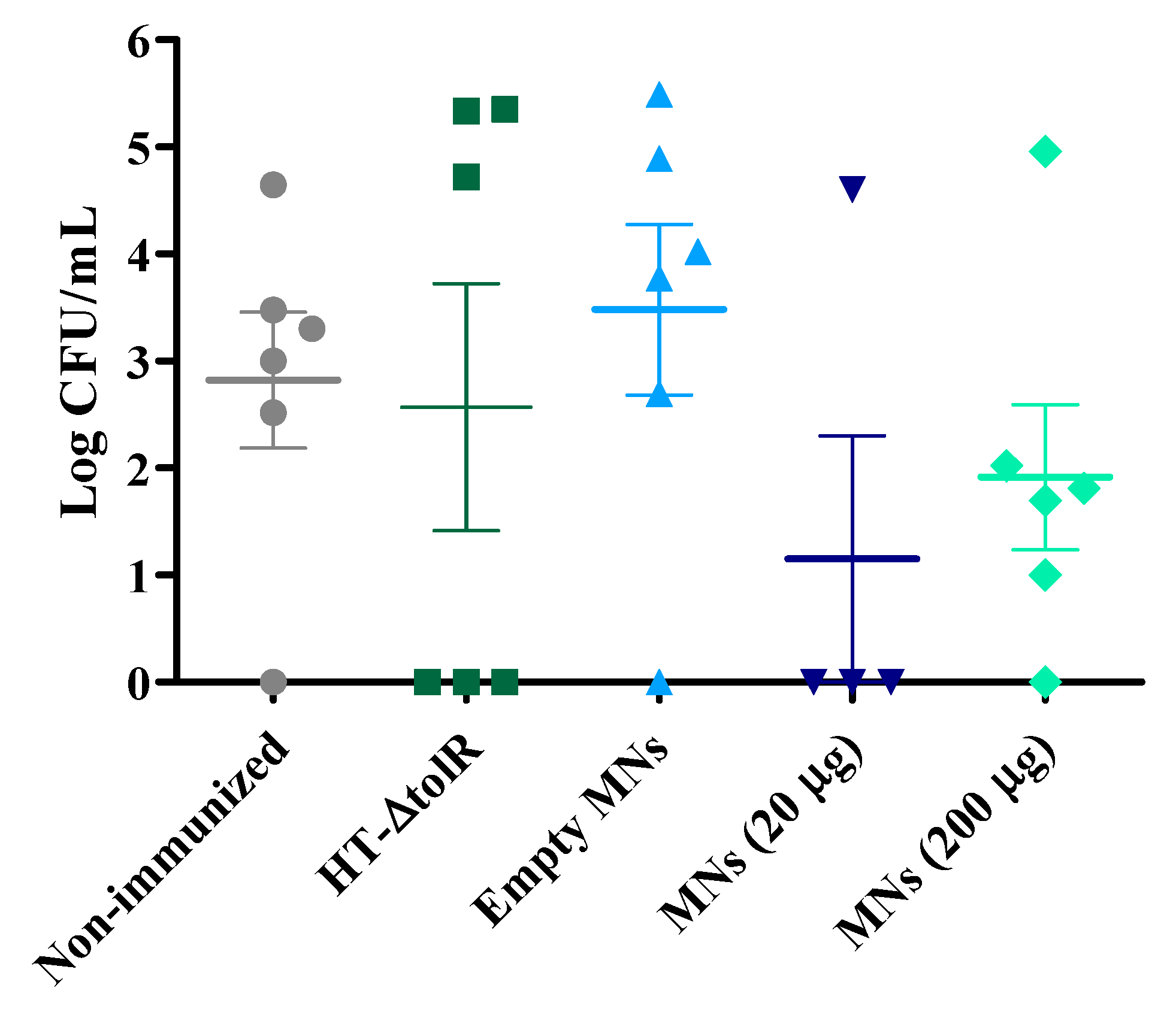
2.5.2. Immunogenicity and Protection with Gantrez® AN119
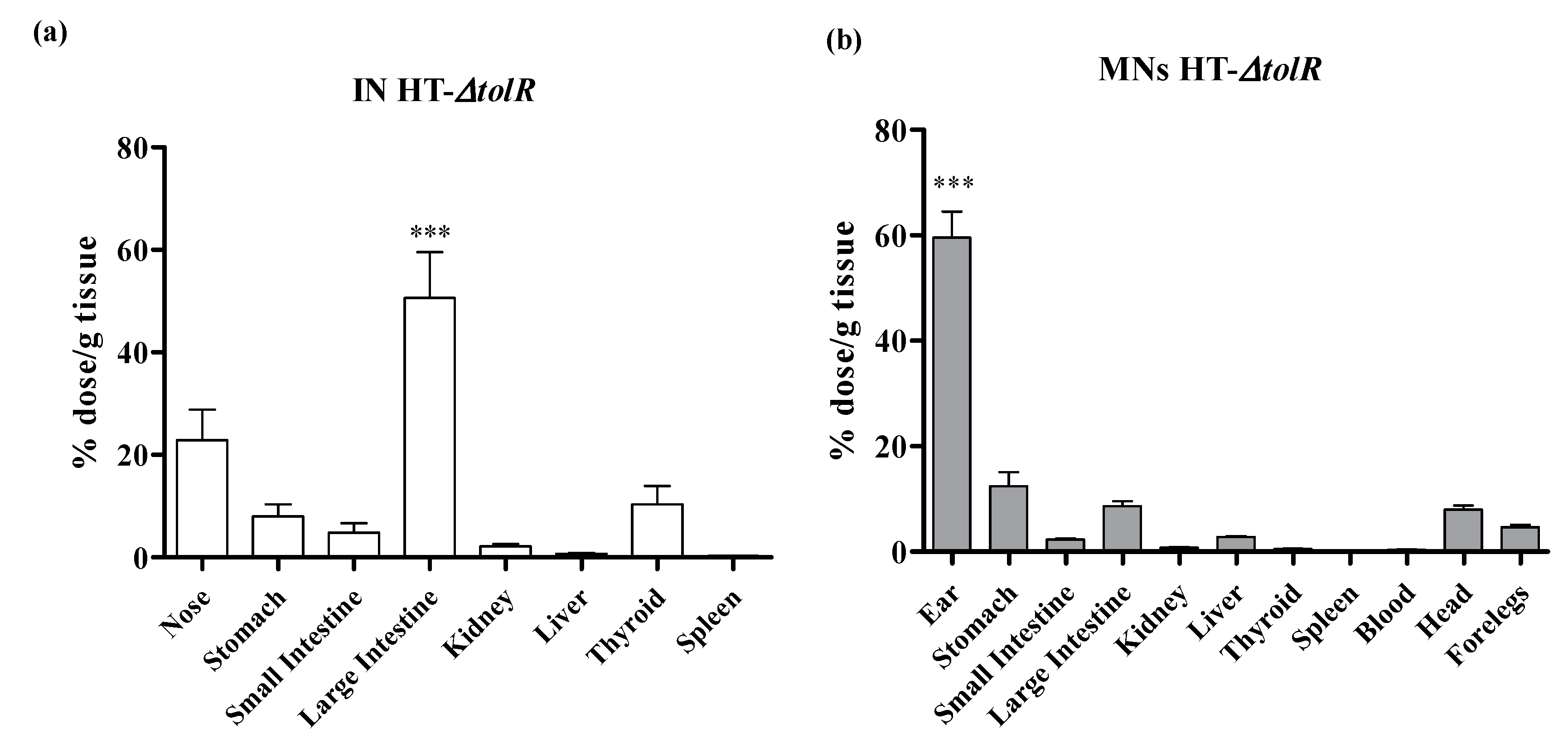
2.6. Biodistribution Studies
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Polymeric MN Arrays Formulation
3.2. Mechanical Characterization of MNs
3.3. Skin Insertion and Dissolution Studies
3.3.1. Insertion in Pig Skin
3.3.2. Insertion in Mice Skin
3.4. Immunization and Protection Studies In Vivo
3.5. Biodistribution Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilleman, M.R. Vaccines in historic evolution and perspective: A narrative of vaccine discoveries. Vaccine 2000, 18, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, J.; Shenton, D.P.; Carlisle, R.C. Novel approaches for the design, delivery and administration of vaccine technologies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streilein, J.W. Skin-associated lymphoid tissues (SALT): Origins and functions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 80, 12s–16s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Prausnitz, M.R. Enabling skin vaccination using new delivery technologies. Drug. Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, A.M.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Dissolving microneedles for intradermal vaccination: Manufacture, formulation, and stakeholder considerations. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2018, 15, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, L.K.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E.; González-Vázquez, P.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Vavia, P.R. Novel bilayer dissolving microneedle arrays with concentrated PLGA nano-microparticles for targeted intradermal delivery: Proof of concept. J. Control. Release 2017, 265, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, J.; Henry, S.; Kalluri, H.; McAllister, D.V.; Pewin, W.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Tolerability, usability and acceptability of dissolving microneedle patch administration in human subjects. Biomaterials 2017, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripolin, A.; Quinn, J.; Larrañeta, E.; Vicente-Perez, E.M.; Barry, J.; Donnelly, R.F. Successful application of large microneedle patches by human volunteers. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaric, M.; Lyubomska, O.; Poux, C.; Hanna, M.L.; McCrudden, M.T.; Malissen, B.; Ingram, R.J.; Power, U.F.; Scott, C.J.; Donnelly, R.F.; et al. Dissolving Microneedle Delivery of Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Antigen Elicits Efficient Cross-Priming and Th1 Immune Responses by Murine Langerhans Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Lutton, R.E.M.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2016, 104, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Hirobe, S.; Yokota, Y.; Ayabe, Y.; Seto, M.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Tougan, T.; Horii, T.; Mukai, Y.; et al. Transcutaneous immunization using a dissolving microneedle array protects against tetanus, diphtheria, malaria, and influenza. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouphael, N.G.; Paine, M.; Mosley, R.; Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Kalluri, H.; Pewin, W.; Frew, P.M.; Yu, T.; Thornburg, N.J.; et al. The safety, immunogenicity, and acceptability of inactivated influenza vaccine delivered by microneedle patch (TIV-MNP 2015): A randomised, partly blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, A.M.; McCrudden, M.T.; Vincente-Perez, E.M.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and characterisation of a dissolving microneedle patch for intradermal vaccination with heat-inactivated bacteria: A proof of concept study. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.I.; Irache, J.M.; de Souza, J.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Gamazo, C. Nanoparticle-based vaccine for mucosal protection against Shigella flexneri in mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coeshott, C.M.; Smithson, S.L.; Verderber, E.; Samaniego, A.; Blonder, J.M.; Rosenthal, G.J.; Westerink, M.J. Pluronic® F127-based systemic vaccine delivery systems. Vaccine 2004, 22, 2396–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, Y.; Camacho, A.; Gil, A.G.; Ramos, R.; de Ceráin, A.L.; Peñuelas, I.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Effective protection of mice against Shigella flexneri with a new self-adjuvant multicomponent vaccine. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, Y.; Camacho, A.I.; Zúñiga-Ripa, A.; Merchán, A.; Rosas, P.; Irache, J.M.; Gamazo, C. Towards a subunit vaccine from a Shigella flexneri ΔtolR mutant. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7509–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Majithiya, R.; Singh, T.R.R.; Morrow, D.I.; Garland, M.J.; Demir, Y.K.; Migalska, K.; Ryan, E.; Gillen, D.; Scott, C.J.; et al. Design, Optimization and Characterisation of Polymeric Microneedle Arrays Prepared by a Novel Laser-Based Micromoulding Technique. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Stewart, S.; Fallows, S.J.; Birkhäuer, L.L.; McCrudden, M.T.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A facile system to evaluate in vitro drug release from dissolving microneedle arrays. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 497, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Moore, J.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; González-Vázquez, P.; Lutton, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A proposed model membrane and test method for microneedle insertion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, W. Comments on the suitability of swine skin as a biological model for human skin. Hautarzt 1996, 47, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.H. Technetium-99 m production issues in the United Kingdom. J. Med. Phys. 2012, 37, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscuolo, E.; Caputo, V.; Diotti, R.A.; Sautto, G.A.; Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Clementi, N. Alternative methods of vaccine delivery: An overview of edible and intradermal vaccines. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Sommerfeld, J.; Lassi, Z.S.; Salam, R.A.; Das, J.K. Global burden, distribution, and interventions for infectious diseases of poverty. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2014, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Function of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in antibody formation. Immunol. Investig. 2010, 39, 303–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Jang, Y.-S. The development of mucosal vaccines for both mucosal and systemic immune induction and the roles played by adjuvants. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Bowersock, T.; Weeratna, R.; Yeoh, T. Current opportunities and challenges in intradermal vaccination. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamazo, C.; Pastor, Y.; Larrañeta, E.; Berzosa, M.; Irache, J.M.; Donnelly, R.F. Understanding the basis of transcutaneous vaccine delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, J.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle patches for vaccination in developing countries. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irache, J.M.; Huici, M.; Konecny, M.; Espuelas, S.; Campanero, M.A. Bioadhesive Properties of Gantrez Nanoparticles. Molecules 2005, 10, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrudden, M.T.; Torrisi, B.M.; Al-Zahrani, S.; McCrudden, C.M.; Zaric, M.; Scott, C.J.; Kissenpfennig, A.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Laser-engineered dissolving microneedle arrays for protein delivery: Potential for enhanced intradermal vaccination. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Perez, E.M.; Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Hegarty, S.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Repeat application of microneedles does not alter skin appearance or barrier function and causes no measurable disturbance of serum biomarkers of infection, inflammation or immunity in mice in vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaric, M.; Lyubomska, O.; Touzelet, O.; Poux, C.; Al-Zahrani, S.; Fay, F.; Wallace, L.; Terhorst, D.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S.; et al. Skin Dendritic Cell Targeting via Microneedle Arrays Laden with Antigen-Encapsulated Poly-d,l-lactide-co-Glycolide Nanoparticles Induces Efficient Antitumor and Antiviral Immune Responses. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2042–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellge, G.; Magalhaes, J.G.; Konradt, C.; Fritz, J.H.; Salgado-Pabon, W.; Eberl, G.; Bandeira, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Phalipon, A. Th17 Cells Are the Dominant T Cell Subtype Primed by Shigella flexneri Mediating Protective Immunity. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, T.; Ura, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Yoshida, H. Intradermal Delivery of Antigens Enhances Specific IgG and Diminishes IgE Production: Potential Use for Vaccination and Allergy Immunotherapy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boullier, S.; Tanguy, M.; Kadaoui, K.A.; Caubet, C.; Sansonetti, P.; Corthésy, B.; Phalipon, A. Secretory IgA-Mediated Neutralization of Shigella flexneri Prevents Intestinal Tissue Destruction by Down-Regulating Inflammatory Circuits. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5879–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Vaccines against mucosal infections. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, M.A.; Maciel, M.; Pasetti, M.F. Human immune responses against Shigella and enterotoxigenic E. coli: Current advances and the path forward. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6803–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyakov, I.M.; Hammond, S.A.; Ahlers, J.D.; Glenn, G.M.; Berzofsky, J.A. Transcutaneous immunization induces mucosal CTLs and protective immunity by migration of primed skin dendritic cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polymers | MW (g/mol) | Solvent | Final Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gantrez® AN119 | 216,000 | Water | 30% |
| Gantrez® AN139 | 1,080,000 | Water | 20% |
| Gantrez® S97 | 1,500,000 | Water | 30% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pastor, Y.; Larrañeta, E.; Erhard, Á.; Quincoces, G.; Peñuelas, I.; Irache, J.M.; Donnelly, R.; Gamazo, C. Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Vaccination against Shigellosis. Vaccines 2019, 7, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040159
Pastor Y, Larrañeta E, Erhard Á, Quincoces G, Peñuelas I, Irache JM, Donnelly R, Gamazo C. Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Vaccination against Shigellosis. Vaccines. 2019; 7(4):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040159
Chicago/Turabian StylePastor, Yadira, Eneko Larrañeta, Álvaro Erhard, Gemma Quincoces, Iván Peñuelas, Juan M. Irache, Ryan Donnelly, and Carlos Gamazo. 2019. "Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Vaccination against Shigellosis" Vaccines 7, no. 4: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040159
APA StylePastor, Y., Larrañeta, E., Erhard, Á., Quincoces, G., Peñuelas, I., Irache, J. M., Donnelly, R., & Gamazo, C. (2019). Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Vaccination against Shigellosis. Vaccines, 7(4), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040159








