The Immunomodulatory Effect of IrSPI, a Tick Salivary Gland Serine Protease Inhibitor Involved in Ixodes ricinus Tick Feeding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Ticks
2.3. Cloning and Sequencing of IrSPI cDNA
2.4. Recombinant IrSPI Protein Production
2.5. IrSPI Refolding
2.6. Circular Dichroism
2.7. Analytical Ultracentrifugation (AUC)—Sedimentation Velocity Experiment
2.8. MALDI-TOF/TOF Analysis
2.9. Serine Protease Inhibition Assays
2.10. Ticks Infected with Tick-Borne Pathogens
2.10.1. Tick Infection with Escherichia coli
2.10.2. Tick Saliva and Tick Organ Collection
2.10.3. Total RNA Extraction
2.10.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.10.5. In Situ Hybridization
2.10.6. Anti-IrSPI Serum Production
2.10.7. Western Blot Analysis
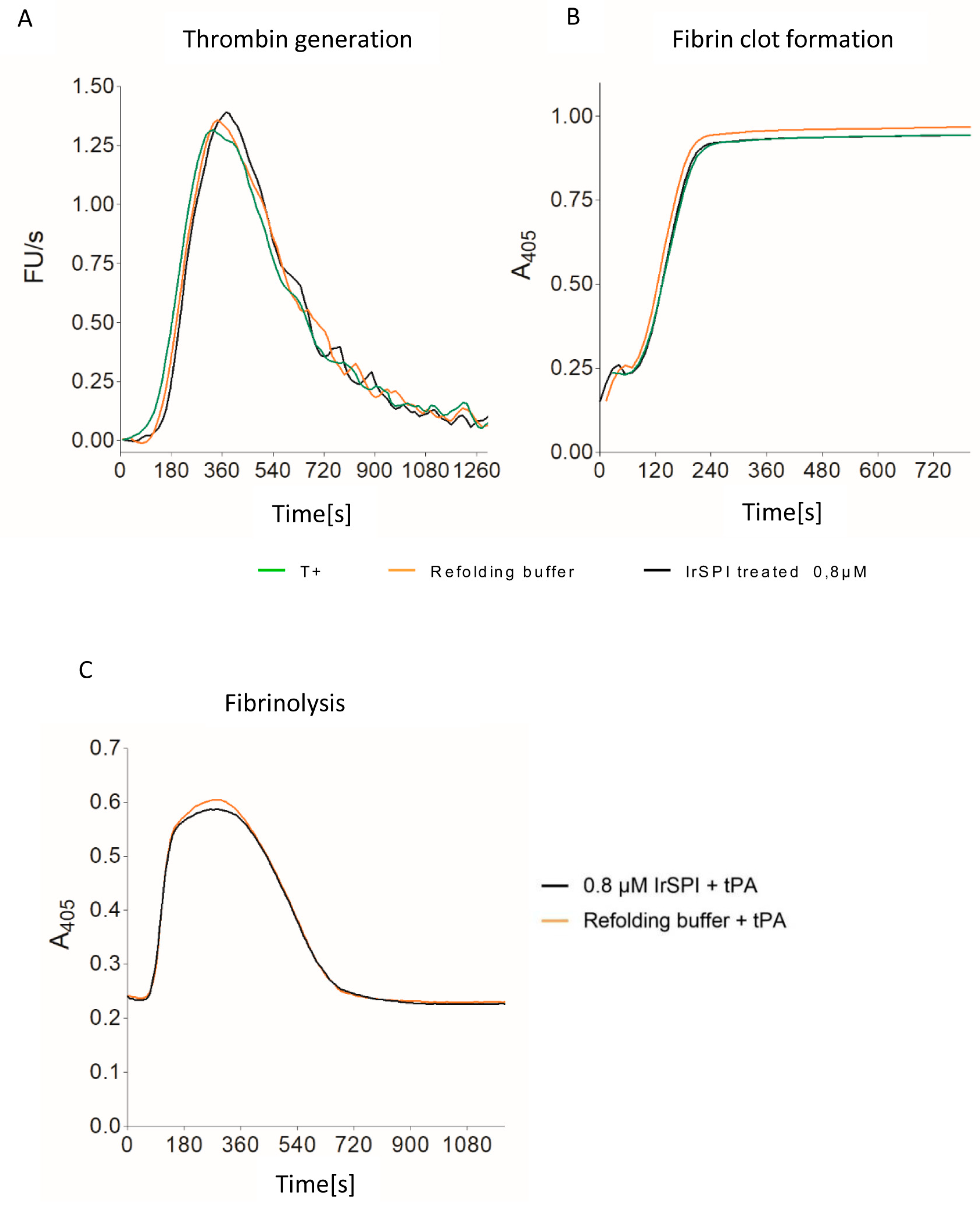
2.10.8. Thrombin Generation, Clot Waveform, and Fibrinolysis Assays
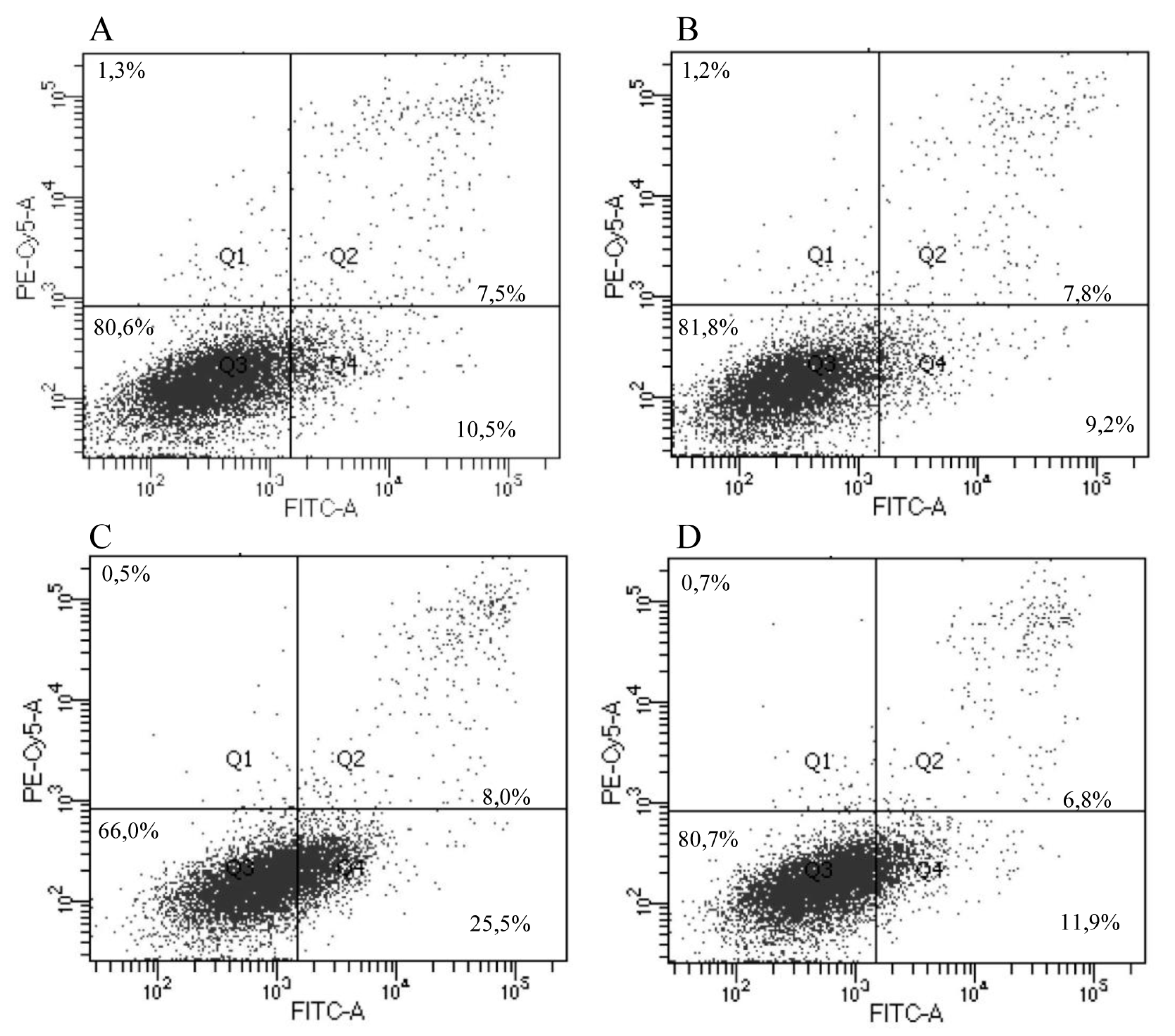
2.10.9. IrSPI Impact on Endothelial Cell Apoptosis
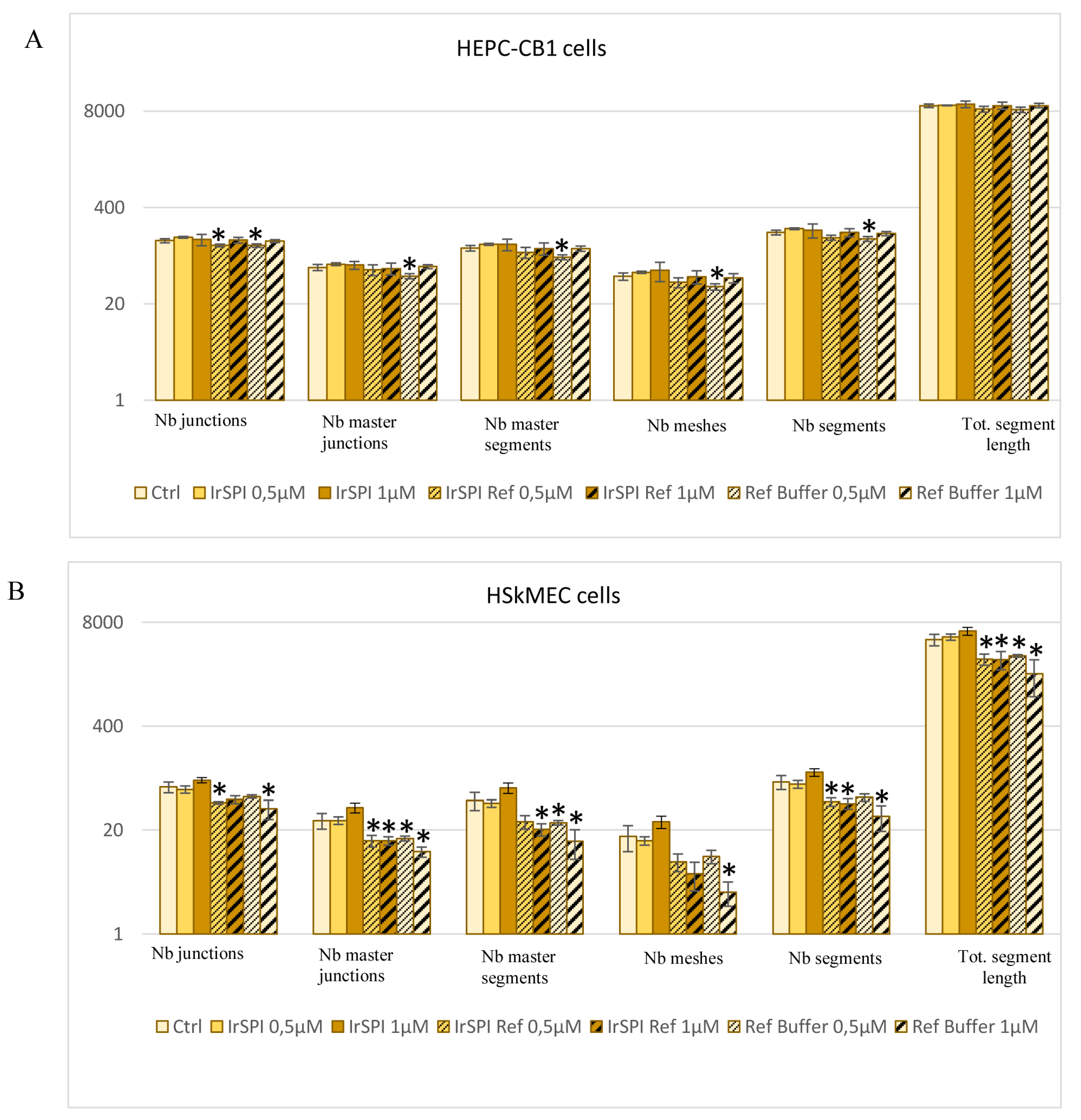
2.10.10. IrSPI Impact on Host Angiogenesis
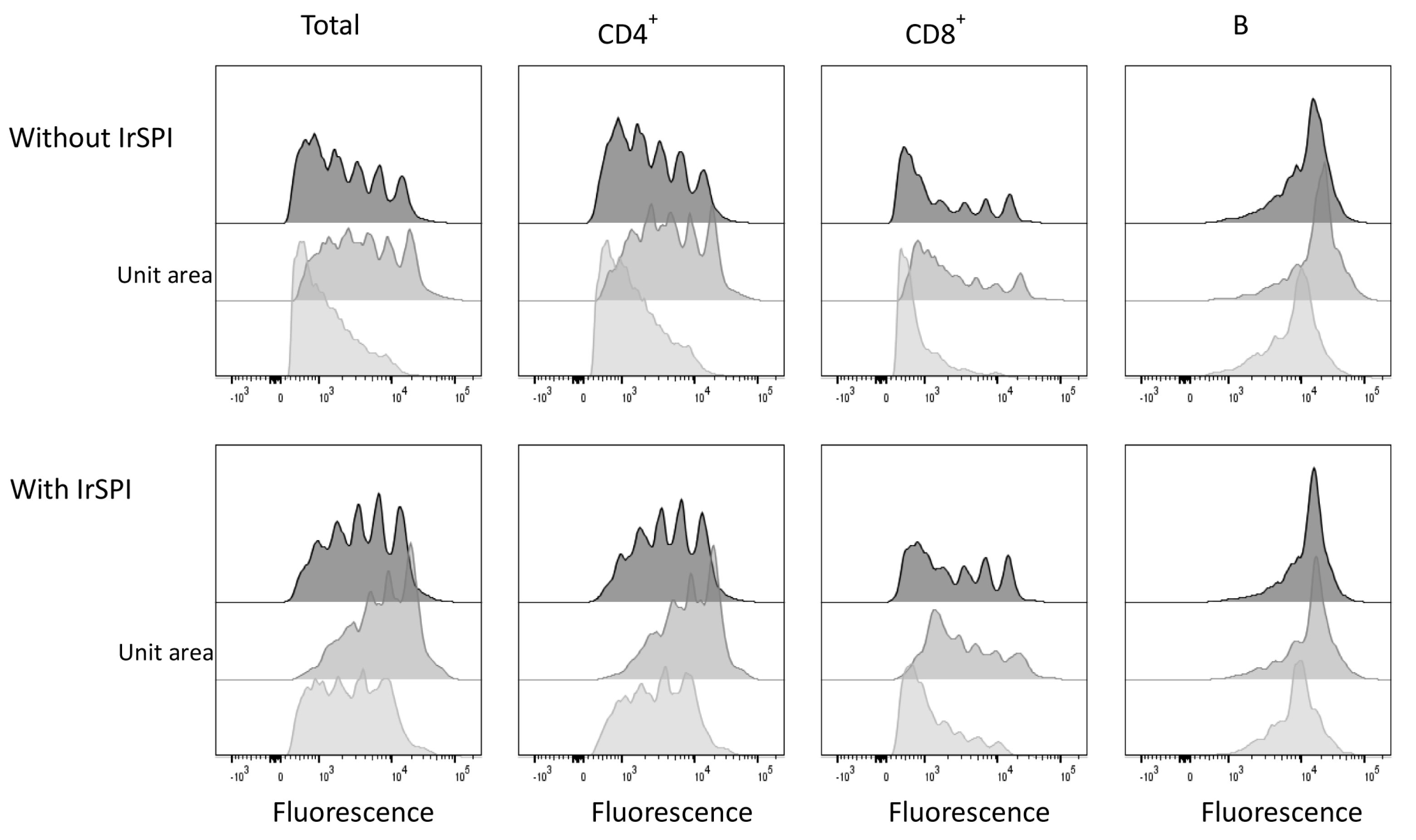
2.10.11. Splenocyte Proliferation Assay
2.10.12. Macrophage Stimulation Assay
2.10.13. Cytokine Profile Analysis
2.10.14. Statistical Analysis
2.10.15. Software
3. Results
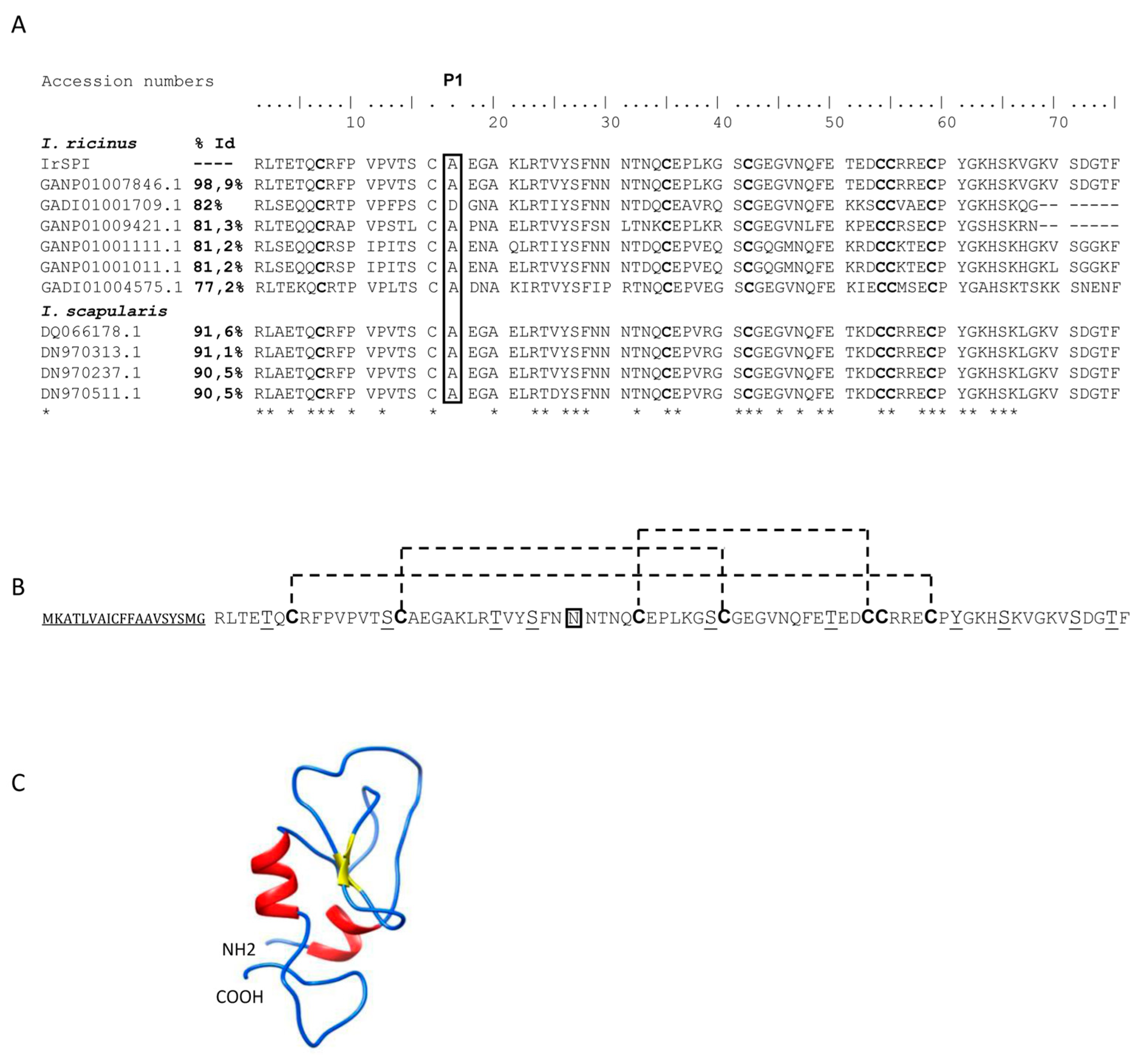
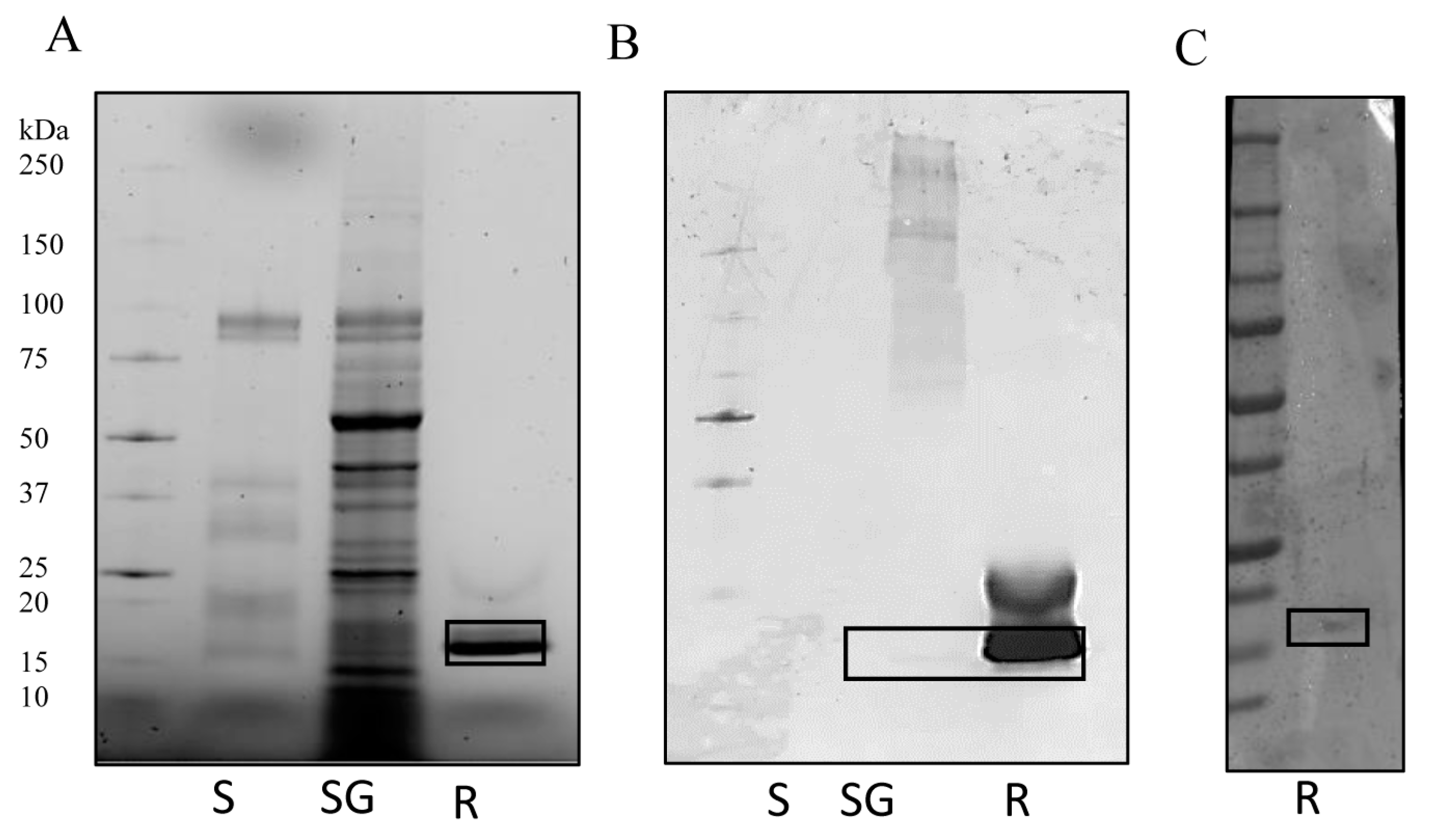
3.1. IrSPI Molecular Characterization
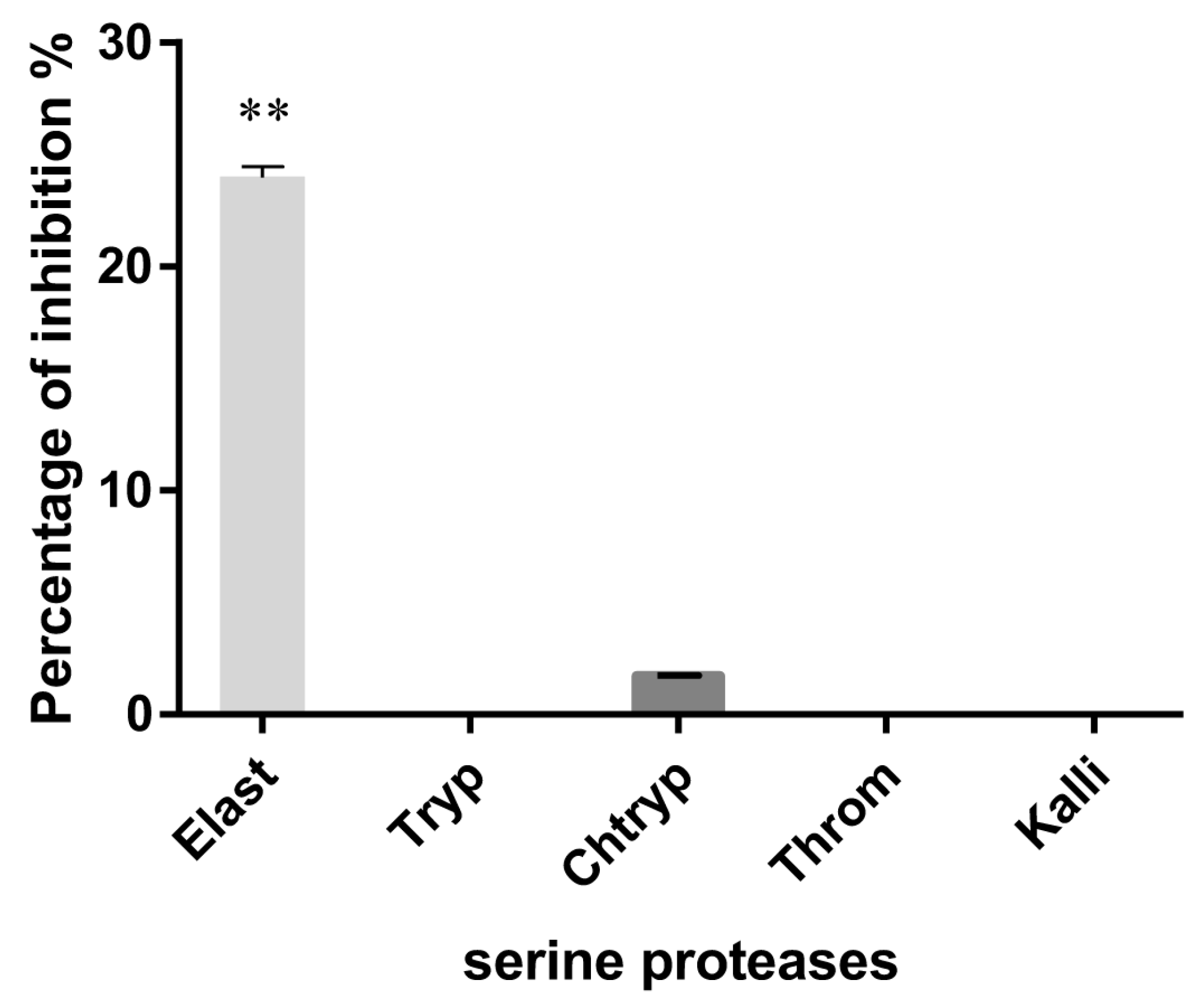
3.2. Serine Protease Inhibition
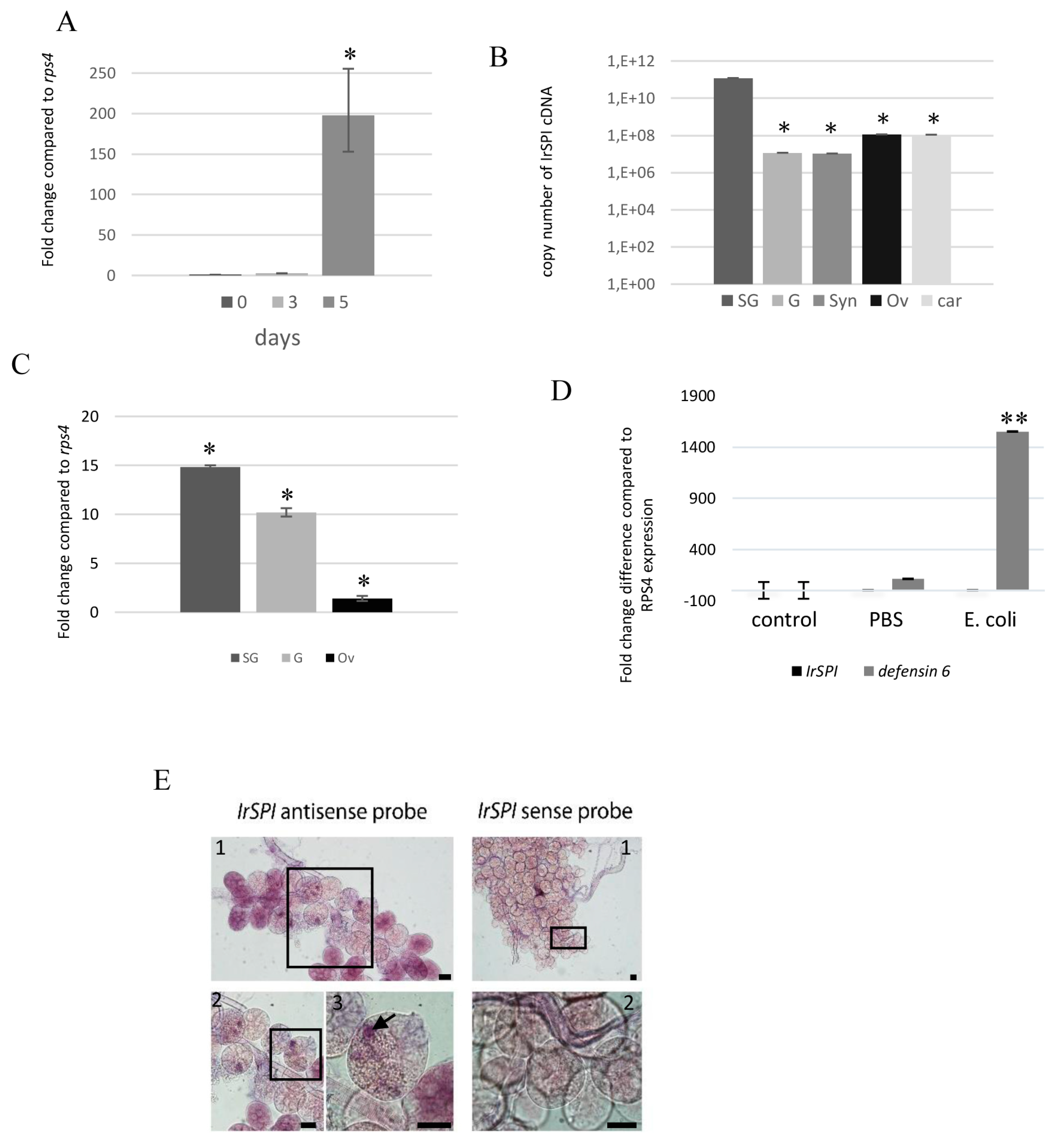
3.3. IrSPI Expression and Localisation
3.4. Anticoagulant Activity
3.5. Apoptosis and Angiogenesis
3.6. Splenocyte Proliferation Assay
3.7. Cytokine Expression in Response to IrSPI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoli, A.; Silaghi, C.; Obiegala, A.; Rudolf, I.; Hubalek, Z.; Foldvari, G.; Plantard, O.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.; Spitalska, E.; et al. Ixodes ricinus and its transmitted pathogens in urban and peri-urban areas in Europe: New hazards and relevance for public health. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simo, L.; Kazimirova, M.; Richardson, J.; Bonnet, S.I. The essential role of tick salivary glands and saliva in tick feeding and pathogen transmission. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Antunes, S.; Bonnet, S.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Domingos, A.G.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Johnson, N.; Kocan, K.M.; Mansfield, K.L.; Nijhof, A.M.; et al. Tick-pathogen interactions and vector competence: Identification of molecular drivers for tick-borne diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; de la Fuente, J.; Cote, M.; Galindo, R.C.; Moutailler, S.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.I. IrSPI, a tick serine protease inhibitor involved in tick feeding and Bartonella henselae infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotte, V.; Bonnet, S.; Le Rhun, D.; Le Naour, E.; Chauvin, A.; Boulouis, H.J.; Lecuelle, B.; Lilin, T.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Transmission of Bartonella henselae by Ixodes ricinus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blisnick, A.A.; Foulon, T.; Bonnet, S.I. Serine protease inhibitors in ticks: An overview of their role in tick biology and tick-borne pathogen transmission. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.E.; Cote, M.; Le Naour, E.; Bonnet, S.I. Environmental factors influencing tick densities over seven years in a French suburban forest. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.; Jouglin, M.; Malandrin, L.; Becker, C.; Agoulon, A.; L’Hostis, M.; Chauvin, A. Transstadial and transovarial persistence of Babesia divergens DNA in Ixodes ricinus ticks fed on infected blood in a new skin-feeding technique. Parasitology 2007, 134, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Kernya, L.; Lee, Y.H.; Goto, Y.; Refregiers, M.; Kardos, J. Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3095–E3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck, P. Size-distribution analysis of macromolecules by sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation and lamm equation modeling. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 1606–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.; Cote, M.; Le Rhun, D.; Lecuelle, B.; Levin, M.L.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.I. Vector competence of the tick Ixodes ricinus for transmission of Bartonella birtlesii. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugarel, M.; Beutin, L.; Scheutz, F.; Loukiadis, E.; Fach, P. Identification of genetic markers for differentiation of Shiga toxin-producing, enteropathogenic, and avirulent strains of Escherichia coli O26. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazan, C.; Bonnet, S.; Cote, M.; Slovak, M.; Park, Y.; Simo, L. A versatile model of hard tick infestation on laboratory rabbits. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 140, e57994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, T.G.; Dietrich, G.; Brandt, K.; Dolan, M.C.; Piesman, J.; Gilmore, R.D., Jr. Saliva, salivary gland, and hemolymph collection from Ixodes scapularis ticks. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 60, e3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonk, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Valdes, J.J.; Rego, R.O.; Grubhoffer, L.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Rahnamaeian, M. Ixodes ricinus defensins attack distantly-related pathogens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koci, J.; Simo, L.; Park, Y. Validation of internal reference genes for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction studies in the tick, Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, L.; Slovak, M.; Park, Y.; Zitnan, D. Identification of a complex peptidergic neuroendocrine network in the hard tick, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 335, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdi, G.; Siguret, V.; Martin, A.C.; Golmard, J.L.; Godier, A.; Samama, C.M.; Gaussem, P.; Gouin-Thibault, I.; Le Bonniec, B. Association rate constants rationalise the pharmacodynamics of apixaban and rivaroxaban. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdi, G.; Gouin-Thibault, I.; Siguret, V.; Gandrille, S.; Gaussem, P.; Le Bonniec, B. FXa-α2-macroglobulin complex neutralizes direct oral anticoagulants targeting FXa in vitro and in vivo. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreau, A.; Kieda, C.; Grillon, C. Nitric oxide modulates the expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules involved in angiogenesis and leukocyte recruitment. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paprocka, M.; Krawczenko, A.; Dus, D.; Kantor, A.; Carreau, A.; Grillon, C.; Kieda, C. CD133 positive progenitor endothelial cell lines from human cord blood. Cytometry A 2011, 79, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, G. Angiogenesis Analyser Tool for Image J. 2012. Available online: http://image.bio.methods.free.fr/ImageJ/?Angiogenesis-Analyzer-for-ImageJ (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y.; Li, L. Divergent folding pathways of two homologous proteins, BPTI and tick anticoagulant peptide: Compartmentalization of folding intermediates and identification of kinetic traps. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 437, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, Y. Cloning and characterization of a novel Kunitz-type inhibitor from scorpion with unique cysteine framework. Toxicon 2013, 72, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simo, L.; Zitnan, D.; Park, Y. Neural control of salivary glands in ixodid ticks. J. Insect. Physiol. 2012, 58, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotal, J.; Langhansova, H.; Lieskovska, J.; Andersen, J.F.; Francischetti, I.M.; Chavakis, T.; Kopecky, J.; Pedra, J.H.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Chmelar, J. Modulation of host immunity by tick saliva. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischetti, I.M.; Mather, T.N.; Ribeiro, J.M. Tick saliva is a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mans, B.J.; Louw, A.I.; Neitz, A.W. Evolution of hematophagy in ticks: Common origins for blood coagulation and platelet aggregation inhibitors from soft ticks of the genus Ornithodoros. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon-Chaidez, F.J.; Muller-Doblies, U.U.; Wikel, S. Characterization of a recombinant immunomodulatory protein from the salivary glands of Dermacentor andersoni. Parasite Immunol. 2003, 25, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnai, S.; Nishikado, H.; Yamada, S.; Imamura, S.; Ito, T.; Onuma, M.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Molecular identification and expression analysis of lipocalins from blood feeding taiga tick, Ixodes persulcatus Schulze. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Fernandez, R.; Perbandt, M.; Rehders, D.; Ziegelmuller, P.; Piganeau, N.; Hahn, U.; Betzel, C.; Chavez Mde, L.; Redecke, L. Three-dimensional structure of a Kunitz-type inhibitor in complex with an elastase-like enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14154–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, H.; Zhou, J. Characterization of a new Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor from the hard tick Rhipicephalus hemaphysaloides. Arch. Insect. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 84, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, T.S.; Oliveira, F.; Torquato, R.J.; Sasaki, S.D.; Araujo, M.S.; Paschoalin, T.; Tanaka, A.S. BmTI-A, a Kunitz type inhibitor from Rhipicephalus microplus able to interfere in vessel formation. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 219, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilgus, T.A.; Roy, S.; McDaniel, J.C. Neutrophils and wound repair: Positive actions and negative reactions. Adv. Wound Care 2013, 2, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.; Mital, K. The role of trypsin:Chymotrypsin in tissue repair. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, J.J.; Schwarz, A.; de Vaca, I.C.; Calvo, E.; Pedra, J.H.; Guallar, V.; Kotsyfakis, M. Tryptogalinin is a tick Kunitz serine protease inhibitor with a unique intrinsic disorder. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Bonnet, S.I. Hard tick factors implicated in pathogen transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Schwarz, A.; Erhart, J.; Ribeiro, J.M. Tissue-and time-dependent transcription in Ixodes ricinus salivary glands and midguts when blood feeding on the vertebrate host. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelar, J.; Anderson, J.M.; Mu, J.; Jochim, R.C.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Kopecky, J. Insight into the sialome of the castor bean tick, Ixodes ricinus. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.X.; Zhang, A.D.; Huang, J.F. Evolution, expansion and expression of the Kunitz/BPTI gene family associated with long-term blood feeding in Ixodes scapularis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.K.; Tsuji, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Alim, M.A.; Huang, X.; Hatta, T.; Fujisaki, K. The Kunitz-like modulatory protein haemangin is vital for hard tick blood-feeding success. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.A.; Torquato, R.J.; Sasaki, S.D.; Justo, G.Z.; Tanaka, A.S. Biochemical characterization of a Kunitz type inhibitor similar to dendrotoxins produced by Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) hemocytes. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewes, C.C.; Dias, R.Y.; Hebeda, C.B.; Simons, S.M.; Barreto, S.A.; Ferreira, J.M., Jr.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M.; Farsky, S.H. Actions of the Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor Amblyomin-X on VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis. Toxicon 2012, 60, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davie, E.W.; Fujikawa, K.; Kurachi, K.; Kisiel, W. The role of serine proteases in the blood coagulation cascade. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1979, 48, 277–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mejri, N.; Franscini, N.; Rutti, B.; Brossard, M. Th2 polarization of the immune response of BALB/c mice to Ixodes ricinus instars, importance of several antigens in activation of specific Th2 subpopulations. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandra, R.N.; Wikel, S.K. Modulation of host-immune responses by ticks (Acari: Ixodidae): Effect of salivary gland extracts on host macrophages and lymphocyte cytokine production. J. Med. Entomol. 1992, 29, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Fernandez, B.; Vercoutere, A.; Chamayou, L.; Andersen, A.; Vigy, O.; Demettre, E.; Seveno, M.; Aprelon, R.; Giraud-Girard, K.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Amblyomma variegatum saliva on bovine cells: Characterization of cellular responses and identification of molecular determinants. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urioste, S.; Hall, L.R.; Telford, S.R., 3rd; Titus, R.G. Saliva of the Lyme disease vector, Ixodes dammini, blocks cell activation by a nonprostaglandin E2-dependent mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Sehra, S.; Goswami, R.; Yao, W.; Yu, Q.; Stritesky, G.L.; Jabeen, R.; McKinley, C.; Ahyi, A.N.; Han, L.; et al. The transcription factor PU.1 is required for the development of IL-9-producing T cells and allergic inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguita, J.; Ramamoorthi, N.; Hovius, J.W.; Das, S.; Thomas, V.; Persinski, R.; Conze, D.; Askenase, P.W.; Rincon, M.; Kantor, F.S.; et al. Salp15, an ixodes scapularis salivary protein, inhibits CD4+ T cell activation. Immunity 2002, 16, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboulle, G.; Crippa, M.; Decrem, Y.; Mejri, N.; Brossard, M.; Bollen, A.; Godfroid, E. Characterization of a novel salivary immunosuppressive protein from Ixodes ricinus ticks. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10083–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skallova, A.; Iezzi, G.; Ampenberger, F.; Kopf, M.; Kopecky, J. Tick saliva inhibits dendritic cell migration, maturation, and function while promoting development of Th2 responses. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6186–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, D.D.; Turcovski-Corrales, S.M.; Key, M.L.; Longo, D.L.; Murphy, W.J. Chemokines and T lymphocyte activation: I. Beta chemokines costimulate human T lymphocyte activation in vitro. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elyaman, W.; Bradshaw, E.M.; Uyttenhove, C.; Dardalhon, V.; Awasthi, A.; Imitola, J.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; van Snick, J.; Renauld, J.C.; et al. IL-9 induces differentiation of TH17 cells and enhances function of FoxP3+ natural regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malefyt, R.D.W.; Abrams, J.S.; Zurawski, S.M.; Lecron, J.C.; Mohan-Peterson, S.; Sanjanwala, B.; Bennett, B.; Silver, J.; de Vries, J.E.; Yssel, H. Differential regulation of IL-13 and IL-4 production by human CD8+ and CD4+ Th0, Th1 and Th2 T cell clones and EBV-transformed B cells. Int. Immunol. 1995, 7, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, L.; Kopecky, J.; Rihova, B. Salivary gland extract from Ixodes ricinus tick modulates the host immune response towards the Th2 cytokine profile. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Thelen, M.; Stein, J.V. How chemokines invite leukocytes to dance. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, J.; Kuthejlova, M.; Pechova, J. Salivary gland extract from Ixodes ricinus ticks inhibits production of interferon-γ by the upregulation of interleukin-10. Parasite Immunol. 1999, 21, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horka, H.; Staudt, V.; Klein, M.; Taube, C.; Reuter, S.; Dehzad, N.; Andersen, J.F.; Kopecky, J.; Schild, H.; Kotsyfakis, M.; et al. The tick salivary protein sialostatin L inhibits the Th9-derived production of the asthma-promoting cytokine IL-9 and is effective in the prevention of experimental asthma. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2669–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, S.G.; Majtan, J.; Kouremenou, C.; Rysnik, O.; Burger, L.F.; Cruz, A.C.; Guzman, M.C.; Nunn, M.A.; Paesen, G.C.; Nuttall, P.A.; et al. Novel immunomodulators from hard ticks selectively reprogramme human dendritic cell responses. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salat, J.; Paesen, G.C.; Rezacova, P.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Kovarova, Z.; Sanda, M.; Majtan, J.; Grunclova, L.; Horka, H.; Andersen, J.F.; et al. Crystal structure and functional characterization of an immunomodulatory salivary cystatin from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coeshott, C.; Ohnemus, C.; Pilyavskaya, A.; Ross, S.; Wieczorek, M.; Kroona, H.; Leimer, A.H.; Cheronis, J. Converting enzyme-independent release of tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-1β from a stimulated human monocytic cell line in the presence of activated neutrophils or purified proteinase 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6261–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, K.; Mika, J. The importance of chemokines in neuropathic pain development and opioid analgesic potency. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffee, N.; Hlawaty, H.; Meddahi-Pelle, A.; Maillard, L.; Louedec, L.; Haddad, O.; Martin, L.; Laguillier, C.; Richard, B.; Oudar, O.; et al. RANTES/CCL5-induced pro-angiogenic effects depend on CCR1, CCR5 and glycosaminoglycans. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Aoki, C.; Yoshio-Hoshino, N.; Takayama, K.; Curiel, D.T.; Nishimoto, N. Interleukin-6 induces both cell growth and VEGF production in malignant mesotheliomas. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, K.S.; Trickler, W.J.; Miller, D.W. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin release in brain microvessel endothelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Salcedo, R.; Young, H.A.; Ponce, M.L.; Ward, J.M.; Kleinman, H.K.; Murphy, W.J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Eotaxin (CCL11) induces in vivo angiogenic responses by human CCR3+ endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7571–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, B.; van Snick, J.; Brombacher, F. IL-9 is a susceptibility factor in Leishmania major infection by promoting detrimental Th2/type 2 responses. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, L.; Dooms, H.; Hoyer, K.K.; Kuswanto, W.; Hofmann, J.; O’Gorman, W.E.; Abbas, A.K. Cutting edge: Mechanisms of IL-2-dependent maintenance of functional regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6426–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinen, T.; Kannan, A.K.; Levine, A.G.; Fan, X.; Klein, U.; Zheng, Y.; Gasteiger, G.; Feng, Y.; Fontenot, J.D.; Rudensky, A.Y. An essential role for the IL-2 receptor in Treg cell function. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brake, D.K.; de Leon, A.A.P. Immunoregulation of bovine macrophages by factors in the salivary glands of Rhipicephalus microplus. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsu, K. Interleukin-5 and IL-5 receptor in health and diseases. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2011, 87, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, P.A.; Trimnell, A.R.; Kazimirova, M.; Labuda, M. Exposed and concealed antigens as vaccine targets for controlling ticks and tick-borne diseases. Parasite Immunol. 2006, 28, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.K.; Tirloni, L.; Pinto, A.F.; Moresco, J.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Mulenga, A. Ixodes scapularis tick saliva proteins sequentially secreted every 24 h during blood feeding. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Conditions | Cytokine/Chemokine | Effect of IrSPI (Percentage) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Splenocytes | |||
| Without ConA | IP10 | −32.8% | 2.21 × 10−3 |
| MCP3 | −72.3% | 8.07 × 10−4 | |
| MIP-1β | −26.0% | 2.11 × 10−3 | |
| RANTES | −15.6% | 3.94 × 10−3 | |
| With ConA | IL-1β | −45.0% | 1.15 × 10−3 |
| IL-13 | −75.1% | 4.47 × 10−4 | |
| IL-18 | −46.0% | 1.63 × 10−7 | |
| IL-6 | −54.8% | 5.80 × 10−6 | |
| IL-9 | −48.8% | 7.06 × 10−3 | |
| TNF-α | −46.1% | 7.23 × 10−6 | |
| IFN-γ | −50.3% | 2.28 × 10−7 | |
| IP10 | −46.5% | 4.30 × 10−5 | |
| MIP-1β | −17.6% | 2.28 × 10−3 | |
| RANTES | −37.9% | 1.26 × 10−4 | |
| Eotaxin | −21.3% | 3.89 × 10−3 | |
| GM-CSF | −71.9% | 8.67 × 10−8 | |
| IL-2 | + 49.2% | 5.62 × 10−4 | |
| Macrophages | |||
| With LPS/IFN-γ | IL-5 | −9.6% | 8.37 × 10−3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blisnick, A.A.; Šimo, L.; Grillon, C.; Fasani, F.; Brûlé, S.; Le Bonniec, B.; Prina, E.; Marsot, M.; Relmy, A.; Blaise-Boisseau, S.; et al. The Immunomodulatory Effect of IrSPI, a Tick Salivary Gland Serine Protease Inhibitor Involved in Ixodes ricinus Tick Feeding. Vaccines 2019, 7, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040148
Blisnick AA, Šimo L, Grillon C, Fasani F, Brûlé S, Le Bonniec B, Prina E, Marsot M, Relmy A, Blaise-Boisseau S, et al. The Immunomodulatory Effect of IrSPI, a Tick Salivary Gland Serine Protease Inhibitor Involved in Ixodes ricinus Tick Feeding. Vaccines. 2019; 7(4):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040148
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlisnick, Adrien A., Ladislav Šimo, Catherine Grillon, Fabienne Fasani, Sébastien Brûlé, Bernard Le Bonniec, Eric Prina, Maud Marsot, Anthony Relmy, Sandra Blaise-Boisseau, and et al. 2019. "The Immunomodulatory Effect of IrSPI, a Tick Salivary Gland Serine Protease Inhibitor Involved in Ixodes ricinus Tick Feeding" Vaccines 7, no. 4: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040148
APA StyleBlisnick, A. A., Šimo, L., Grillon, C., Fasani, F., Brûlé, S., Le Bonniec, B., Prina, E., Marsot, M., Relmy, A., Blaise-Boisseau, S., Richardson, J., & Bonnet, S. I. (2019). The Immunomodulatory Effect of IrSPI, a Tick Salivary Gland Serine Protease Inhibitor Involved in Ixodes ricinus Tick Feeding. Vaccines, 7(4), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040148






