In Vivo Administration of Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Increases the Immune Effectiveness of Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Vaccination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Manufacture of a DC Vaccine and Vaccination
2.3. Surface Marker Analysis of the Obtained mDCs
2.4. Immune Monitoring with Tetramer Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
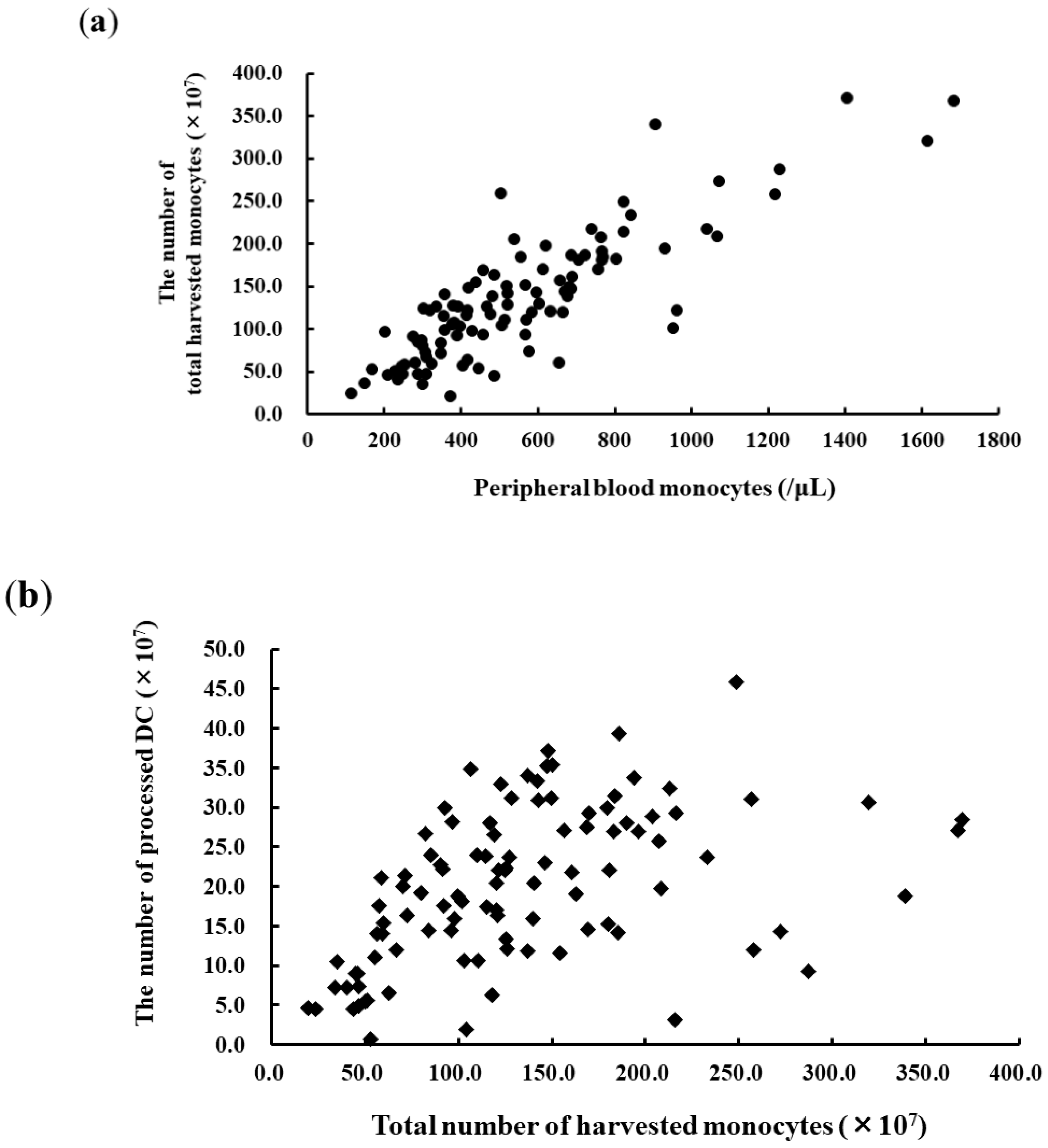
3.1. Apheresis for DC Vaccination and DC Products
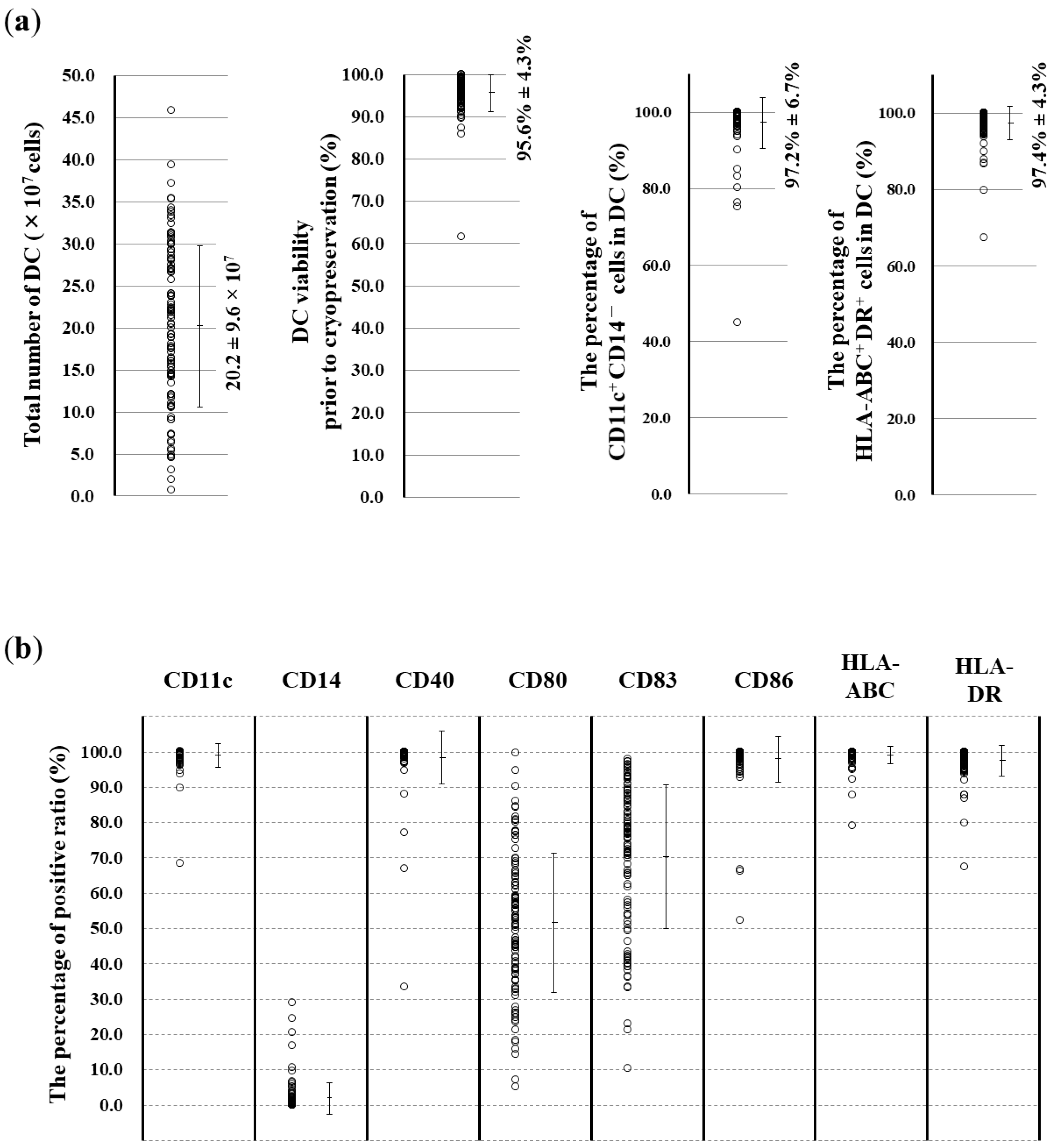
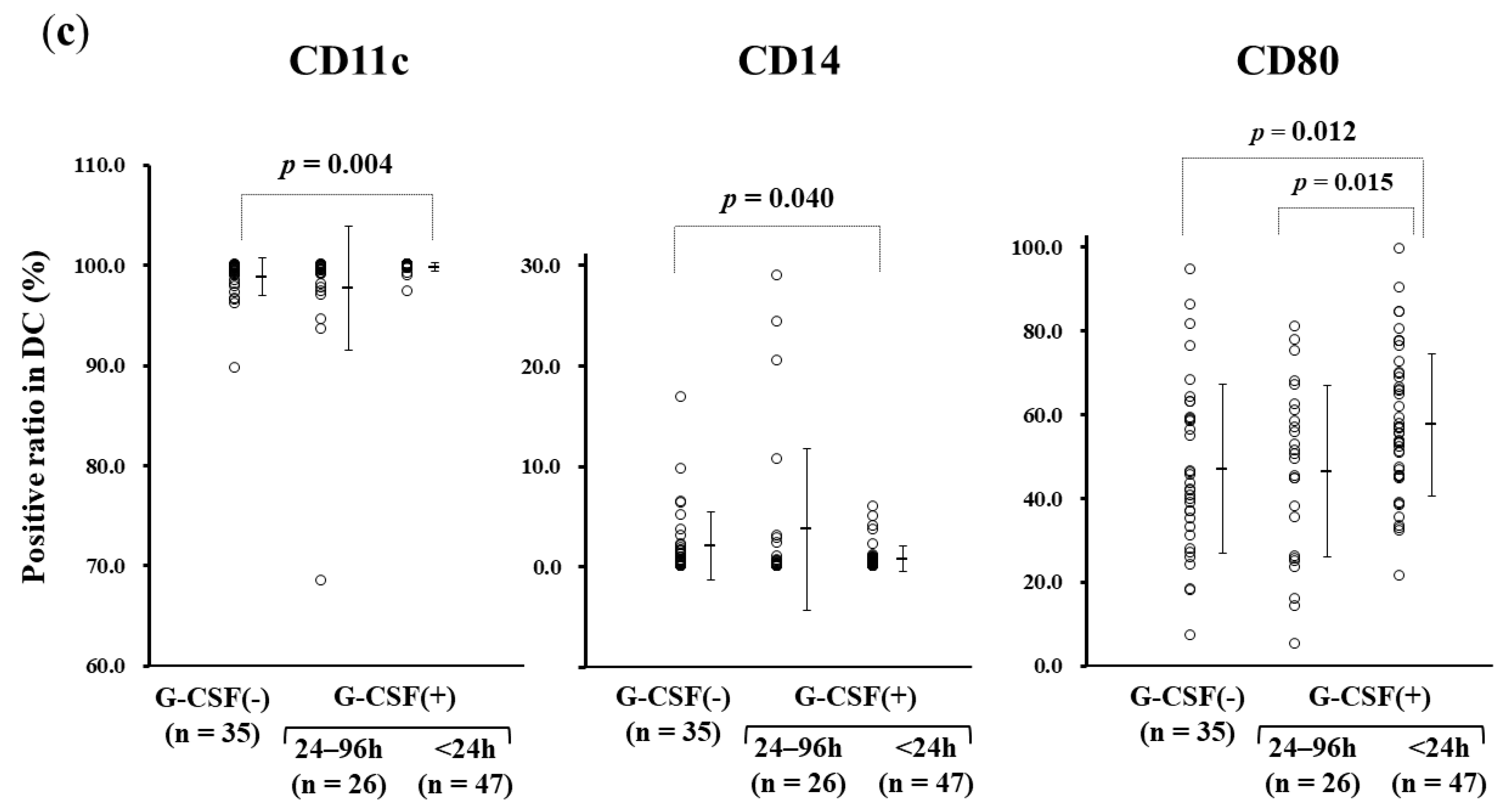
3.2. Surface Marker Analysis of the Obtained DCs
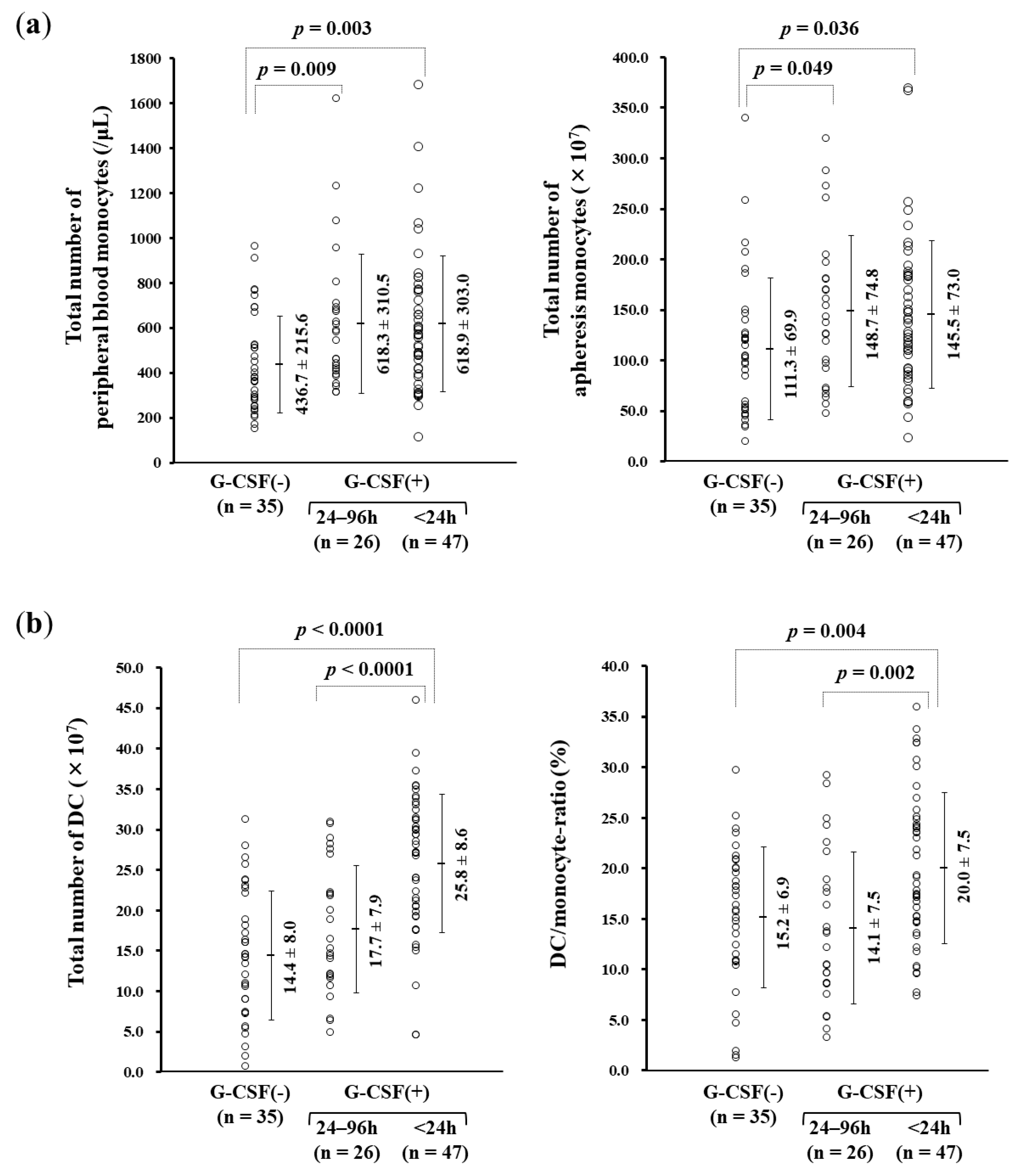
3.3. rhG-CSF Administration Influencing Monocyte-derived DC Manufacture
3.4. The Acquisition of WT1-specific CTLs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.W.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.; Hwu, W.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Kluger, H.; Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Segal, N.H.; Ariyan, C.E.; Gordon, R.A.; Reed, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.S.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Yu, B.; Gallenstein, D.; Horak, C.E.; Inzunza, H.D.; Zhao, X.; Martinez, A.J.; Wang, W.; Gibney, G.; et al. Safety, efficacy, and biomarkers of nivolumab with vaccine in ipilimumab-refractory or -naive melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4311–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M. Decisions about dendritic cells: Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteven, M.; Van den Bergh, J.M.J.; Marcq, E.; Smits, E.L.J.; Van Tendeloo, V.F.I.; Hobo, W.; Lion, E. Dendritic cells and programmed death-1 blockade: A joint venture to combat cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.W.; Adams, S.; Bhardwaj, N. Manipulating dendritic cell biology for the active immunotherapy of cancer. Blood 2004, 104, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestle, F.O.; Farkas, A.; Conrad, C. Dendritic-cell-based therapeutic vaccination against cancer. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantoff, P.W.; Higano, C.S.; Shore, N.D.; Berger, E.R.; Small, E.J.; Penson, D.F.; Redfern, C.H.; Ferrari, A.C.; Dreicer, R.; Sims, R.B.; et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, S.; Sano, K.; Hirabayashi, K.; Koya, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Mizuno, Y.; Yamaoka, N.; Yuzawa, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Ito, K.; et al. Dendritic cell-based adjuvant vaccination targeting Wilms’ tumor 1 in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Vaccines 2015, 3, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Shimodaira, S.; Nagai, K.; Ogasawara, M.; Takahashi, H.; Abe, H.; Tanii, M.; Okamoto, M.; Tsujitani, S.; Yusa, S.; et al. Prognostic factors related to add-on dendritic cell vaccines on patients with inoperable pancreatic cancer receiving chemotherapy: A multicenter analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koido, S.; Homma, S.; Okamoto, M.; Takakura, K.; Mori, M.; Yoshizaki, S.; Tsukinaga, S.; Odahara, S.; Koyama, S.; Imazu, H.; et al. Treatment with chemotherapy and dendritic cells pulsed with multiple Wilms’ tumor 1 (WT1)-specific MHC class I/II-restricted epitopes for pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4228–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Shimodaira, S.; Ogasawara, M.; Ota, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Abe, H.; Morita, Y.; Nagai, K.; Tsujitani, S.; Okamoto, M.; et al. Lung adenocarcinoma may be a more susceptive subtype to a dendritic cell-based cancer vaccine than other subtypes of non-small cell lung cancers: A multicenter retrospective analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Shimodaira, S.; Maejima, S.; Udagawa, N.; Sano, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Ochiai, T.; Koide, M.; Uehara, S.; et al. Dendritic cell-based immunotherapy targeting Wilms’ Tumor 1 (WT1) in patients with relapsed malignant glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Yanagisawa, R.; Yoshikawa, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Yoshizawa, K.; Tanaka, M.; Sakashita, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kurata, T.; et al. Safety and tolerability of allogeneic dendritic cell vaccination with induction of WT1-specific T cells in a pediatric donor and pediatric patient with relapsed leukemia: A case report and review of the literature. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, S.; Hirabayashi, K.; Yanagisawa, R.; Higuchi, Y.; Sano, K.; Koizumi, T. Dendritic cell-based cancer immunotherapy targeting Wilms’ Tumor 1 for pediatric cancer. In Wilms Tumor; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M., Ed.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2016; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hoos, A. Evolution of end points for cancer immunotherapy trials. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 8, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figdor, C.G.; de Vries, I.J.; Lesterhuis, W.J.; Melief, C.J. Dendritic cell immunotherapy: Mapping the way. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yanagisawa, R.; Hirabayashi, K.; Ito, K.; Koizumi, T.; Maejima, S.; Udagawa, N. Smoking influences the yield of dendritic cells for cancer immunotherapy. Pharm. Regul. Aff. 2015, 4, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Anderlini, P.; Champlin, R.E. Biologic and molecular effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in healthy individuals: Recent findings and current challenges. Blood 2008, 111, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aapro, M.S.; Bohlius, J.; Cameron, D.A.; Dal Lago, L.; Donnelly, J.P.; Kearney, N.; Lyman, G.H.; Pettengell, R.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.; Walewski, J.; et al. 2010 update of EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, R.C.; Mansi, J.L.; Keerie, C.; Yellowlees, A.; Crawford, S.; Benstead, K.; Matthew, R.; Adamson, D.; Chan, S.; Grieve, R.; et al. A randomised trial of secondary prophylaxis using granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (‘SPROG’ trial) for maintaining dose intensity of standard adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer by the Anglo-Celtic Cooperative Group and NCRN. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.; Becker, P.S.; Armitage, J.O.; Blayney, D.W.; Chavez, J.; Curtin, P.; Dinner, S.; Fynan, T.; Gojo, I.; Griffiths, E.A.; et al. Myeloid Growth Factors, Version 2.2017, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2017, 15, 1520–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, S.; Hirabayashi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Yokokawa, K. Future prospective of cancer vaccination technology in Japan. Pharm. Regul. Aff. 2015, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Elisseeva, O.A.; Tsuboi, A.; Ogawa, H.; Tamaki, H.; Li, H.; Oji, Y.; Kim, E.H.; Soma, T.; Asada, M.; et al. Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses specific for peptides of the wild-type Wilms’ tumor gene (WT1) product. Immunogenetics 2000, 51, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohminami, H.; Yasukawa, M.; Fujita, S. HLA class I-restricted lysis of leukemia cells by a CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clone specific for WT1 peptide. Blood 2000, 95, 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi, A.; Oka, Y.; Udaka, K.; Murakami, M.; Masuda, T.; Nakano, A.; Nakajima, H.; Yasukawa, M.; Hiraki, A.; Oji, Y.; et al. Enhanced induction of human WT1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes with a 9-mer WT1 peptide modified at HLA-A*2402-binding residues. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2002, 51, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Horiuchi, K.; Koya, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Yamaoka, N.; Yuzawa, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Higuchi, Y.; et al. Induction of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes by chemoradiotherapy in patients receiving Wilms’ tumor 1-targetted dendritic cell vaccinations for pancreatic cancer. OMICS J. Radiol. 2015, 4, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Koya, T.; Yuzawa, M.; Yamaoka, N.; Mizuno, Y.; Yoshizawa, K.; Hirabayashi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, K.; Shimodaira, S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay for the detection of Wilms’ tumor 1-specific T cells induced by dendritic cell vaccination. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, S.; Koya, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Koido, S. Quality verification of dendritic cell-based cancer vaccine. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2016, 7, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaka, A.; Saionji, K.; Kuwaki, T.; Takeshima, T.; Igari, J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration modulates the surface expression of effector cells molecules on human monocytes. Br. J. Haematol. 1995, 89, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boneberg, E.M.; Hareng, L.; Gantner, F.; Wendel, A.; Hartung, T. Human monocytes express functional receptors for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor that mediate suppression of monokines and interferon-gamma. Blood 2000, 95, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Z.; Zhang, J.Q.; Sun, L.X. Mechanisms for T cell tolerance induced with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 70, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaughnessy, P.J.; Bachier, C.; Lemaistre, C.F.; Akay, C.; Pollock, B.H.; Gazitt, Y. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes more dendritic cell subsets than granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor with no polarization of dendritic cell subsets in normal donors. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Nagayama, H.; Tadokoro, K.; Juji, T.; Takahashi, T.A. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase, stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38mapk are involved in IL-10-mediated selective repression of TNF-alpha-induced activation and maturation of human peripheral blood monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Nagayama, H.; Enomoto, M.; Morimoto, C.; Tadokoro, K.; Juji, T.; Takahashi, T.A. TGF-beta 1 reciprocally controls chemotaxis of human peripheral blood monocyte-derived dendritic cells via chemokine receptors. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.H. Costimulation of T lymphocytes: The role of CD28, CTLA-4, and B7/BB1 in interleukin-2 production and immunotherapy. Cell 1992, 71, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Anasetti, C.; Hansen, J.A.; Melrose, J.; Brunvand, M.; Bradshaw, J.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Linsley, P.S. Induction of alloantigen-specific hyporesponsiveness in human T lymphocytes by blocking interaction of CD28 with its natural ligand B7/BB1. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.W.; Koulova, L.; Soergel, S.A.; Clark, E.A.; Steinman, R.M.; Dupont, B. The B7/BB1 antigen provides one of several costimulatory signals for the activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes by human blood dendritic cells in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, P.; Freeman, G.J.; Nadler, L.M.; Fletcher, M.C.; Kamoun, M.; Turka, L.A.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Thompson, C.B.; June, C.H. Antibody and B7/BB1-mediated ligation of the CD28 receptor induces tyrosine phosphorylation in human T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, M.; Cayabyab, M.; Buck, D.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L. Involvement of CD28 in MHC-unrestricted cytotoxicity mediated by a human natural killer leukemia cell line. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Gool, S.W.; de Boer, M.; Ceuppens, J.L. CD28 ligation by monoclonal antibodies or B7/BB1 provides an accessory signal for the cyclosporin A-resistant generation of cytotoxic T cell activity. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| G-CSF (75 μg of Filgrastim) 16–18 h Prior to Apheresis (N = 54) | Treated | Untreated | p-Value ¶ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 39 | 15 | ||
| Number of DCs in 1 course (mean ± SD) | 9.13 ± 2.42 × 107 | 8.64 ± 2.80 × 107 | p = 0.320 |
| Induction ratio of WT1-CTLs * after one course (%) # | 36 (92.3%) | 10 (66.7%) | p = 0.019 |
| Median level of WT1-CTLs * after one course (range) | 0.05% (0.01–0.33) | 0.06% (0.01–0.38) | p = 0.712 |
| Median growth rate of WT1-CTLs * between the 1st and 7th session (range) | 0.03% (−0.02–0.31) | 0.02% (−0.03–0.38) | p = 0.462 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimodaira, S.; Yanagisawa, R.; Koya, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Togi, M.; Kato, T., Jr.; Kobayashi, T.; Koizumi, T.; et al. In Vivo Administration of Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Increases the Immune Effectiveness of Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Vaccination. Vaccines 2019, 7, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7030120
Shimodaira S, Yanagisawa R, Koya T, Hirabayashi K, Higuchi Y, Sakamoto T, Togi M, Kato T Jr., Kobayashi T, Koizumi T, et al. In Vivo Administration of Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Increases the Immune Effectiveness of Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Vaccination. Vaccines. 2019; 7(3):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7030120
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimodaira, Shigetaka, Ryu Yanagisawa, Terutsugu Koya, Koichi Hirabayashi, Yumiko Higuchi, Takuya Sakamoto, Misa Togi, Tomohisa Kato, Jr., Takashi Kobayashi, Tomonobu Koizumi, and et al. 2019. "In Vivo Administration of Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Increases the Immune Effectiveness of Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Vaccination" Vaccines 7, no. 3: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7030120
APA StyleShimodaira, S., Yanagisawa, R., Koya, T., Hirabayashi, K., Higuchi, Y., Sakamoto, T., Togi, M., Kato, T., Jr., Kobayashi, T., Koizumi, T., Koido, S., & Sugiyama, H. (2019). In Vivo Administration of Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Increases the Immune Effectiveness of Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Vaccination. Vaccines, 7(3), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7030120







