Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Interaction between HBV and TLRs
2.1. Recognition of HBV by Innate Immunity
2.2. Expression and Function of TLRs are Impaired in Chronic HBV Infection
2.3. Modulation of TLR Signaling Pathway by HBV
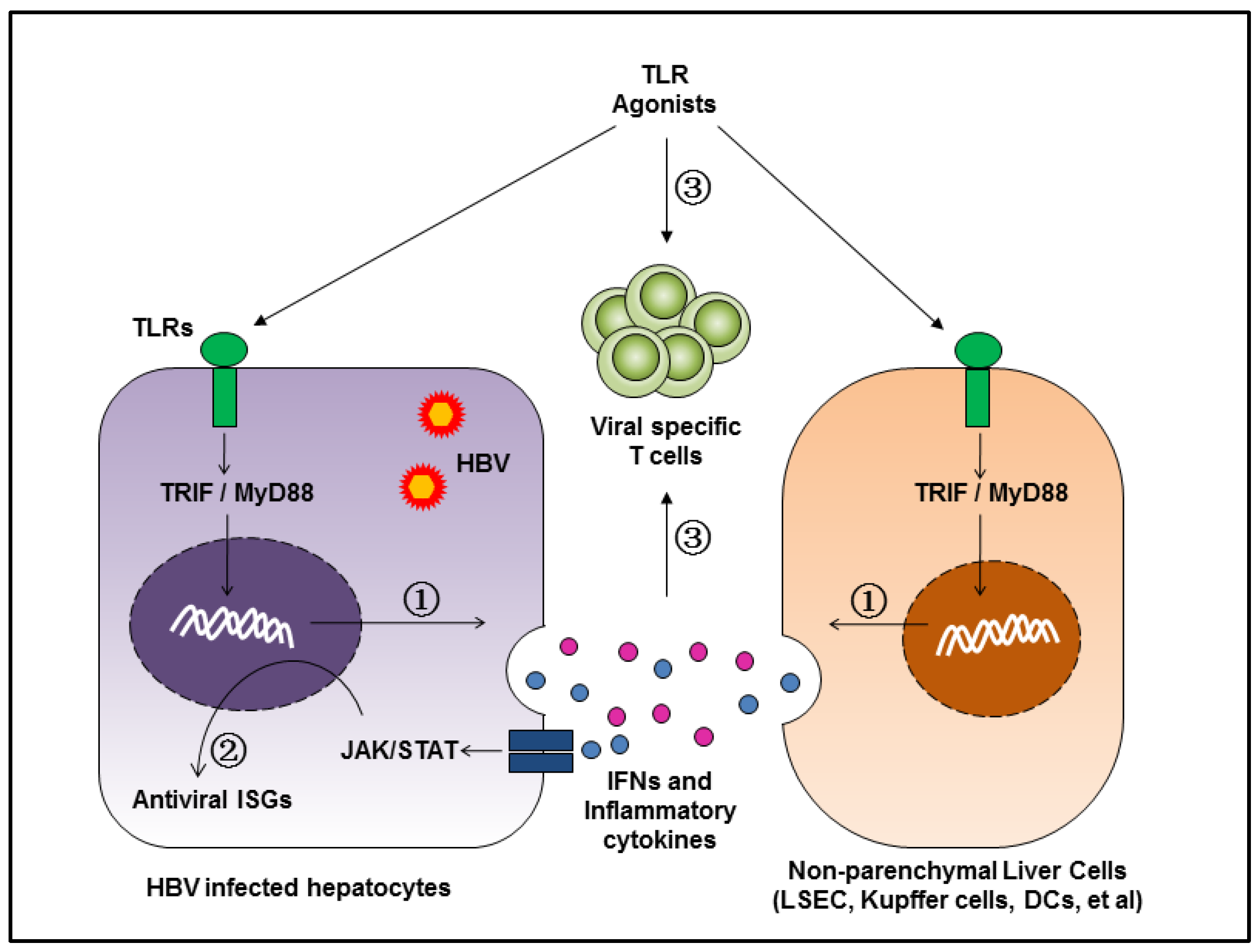
3. Inhibition of HBV Replication by TLR-Mediated Innate Immune Responses
3.1. Cell Culture Models
3.2. In Vivo Models
4. Modulation of HBV-Specific Immune Responses by TLR Agonists
5. Potential Therapeutic Approaches for Eliminating Chronic HBV Infection Based on TLR Signaling Pathways
6. TLR Agonists as Adjuvants of HBV Vaccines
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2006, 1, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehermann, B.; Nascimbeni, M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, G.J.; Reignat, S.; Maini, M.K.; Whalley, S.A.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.; Brown, D.; Amlot, P.L.; Williams, R.; Vergani, D.; et al. Incubation phase of acute hepatitis B in man: Dynamic of cellular immune mechanisms. Hepatology 2000, 32, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F.V. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, G.J.; Reignat, S.; Brown, D.; Ogg, G.S.; Jones, L.; Seneviratne, S.L.; Williams, R.; Dusheiko, G.; Bertoletti, A. Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Implications for immunotherapy. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5707–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, C.; Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Amadei, B.; Di Vincenzo, P.; Giuberti, T.; Laccabue, D.; Zerbini, A.; Cavalli, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific T-cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paludan, S.R.; Bowie, A.G. Immune sensing of DNA. Immunity 2013, 38, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.; Peppa, D.; Khanna, P.; Nebbia, G.; Jones, M.; Brendish, N.; Lascar, R.M.; Brown, D.; Gilson, R.J.; Tedder, R.J.; et al. Temporal analysis of early immune responses in patients with acute hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Boni, C.; Massari, M.; Mori, C.; Zerbini, A.; Orlandini, A.; Sacchelli, L.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. Early kinetics of innate and adaptive immune responses during hepatitis B virus infection. Gut 2009, 58, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA sensor RIG-I dually functions as an innate sensor and direct antiviral factor for hepatitis B virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangsay, S.; Gruffaz, M.; Isorce, N.; Testoni, B.; Michelet, M.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Maadadi, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Parent, R.; Rivoire, M.; et al. Early inhibition of hepatocyte innate responses by hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlomai, A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ramanan, V.; Bhatta, A.; de Jong, Y.P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Rice, C.M. Modeling host interactions with hepatitis B virus using primary and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12193–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogawa, M.; Robek, M.D.; Furuichi, Y.; Chisari, F.V. Toll-like receptor signaling inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7269–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lu, M.; Meng, Z.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Szczeponek, A.; Krux, F.; Dittmer, U.; Roggendorf, M.; Gerken, G.; et al. Toll-like receptor-mediated control of HBV replication by nonparenchymal liver cells in mice. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Meng, Z.; Broering, R.; Yang, D.; Schlaak, J.F.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. Role of Toll-like receptor 2 in the immune response against hepadnaviral infection. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, D.; Ma, D.; Chang, J.; Dougherty, A.M.; Cuconati, A.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T. Activation of pattern recognition receptor-mediated innate immunity inhibits the replication of hepatitis B virus in human hepatocyte-derived cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R.E.; Guerra, B.; Chavez, D.; Giavedoni, L.; Hodara, V.L.; Brasky, K.M.; Fosdick, A.; Frey, C.R.; Zheng, J.; Wolfgang, G.; et al. GS-9620, an oral agonist of Toll-like receptor-7, induces prolonged suppression of hepatitis B virus in chronically infected chimpanzees. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvanathan, K.; Skinner, N.A.; Thompson, A.J.; Riordan, S.M.; Sozzi, V.; Edwards, R.; Rodgers, S.; Kurtovic, J.; Chang, J.; Lewin, S.; et al. Regulation of Toll-like receptor-2 expression in chronic hepatitis B by the precore protein. Hepatology 2007, 45, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, F.; et al. Expression profiles and function of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 128, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, I.E.; Zannetti, C.; Lucifora, J.; Norder, H.; Protzer, U.; Hainaut, P.; Zoulim, F.; Tommasino, M.; Trepo, C.; Hasan, U.; et al. Hepatitis B virus impairs TLR9 expression and function in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Lin, S.C.; Wei, S.C.; Hu, J.T.; Chang, H.Y.; Huang, S.H.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J.; Hsu, P.N.; Yang, S.S.; et al. Reduced Toll-like receptor 3 expression in chronic hepatitis B patients and its restoration by interferon therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Zelinskyy, G.; Buer, J.; Dittmer, U.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. The IL-1R/TLR signaling pathway is essential for efficient CD8+ T-cell responses against hepatitis B virus in the hydrodynamic injection mouse model. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangsay, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Michelet, M.; Floriot, O.; Bonnin, M.; Gruffaz, M.; Rivoire, M.; Fletcher, S.; Javanbakht, H.; Lucifora, J.; et al. Expression and functionality of Toll- and RIG-like receptors in HepaRG cells. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosel, M.; Quasdorff, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Webb, D.; Zedler, U.; Broxtermann, M.; Tedjokusumo, R.; Esser, K.; Arzberger, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiner, K.M.; Schaller, H.; Knolle, P.A. Endothelial cell-mediated uptake of a hepatitis B virus: A new concept of liver targeting of hepatotropic microorganisms. Hepatology 2001, 34, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleau, C.; Filliol, A.; Samson, M.; Lamontagne, L. Mouse Hepatitis Virus Infection Induces a Toll-Like Receptor 2-Dependent Activation of Inflammatory Functions in Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells during Acute Hepatitis. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9096–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Tal, G.; Lider, O.; Shaul, Y. Cytokine induction by the hepatitis B virus capsid in macrophages is facilitated by membrane heparan sulfate and involves TLR2. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanlandschoot, P.; Van Houtte, F.; Serruys, B.; Leroux-Roels, G. Contamination of a recombinant hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid preparation with a human B-cell activator. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2535–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanlandschoot, P.; Van Houtte, F.; Ulrichts, P.; Tavernier, J.; Leroux-Roels, G. Immunostimulatory potential of hepatitis B nucleocapsid preparations: Lipopolysaccharide contamination should not be overlooked. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Montfoort, N.; van der Aa, E.; van den Bosch, A.; Brouwers, H.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Janssen, H.L.; Javanbakht, H.; Buschow, S.I.; Woltman, A.M. Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Activates Myeloid Dendritic Cells via a Soluble CD14-Dependent Mechanism. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6187–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Shen, H.C.; Jia, N.N.; Wang, H.; Lin, L.Y.; An, B.Y.; Gui, H.L.; Guo, S.M.; Cai, W.; Yu, H.; et al. Patients with chronic hepatitis B infection display deficiency of plasmacytoid dendritic cells with reduced expression of TLR9. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Yao, H.P.; Lv, G.C.; Chen, Z. Downregulation of TLR7/9 leads to deficient production of IFN-alpha from plasmacytoid dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis B. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Lai, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, J.; Hou, J.; Han, M.; Ning, Q. Upregulation of NKG2C+ natural killer cells, TLR-2 expression on monocytes and downregulation of regulatory T-cells influence PEG-IFN treatment efficacy in entecavir-suppressed patients with CHB. Antivir. Ther. 2015, 20, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvanathan, K.; Lang, T.; Ryan, K.; Wilson, R.; Skinner, N.A.; Thompson, A.J.; Ahn, S.H.; Weilert, F.; Abbott, W.; Gane, E.; et al. Toll-IL1 receptor-mediated innate immune responses vary across HBV genotype and predict treatment response to pegylated-IFN in HBeAg-positive CHB patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Ge, J.; Liu, C.; Pang, J.; Huang, Z.; Peng, J.; Sun, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X. Impaired expression and function of TLR8 in chronic HBV infection and its association with treatment responses during peg-IFN-alpha-2a antiviral therapy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F. Interplay between hepatitis B virus and TLR2-mediated innate immune responses: Can restoration of TLR2 functions be a new therapeutic option? J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, A.I.; Pezacki, J.P.; Wodicka, L.; Brideau, A.D.; Supekova, L.; Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Bukh, J.; Purcell, R.H.; Schultz, P.G.; et al. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis C virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15669–15674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, S.; Yuan, Z. HBsAg inhibits TLR9-mediated activation and IFN-alpha production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Broering, R.; Trippler, M.; Poggenpohl, L.; Fiedler, M.; Gerken, G.; Lu, M.; Schlaak, J.F. Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses are attenuated in the presence of high levels of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Lo, C.; Skinner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Visvanathan, K.; Mansell, A. The hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) targets and suppresses activation of the toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Warner, N.; Ryan, K.; Selleck, L.; Colledge, D.; Rodgers, S.; Li, K.; Revill, P.; Locarnini, S. The hepatitis B e antigen suppresses IL-1β-mediated NF-κB activation in hepatocytes. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, e499–e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; Kato, N.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes through interference with interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and dampening of the interaction between TBK1/IKKϵ and DDX3. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wu, A.; Cui, L.; Hao, R.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, D. Hepatitis B virus polymerase suppresses NF-κB signaling by inhibiting the activity of IKKs via interaction with Hsp90β. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayesh, M.E.H.; Ezzikouri, S.; Chi, H.; Sanada, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Kitab, B.; Haraguchi, T.; Matsuyama, R.; Nkogue, C.N.; Hatai, H.; et al. Interferon-β response is impaired by hepatitis B virus infection in Tupaia belangeri. Virus Res. 2017, 237, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, Z.; Qiu, S.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Schlaak, J.F.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. Lipopolysaccharide-induced innate immune responses in primary hepatocytes downregulates woodchuck hepatitis virus replication via interferon-independent pathways. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, H.; Tang, L.; Lu, M.; Yan, R.; Guo, H.; Sun, J.; et al. Transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 transcriptionally suppresses hepatitis B virus replication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClary, H.; Koch, R.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. Relative sensitivity of hepatitis B virus and other hepatotropic viruses to the antiviral effects of cytokines. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Huang, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid treatment leads to the interferon-dependent clearance of hepatitis B virus in a hydrodynamic injection mouse model. J. Virol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggendorf, M.; Kosinska, A.D.; Liu, J.; Lu, M. The Woodchuck, a Nonprimate Model for Immunopathogenesis and Therapeutic Immunomodulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, S.T.B.; Liu, K.H.; Ascenzi, M.A.; Baldwin, B.H.; Bellezza, C.A.; Cote, P.J.; Zheng, X.; Wolfgang, G.; Turnas, D. Antiviral efficacy and induction of an antibody response against surface antigen with the TLR7 agonist GS-9620 in the woodchuck model of chronic HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, S441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pei, R.; Zhang, E.; Kemper, T.; Vollmer, J.; Davis, H.L.; Glebe, D.; Gerlich, W.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. Combination therapy including CpG oligodeoxynucleotides and entecavir induces early viral response and enhanced inhibition of viral replication in a woodchuck model of chronic hepadnaviral infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 125, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolowicz, K.E.; Iyer, R.P.; Czerwinski, S.; Suresh, M.; Yang, J.; Padmanabhan, S.; Sheri, A.; Pandey, R.K.; Skell, J.; Marquis, J.K.; et al. Antiviral Efficacy and Host Innate Immunity Associated with SB 9200 Treatment in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Lim, Y.S.; Gordon, S.C.; Visvanathan, K.; Sicard, E.; Fedorak, R.N.; Roberts, S.; Massetto, B.; Ye, Z.; Pflanz, S.; et al. The oral toll-like receptor-7 agonist GS-9620 in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Zhang, E.; Johrden, L.; Liu, J.; Seiz, P.L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Kemper, T.; Fiedler, M.; Glebe, D.; et al. Combination of DNA prime--adenovirus boost immunization with entecavir elicits sustained control of chronic hepatitis B in the woodchuck model. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Wu, W.; Kosinska, A.; Zhang, X.; Moller, I.; Seiz, P.; Glebe, D.; Wang, B.; et al. Enhancing virus-specific immunity in vivo by combining therapeutic vaccination and PD-L1 blockade in chronic hepadnaviral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, P.; Zhang, C.; Han, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Z. Therapeutic recovery of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-induced hepatocyte-intrinsic immune defect reverses systemic adaptive immune tolerance. Hepatology 2013, 58, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Wang, J.; Dou, S.; Yang, X.; Ni, X.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Nanoparticles encapsulating hepatitis B virus cytosine-phosphate-guanosine induce therapeutic immunity against HBV infection. Hepatology 2014, 59, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Wohlleber, D.; Reisinger, F.; Jenne, C.N.; Cheng, R.L.; Abdullah, Z.; Schildberg, F.A.; Odenthal, M.; Dienes, H.P.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Intrahepatic myeloid-cell aggregates enable local proliferation of CD8(+) T cells and successful immunotherapy against chronic viral liver infection. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.M.; Dong, C. Toll-like receptor regulation of effector T lymphocyte function. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottalorda, A.; Verschelde, C.; Marcais, A.; Tomkowiak, M.; Musette, P.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Marvel, J.; Bonnefoy-Berard, N. TLR2 engagement on CD8 T cells lowers the threshold for optimal antigen-induced T cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, D.; Zheng, L.; Srivastava, R.; Asprodites, N.; Velasco-Gonzalez, C.; Davila, E. When Toll-like receptor and T-cell receptor signals collide: A mechanism for enhanced CD8 T-cell effector function. Blood 2010, 116, 3494–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komai-Koma, M.; Jones, L.; Ogg, G.S.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y. TLR2 is expressed on activated T cells as a costimulatory receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asprodites, N.; Zheng, L.; Geng, D.; Velasco-Gonzalez, C.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Davila, E. Engagement of Toll-like receptor-2 on cytotoxic T-lymphocytes occurs in vivo and augments antitumor activity. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 3628–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, D.; Zheng, L.; Srivastava, R.; Velasco-Gonzalez, C.; Riker, A.; Markovic, S.N.; Davila, E. Amplifying TLR-MyD88 signals within tumor-specific T cells enhances antitumor activity to suboptimal levels of weakly immunogenic tumor antigens. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7442–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Blauvelt, C.P.; Kumaraswami, V.; Nutman, T.B. Cutting edge: Diminished T cell TLR expression and function modulates the immune response in human filarial infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3885–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendigs, S.; Salzer, U.; Lipford, G.B.; Wagner, H.; Heeg, K. CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides co-stimulate primary T cells in the absence of antigen-presenting cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabiasco, J.; Devevre, E.; Rufer, N.; Salaun, B.; Cerottini, J.C.; Speiser, D.; Romero, P. Human effector CD8+ T lymphocytes express TLR3 as a functional coreceptor. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8708–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.S.; Zoulim, F.; Dusheiko, G.; Ghany, M.G. Hepatitis B cure: From discovery to regulatory approval. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.; Abdul Basit, S.; Jayaraj, M.; Gish, R.G. Drugs in Development for Hepatitis B. Drugs 2017, 77, 1263–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, H.B.; Baer, G.; Baron, S.; Buckler, C.E.; Gibbs, C.J.; Iadarola, M.J.; London, W.T.; Rice, J. A modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex that induces interferon in primates. J. Infect. Dis. 1975, 132, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, R.H.; London, W.T.; McAuliffe, V.J.; Palmer, A.E.; Kaplan, P.M.; Gerin, J.L.; Wagner, J.; Popper, H.; Lvovsky, E.; Wong, D.C.; et al. Modification of chronic hepatitis-B virus infection in chimpanzees by administration of an interferon inducer. Lancet 1976, 2, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijichi, K.; Mitamura, K.; Ida, S.; Machida, H.; Shimada, K. In vivo antiviral effects of mismatched double-stranded RNA on duck hepatitis B virus. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 43, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Wang, Y.; Dixon, R.; Bowden, S.; Qiao, M.; Einck, L.; Locarnini, S. The use of ampligen alone and in combination with ganciclovir and coumermycin A1 for the treatment of ducks congenitally-infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Antivir. Res. 1993, 21, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Li, L.; Daffis, S.; Lucifora, J.; Bonnin, M.; Maadadi, S.; Salas, E.; Chu, R.; Ramos, H.; Livingston, C.M.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist GS-9620 Induces Prolonged Inhibition of HBV via a Type I Interferon-Dependent Mechanism. J. Hepatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Brunetto, M.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Ferrari, C.; Massetto, B.; Nguyen, A.H.; Joshi, A.; Woo, J.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Tan, A.T.; Ussher, J.E.; Sandalova, E.; Tang, X.Z.; Tan-Garcia, A.; To, N.; Hong, M.; Chia, A.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Toll-like receptor 8 agonist and bacteria trigger potent activation of innate immune cells in human liver. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzler, H.; Barrat, F.J.; Hessel, E.M.; Coffman, R.L. Therapeutic targeting of innate immunity with Toll-like receptor agonists and antagonists. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayat, M.; Netea, M.G.; Rezaei, N. Targeting of Toll-like receptors: A decade of progress in combating infectious diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevens, F.; Zuckerman, J.N.; Burroughs, A.K.; Jung, M.C.; Bayas, J.M.; Kallinowski, B.; Rivas, E.F.; Duvoux, C.; Neuhaus, P.; Saliba, F.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an experimental adjuvanted hepatitis B candidate vaccine in liver transplant patients. Liver Transplant. 2006, 12, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, P.; Moens, G.; Desombere, I.; Dewijngaert, J.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Wettendorff, M.; Thoelen, S. The immunogenicity and reactogenicity profile of a candidate hepatitis B vaccine in an adult vaccine non-responder population. Vaccine 2002, 20, 3644–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Cooper, C. A review of the role of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides as toll-like receptor 9 agonists in prophylactic and therapeutic vaccine development in infectious diseases. Drugs R&D 2008, 9, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.L.; Davis, H.L.; Morris, M.L.; Efler, S.M.; Adhami, M.A.; Krieg, A.M.; Cameron, D.W.; Heathcote, J. CPG 7909, an immunostimulatory TLR9 agonist oligodeoxynucleotide, as adjuvant to Engerix-B HBV vaccine in healthy adults: A double-blind phase I/II study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 24, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, C.A.; Pihlgren, M.; Tougne, C.; Efler, S.M.; Morris, M.L.; AlAdhami, M.J.; Cameron, D.W.; Cooper, C.L.; Heathcote, J.; Davis, H.L.; et al. Co-administration of CpG oligonucleotides enhances the late affinity maturation process of human anti-hepatitis B vaccine response. Vaccine 2004, 23, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, S.A.; Dobson, S.; McNeil, S.; Langley, J.M.; Smith, B.; McCall-Sani, R.; Levitt, D.; Nest, G.V.; Gennevois, D.; Eiden, J.J. Comparison of the safety and immunogenicity of hepatitis B virus surface antigen co-administered with an immunostimulatory phosphorothioate oligonucleotide and a licensed hepatitis B vaccine in healthy young adults. Vaccine 2006, 24, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, S.A.; Ward, B.; Cooper, C.; Predy, G.; Diaz-Mitoma, F.; Dionne, M.; Embree, J.; McGeer, A.; Zickler, P.; Moltz, K.H.; et al. Comparison of safety and immunogenicity of two doses of investigational hepatitis B virus surface antigen co-administered with an immunostimulatory phosphorothioate oligodeoxyribonucleotide and three doses of a licensed hepatitis B vaccine in healthy adults 18–55 years of age. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2556–2563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barry, M.; Cooper, C. Review of hepatitis B surface antigen-1018 ISS adjuvant-containing vaccine safety and efficacy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2007, 7, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.; Lentino, J.; Kopp, J.; Murray, L.; Ellison, W.; Rhee, M.; Shockey, G.; Akella, L.; Erby, K.; Heyward, W.L.; et al. Immunogenicity of a two-dose investigational hepatitis B vaccine, HBsAg-1018, using a toll-like receptor 9 agonist adjuvant compared with a licensed hepatitis B vaccine in adults. Vaccine 2017, 33, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablan, B.P.; Kim, D.J.; Barzaga, N.G.; Chow, W.C.; Cho, M.; Ahn, S.H.; Hwang, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Namini, H.; Heyward, W.L. Demonstration of safety and enhanced seroprotection against hepatitis B with investigational HBsAg-1018 ISS vaccine compared to a licensed hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.L.; Davis, H.L.; Angel, J.B.; Morris, M.L.; Elfer, S.M.; Seguin, I.; Krieg, A.M.; Cameron, D.W. CPG 7909 adjuvant improves hepatitis B virus vaccine seroprotection in antiretroviral-treated HIV-infected adults. AIDS 2005, 19, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.L.; Angel, J.B.; Seguin, I.; Davis, H.L.; Cameron, D.W. CPG 7909 adjuvant plus hepatitis B virus vaccination in HIV-infected adults achieves long-term seroprotection for up to 5 years. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.; Mackie, D. Hepatitis B surface antigen-1018 ISS adjuvant-containing vaccine: A review of HEPLISAV safety and efficacy. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, J.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Groeger, J.; Wiersma, S.T. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: New estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, E.; Lu, M. Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines 2018, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010006
Ma Z, Cao Q, Xiong Y, Zhang E, Lu M. Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines. 2018; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhiyong, Qian Cao, Yong Xiong, Ejuan Zhang, and Mengji Lu. 2018. "Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B" Vaccines 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010006
APA StyleMa, Z., Cao, Q., Xiong, Y., Zhang, E., & Lu, M. (2018). Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010006




