Structural Analysis and Epitope Prediction of MHC Class-1-Chain Related Protein-A for Cancer Vaccine Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval and Comparative Modelling
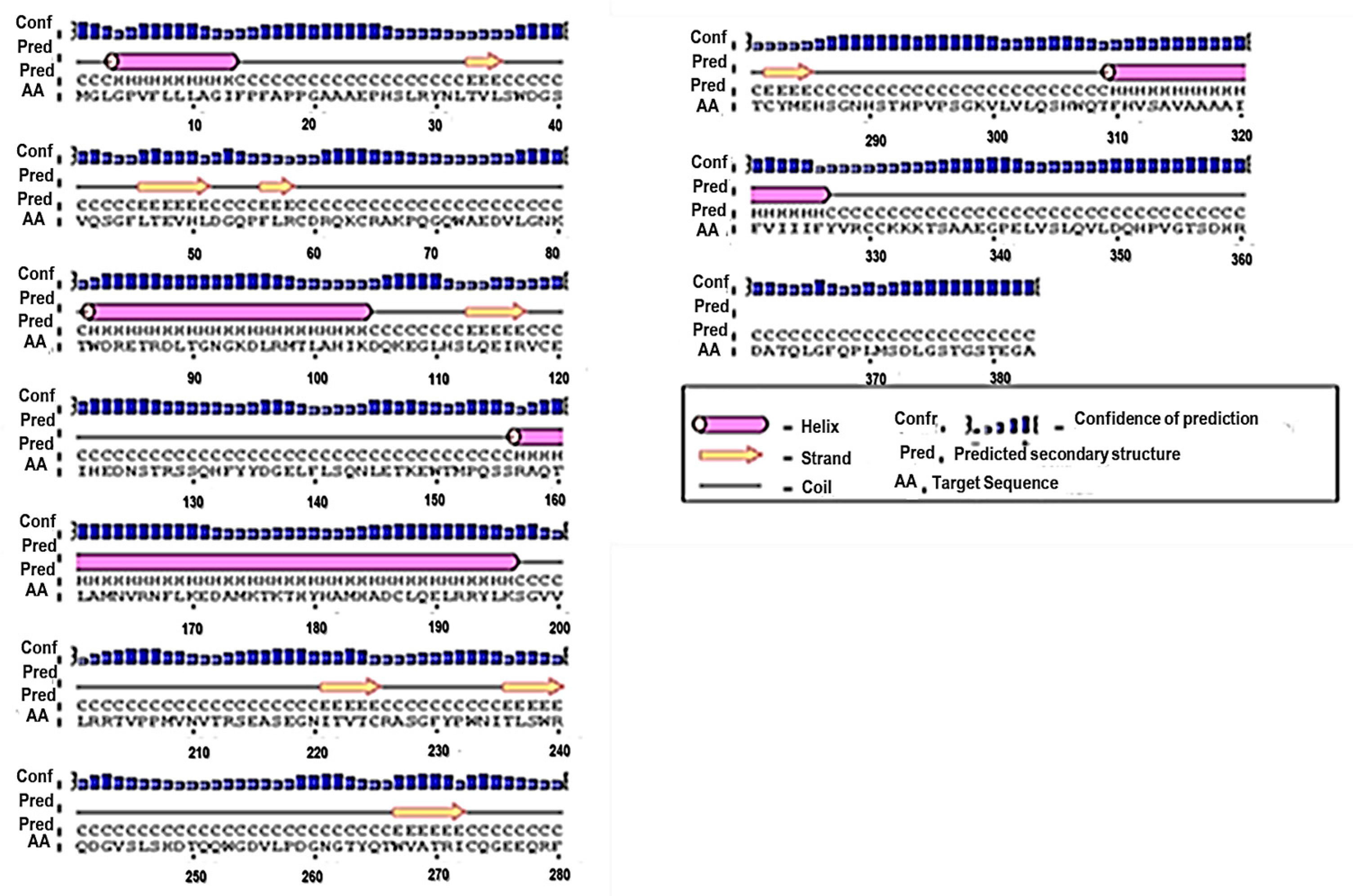
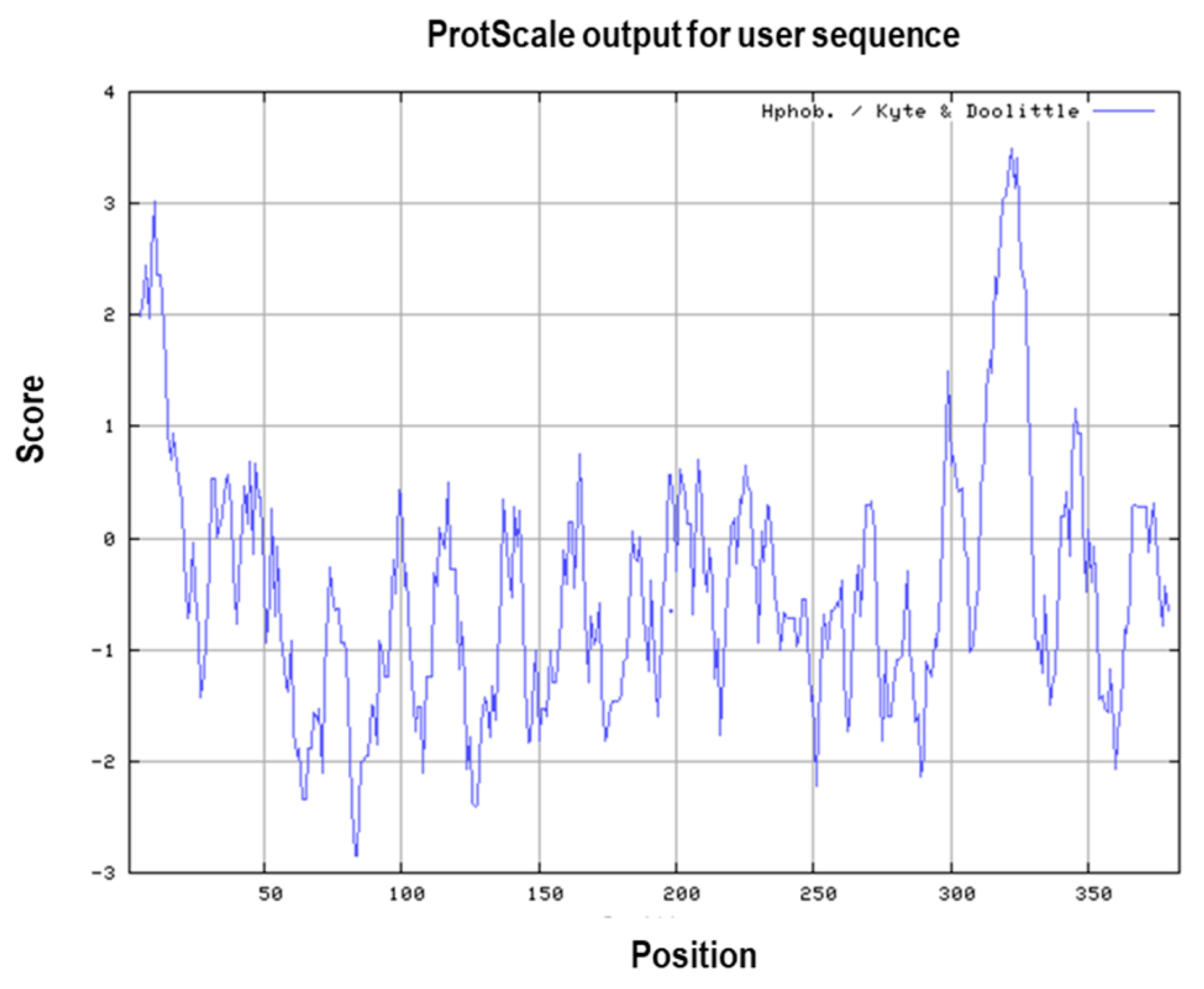
2.2. Primary and Secondary Structural Prediction
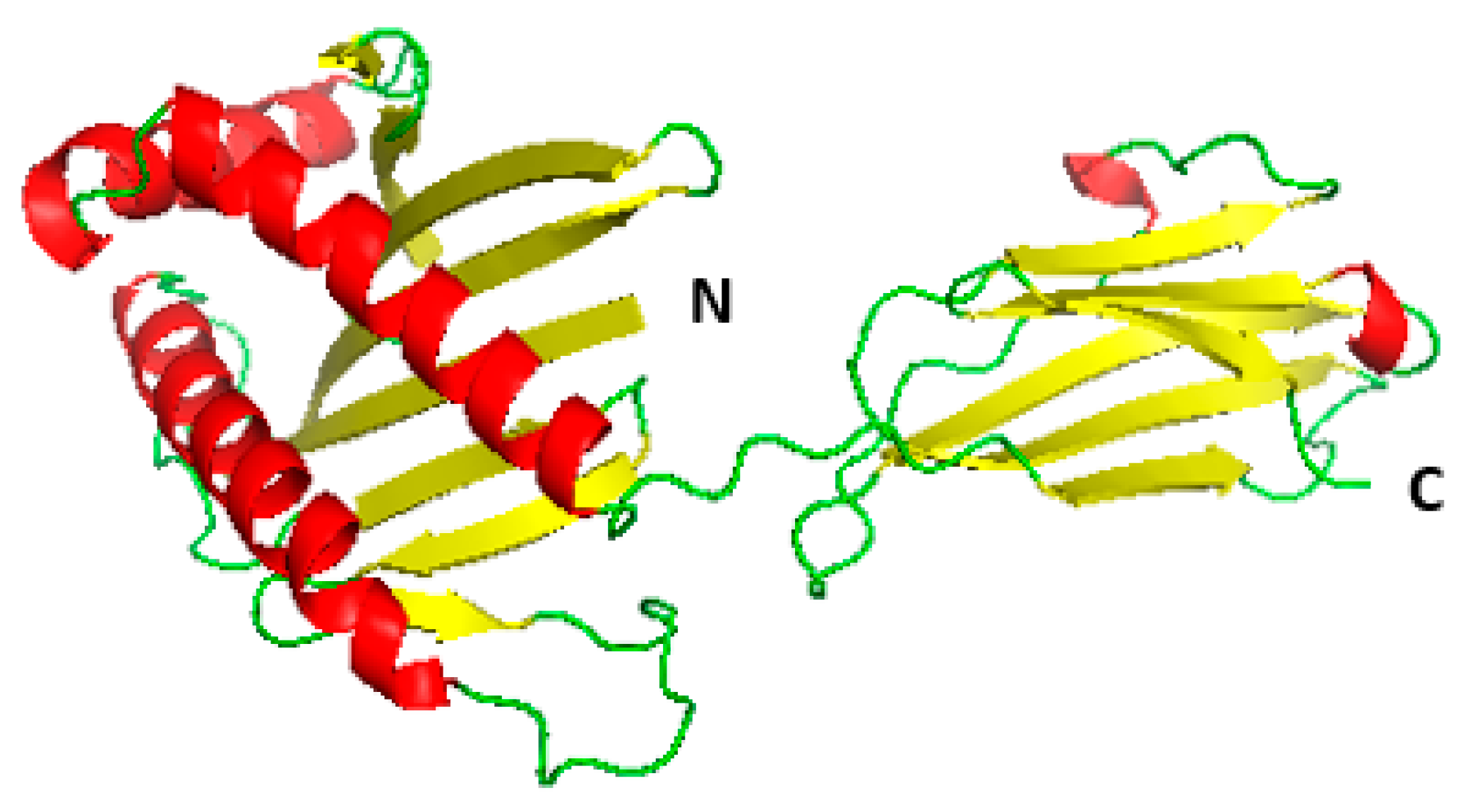
2.3. Homology Modelling of MIC-A Protein
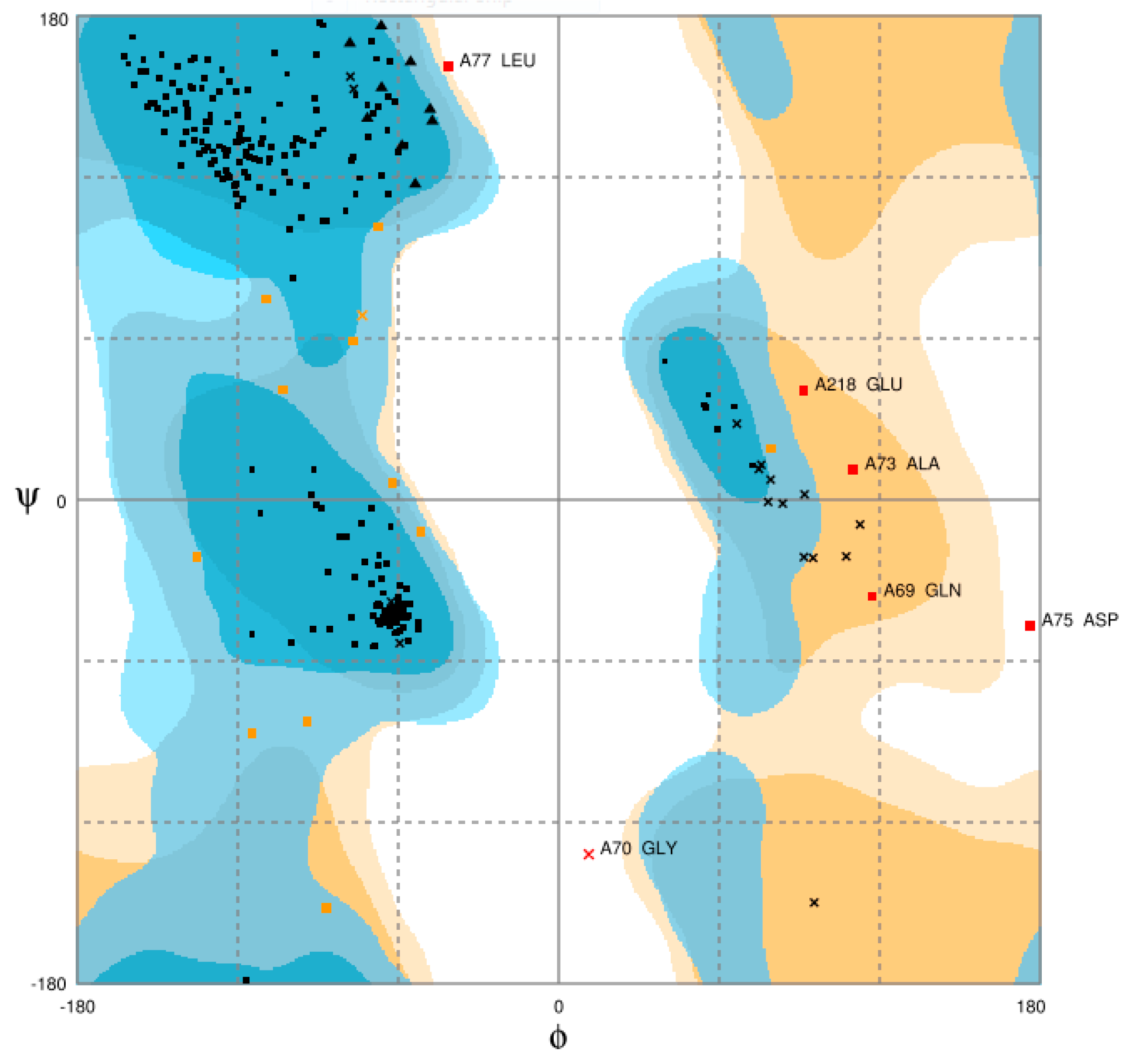
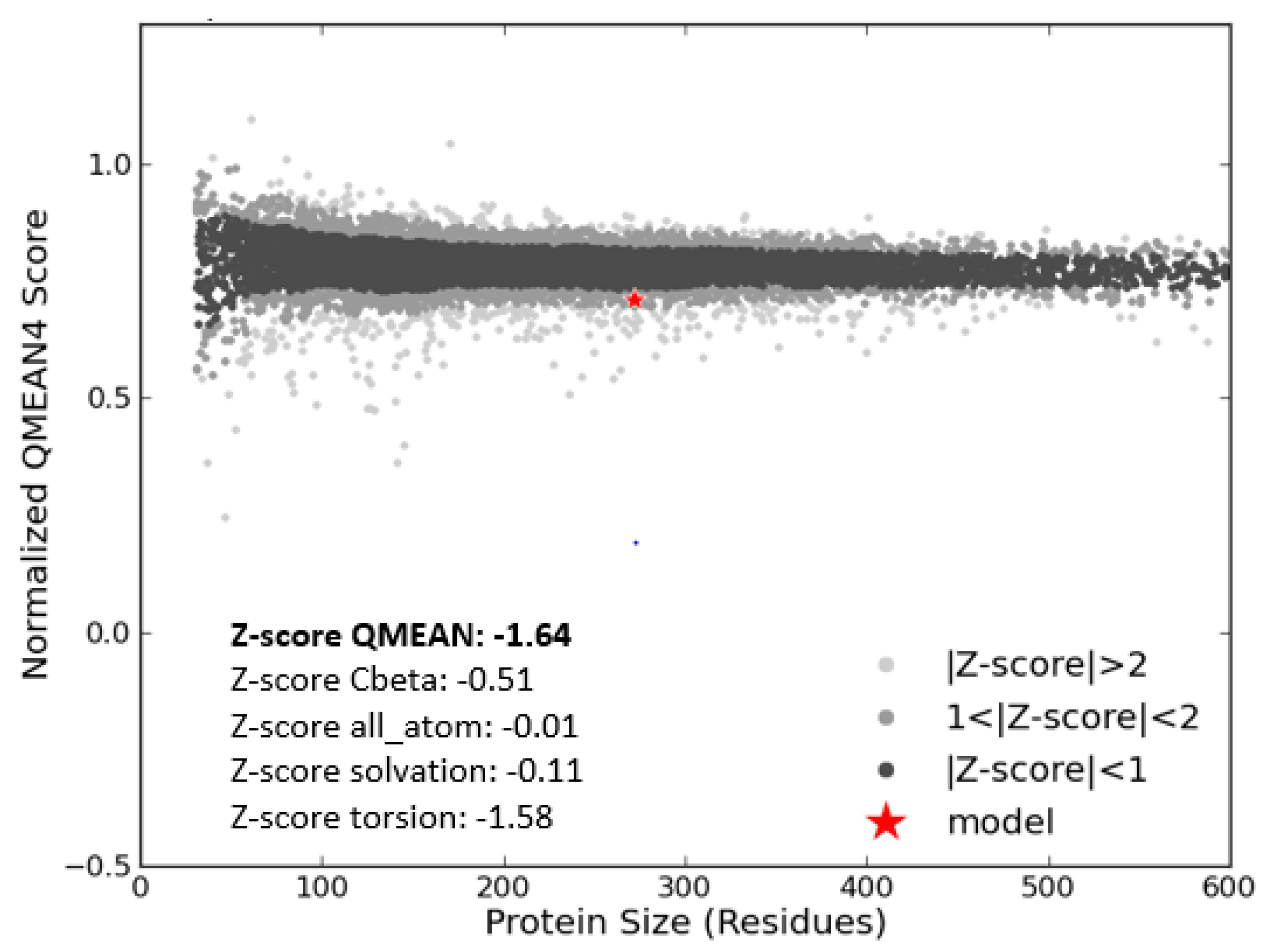
2.4. Model Evaluation and Stereochemical Analysis
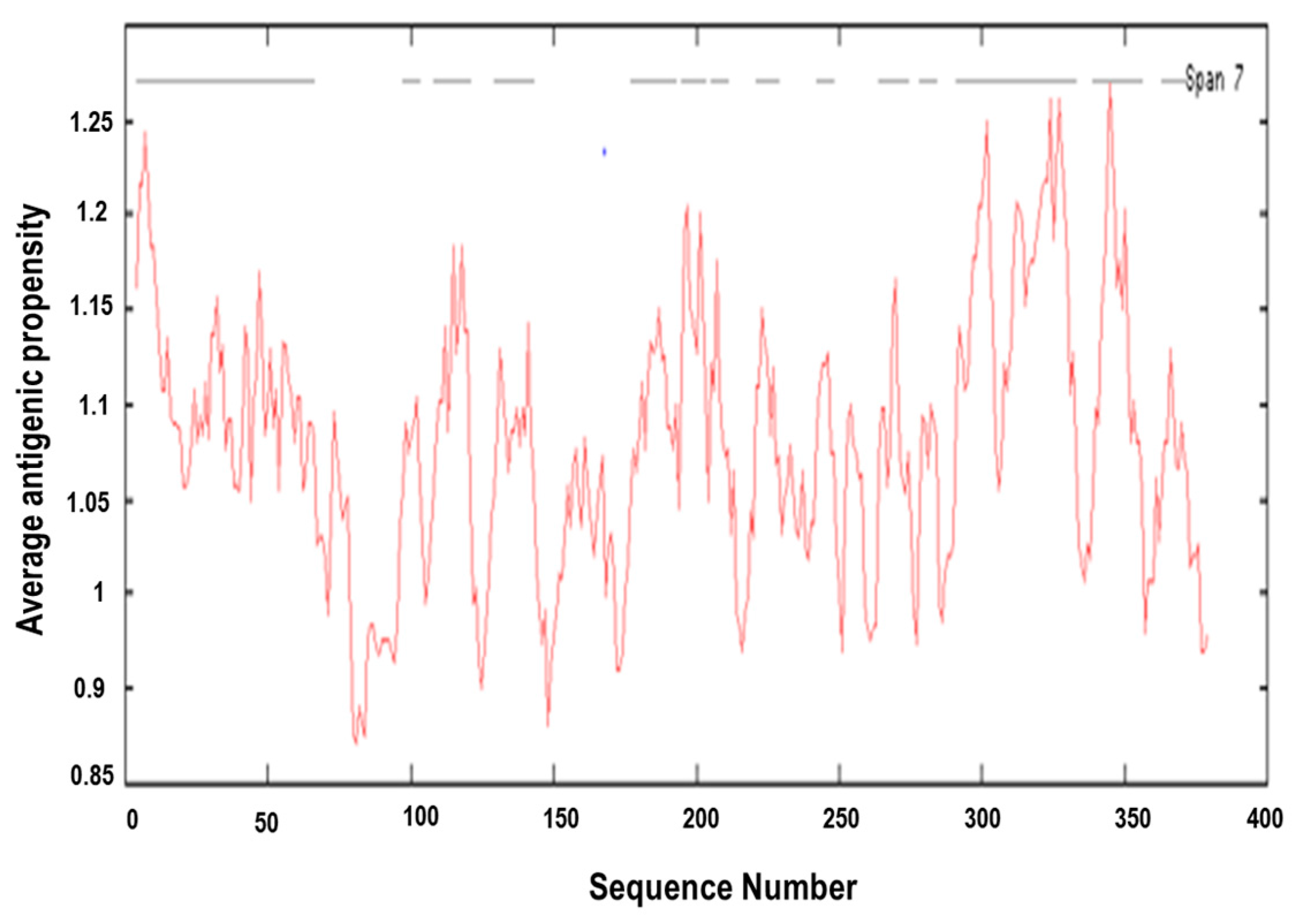
2.5. Antigenic Epitope Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Primary and Secondary Structure of the MIC-A Protein
3.2. Homology Modelling of MIC-A Protein
3.3. Model Evaluation and Stereochemical Analysis
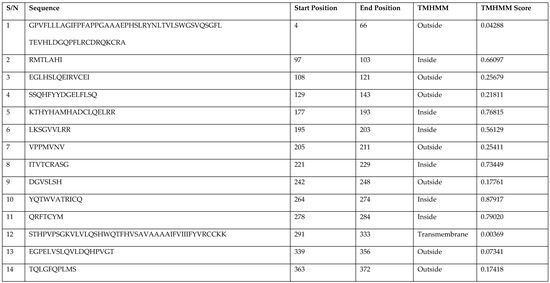
3.4. Prediction of Antigenic Epitopes on MIC-A Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Gelber, R.D.; Coates, A.S.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Progress and promise: Highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldhauer, I.; Steinle, A. NK cells and cancer immunosurveillance. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5932–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kruijf, E.M.; Sajet, A.; van Nes, J.G.; Putter, H.; Smit, V.T.; Eagle, R.A.; Jafferji, I.; Trowsdale, J.; Liefers, G.J.; van de Velde, C.J.; et al. NKG2D ligand tumor expression and association with clinical outcome in early breast cancer patients: An observational study. BMC Cancer 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, G.P.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Mandelboim, O. An integrated view of the regulation of NKG2D ligands. Immunology 2009, 128, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, T.I.; Markel, G.; Mandelboim, O. Tumor and viral recognition by natural killer cells receptors. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Groh, V.; Wu, J.; Steinle, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 1999, 285, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosman, D.; Mullberg, J.; Sutherland, C.L.; Chin, W.; Armitage, R.; Fanslow, W. ULBPs, novel MHC class I-related molecules, bind to CMV glycoprotein UL16and stimulate NK cytotoxicity through the NKG2D receptor. Immunity 2001, 14, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diefenbach, A.; Hsia, J.K.; Hsiung, M.Y.; Raulet, D.H. A novel ligand for the NKG2D receptor activates NK cells and macrophages and induces tumor immunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertsson, P.A.; Basse, P.H.; Hokland, M.; Goldfarb, R.H.; Nagelkerke, J.F.; Nannmark, U.; Kuppen, P.J. NK cells and the tumour microenvironment: Implications for NK-cell function and anti-tumour activity. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, T.; Angustias, F.M.; Sierra, A.; Garrido, A.; Herruzo, A.; Escobedo, A.; Fabra, A.; Garrido, F. High frequency of altered HLA class I phenotypes in invasive breast carcinomas. Hum. Immunol. 1996, 50, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGivary, R.W.; Eagle, R.A.; Rolland, P.; Jafferji, I.; Trowsdale, J.; Durrant, L.G. ULBP2 and RAET1E NKG2D ligands are independent predictors of poor prognosis in ovarian cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Geer, L.Y.; Marchler-Bauer, A.; Geer, R.C.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Liu, C.; Shi, W.; Bryant, S.H. The NCBI BioSystems database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchan, D.W.A.; Minneci, F.; Nugent, T.C.O.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D.T. Scalable web services for the PSIPRED Protein Analysis Workbench. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.T. Protein secondary structure prediction based on position specific scoring matrices 1. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 292, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Cassarino, T.G.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; de Beer, T.A.; Tauriello, G.; Studer, G.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Repository-new features and functionality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D313–D319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; DeLano Scientific: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002; p. 700. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, S.C.; Davis, I.W.; Arendall, W.B.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Word, J.M.; Prisant, M.G.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. Structure validation by Calpha geometry: Phi, psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins 2002, 50, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkert, P.; Künzli, M.; Schwede, T. QMEAN server for protein model quality estimation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, C.A.; Gomez, F.A.; Mercado, L.; Ramírez, R.; Marshall, S.H. Piscirickettsia salmonis imbalances the innate immune response to succeed in a productive infection in a salmonid cell line model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaskar, A.S.; Tongaonkar, P.C. A semi-empirical method for prediction of antigenic determinants on protein antigens. FEBS Lett. 1990, 276, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; Heijne, V.G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Målen, H.; Pathak, S.; Søfteland, T.; De Souza, G.A.; Wiker, H.G. Definition of novel cell envelope associated proteins in Triton X-114 extracts of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. BMC Microbiol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.L.; MacArthur, M.W.; Hutchinson, E.G.; Thornton, J.M. Stereochemical quality of protein structure coordinates. Proteins 1992, 12, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, E.; Joo, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Raman, S.; Thompson, J.; Karplus, K. Improving physical realism, stereochemistry, and side-chain accuracy in homology modeling: Four approaches that performed well in CASP8. Proteins 2009, 77, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinnell, F.; Feld, M.K. Fibronectin adsorption on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces detected by antibody binding and analyzed during cell adhesion in serum-containing medium. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 4888–4893. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.Y.; Wilhelm, S.D.; Audette, C.; Jones, G.; Leece, B.A.; Lazar, A.C.; Goldmacher, V.S.; Singh, R.; Kovtun, Y.; Widdison, W.C.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of hydrophilic linkers for antibody–maytansinoid conjugates. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3606–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnhammer, E.L.; Von Heijne, G.; Krogh, A. A hidden Markov model for predicting transmembrane helices in protein sequences. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1998, 6, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chalupny, N.J.; Rein-Weston, A.; Dosch, S.; Cosman, D. Down-regulation of the NKG2D ligand MICA by the human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein UL142. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Mandai, M.; Hamanishi, J.; Matsumura, N.; Suzuki, A.; Yagi, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Baba, T.; Fujii, S.; Konishi, I. Clinical significance of the NKG2D ligands, MICA/B and ULBP2 in ovarian cancer: High expression of ULBP2 is an indicator of poor prognosis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouch, D.H.; O’brien, K.L.; Simmons, N.L.; King, S.L.; Abbink, P.; Maxfield, L.F.; Sun, Y.H.; La Porte, A.; Riggs, A.M.; Lynch, D.M.; et al. Mosaic HIV-1 vaccines expand the breadth and depth of cellular immune responses in rhesus monkeys. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, A.M.; Skariah, S.; Mordue, D.G.; Knoll, L.J. A transmembrane domain-containing surface protein from Toxoplasma gondii augments replication in activated immune cells and establishment of a chronic infection. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashfaq, U.A.; Ahmed, B. De novo structural modeling and conserved epitopes prediction of Zika virus envelop protein for vaccine development. Viral Immunol. 2016, 29, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Parvege, M.M. In silico structural analysis of Hantaan virus glycoprotein G2 and conserved epitope prediction for vaccine development. J. Appl. Virol. 2014, 3, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwary, N.I.A.; Islam, M.S.; Sohel, M.; Ara, I.; Sikder, M.O.F.; Shahik, S.M. In silico structure analysis and epitope prediction of E3 CR1-beta protein of Human Adenovirus E for vaccine design. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| S/N | Sequence | Start Position | End Position | TMHMM | TMHMM Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GPVFLLLAGIFPFAPPGAAAEPHSLRYNLTVLSWGSVQSGFL TEVHLDGQPFLRCDRQKCRA | 4 | 66 | Outside | 0.04288 |
| 2 | RMTLAHI | 97 | 103 | Inside | 0.66097 |
| 3 | EGLHSLQEIRVCEI | 108 | 121 | Outside | 0.25679 |
| 4 | SSQHFYYDGELFLSQ | 129 | 143 | Outside | 0.21811 |
| 5 | KTHYHAMHADCLQELRR | 177 | 193 | Inside | 0.76815 |
| 6 | LKSGVVLRR | 195 | 203 | Inside | 0.56129 |
| 7 | VPPMVNV | 205 | 211 | Outside | 0.25411 |
| 8 | ITVTCRASG | 221 | 229 | Inside | 0.73449 |
| 9 | DGVSLSH | 242 | 248 | Outside | 0.17761 |
| 10 | YQTWVATRICQ | 264 | 274 | Inside | 0.87917 |
| 11 | QRFTCYM | 278 | 284 | Inside | 0.79020 |
| 12 | STHPVPSGKVLVLQSHWQTFHVSAVAAAAIFVIIIFYVRCCKK | 291 | 333 | Transmembrane | 0.00369 |
| 13 | EGPELVSLQVLDQHPVGT | 339 | 356 | Outside | 0.07341 |
| 14 | TQLGFQPLMS | 363 | 372 | Outside | 0.17418 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adekiya, T.A.; Aruleba, R.T.; Khanyile, S.; Masamba, P.; Oyinloye, B.E.; Kappo, A.P. Structural Analysis and Epitope Prediction of MHC Class-1-Chain Related Protein-A for Cancer Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2018, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010001
Adekiya TA, Aruleba RT, Khanyile S, Masamba P, Oyinloye BE, Kappo AP. Structural Analysis and Epitope Prediction of MHC Class-1-Chain Related Protein-A for Cancer Vaccine Development. Vaccines. 2018; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdekiya, Tayo Alex, Raphael Taiwo Aruleba, Sbonelo Khanyile, Priscilla Masamba, Babatunji Emmanuel Oyinloye, and Abidemi Paul Kappo. 2018. "Structural Analysis and Epitope Prediction of MHC Class-1-Chain Related Protein-A for Cancer Vaccine Development" Vaccines 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010001
APA StyleAdekiya, T. A., Aruleba, R. T., Khanyile, S., Masamba, P., Oyinloye, B. E., & Kappo, A. P. (2018). Structural Analysis and Epitope Prediction of MHC Class-1-Chain Related Protein-A for Cancer Vaccine Development. Vaccines, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines6010001