The Impact of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Vaccination and Mycobacterium bovis Infection on Diagnostic Antibody Tests for Mycobacterial Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Protocol
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Skin Testing
2.4. Serum Collection
2.5. IDEXX M. Bovis Antibody Test
- (sample OD minus mean negative plate control OD)
- (mean positive plate control OD minus mean negative plate control OD)
2.6. IDEXX MAP Antibody Test
- (sample OD minus mean negative plate control OD) × 100
- (mean positive plate control OD minus mean negative plate control OD)
2.7. Enferplex TB Antibody Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
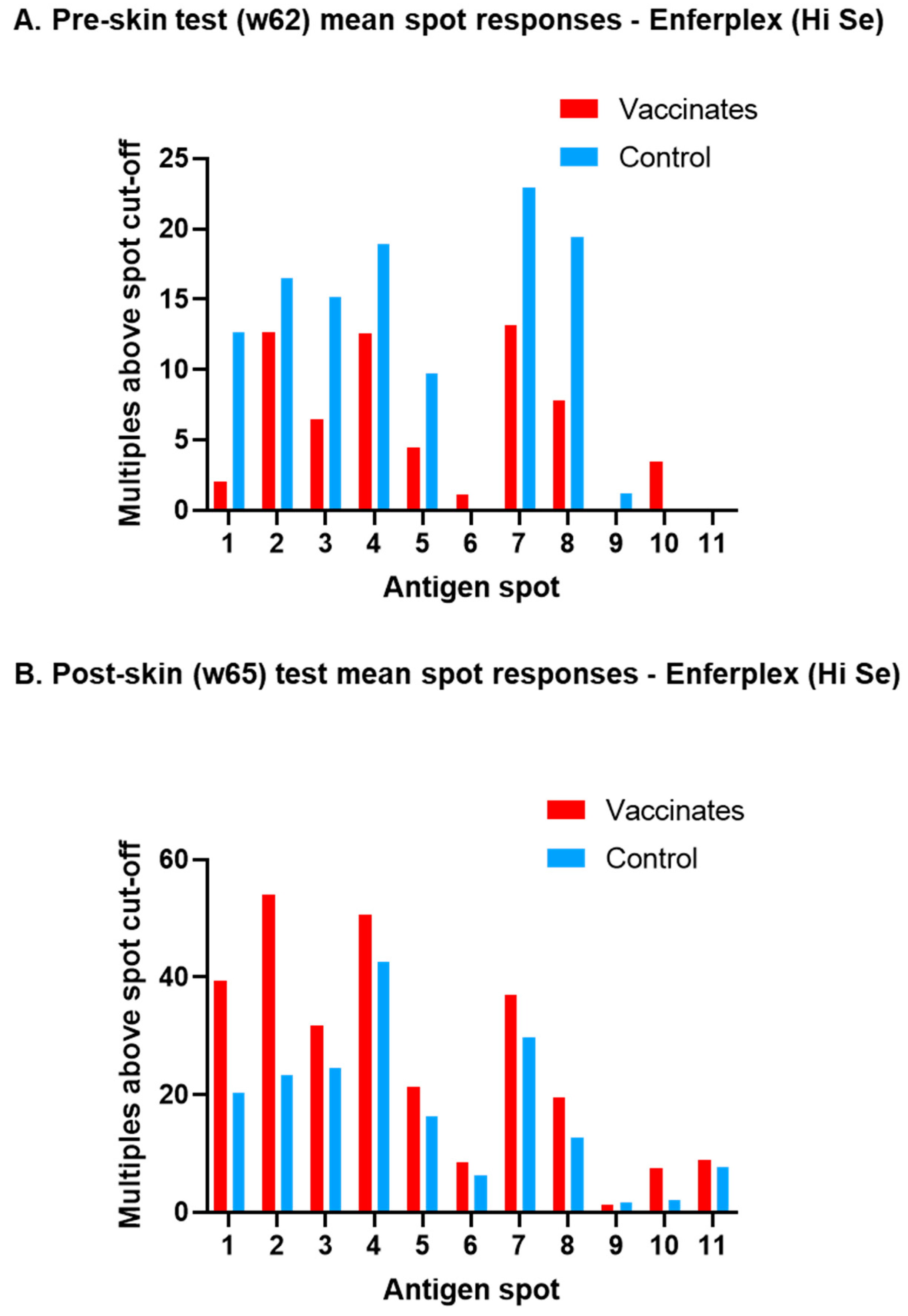
3.1. M. bovis-Specific Antibody Responses
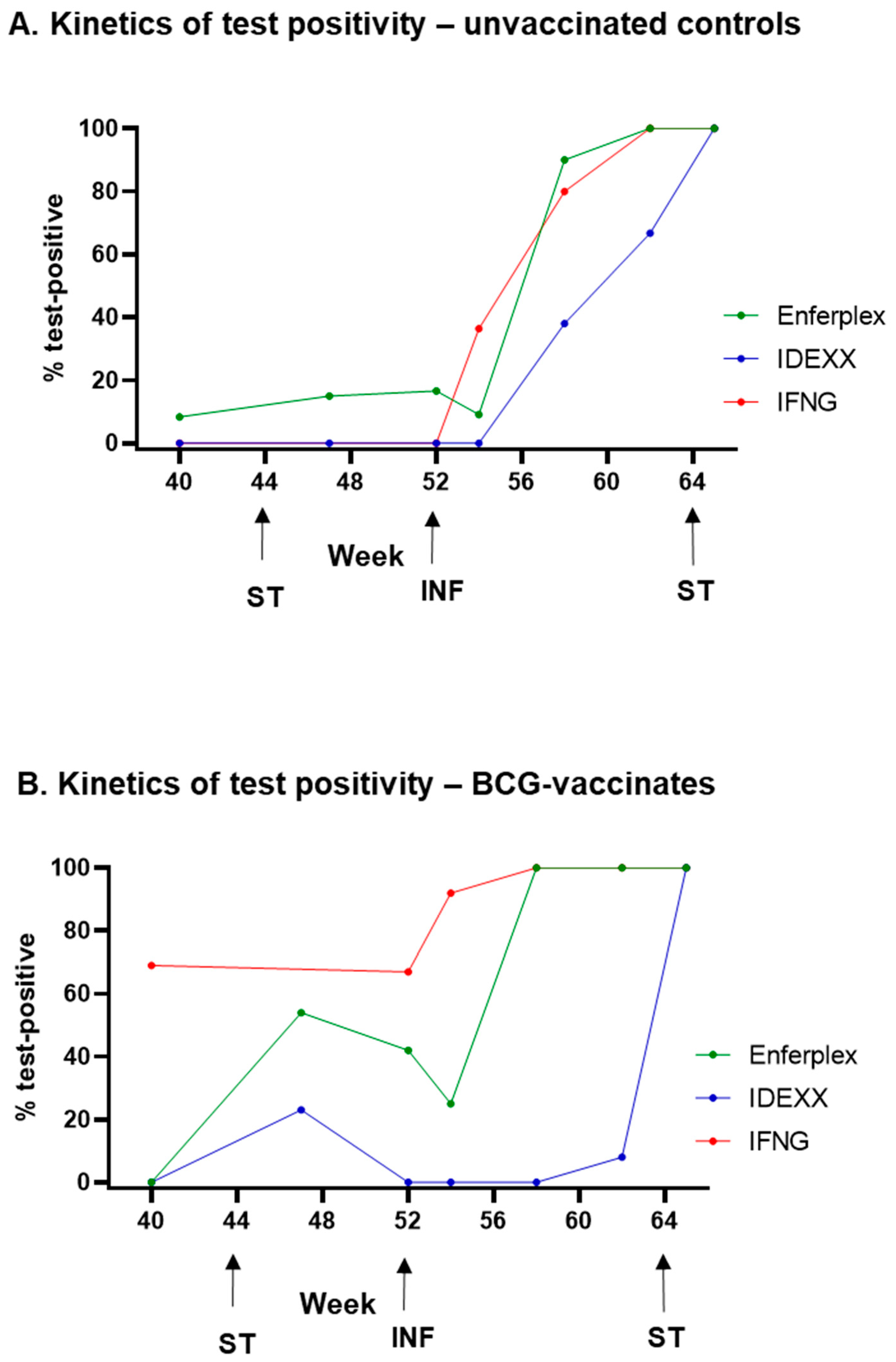
3.2. Post-Infection Antibody Versus Interferon-Gamma Test Kinetics
3.3. M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) Antibody Test Cross-Reactivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sawyer, J.; Rhodes, S.; Jones, G.J.; Hogarth, P.J.; Vordermeier, H.M. Mycobacterium bovis and its impact on human and animal tuberculosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 001769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, B.; Pereira, A.C.; Reis, A.C.; Cunha, M.V. Estimates of the global and continental burden of animal tuberculosis in key livestock species worldwide: A meta-analysis study. One Health 2020, 10, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, W.R.; Palmer, M.V.; Buddle, B.M.; Vordermeier, H.M. Bovine tuberculosis vaccine research: Historical perspectives and recent advances. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosivi, O.; Grange, J.M.; Daborn, C.J.; Raviglione, M.C.; Fujikura, T.; Cousins, D.; Robinson, R.A.; Huchzermeyer, H.F.; de Kantor, I.; Meslin, F.X. Zoonotic tuberculosis due to Mycobacterium bovis in developing countries. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemal, J.; Sibhat, B.; Abraham, A.; Terefe, Y.; Tulu, K.T.; Welay, K.; Getahun, N. Bovine tuberculosis in eastern Ethiopia: Prevalence, risk factors and its public health importance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Lago, L.; Navarro, Y.; Garcia-de-Viedma, D. Current knowledge and pending challenges in zoonosis caused by Mycobacterium bovis: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, S94–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, C.; Donnelly, C.; Hewinson, G.; Winter, M.; Wood, J. Bovine TB Strategy Review; Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Casal, C.; Infantes, J.A.; Risalde, M.A.; Diez-Guerrier, A.; Dominguez, M.; Moreno, I.; Romero, B.; de Juan, L.; Saez, J.L.; Juste, R.; et al. Antibody detection tests improve the sensitivity of tuberculosis diagnosis in cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 112, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, C.; Diez-Guerrier, A.; Alvarez, J.; Rodriguez-Campos, S.; Mateos, A.; Linscott, R.; Martel, E.; Lawrence, J.C.; Whelan, C.; Clarke, J.; et al. Strategic use of serology for the diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis after intradermal skin testing. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, W.R.; Palmer, M.V.; Stafne, M.R.; Bass, K.E.; Maggioli, M.F.; Thacker, T.C.; Linscott, R.; Lawrence, J.C.; Nelson, J.T.; Esfandiari, J.; et al. Effects of Serial Skin Testing with Purified Protein Derivative on the Level and Quality of Antibodies to Complex and Defined Antigens in Mycobacterium bovis-Infected Cattle. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, W.R.; Palmer, M.V.; Thacker, T.C.; Bannantine, J.P.; Vordermeier, H.M.; Hewinson, R.G.; Greenwald, R.; Esfandiari, J.; McNair, J.; Pollock, J.M.; et al. Early Antibody Responses to Experimental Mycobacterium bovis Infection of Cattle. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, A.J.; Brooks Pollock, E.; McKinley, T.J.; Mitchell, A.P.; Jones, G.J.; Vordermeier, M.; Wood, J.L. Potential benefits of cattle vaccination as a supplementary control for bovine tuberculosis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, A.O.; Coad, M.; Upadhyay, B.L.; Clifford, D.J.; Hewinson, R.G.; Vordermeier, H.M. Lack of correlation between BCG-induced tuberculin skin test sensitisation and protective immunity in cattle. Vaccine 2011, 29, 5453–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.J.; Konold, T.; Hurley, S.; Holder, T.; Steinbach, S.; Coad, M.; Neil Wedlock, D.; Buddle, B.M.; Singh, M.; Martin Vordermeier, H. Test performance data demonstrates utility of a cattle DIVA skin test reagent (DST-F) compatible with BCG vaccination. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyashchenko, K.; Whelan, A.O.; Greenwald, R.; Pollock, J.M.; Andersen, P.; Hewinson, R.G.; Vordermeier, H.M. Association of tuberculin-boosted antibody responses with pathology and cell-mediated immunity in cattle vaccinated with Mycobacterium bovis BCG and infected with M. bovis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2462–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nol, P.; Palmer, M.V.; Waters, W.R.; Aldwell, F.E.; Buddle, B.M.; Triantis, J.M.; Linke, L.M.; Phillips, G.E.; Thacker, T.C.; Rhyan, J.C.; et al. Efficacy of oral and parenteral routes of Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccination against experimental bovine tuberculosis in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus): A feasibility study. J. Wildl. Dis. 2008, 44, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, C.; Whelan, A.O.; Shuralev, E.; Kwok, H.F.; Hewinson, G.; Clarke, J.; Vordermeier, H.M. Performance of the Enferplex TB assay with cattle in Great Britain and assessment of its suitability as a test to distinguish infected and vaccinated animals. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.; Donat, K.; Weber, M.F.; Kelton, D.; Nielsen, S.S.; Eisenberg, S.; Arrigoni, N.; Juste, R.; Saez, J.L.; Dhand, N.; et al. Control of paratuberculosis: Who, why and how. A review of 48 countries. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didkowska, A.; Krajewska-Wedzina, M.; Klich, D.; Prolejko, K.; Orlowska, B.; Anusz, K. The Risk of False-Positive Serological Results for Paratuberculosis in Mycobacterium bovis-Infected Cattle. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilenbaum, W.; Marassi, C.D.; Varges, R.; Medeiros, L.; Oelemann, W.M.; Fonseca, L.S. Occurrence of false-positive results in three paratuberculosis-ELISAs performed in a tuberculous herd. Vet. Res. Commun. 2009, 33, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, I.; Tryland, M.; Wiker, H.G.; Reitan, L.J. AhpC, AhpD, and a secreted 14-kilodalton antigen from Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis distinguish between paratuberculosis and bovine tuberculosis in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, T.; Coad, M.; Allan, G.; Hogarth, P.J.; Vordermeier, H.M.; Jones, G.J. Vaccination of calves with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Danish strain 1331 results in a duration of immunity of at least 52 weeks. Vaccine 2023, 41, 7290–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, W.R.; Buddle, B.M.; Vordermeier, H.M.; Gormley, E.; Palmer, M.V.; Thacker, T.C.; Bannantine, J.P.; Stabel, J.R.; Linscott, R.; Martel, E.; et al. Development and Evaluation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Use in the Detection of Bovine Tuberculosis in Cattle. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, A.; Clarke, J.; Hayton, A.; Adler, A.; Cutler, K.; Shaw, D.J.; Whelan, C.; Watt, N.J.; Harkiss, G.D. Diagnostic accuracy of the Enferplex Bovine Tuberculosis antibody test in cattle sera. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, M.; Morgan, J.H.; Hope, J.C.; Villarreal-Ramos, B.; Martin, M.; Howard, C.J. The effect of repeated tuberculin skin testing of cattle on immune responses and disease following experimental infection with Mycobacterium bovis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 102, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A.W.; Graham, J.; Milne, G.; Guelbenzu-Gonzalo, M.; Strain, S. Is There a Relationship Between Bovine Tuberculosis (bTB) Herd Breakdown Risk and Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Status? An Investigation in bTB Chronically and Non-chronically Infected Herds. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
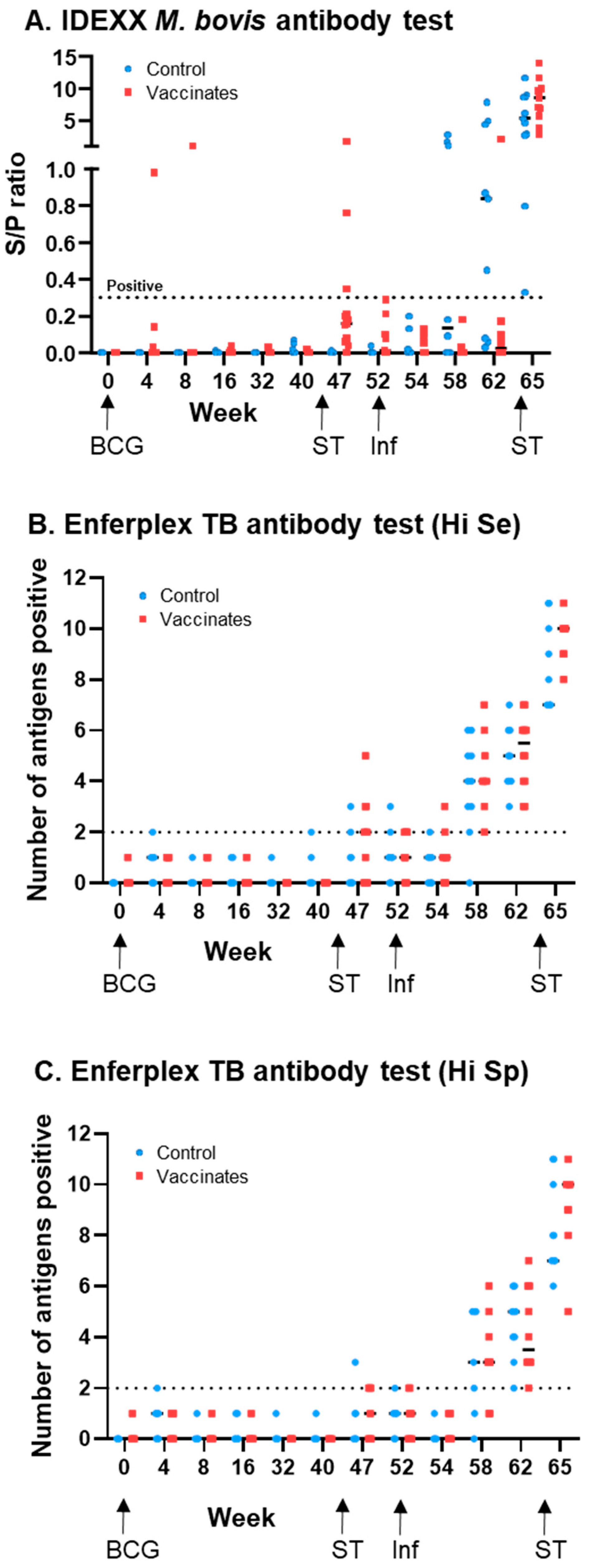

| M. bovis IDEXX: % Positive (Number Positive/Total) | M. bovis Enferplex (Hi Se): % Positive (Number Positive/Total) | M. bovis Enferplex (Hi Sp): % Positive (Number Positive/Total) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week | Control Group | BCG Group | Control Group | BCG Group | Control Group | BCG Group |
| 0 | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) |
| 4 | 0 (0/14) | 7 (1/14) | 7 (1/14) | 0 (0/14) | 7 (1/14) | 0 (0/14) |
| 8 | 0 (0/13) | 8 (1/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/14) |
| 16 | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) |
| 32 | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) |
| 40 | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) | 8 (1/12) | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/12) | 0 (0/13) |
| 47 | 0(0/13) | 23 (3/13) | 15 (2/13) | 54 (7/13) | 8 (1/13) | 38 (5/13) |
| 52 | 0 (0/12) | 0 (0/11) | 17 (2/12) | 42 (5/12) | 8 (1/12) | 25 (3/12) |
| 54 | 0 (0/11) | 0 (0/12) | 9 (1/11) | 25 (3/12) | 0 (0/11) | 0 (0/12) |
| 58 | 38 (3/8) | 0 (0/12) | 90 (9/10) | 100 (12/12) | 70 (7/10) | 75 (9/12) |
| 62 | 67 (6/9) | 8 (1/12) | 100 (9/9) | 100 (12/12) | 100 (9/9) | 100 (12/12) |
| 65 | 100 (11/11) | 100 (11/11) | 100 (11/11) | 100 (11/11) | 100 (11/11) | 100 (11/11) |
| Median S/P Ratio (%) [95% CI of the Median] | Test Outcome % Positive (Number Positive/Total Tested) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week | Control Group | BCG Group | Control Group | BCG Group |
| 0 | 5.5 [4, 11] | 3.5 [2, 6] | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) |
| 4 | 7.5 [4, 16] | 12.5 [9, 17] * | 0 (0/14) | 0 (0/14) |
| 8 | 9 [5, 11] | 13 [6, 33] ** | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/14) |
| 16 | 6 [4, 8] | 8 [5, 14] | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/14) |
| 32 | 5 [4, 12] | 7 [4, 12] | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) |
| 40 | 7 [5, 9] | 8 [5, 12] | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) |
| 47 | 10 [5, 13] | 23 [9, 31] ** | 0 (0/13) | 0 (0/13) |
| 52 | 8 [8, 14] | 15 [6, 20] * | 0 (0/12) | 0 (0/11) |
| 54 | 12 [9, 25] * | 16.5 [10, 24] *** | 0 (0/11) | 0 (0/12) |
| 58 | 64.5 [12, 157] *** | 49.5 [22, 69] **** | 50 (4/8) | 42 (5/12) |
| 62 | 141 [92, 197] **** | 64 [31, 114] **** | 89 (8/9) | 50 (6/12) |
| 65 | 131 [47, 208] **** | 71 [24, 120] **** | 82 (9/11) | 64 (7/11) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holder, T.; Robinson, N.; Jones, G.J. The Impact of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Vaccination and Mycobacterium bovis Infection on Diagnostic Antibody Tests for Mycobacterial Infections. Vaccines 2025, 13, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060578
Holder T, Robinson N, Jones GJ. The Impact of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Vaccination and Mycobacterium bovis Infection on Diagnostic Antibody Tests for Mycobacterial Infections. Vaccines. 2025; 13(6):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060578
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolder, Thomas, Nick Robinson, and Gareth J. Jones. 2025. "The Impact of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Vaccination and Mycobacterium bovis Infection on Diagnostic Antibody Tests for Mycobacterial Infections" Vaccines 13, no. 6: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060578
APA StyleHolder, T., Robinson, N., & Jones, G. J. (2025). The Impact of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Vaccination and Mycobacterium bovis Infection on Diagnostic Antibody Tests for Mycobacterial Infections. Vaccines, 13(6), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060578








