Genetic Sequencing of a Bacterial Pneumonia Vaccine Produced in 1916
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Isolation
2.2. Real-Time PCR
2.3. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
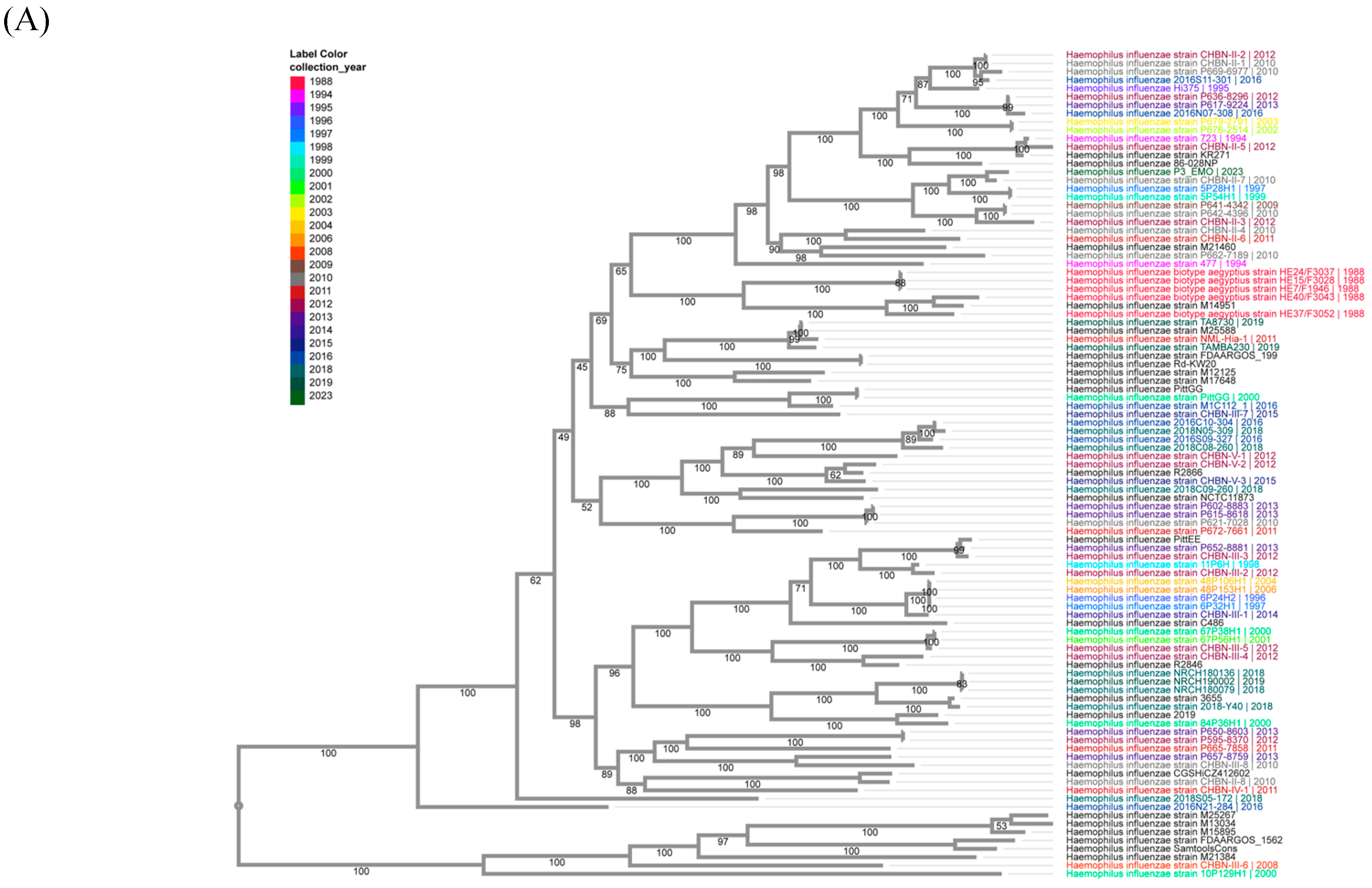
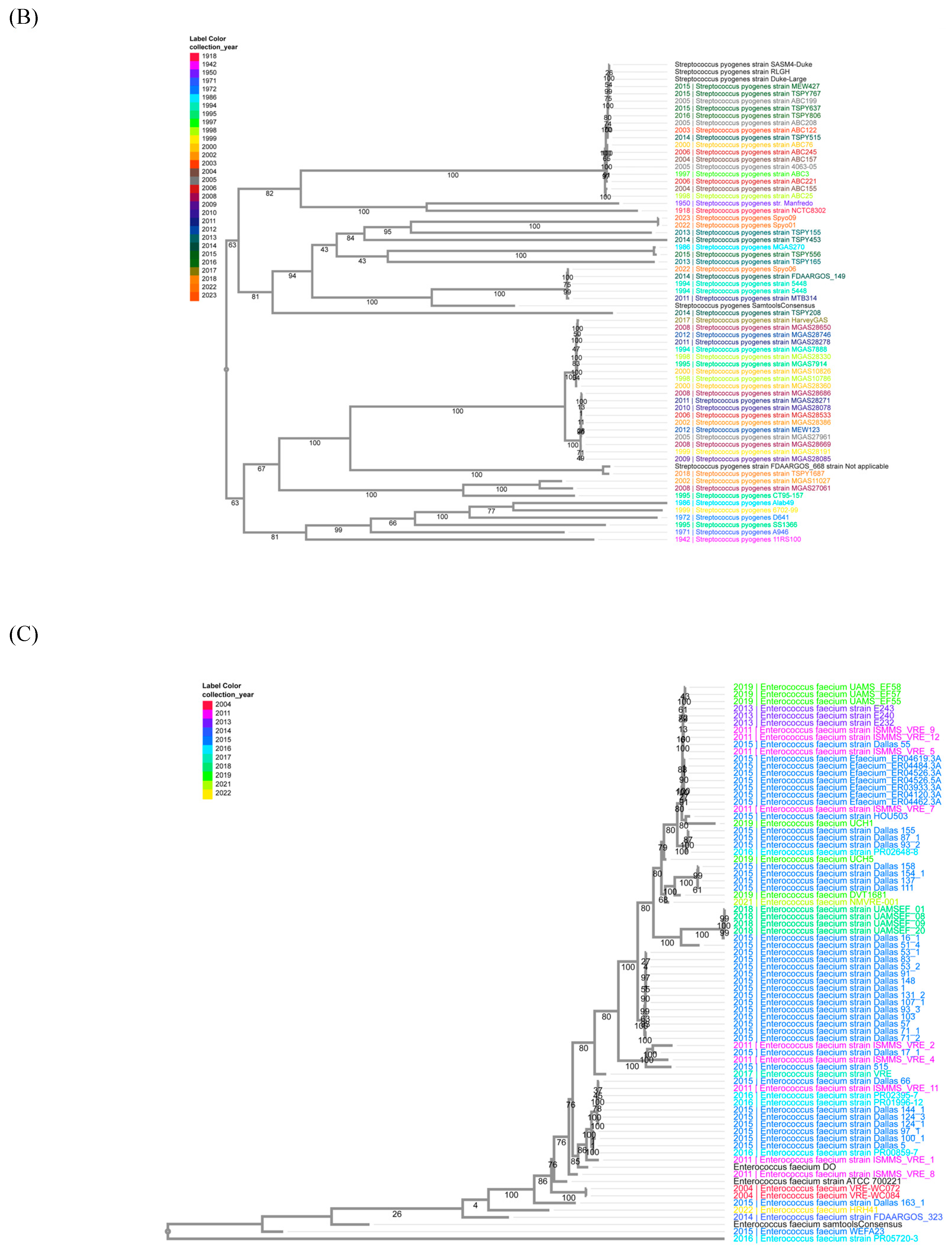
2.5. Phylogenetic Trees
3. Results
3.1. DNA Recovery
3.2. Illumina Sequencing
3.3. Sequence Alignment to the Three Bacterial Reference Genomes
3.4. Identifying the Best-Aligned Species from the H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, and S. pyogenes Genomes
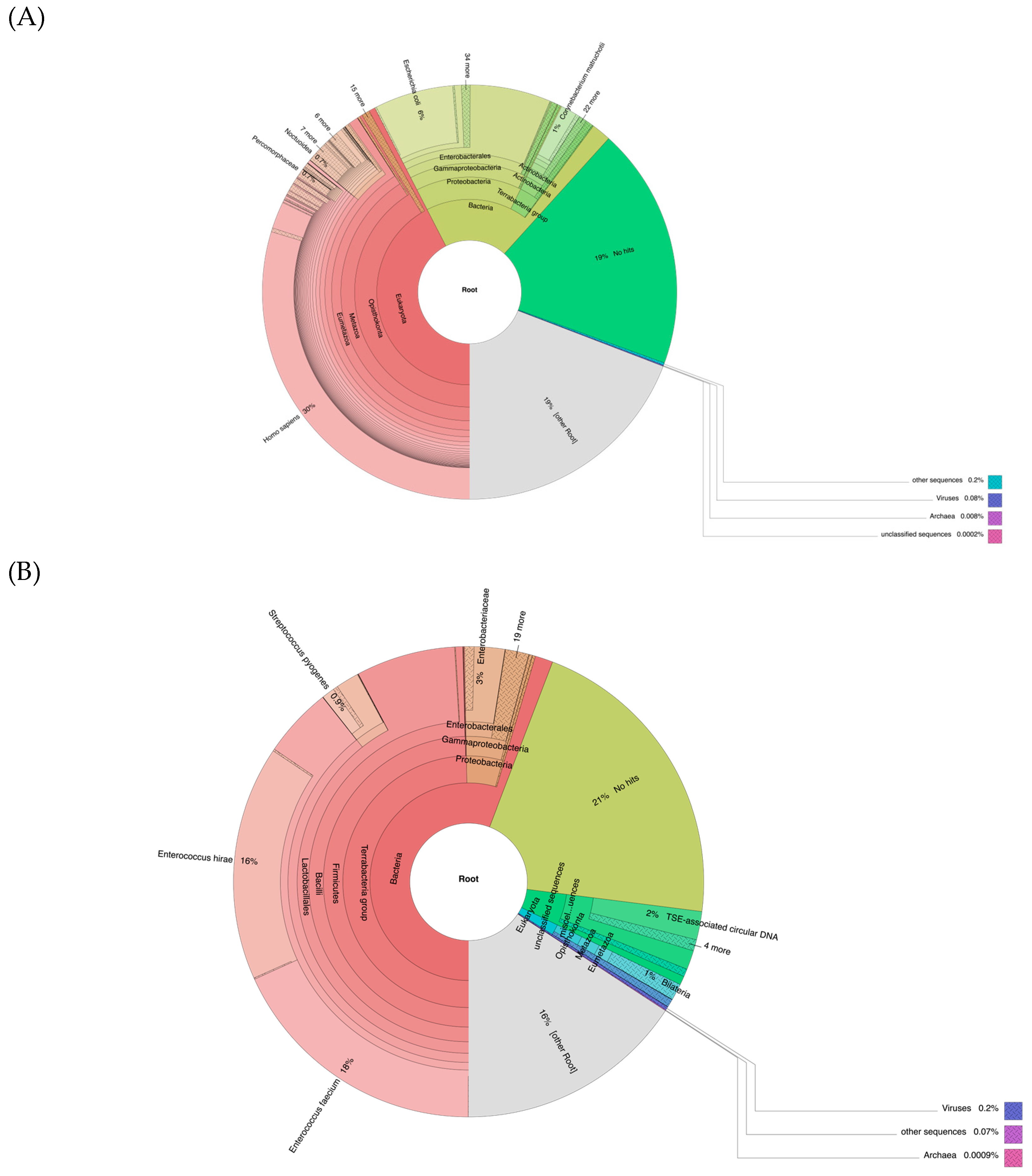
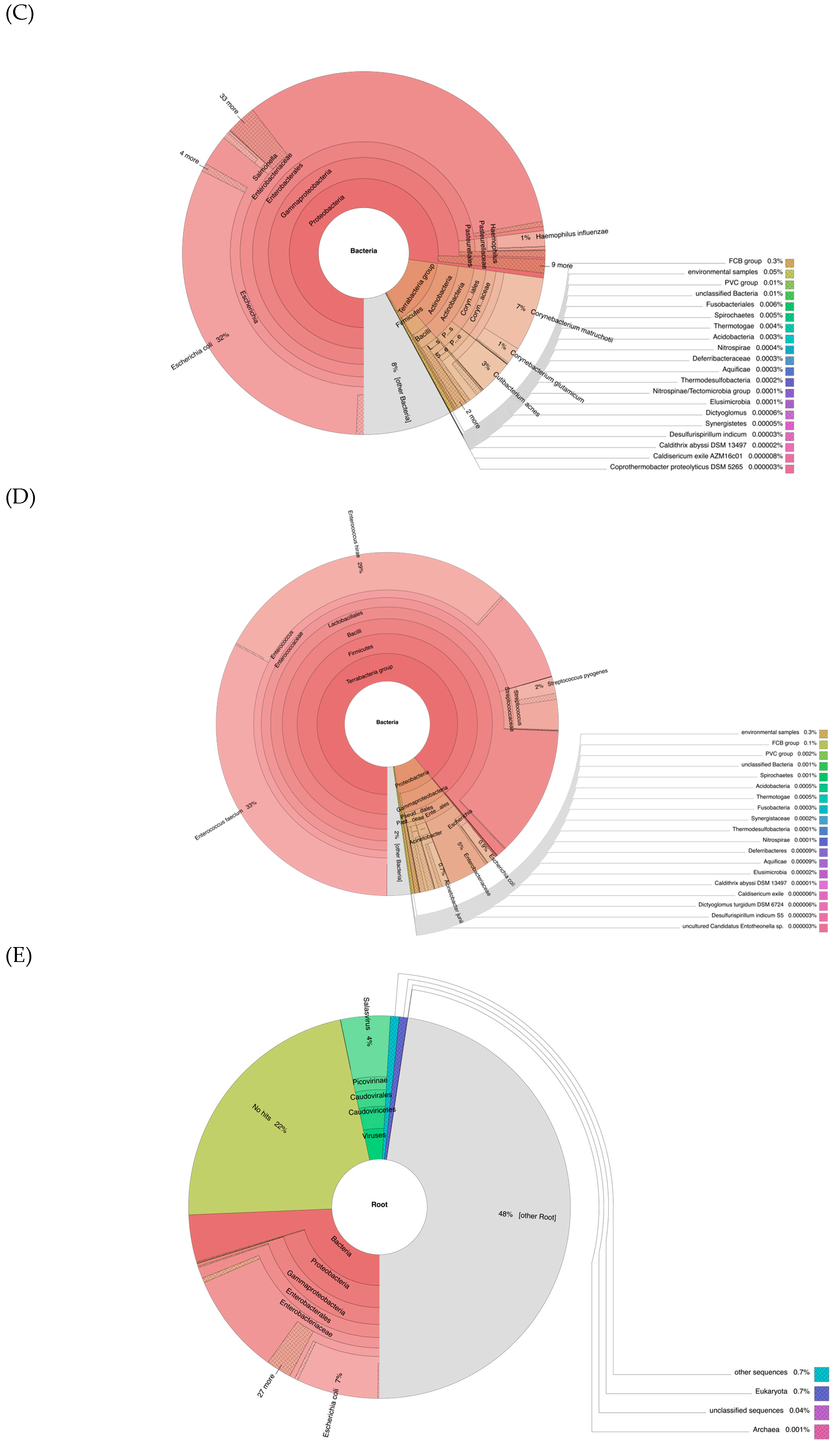
3.5. Metagenomic Analyses
3.6. Sequence Alignment to Enterococcus faecium from the Data of the Second Ampule
3.7. Consensus Sequences of H. influenzae, S. pyogenes, and E. faecium in Vaccine
4. Discussion
4.1. Serotypes of Consensus Genomes Obtained
4.2. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Profiles in Obtained Bacterial Strains
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasteur, L. Sur les maladies virulentes et en particulier sur la maladie appelée vulgairement «choléra des poules». Recl. Méd. Vet. 1880, 57, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A. Louis pasteur, the father of immunology? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.N.K. The Nobel Chronicles. Lancet 1998, 352, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.; Morgan, W.P.; Colebrook, L.; Dodgson, R.W. Observations on prophylactic inoculation against pneumococcus infections, and on the results which have been achieved by it. Lancet 1914, 183, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabenstein, J.D.; Klugman, K.P. A century of pneumococcal vaccination research in humans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18 (Suppl. S5), 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyler, J.M. The state of science, microbiology, and vaccines circa 1918. Public Health Rep. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S3), 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, J.J. The prevailing pandemic of influenza. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1918, 71, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.O. Observations on the Bacteriology of Influenza. J. Infect. Dis. 1919, 25, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzum, J.W.; Pilot, I.; Stangl, F.H.; Bonar, B.E. Pandemic influenza and pneumonia in a large civil hospital. JAMA 1918, 71, 1562–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.J. The Bacteriology of Influenza. Proc. Inst. Med. Path. 1919, 2, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Fauci, A.S. Predominant role of bacterial pneumonia as a cause of death in pandemic influenza: Implications for pandemic influenza preparedness. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.H. Bacteriology and Possibility of Antiinfluenza Vaccine as a Prophylactic; A.R. Elliott Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1918. [Google Scholar]
- Duval, C.W.; Harris, W.H. The antigenic property of the Pfeiffer bacillus as related to its value in the prophylaxis of epidemic influenza. J. Immunol. 1919, 4, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haythorn, S. Studies on Epidemic Influenza Comprising Clinical and Laboratory Investigations by Members of the Faculty of the School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; University of Pittsburgh Medical School: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1919; pp. 97–153. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, Y.W.; Klugman, K.P.; Morens, D.M. Efficacy of whole-cell killed bacterial vaccines in preventing pneumonia and death during the 1918 influenza pandemic. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaker, A.J.; Irvine, R.S. Prophylactic use of mixed vaccine against pandemic influenza and its complications: At the naval training station, San Francisco. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1919, 72, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyler, J.M. The fog of research: Influenza vaccine trials during the 1918-19 pandemic. J. Hist. Med. Allied. Sci. 2009, 64, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenow, E.; Sturdivant, B. Studies in Influenza and Pneumonia: IV. Further Results of Prophylactic Inoculations. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1919, 73, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, D.T. The Efficiency of Bacterial Vaccines on Mortality during the ’Spanish’ Influenza Pandemic of 1918-19. Soc. Hist. Med. 2023, 36, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, E.O.; Sharp, W. Influenza studies: IV. Effect of vaccination against influenza and some other respiratory infections. J. Infect. Dis. 1921, 28, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, T.; Salk, J.E.; Pearson, H.E.; Brown, P.N. Protective Effect of Vaccination against Induced Influenza A. J. Clin. Investig. 1945, 24, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Genome Project Data Processing, S. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Zhang, Q.; Larson, D.E.; Shen, D.; McLellan, M.D.; Lin, L.; Miller, C.A.; Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Wilson, R.K. VarScan 2: Somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, N.; Doster, E.; Worley, H.; Pinnell, L.J.; Bravo, J.E.; Ferm, P.; Marini, S.; Prosperi, M.; Noyes, N.; Morley, P.S.; et al. MEGARes and AMR++, v3.0: An updated comprehensive database of antimicrobial resistance determinants and an improved software pipeline for classification using high-throughput sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D744–D752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.C.; Holt, K.E. hicap: In Silico Serotyping of the Haemophilus influenzae Capsule Locus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdicek, M.; Hanslikova, J.; Nykrynova, M.; Dufkova, K.; Kocmanova, I.; Kubackova, P.; Mayer, J.; Lengerova, M. New Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Enterococcus faecium Based on Whole Genome Sequencing Data. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0510722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.J.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Shukla, M.; Vonstein, V.; Wattam, A.R.; Yoo, H. PATtyFams: Protein Families for the Microbial Genomes in the PATRIC Database. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.; Antao, T.; Chang, J.T.; Chapman, B.A.; Cox, C.J.; Dalke, A.; Friedberg, I.; Hamelryck, T.; Kauff, F.; Wilczynski, B.; et al. Biopython: Freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homan, W.L.; Tribe, D.; Poznanski, S.; Li, M.; Hogg, G.; Spalburg, E.; Van Embden, J.D.; Willems, R.J. Multilocus sequence typing scheme for Enterococcus faecium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M. Steroid Medicines and Upjohn: A Profile of Chemical Innovation. 2019. Available online: https://www.acs.org/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/upjohn-steroid-medicines.html#:~:text=The%20company%20was%20founded%20in,and%20therefore%20being%20easily%20digested (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- Barry, J.M. The Great Influenza: The Epic Story of the Deadliest Plague in History; Penguin Books: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schrick, L.; Tausch, S.H.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Damaso, C.R.; Esparza, J.; Nitsche, A. An Early American Smallpox Vaccine Based on Horsepox. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1491–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, A.; Souza, A.R.V.; Esparza, J.; Nitsche, A.; Damaso, C.R. Re-assembly of nineteenth-century smallpox vaccine genomes reveals the contemporaneous use of horsepox and horsepox-related viruses in the USA. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Beare, P.A.; Best, S.M.; Morens, D.M.; Bloom, M.E.; Taubenberger, J.K. Genetic sequencing of a 1944 Rocky Mountain spotted fever vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezel, J.; Bartos, J.; Voglmayr, H.; Greilhuber, J. Nuclear DNA content and genome size of trout and human. Cytom. A 2003, 51, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tells of vaccine to stop influenza. The New York Times, 2 October 1918; 10.
- Pittman, M. Variation and Type Specificity in the Bacterial Species Hemophilus Influenzae. J. Exp. Med. 1931, 53, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor-Williams, G.; Frankland, J.; Isaacs, D.; Mayon-White, R.T.; MacFarlane, J.A.; Slack, M.P.; Anderson, E.; Rees, D.G.; Moxon, E.R. Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in the Oxford region. Arch. Dis. Child. 1989, 64, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, J.D.; Pierce, R.; Deaver, K.; Franklin, R.; Bosley, G.; Pigott, N.; Broome, C.V. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease: A population-based evaluation of the role of capsular polysaccharide serotype. Haemophilus Influenzae Study Group. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 165 (Suppl. S1), S34–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancefield, R.C. The Antigenic Complex of Streptococcus Haemolyticus: V. Anaphylaxis with the Type-Specific Substance. J. Exp. Med. 1928, 47, 857–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufhold, A.; Podbielski, A.; Johnson, D.R.; Kaplan, E.L.; Lutticken, R. M protein gene typing of Streptococcus pyogenes by nonradioactively labeled oligonucleotide probes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beall, B.; Facklam, R.; Thompson, T. Sequencing emm-specific PCR products for routine and accurate typing of group A streptococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facklam, R.; Beall, B.; Efstratiou, A.; Fischetti, V.; Johnson, D.; Kaplan, E.; Kriz, P.; Lovgren, M.; Martin, D.; Schwartz, B.; et al. emm typing and validation of provisional M types for group A streptococci. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.R.; Davies, M.R.; Velusamy, S.; Delforge, V.; Erhart, A.; Darboe, S.; Steer, A.; Walker, M.J.; Beall, B.; Botteaux, A.; et al. Updated emm-typing protocol for Streptococcus pyogenes. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 946.E5–946.E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeesters, P.R.; de Crombrugghe, G.; Tsoi, S.K.; Leclercq, C.; Baker, C.; Osowicki, J.; Verhoeven, C.; Botteaux, A.; Steer, A.C. Global Streptococcus pyogenes strain diversity, disease associations, and implications for vaccine development: A systematic review. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e181–e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, S.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Curren, B.F.; Harbison-Price, N.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Jespersen, M.G.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of Group A Streptococcus infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway-Pena, J.R.; Nallapareddy, S.R.; Arias, C.A.; Eliopoulos, G.M.; Murray, B.E. Analysis of clonality and antibiotic resistance among early clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, R.J.; Top, J.; van Schaik, W.; Leavis, H.; Bonten, M.; Siren, J.; Hanage, W.P.; Corander, J. Restricted gene flow among hospital subpopulations of Enterococcus faecium. mBio 2012, 3, e00151-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, F.; van Schaik, W.; McGuire, A.M.; Godfrey, P.; Griggs, A.; Mazumdar, V.; Corander, J.; Cheng, L.; Saif, S.; Young, S.; et al. Emergence of epidemic multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecium from animal and commensal strains. mBio 2013, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, M.I.; Baylay, A.J.; Wong, R.L.; Piddock, L.J. Overexpression of patA and patB, which encode ABC transporters, is associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylay, A.J.; Piddock, L.J. Clinically relevant fluoroquinolone resistance due to constitutive overexpression of the PatAB ABC transporter in Streptococcus pneumoniae is conferred by disruption of a transcriptional attenuator. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, M.; Reynolds, P.E.; Depardieu, F.; Evers, S.; Dutka-Malen, S.; Quintiliani, R., Jr.; Courvalin, P. Mechanisms of glycopeptide resistance in enterococci. J. Infect. 1996, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, M.; Wan, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Tao, X.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. Screening probiotic strains for safety: Evaluation of virulence and antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococci from healthy Chinese infants. J. Dairy. Sci. 2016, 99, 4282–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, Y.; Galimand, M.; Leclercq, R.; Duval, J.; Courvalin, P. Characterization of the chromosomal aac(6′)-Ii gene specific for Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, T.; Ogawa, W.; Kuroda, T.; Katsu, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Gene cloning and characterization of EfmA, a multidrug efflux pump, from Enterococcus faecium. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J. The importance of efflux pumps in bacterial antibiotic resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhullar, K.; Waglechner, N.; Pawlowski, A.; Koteva, K.; Banks, E.D.; Johnston, M.D.; Barton, H.A.; Wright, G.D. Antibiotic resistance is prevalent in an isolated cave microbiome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Sheng, Z.M.; Williams, S.L.; Taubenberger, J.K. Two complete 1918 influenza A/H1N1 pandemic virus genomes characterized by next-generation sequencing using RNA isolated from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded autopsy lung tissue samples along with evidence of secondary bacterial co-infection. mBio 2024, 15, e0321823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabina, J.; Leamon, J.H. Bias in Whole Genome Amplification: Causes and Considerations. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1347, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
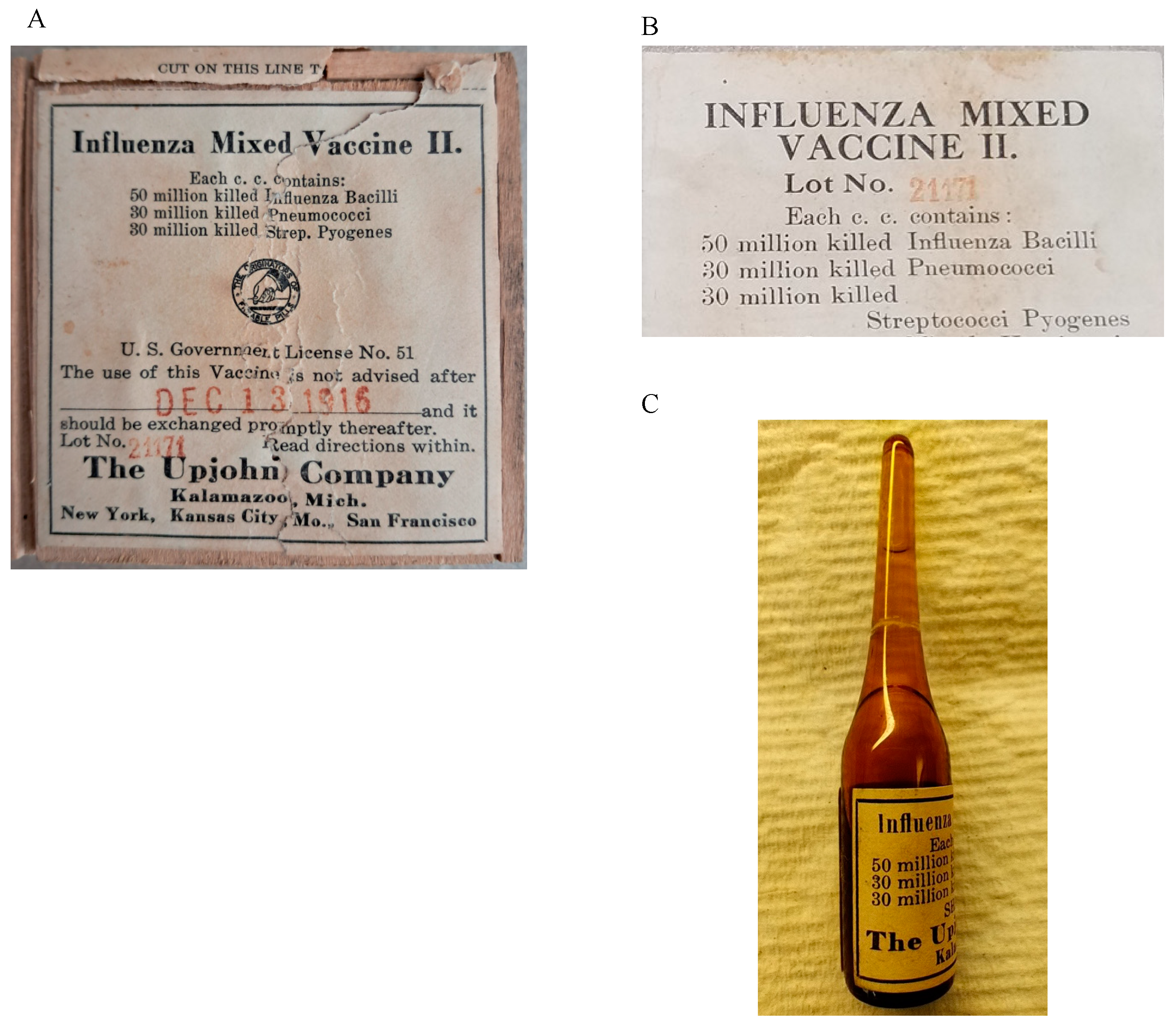

| Vaccine Vial | Sequencer | Reference Genomes | Total Reads | Reads Aligned 1 Time | Reads Aligned > 1 Time | Overall Alignment Rate | Genome Coverage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First ampule | MiSeq | H. influenzae (CP007470.1) | 22,551,907 | 34,700 | 1696 | 0.14% | 0.4916499 |
| S. pneumoniae (CP020549.1) | 22,551,907 | 2256 | 34 | 0.01% | 0.0173710 | ||
| S. pyogenes (LS483338.1) | 22,551,907 | 14,483 | 1079 | 0.06% | 0.0775702 | ||
| NextSeq | H. influenzae (CP007470.1) | 517,835,296 | 665,650 | 27,100 | 0.13% | 0.9324558 | |
| S. pneumoniae (CP020549.1) | 517,835,296 | 46,512 | 570 | 0.01% | 0.0586087 | ||
| S. pyogenes (LS483338.1) | 517,835,296 | 223,372 | 11,997 | 0.05% | 0.5378864 | ||
| Second ampule | MiSeq | H. influenzae (CP007470.1) | 15,368,293 | 47,655 | 18,466 | 0.43% | 0.0455131 |
| S. pneumoniae (CP020549.1) | 15,368,293 | 78,295 | 76 | 0.51% | 0.0115521 | ||
| S. pyogenes (LS483338.1) | 15,368,293 | 144,894 | 76,102 | 1.44% | 0.2916496 | ||
| NextSeq | H. influenzae (CP007470.1) | 416,537,815 | 1,303,480 | 489,618 | 0.43% | 0.4993817 | |
| S. pneumoniae (CP020549.1) | 416,537,815 | 2,119,681 | 2036 | 0.51% | 0.0461191 | ||
| S. pyogenes (LS483338.1) | 416,537,815 | 3,873,131 | 2,060,507 | 1.42% | 0.9377816 | ||
| Negative control | MiSeq | H. influenzae (CP007470.1) | 10,199,050 | 45 | 612 | 0.01% | 0.0007859 |
| S. pneumoniae (CP020549.1) | 10,199,050 | 26 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.0004585 | ||
| S. pyogenes (LS483338.1) | 10,199,050 | 44 | 28 | 0.00% | 0.0017173 |
| Consensus Genomes | Start | Stop | Orientation | Model Type | Drug Class | Resistance Mechanism | AMR Gene Family |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. influenzae | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| S. pyogenes | 202,711 | 204,495 | + | protein homolog model | fluoroquinolone antibiotic | antibiotic efflux | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump |
| 1,370,493 | 1,371,236 | - | protein homolog model | glycopeptide antibiotic | antibiotic target alteration | vanY; glycopeptide resistance gene cluster | |
| E. faecium | 99,816 | 100,640 | - | protein homolog model | glycopeptide antibiotic | antibiotic target alteration | vanY; glycopeptide resistance gene cluster |
| 472,276 | 472,938 | - | protein homolog model | glycopeptide antibiotic | antibiotic target alteration | vanY; glycopeptide resistance gene cluster | |
| 630,791 | 631,339 | - | protein homolog model | aminoglycoside antibiotic | antibiotic inactivation | AAC(6′) | |
| 1,624,902 | 1,626,188 | + | protein homolog model | macrolide antibiotic; fluoroquinolone antibiotic | antibiotic efflux | major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump |
| ST | copA | dnaE | HP2027 | mdlA | narB | pbp2B | rpoD | uvrA | Clonal_Complex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 422 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | CC89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Gygli, S.M.; Steen, T.Y.; Taubenberger, J.K. Genetic Sequencing of a Bacterial Pneumonia Vaccine Produced in 1916. Vaccines 2025, 13, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050491
Xiao Y, Gygli SM, Steen TY, Taubenberger JK. Genetic Sequencing of a Bacterial Pneumonia Vaccine Produced in 1916. Vaccines. 2025; 13(5):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050491
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yongli, Sebastian M. Gygli, Tomoko Y. Steen, and Jeffery K. Taubenberger. 2025. "Genetic Sequencing of a Bacterial Pneumonia Vaccine Produced in 1916" Vaccines 13, no. 5: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050491
APA StyleXiao, Y., Gygli, S. M., Steen, T. Y., & Taubenberger, J. K. (2025). Genetic Sequencing of a Bacterial Pneumonia Vaccine Produced in 1916. Vaccines, 13(5), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050491






