Application of Humanized MHC Transgenic Mice in the Screening of HLA–Restricted T Cell Epitopes for Influenza Vaccines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval of the A/California/07/2009 (H1N1) Genes
2.2. Bioinformatic Prediction Strategy for T Cell Epitopes Derived from the IAV
2.3. Peptides
2.4. Mice and Ethical Approval
2.5. Influenza Virus Infection
2.6. Spleen Single-Cell Preparation
2.7. ELISpot Assay
2.8. Antibody Detection
2.9. Mouse Immunization and the Viral Challenge
2.10. Titration of Influenza Virus in the Lungs of Mice
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
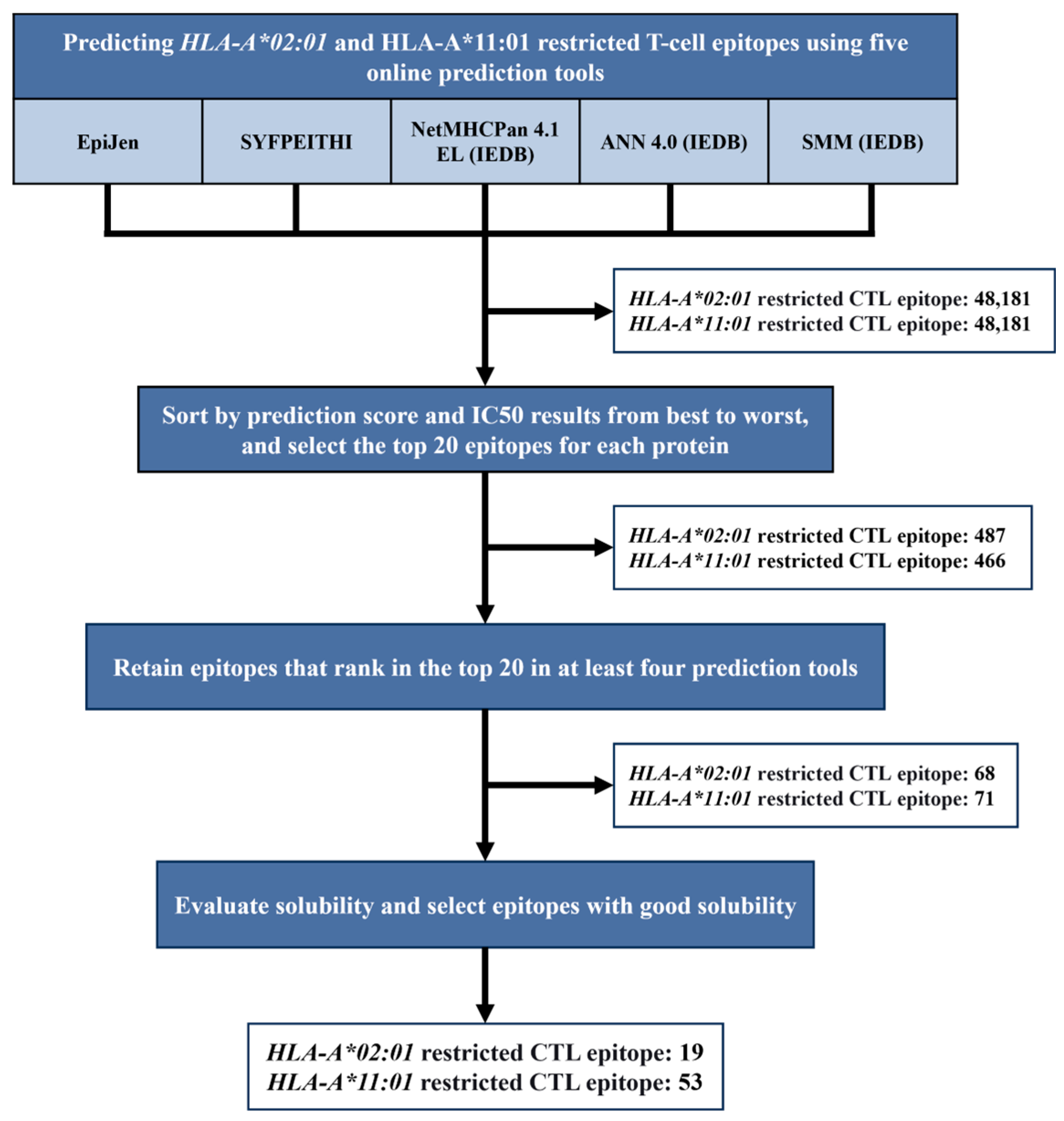
3.1. Epitope Prediction and Screening
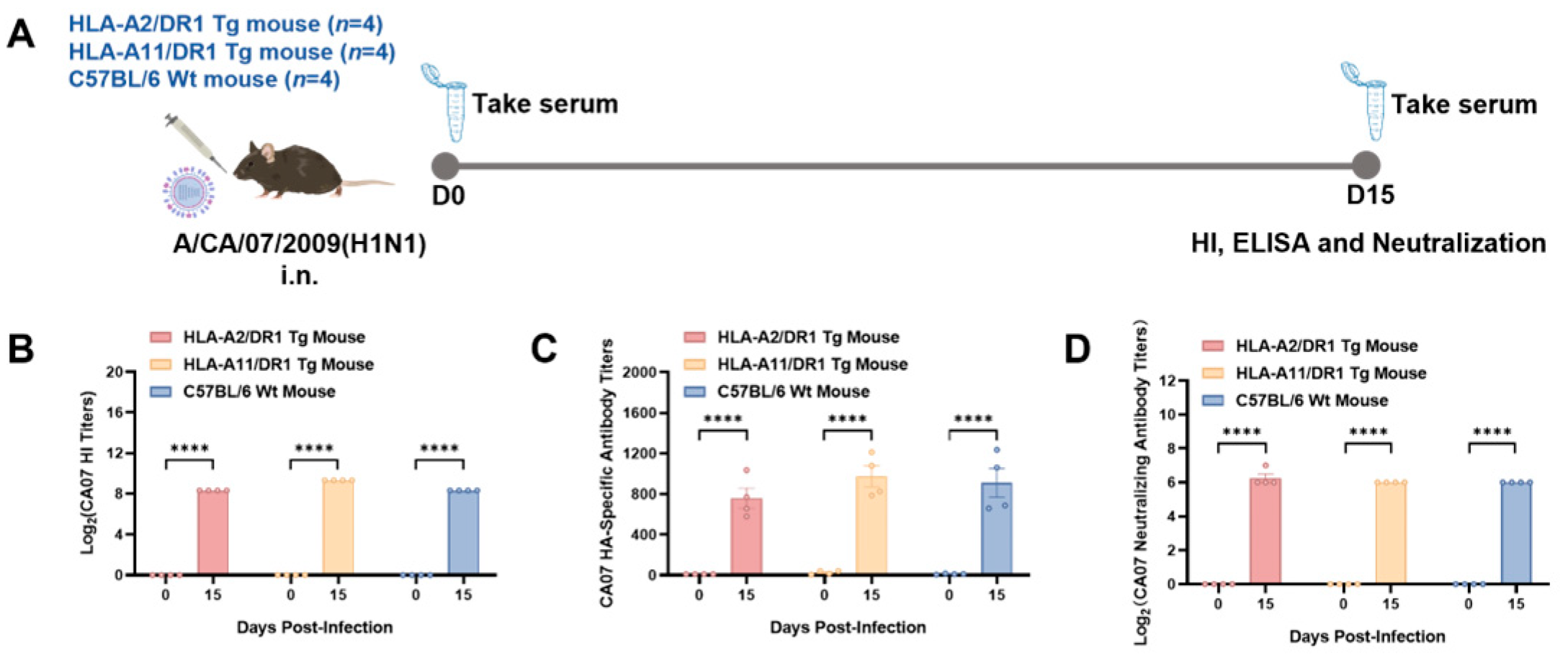
3.2. HLA-A2/DR1 and HLA-A11/DR1 Mice Can Generate Humoral Immune Responses After Influenza Virus Infection
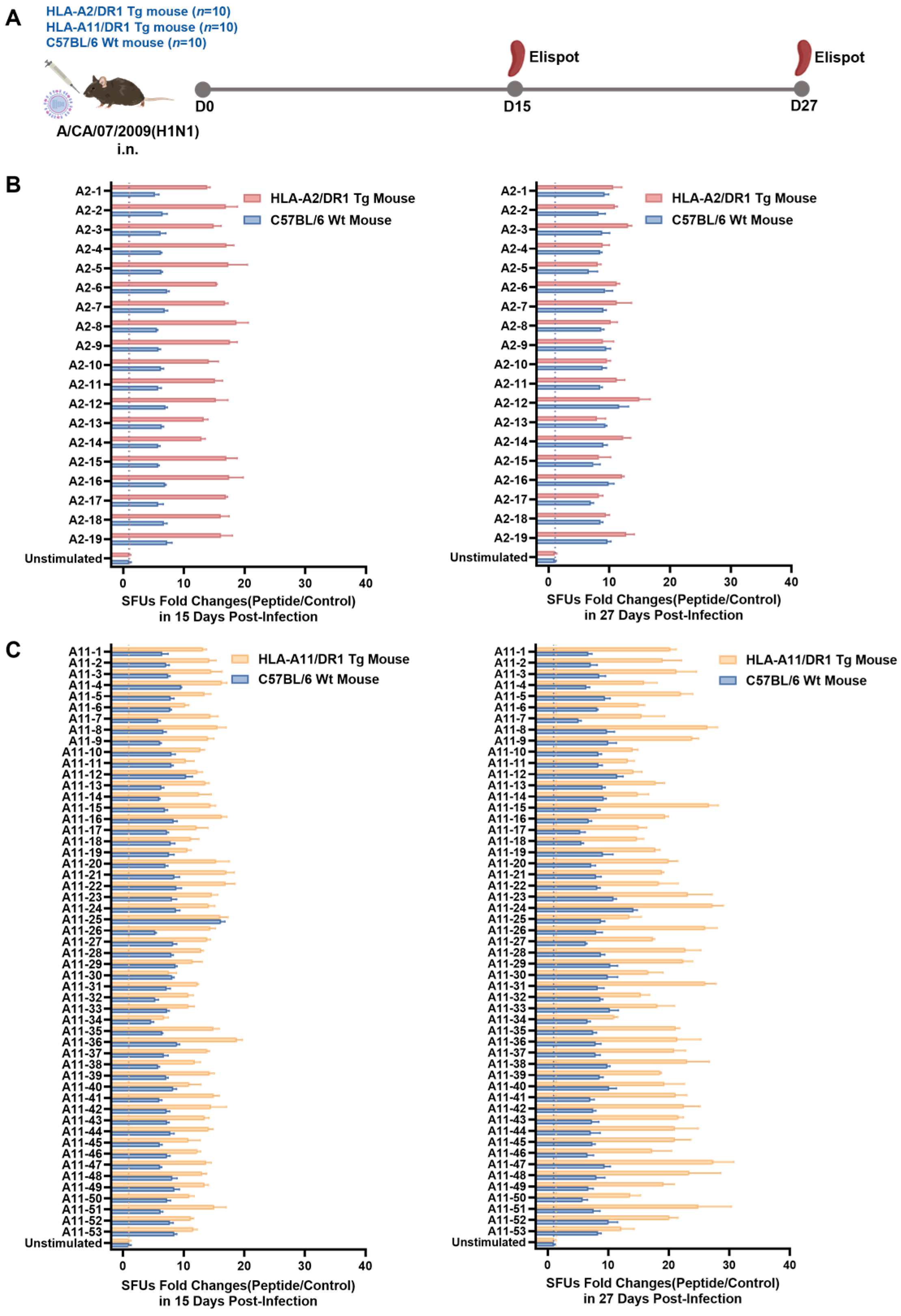
3.3. HLA-A2/DR1 and HLA-A11/DR1 Mice Exhibited Cellular Immune Responses After Influenza Virus Infection
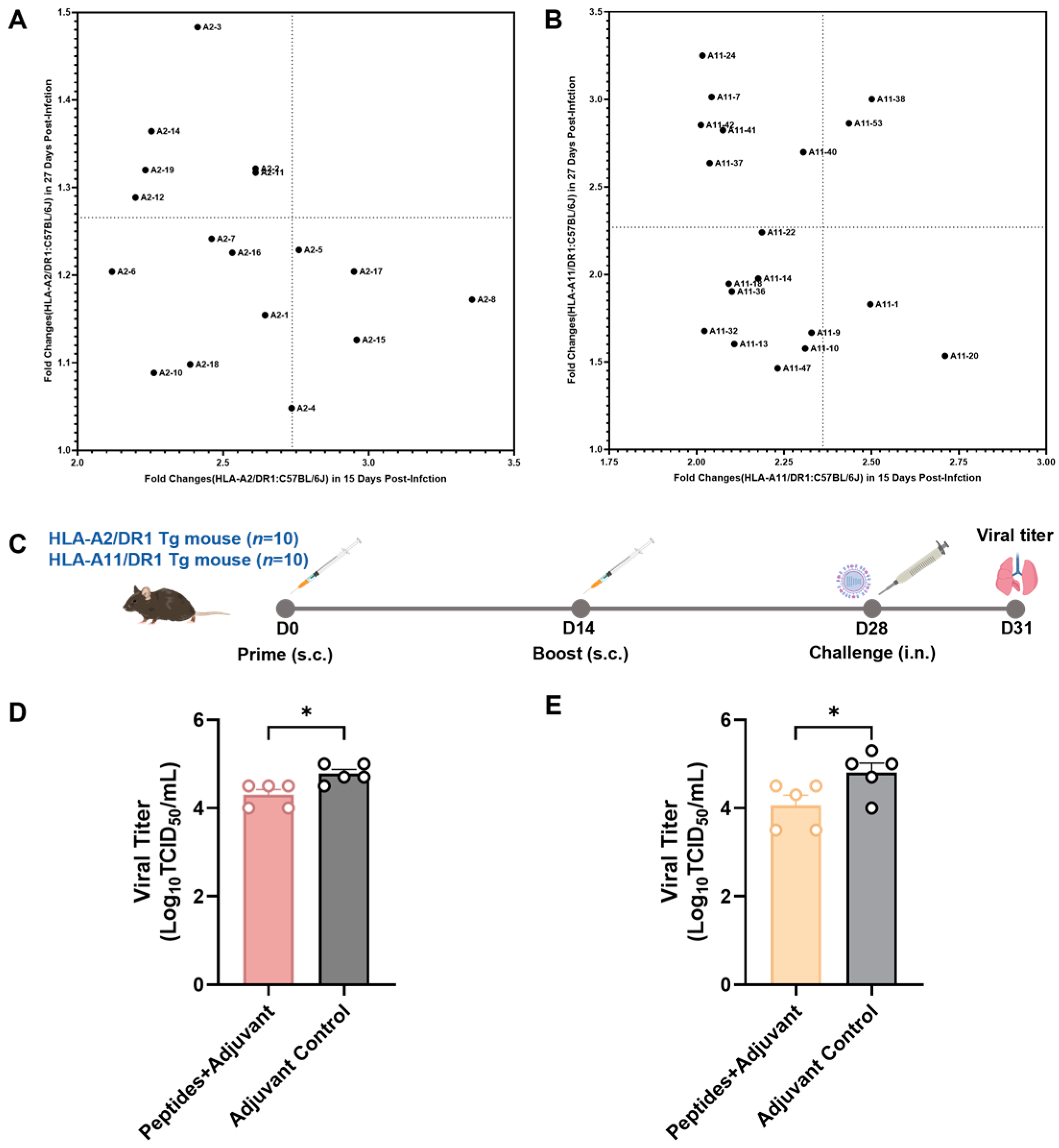
3.4. Screening of Vaccine Candidate HLA-Restricted T Cell Epitope Peptides and Evaluation of Their Protective Efficacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouvier, N.M.; Palese, P. The biology of influenza viruses. Vaccine 2008, 26 (Suppl. 4), D49–D53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.J.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Peiris, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliano, A.D.; Roguski, K.M.; Chang, H.H.; Muscatello, D.J.; Palekar, R.; Tempia, S.; Cohen, C.; Gran, J.M.; Schanzer, D.; Cowling, B.J.; et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, A.X.; de Jong, S.P.J.; Russell, C.A. Co-evolution of immunity and seasonal influenza viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.M.; Askonas, B.A. Influenza nucleoprotein-specific cytotoxic T-cell clones are protective in vivo. Immunology 1986, 58, 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- The Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines: Report of the Ninth Meeting of the Advisory Group of the WHO Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/130837 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Leong, S.L.; Gras, S.; Grant, E.J. Fighting flu: Novel CD8(+) T-cell targets are required for future influenza vaccines. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2024, 13, e1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Li, X.; Goraya, M.U.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.L. Evolution of Influenza A Virus by Mutation and Re-Assortment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treanor, J. Influenza vaccine--outmaneuvering antigenic shift and drift. New Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Begom, S.; Bermingham, A.; Hoschler, K.; Adamson, W.; Carman, W.; Bean, T.; Barclay, W.; Deeks, J.J.; Lalvani, A. Cellular immune correlates of protection against symptomatic pandemic influenza. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Qiu, C.; Quiñones-Parra, S.; Zhu, Z.; Loh, L.; Tian, D.; Ren, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Recovery from severe H7N9 disease is associated with diverse response mechanisms dominated by CD8⁺ T cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones-Parra, S.; Grant, E.; Loh, L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Campbell, K.A.; Tong, S.Y.; Miller, A.; Doherty, P.C.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Rossjohn, J.; et al. Preexisting CD8+ T-cell immunity to the H7N9 influenza A virus varies across ethnicities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asemissen, A.M.; Keilholz, U.; Tenzer, S.; Müller, M.; Walter, S.; Stevanovic, S.; Schild, H.; Letsch, A.; Thiel, E.; Rammensee, H.G.; et al. Identification of a highly immunogenic HLA-A*01-binding T cell epitope of WT1. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7476–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, D.J.; Orsulic, S. Mouse models of cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, M.; Fu, W.; He, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, S.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Comparison of H7N9 and H9N2 influenza infections in mouse model unravels the importance of early innate immune response in host protection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 941078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmans, C.M.C.; de Groot, N.G.; Bontrop, R.E. Comparative genetics of the major histocompatibility complex in humans and nonhuman primates. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2020, 47, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Kou, Z.; Lone, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhou, Y. Generation of human MHC (HLA-A11/DR1) transgenic mice for vaccine evaluation. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2016, 12, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.N.; Li, W.; Li, Y.C.; Zhou, C.S.; Kang, X.P.; Jiang, T. Dual R108K and G189D Mutations in the NS1 Protein of A/H1N1 Influenza Virus Counteract Host Innate Immune Responses. Viruses 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, T.; Mifsud, E.J.; Ohno, M.; Nomura, N.; Sasada, M.; Fujikura, D.; Daito, T.; Shingai, M.; Ohara, Y.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Inactivated whole virus particle vaccine with potent immunogenicity and limited IL-6 induction is ideal for influenza. Vaccine 2019, 37, 2158–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. On the Calculation of TCID(50) for Quantitation of Virus Infectivity. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toebes, M.; Coccoris, M.; Bins, A.; Rodenko, B.; Gomez, R.; Nieuwkoop, N.J.; van de Kasteele, W.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Haanen, J.B.; Ovaa, H.; et al. Design and use of conditional MHC class I ligands. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrani, C.; Oseroff, C.; Sidney, J.; Chesnut, R.W.; Sette, A. Human memory CTL response specific for influenza A virus is broad and multispecific. Hum. Human. Immunol. 2000, 61, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Bilsel, P.; del Guercio, M.F.; Marinkovic-Petrovic, A.; Southwood, S.; Stewart, S.; Ishioka, G.; Kotturi, M.F.; Botten, J.; Sidney, J.; et al. Identification of broad binding class I HLA supertype epitopes to provide universal coverage of influenza A virus. Hum. Human. Immunol. 2010, 71, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.C.; Khan, A.M. Mapping HLA-A2, -A3 and -B7 supertype-restricted T-cell epitopes in the ebolavirus proteome. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, P.; Song, N.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, G.; Fa, Y.; Ye, H.; Lone, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Identification of novel HLA-A11-restricted T-cell epitopes in the Ebola virus nucleoprotein. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paget, J.; Spreeuwenberg, P.; Charu, V.; Taylor, R.J.; Iuliano, A.D.; Bresee, J.; Simonsen, L.; Viboud, C. Global mortality associated with seasonal influenza epidemics: New burden estimates and predictors from the GLaMOR Project. J. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 020421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Españo, E.; Padasas, B.T.; Son, J.H.; Oh, J.; Webby, R.J.; Lee, Y.R.; Park, C.S.; Kim, J.K. Influenza Virus-Derived CD8 T Cell Epitopes: Implications for the Development of Universal Influenza Vaccines. Immune Netw. 2024, 24, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiny, A.T.; Miotto, O.; Srinivasan, K.N.; Khan, A.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Brusic, V.; Tan, T.W.; August, J.T. Evolutionarily conserved protein sequences of influenza a viruses, avian and human, as vaccine targets. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Sandt, C.E.; Kreijtz, J.H.; de Mutsert, G.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Hillaire, M.L.; Vogelzang-van Trierum, S.E.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Human cytotoxic T lymphocytes directed to seasonal influenza A viruses cross-react with the newly emerging H7N9 virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillaire, M.L.B.; Vogelzang-van Trierum, S.E.; Kreijtz, J.; de Mutsert, G.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Osterhaus, A.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Human T-cells directed to seasonal influenza A virus cross-react with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) and swine-origin triple-reassortant H3N2 influenza viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y.; Ha do, L.A.; Simmons, C.; de Jong, M.D.; Chau, N.V.; Schumacher, R.; Peng, Y.C.; McMichael, A.J.; Farrar, J.J.; Smith, G.L.; et al. Memory T cells established by seasonal human influenza A infection cross-react with avian influenza A (H5N1) in healthy individuals. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3478–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Larsen, M.V.; Nielsen, M.; Harndahl, M.; Justesen, S.; Dziegiel, M.H.; Buus, S.; Tang, S.T.; Lund, O.; Claesson, M.H. HLA class I binding 9mer peptides from influenza A virus induce CD4 T cell responses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Bilsel, P.; del Guercio, M.F.; Stewart, S.; Marinkovic-Petrovic, A.; Southwood, S.; Crimi, C.; Vang, L.; Walker, L.; Ishioka, G.; et al. Universal influenza DNA vaccine encoding conserved CD4+ T cell epitopes protects against lethal viral challenge in HLA-DR transgenic mice. Vaccine 2010, 28, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, T.K.; Singh, A.K.; Bonin, J.L.; Nafiz, T.N.; Salmon, S.L.; Metzger, D.W. Lethal synergy between SARS-CoV-2 and Streptococcus pneumoniae in hACE2 mice and protective efficacy of vaccination. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e159422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, P.; Peng, L.; Yang, L.; Suzuki, K.; Fang, Z.; Renauer, P.A.; Lin, Q.; Bai, M.; Li, T.; Clark, P.; et al. RAMIHM generates fully human monoclonal antibodies by rapid mRNA immunization of humanized mice and BCR-seq. Cell Chem. Biol. 2023, 30, 85–96.e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douam, F.; Ploss, A. The use of humanized mice for studies of viral pathogenesis and immunity. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 29, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascolo, S. HLA class I transgenic mice: Development, utilisation and improvement. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 919–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, V.; David, C.S. Role of HLA class II genes in susceptibility/resistance to inflammatory arthritis: Studies with humanized mice. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajot, A.; Michel, M.L.; Fazilleau, N.; Pancré, V.; Auriault, C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Lemonnier, F.A.; Lone, Y.C. A mouse model of human adaptive immune functions: HLA-A2.1-/HLA-DR1-transgenic H-2 class I-/class II-knockout mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 3060–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, S.J.; Cano, P.; Hollenbach, J.A.; He, J.; Hurley, C.K.; Middleton, D.; Moraes, M.E.; Pereira, S.E.; Kempenich, J.H.; Reed, E.F.; et al. Common and well-documented HLA alleles: 2012 update to the CWD catalogue. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleguezuelos, O.; Dille, J.; de Groen, S.; Oftung, F.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Islam, M.A.; Næss, L.M.; Hungnes, O.; Aldarij, N.; Idema, D.L.; et al. Immunogenicity, Safety, and Efficacy of a Standalone Universal Influenza Vaccine, FLU-v, in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.N.; Bunce, C.J.; Horlock, C.; Watson, J.M.; Warrington, S.J.; Georges, B.; Brown, C.B. A novel peptide-based pan-influenza A vaccine: A double blind, randomised clinical trial of immunogenicity and safety. Vaccine 2015, 33, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, E.J.; Quiñones-Parra, S.M.; Clemens, E.B.; Kedzierska, K. Human influenza viruses and CD8(+) T cell responses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 16, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreijtz, J.H.; de Mutsert, G.; van Baalen, C.A.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Cross-recognition of avian H5N1 influenza virus by human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte populations directed to human influenza A virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5161–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antrobus, R.D.; Coughlan, L.; Berthoud, T.K.; Dicks, M.D.; Hill, A.V.; Lambe, T.; Gilbert, S.C. Clinical assessment of a novel recombinant simian adenovirus ChAdOx1 as a vectored vaccine expressing conserved Influenza A antigens. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2014, 22, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antrobus, R.D.; Lillie, P.J.; Berthoud, T.K.; Spencer, A.J.; McLaren, J.E.; Ladell, K.; Lambe, T.; Milicic, A.; Price, D.A.; Hill, A.V.; et al. A T cell-inducing influenza vaccine for the elderly: Safety and immunogenicity of MVA-NP+M1 in adults aged over 50 years. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsmon, J.; Caraco, Y.; Ziv-Sefer, S.; Shaikevich, D.; Abramov, E.; Volokhov, I.; Bruzil, S.; Haima, K.Y.; Gottlieb, T.; Ben-Yedidia, T. Priming by a novel universal influenza vaccine (Multimeric-001)-a gateway for improving immune response in the elderly population. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5816–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux-Roels, I.; Waerlop, G.; Tourneur, J.; De Boever, F.; Maes, C.; Bruhwyler, J.; Guyon-Gellin, D.; Moris, P.; Del Campo, J.; Willems, P.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Reference-Controlled, Phase 2a Study Evaluating the Immunogenicity and Safety of OVX836, A Nucleoprotein-Based Influenza Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 852904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrobus, R.D.; Berthoud, T.K.; Mullarkey, C.E.; Hoschler, K.; Coughlan, L.; Zambon, M.; Hill, A.V.; Gilbert, S.C. Coadministration of seasonal influenza vaccine and MVA-NP+M1 simultaneously achieves potent humoral and cell-mediated responses. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2014, 22, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.J.; Mailliard, R.B.; Khan, A.M.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Guzman, N.; Paulaitis, M.; de Melo, A.B.; Cordeiro, M.T.; Gil, L.V.; et al. Identification of conserved and HLA promiscuous DENV3 T-cell epitopes. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Katz, M.; Erickson, J.J.; Lan, J.; Ecker, A.; Zhang, Y.; Joyce, S.; Williams, J.V. Novel HLA-B7-restricted human metapneumovirus epitopes enhance viral clearance in mice and are recognized by human CD8(+) T cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounds, C.E.; Terry, F.E.; Moise, L.; Hannaman, D.; Martin, W.D.; De Groot, A.S.; Suschak, J.J.; Dupuy, L.C.; Schmaljohn, C.S. An immunoinformatics-derived DNA vaccine encoding human class II T cell epitopes of Ebola virus, Sudan virus, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus is immunogenic in HLA transgenic mice. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 2824–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardyan, A.; Osen, W.; Zörnig, I.; Podola, L.; Agarwal, M.; Aulmann, S.; Ruggiero, E.; Schmidt, M.; Halama, N.; Leuchs, B.; et al. Identification of NY-BR-1-specific CD4(+) T cell epitopes using HLA-transgenic mice. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Peptide | Protein | Starting Position | Ending Position | Length | HLA Restriction |
| A2-1 | TVLEKNVTV | HA | 35 | 43 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-2 | AIDEITNKV | HA | 388 | 396 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-3 | KLNREEIDGV | HA | 511 | 520 | 10 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-4 | RMGTVTTEA | M1 | 134 | 142 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-5 | AIYSKDNSV | NA | 98 | 106 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-6 | KLSDYDGRL | NP | 48 | 56 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-7 | GMDPRMCSL | NP | 158 | 166 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-8 | TMDSNTLEL | NP | 373 | 381 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-9 | YLSDMTLEEM | NS1 | 89 | 98 | 10 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-10 | GMVTRFESL | NS2 | 17 | 25 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-11 | SLGETVMRM | NS2 | 31 | 39 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-12 | VMRMGDLHYL | NS2 | 36 | 45 | 10 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-13 | QLGQKFEEI | NS2 | 55 | 63 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-14 | WLIEEMRHRL | NS2 | 65 | 74 | 10 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-15 | QLLLEVEQEI | NS2 | 91 | 100 | 10 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-16 | ALLKHRFEI | PA | 70 | 78 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-17 | SMIEAESSV | PA | 594 | 602 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-18 | RLIDFLKDV | PB1 | 162 | 170 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| A2-19 | SLLEMCHST | PB2 | 279 | 287 | 9 | HLA-A*02:01 |
| Name | Peptide | Protein | Starting Position | Ending Position | Length | HLA Restriction |
| A11-1 | GVAPLHLGK | HA | 63 | 71 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-2 | SSWPNHDSNK | HA | 138 | 147 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-3 | HAGAKSFYK | HA | 155 | 163 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-4 | FVGSSRYSK | HA | 217 | 225 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-5 | NIHPITIGK | HA | 311 | 319 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-6 | NTQFTAVGK | HA | 404 | 412 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-7 | RSQLKNNAK | HA | 467 | 475 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-8 | RLESVFAGK | M1 | 27 | 35 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-9 | FTLTVPSER | M1 | 64 | 72 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-10 | TVPSERGLQR | M1 | 67 | 76 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-11 | NMDRAVKLYK | M1 | 92 | 101 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-12 | AVKLYKKLK | M1 | 96 | 104 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-13 | RLFFKCIYRR | M2 | 44 | 53 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-14 | STEGVPESMR | M2 | 63 | 72 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-15 | LTQGALLNDK | NA | 134 | 143 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-16 | GTIKDRSPYR | NA | 147 | 156 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-17 | KSWRNNILR | NA | 217 | 225 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-18 | ASYKIFRIEK | NA | 251 | 260 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-19 | SSNGANGVK | NA | 339 | 347 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-20 | SAFDERRNK | NP | 69 | 77 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-21 | SLMQGSTLPR | NP | 165 | 174 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-22 | RSGAAGAAVK | NP | 175 | 184 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-23 | RVSSFIRGKK | NP | 342 | 351 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-24 | SVQPTFSVQR | NP | 407 | 416 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-25 | SVQRNLPFER | NP | 413 | 422 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-26 | GVFELSDEK | NP | 462 | 470 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-27 | KQIVEWILK | NS1 | 62 | 70 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-28 | KIIGPLCVR | NS1 | 110 | 118 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-29 | RLDQAIMEK | NS1 | 118 | 126 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-30 | AIMEKNIVLK | NS1 | 122 | 131 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-31 | RLETLILLR | NS1 | 140 | 148 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-32 | MVTRFESLK | NS2 | 18 | 26 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-33 | DSLGETVMR | NS2 | 30 | 38 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-34 | TVMRMGDLH | NS2 | 35 | 43 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-35 | SICNTTGVEK | PA | 93 | 102 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-36 | ASWVQNEFNK | PA | 404 | 413 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-37 | RTNGTSKIK | PA | 566 | 574 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-38 | SVKEKDMTK | PA | 601 | 609 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-39 | MTKEFFENK | PA | 607 | 615 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-40 | KVCRTLLAK | PA | 635 | 643 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-41 | NSFLTHALK | PA | 708 | 716 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-42 | QTYDWTLNR | PB1 | 127 | 135 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-43 | MVTQRTIGK | PB1 | 199 | 207 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-44 | SILNLGQKK | PB1 | 422 | 430 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-45 | ATTHSWIPK | PB1 | 661 | 669 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-46 | SSMVEAMVSR | PB1 | 712 | 721 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-47 | TTVDHMAIIK | PB2 | 23 | 32 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-48 | TTSTVHYPK | PB2 | 105 | 113 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-49 | STVHYPKVYK | PB2 | 107 | 116 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-50 | KVYKTYFEK | PB2 | 113 | 121 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-51 | GTFGPVHFR | PB2 | 128 | 136 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-52 | RTSGSSVKK | PB2 | 332 | 340 | 9 | HLA-A*11:01 |
| A11-53 | SINELSNLAK | PB2 | 709 | 718 | 10 | HLA-A*11:01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Sun, K.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Yang, T.; Yuan, K.; Li, M.; et al. Application of Humanized MHC Transgenic Mice in the Screening of HLA–Restricted T Cell Epitopes for Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines 2025, 13, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030331
Wei Y, Sun K, Han X, Sun Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Yin Q, Yang T, Yuan K, Li M, et al. Application of Humanized MHC Transgenic Mice in the Screening of HLA–Restricted T Cell Epitopes for Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines. 2025; 13(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yuwei, Keyu Sun, Xuelian Han, Yali Sun, Jiejie Zhang, Yuan Wang, Qi Yin, Tiantian Yang, Kai Yuan, Min Li, and et al. 2025. "Application of Humanized MHC Transgenic Mice in the Screening of HLA–Restricted T Cell Epitopes for Influenza Vaccines" Vaccines 13, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030331
APA StyleWei, Y., Sun, K., Han, X., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Yin, Q., Yang, T., Yuan, K., Li, M., & Zhao, G. (2025). Application of Humanized MHC Transgenic Mice in the Screening of HLA–Restricted T Cell Epitopes for Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines, 13(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030331





