Four-Color Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay: A Rapid Method for Evaluating Neutralizing Antibodies Against Quadrivalent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Vaccine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell and Virus
2.2. Serum
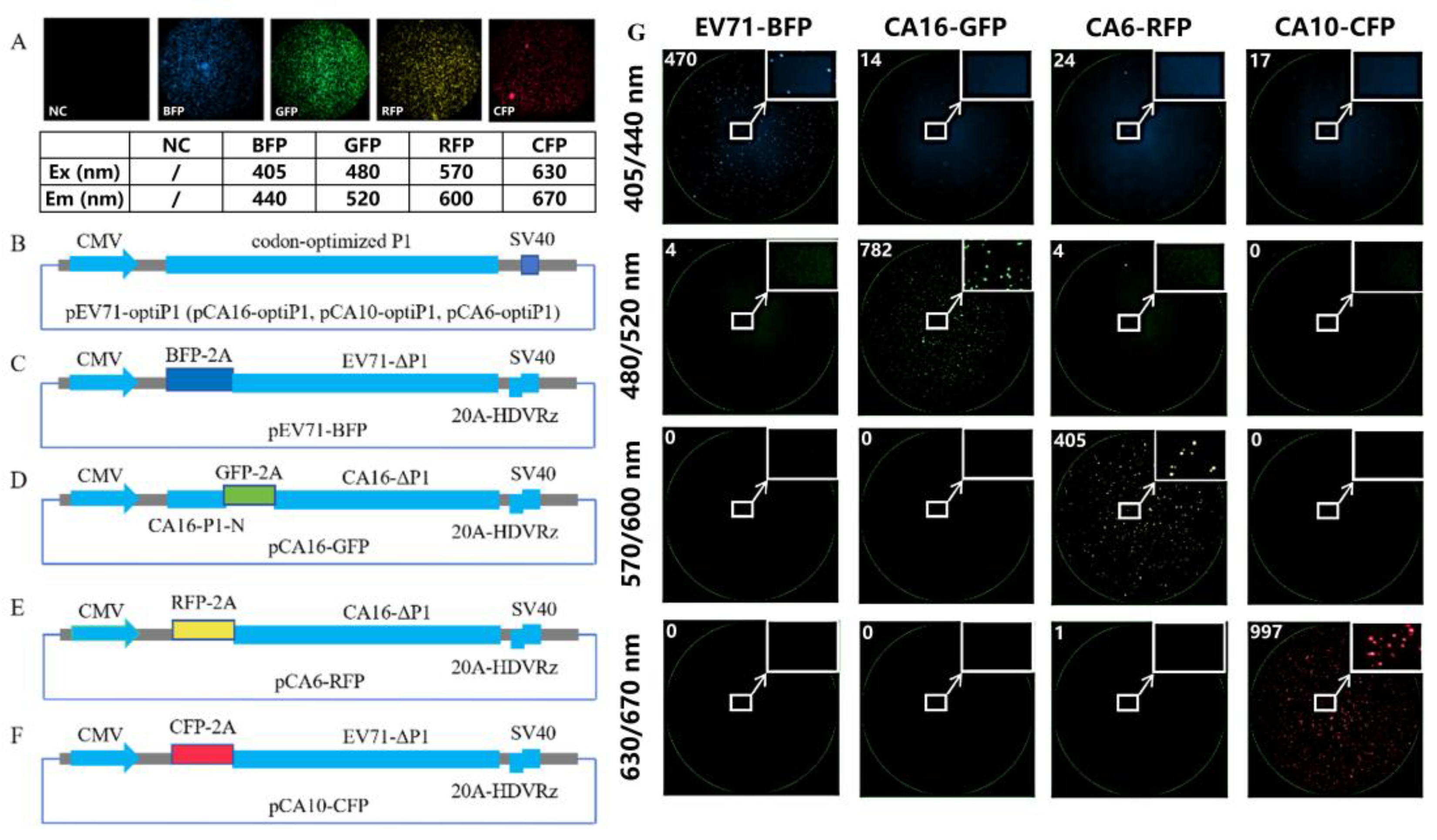
2.3. Fluorescent Gene Selection
2.4. Construction of Pseudovirus Packing Plasmid and Detection of Fluorescent Gene Expression
2.4.1. Genomic Sequences of the Viruses
2.4.2. Vector Backbone
2.4.3. Capsids
2.4.4. Replicons
2.4.5. Detection of Fluorescence Gene Expression
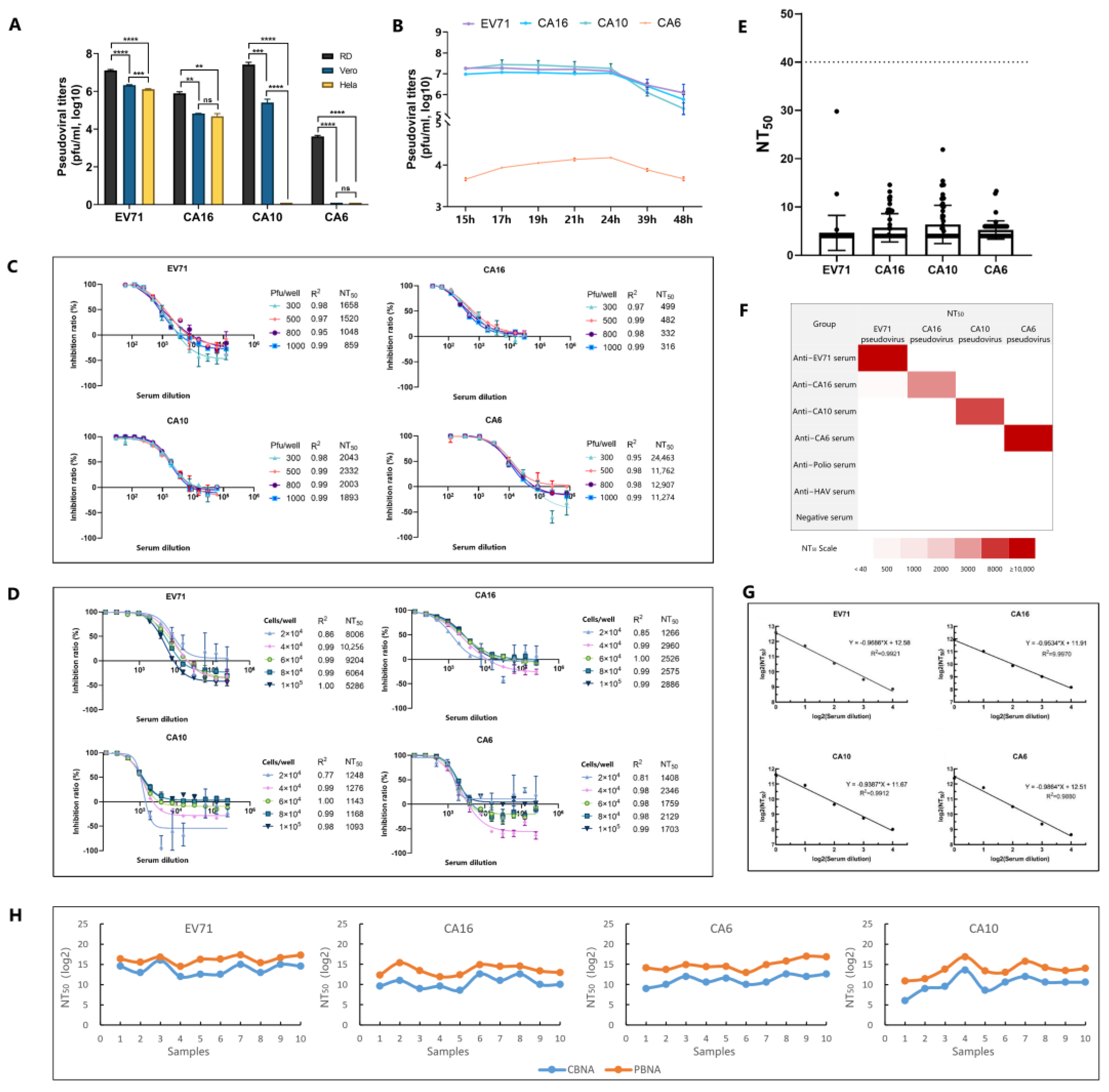
2.5. Pseudovirus Preparation
2.6. Pseudoviral Titer Estimation
2.7. Neutralization Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA6 | Coxsackievirus A6 |
| CA10 | Coxsackievirus A10 |
| CA16 | Coxsackievirus A16 |
| CBNA | Cell-based neutralization assay |
| CC | Cell control |
| EV71 | Enterovirus 71 |
| HFMD | Hand, foot, and mouth disease |
| NIFDC | National Institutes for Food and Drug Control |
| NtAbs | Neutralizing antibodies |
| NT50 | Neutralizing antibody titer |
| PBNA | Pseudovirus-based neutralization assay |
| VC | Viral control |
References
- Zhu, P.; Ji, W.-Q.; Li, D.; Li, Z.-J.; Chen, Y.; Dai, B.-W.; Han, S.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Jin, Y.-F.; Duan, G.-C. Current status of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-P.; Tan, X.-J.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.; Gong, L.-M.; Hong, M.; Shi, Y.-L.; Zhu, S.-L.; Zhang, B.-M.; Zhang, S.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of coxsackievirus A16: Intratype and prevalent intertype recombination identified. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathyraj, S.; Arunkumar, G.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Hober, D. Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD): Emerging epidemiology and the need for a vaccine strategy. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 205, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.-H.; Huang, Y.-P.; Liu, M.-C.; Tsou, T.-P.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, T.-L.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chao, Y.-N.; Chang, L.-Y.; Hsu, C.-M. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis 2011, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, Z.-R.; Wu, P.; Liao, Q.-H.; Liu, F.-F.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Chen, Q.; Yu, S.-B.; et al. Emerging enteroviruses causing hand, foot and mouth disease, China, 2010–2016. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2018, 24, 1902–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.; Chong, P. Is a multivalent hand, foot, and mouth disease vaccine feasible? Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 2688–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirand, A.; Henquell, C.; Archimbaud, C.; Ughetto, S.; Antona, D.; Bailly, J.-L.; Peigue-Lafeuille, H. Outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease/herpangina associated with coxsackievirus A6 and A10 infections in 2010, France: A large citywide, prospective observational study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E110–E118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmgren, L.; Li, X.-G.; Wilson, C.; Ball, R.; Wang, J.-Z.; Cichutek, K.; Pfleiderer, M.; Kato, A.; Cavaleri, M.; Southern, J.; et al. A global regulatory science agenda for vaccines. Vaccine 2013, 31 (Suppl. S2), B163–B175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.-L.; Griffiths, E.; Martin, J. WHO working group meeting to develop WHO Recommendations to assure the quality, safety and efficacy of enterovirus 71 vaccines. Vaccine 2020, 38, 4917–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-C.; Zhang, M.-M.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, P.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xu, J.-Q. From monovalent to multivalent vaccines, the exploration for potential preventive strategies against hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Dong, Z.-P.; Wang, Q.; Carr, M.-J.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Li, D.; Shi, W.-F. Characterization of an inactivated whole-virus bivalent vaccine that induces balanced protective immunity against coxsackievirus A6 and A10 in mice. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7095–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caine, E.-A.; Fuchs, J.; Das, S.-C.; Partidos, C.-D.; Osorio, J.-E. Efficacy of a Trivalent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Vaccine against Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackieviruses A16 and A6 in Mice. Viruses 2015, 7, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Guo, M.-S.; Rung, S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Yang, Y.-T.; Liu, W.-C.; Chow, Y.-H.; Shieh, D.-B.; Wang, J.-R.; Chong, P. Immunological and biochemical characterizations of coxsackievirus A6 and A10 viral particles. Antiviral Res. 2016, 129, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Ln, H.-J.; Lee, J.-A.; Yoo, J.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; Chung, G.-T.; Choi, Y.-K.; Chung, J.-K.; Cho, S.-J.; Lee, J.-W. The immunogenicity and protection effect of an inactivated coxsackievirus A6, A10, and A16 vaccine against hand, foot, and mouth disease. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3445–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dai, W.-L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, P.; Wang, S.-X.; Ye, X.-H.; Liu, Q.-W.; Zhou, D.-M.; Huang, Z. A virus-like particle-based tetravalent vaccine for hand, foot, and mouth disease elicits broad and balanced protective immunity. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Bae, K.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kang, J.-H.; Choi, U.-Y. Seroprevalence of Neutralizing Antibodies Against Candidate Serotypes of Enterovirus Vaccines Among Korean Children. Viral Immunol. 2021, 34, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, E.; Nguyen, D.; Celma, C.; Blomqvist, S.; Horby, P.; Simmonds, P.; Harvala, H. Seroprevalence and Virologic Surveillance of Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A6, United Kingdom, 2006–2017. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2021, 27, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Dong, F.Y.; Cui, B.P.; Cui, L.S.; Liu, P.; Ma, C.; Zheng, H.F.; Wu, X.; Liang, Z.-L. Development of a Pseudovirus-based assay for measuring neutralizing antibodies against coxsackievirus A10. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2020, 16, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Mao, Q.-Y.; Yao, X.; Chen, P.; Chen, X.-M.; Shao, J.; Gao, F.; Yu, X.; Zhu, F.-C.; Li, R.-C.; et al. Development and evaluation of a Pseudovirus-luciferase assay for rapid and quantitative detection of neutralizing antibodies against enterovirus 71. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, P.; Gao, F.; Bian, L.-L.; Sun, S.-Y.; Dong, F.-Y.; Hu, Y.-L.; Mao, Q.-Y.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X.; et al. A surrogate assay for measuring coxsackievirus A6 neutralizing antibodies. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.X.; Mao, Q.-Y.; Hu, Y.-L.; Lang, S.-H.; Sun, S.-Y.; Li, K.-L.; Gao, F.; Bian, L.-L.; Yang, C.; Cui, B.-P.; et al. A potential therapeutic neutralization monoclonal antibody specifically against multi-coxsackievirus A16 strains challenge. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 15, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.-S.; Oh, S.; Antigua, K.J.C.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, B.K.; Yun, Y.S.; Kang, D.H.; Min, S.C.; Lim, B.-K.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Development of a universal cloning system for reverse genetics of human enteroviruses. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0316722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjilaou, A.; Green, A.M.; Coloma, J.; Harris, E. Single-cell analysis of B cell/antibody cross-reactivity using a novel multicolor fluorospot assay. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3490–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.-N.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Zhou, L.-Z.; Weng, S.-H.; et al. Broadly therapeutic antibody provides cross-serotype protection against enteroviruses via Fc effector functions and by mimicking SCARB2. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 2939–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.-M.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Kotecha, A.; Fry, E.E.; Kelly, J.T.; Wang, X.-X.; Rao, Z.-H.; Rowlands, D.J.; Ren, J.-S.; Stuart, D.I. Unexpected mode of engagement between enterovirus 71 and its receptor SCARB2. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Z.-Q.; Liu, Q.-W.; Ye, X.-H.; Cai, Y.-C.; Wang, X.-L.; Shi, J.-P.; Li, D.-P.; Jin, X.; An, W.-Q.; Huang, Z. A virus-like particle based bivalent vaccine confers dual protection against enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 infections in mice. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4296–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-C.; Ku, Z.-Q.; Liu, Q.-W.; Leng, Q.-B.; Huang, Z. A combination vaccine comprising of inactivated enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 elicits balanced protective immunity against both viruses. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-F.; Zheng, Q.-B.; Li, S.-W.; He, M.-Z.; Wu, Y.-T.; Li, Y.-C.; Zhu, R.; Yu, H.; Hong, Q.-Y.; Jiang, J.; et al. Atomic structures of Coxsackievirus A6 and its complex with a neutralizing antibody. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; He, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; et al. Four-Color Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay: A Rapid Method for Evaluating Neutralizing Antibodies Against Quadrivalent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Vaccine. Vaccines 2025, 13, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030320
Gao F, Xu L, Wang Q, Wang G, Liu M, Li L, He Q, Zhang X, Wang Y, Mao Q, et al. Four-Color Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay: A Rapid Method for Evaluating Neutralizing Antibodies Against Quadrivalent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Vaccine. Vaccines. 2025; 13(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030320
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fan, Lingjie Xu, Qian Wang, Gang Wang, Mingchen Liu, Lu Li, Qian He, Xuanxuan Zhang, Ying Wang, Qunying Mao, and et al. 2025. "Four-Color Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay: A Rapid Method for Evaluating Neutralizing Antibodies Against Quadrivalent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Vaccine" Vaccines 13, no. 3: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030320
APA StyleGao, F., Xu, L., Wang, Q., Wang, G., Liu, M., Li, L., He, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Mao, Q., Liang, Z., Wang, T., Ma, X., & Wu, X. (2025). Four-Color Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay: A Rapid Method for Evaluating Neutralizing Antibodies Against Quadrivalent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Vaccine. Vaccines, 13(3), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030320





