Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein of Streptococcus suis as Potential Candidate Protein for Antibodies Against S. suis Detection and Subunit Vaccine Development: In Silico and In Vitro Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Virulence Genes from the Whole Genome Sequence of S. suis BM407
2.2. Selection of Appropriate Genes Using Bioinformatic Tools
2.3. Designing of Primers Targeting Extracellular Factor Protein (epf) Gene and Virtual Digestion of Amplicon
2.4. Analysis of Candidate Protein Properties
2.5. Bacterial Identification and Genomic DNA Extraction
2.6. Amplification of the Partial Extracellular Factor Protein (epf) Gene Using Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Vector and Insert Digestion, Dephosphorylation, and Ligation
2.8. DNA Recombinant Transformation and Expression in Escherichia coli DH10β
2.9. Recombinant Protein Purification and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.10. Protein Quantification Using Bradford Assay
2.11. Binding Evaluation of Recombinant Extracellular Protein and S. suis Serotype 2 Against Antibodies Using an Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.12. Sensitivity and Specificity of Coated Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein Compared to Coated Whole S. suis Serotype 2 Cell Lysates
2.13. Whole Plasmid Sequencing of Constructed Partial epf Gene-pQE81L-KAN Vector
2.14. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.15. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Binding Prediction for T-Cell Epitope and B-Cell Epitope Prediction of Recombinant Protein
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection and Properties of the Targeted Protein
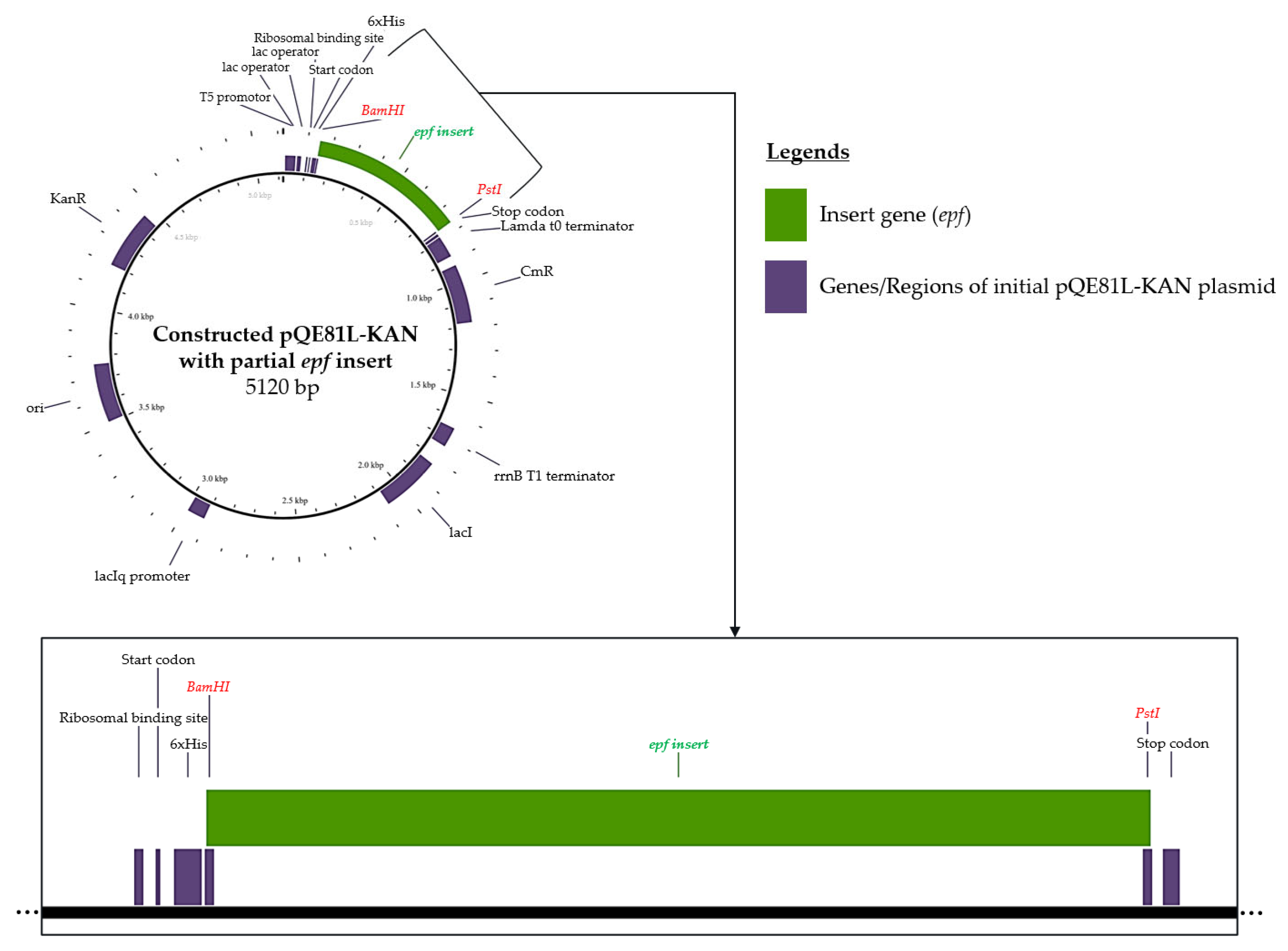
3.2. In Silico of Targeted Genes—Plasmid Vector Construction
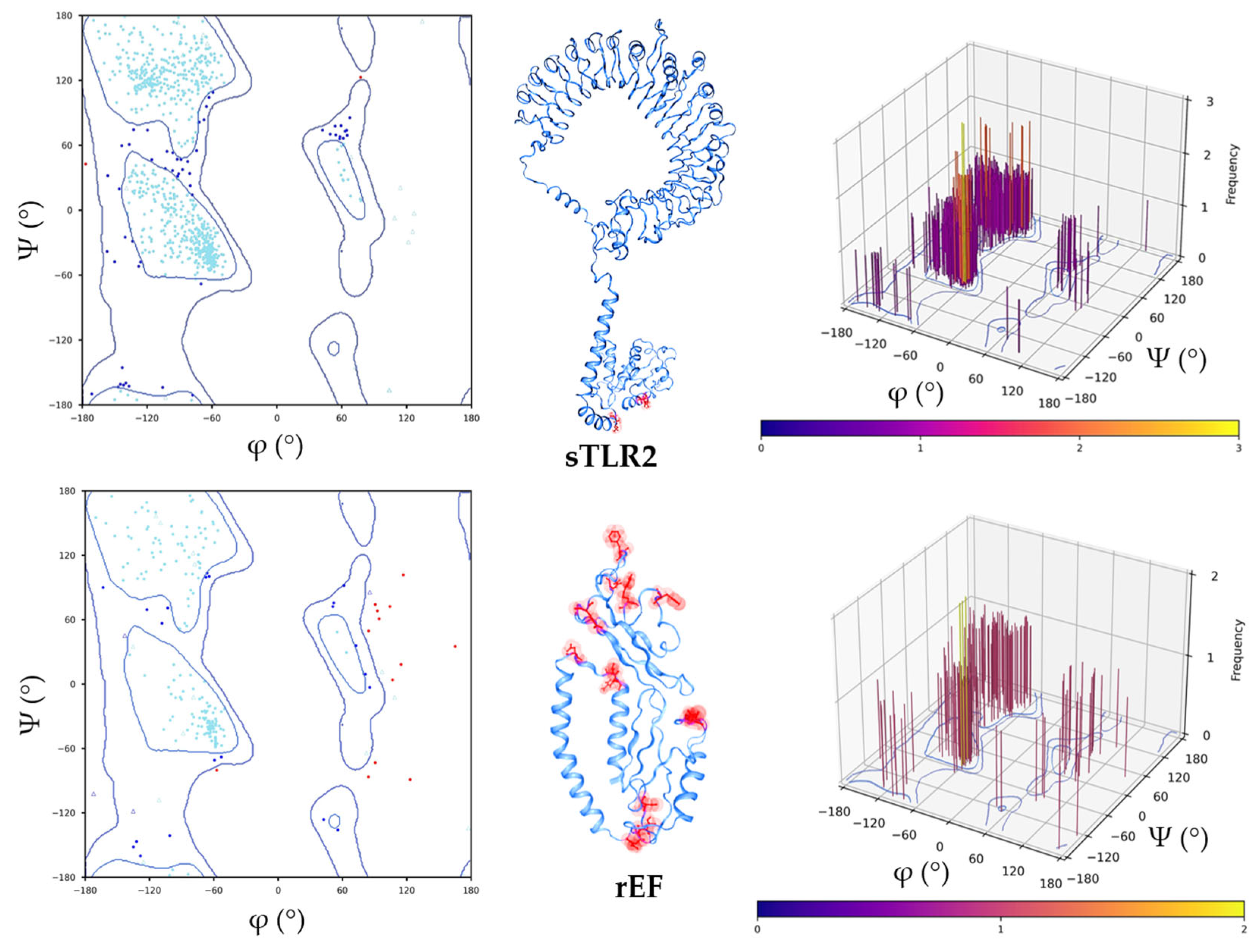
3.3. Structure Retrieval and Evaluation of Swine Toll-Like Receptor 2 (sTLR2) and the rEF Protein
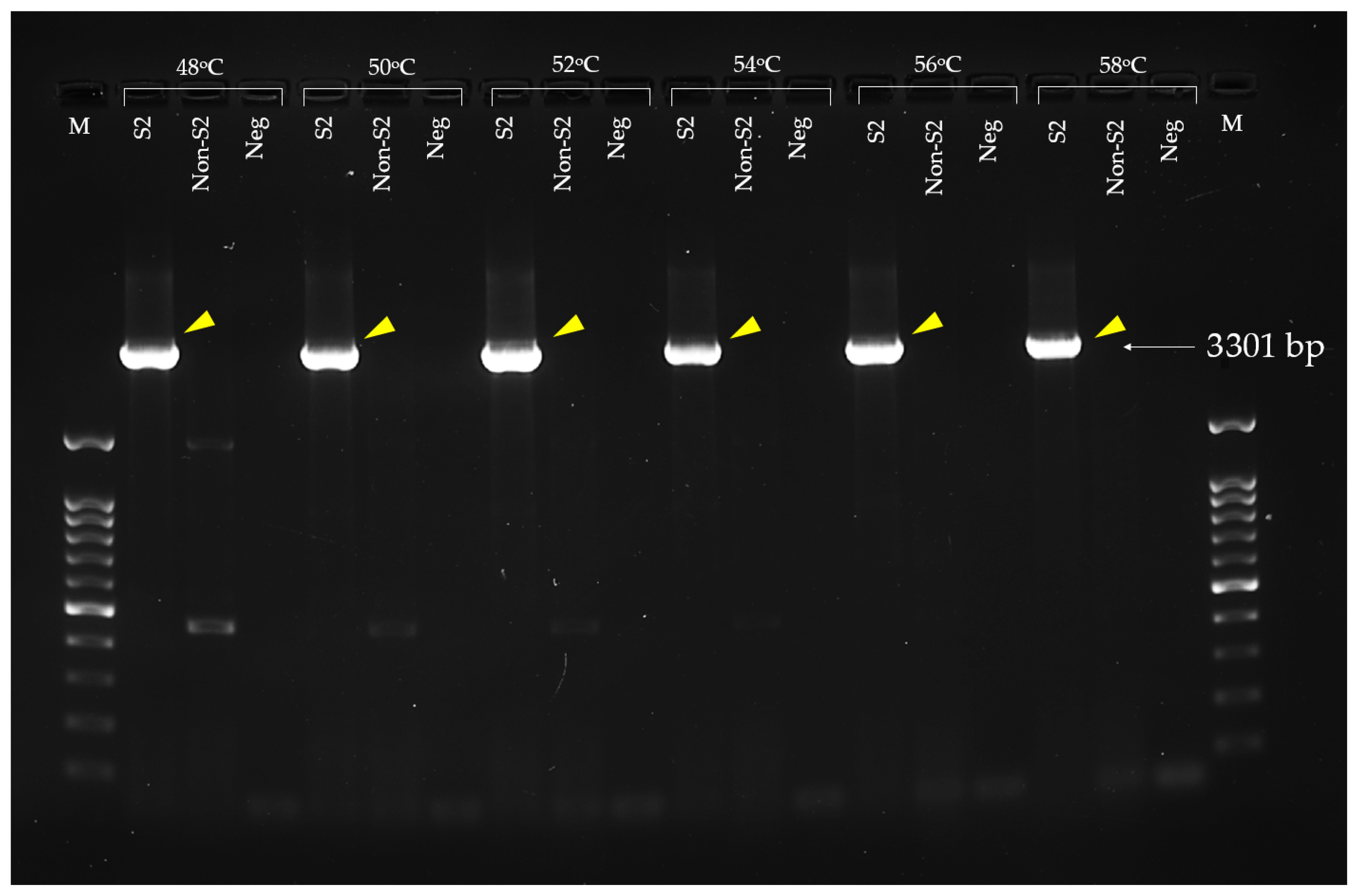
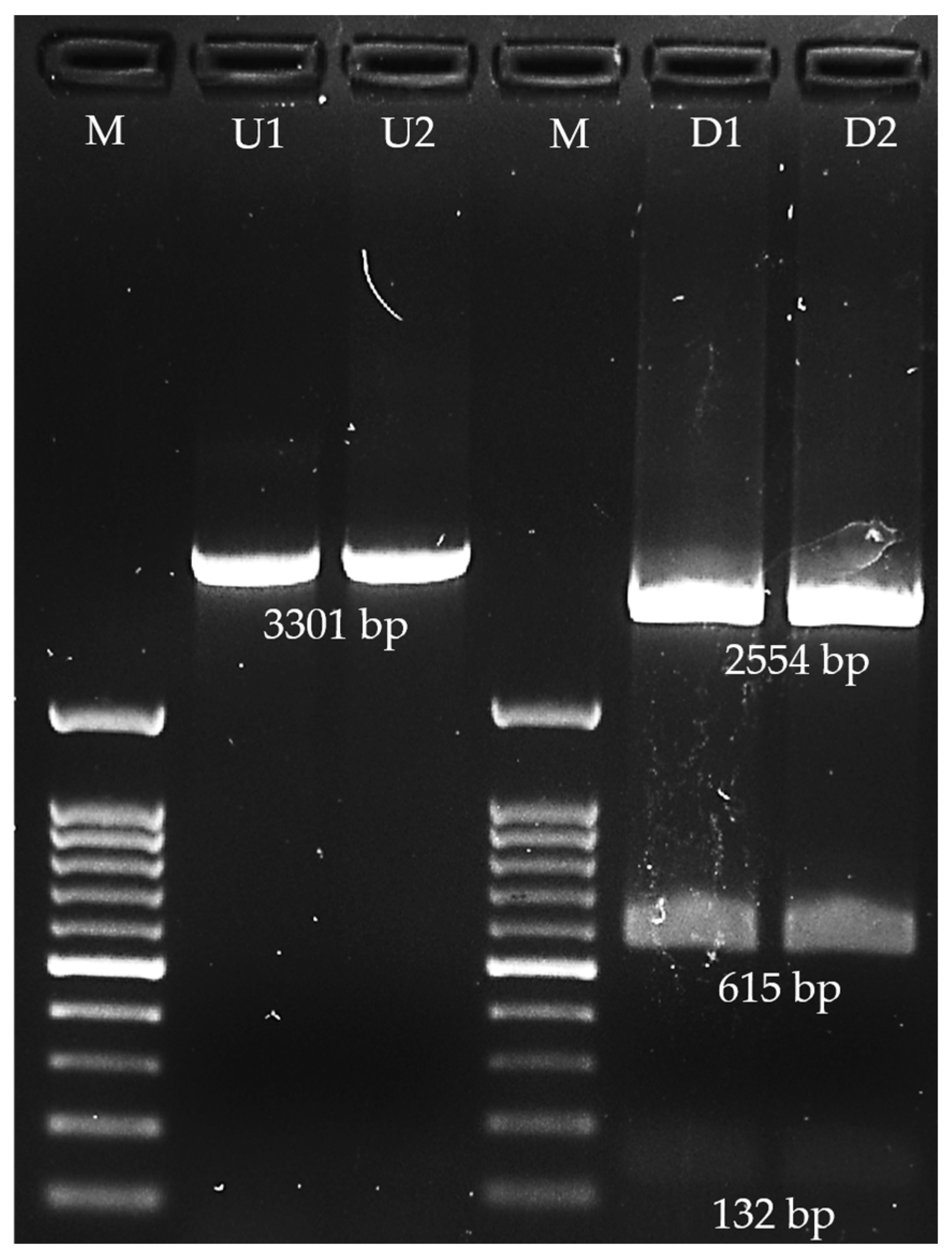
3.4. Extracellular Factor Protein (epf) Gene Amplification and Recombinant EF Protein Expression
3.5. Purification of Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein
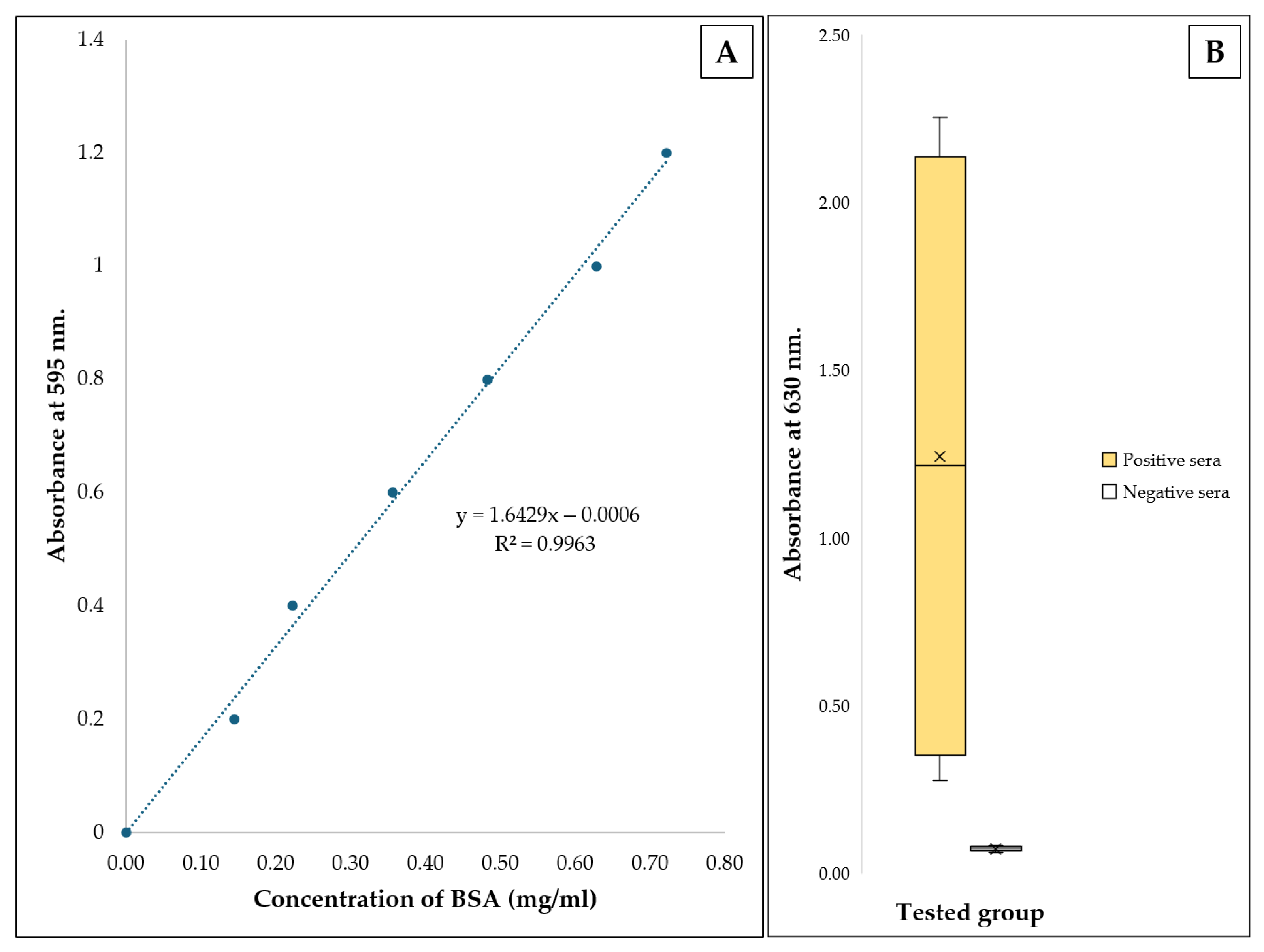
3.6. Binding Evaluation of Recombinant Extracellular Protein and S. suis Serotype 2 Against Antibodies
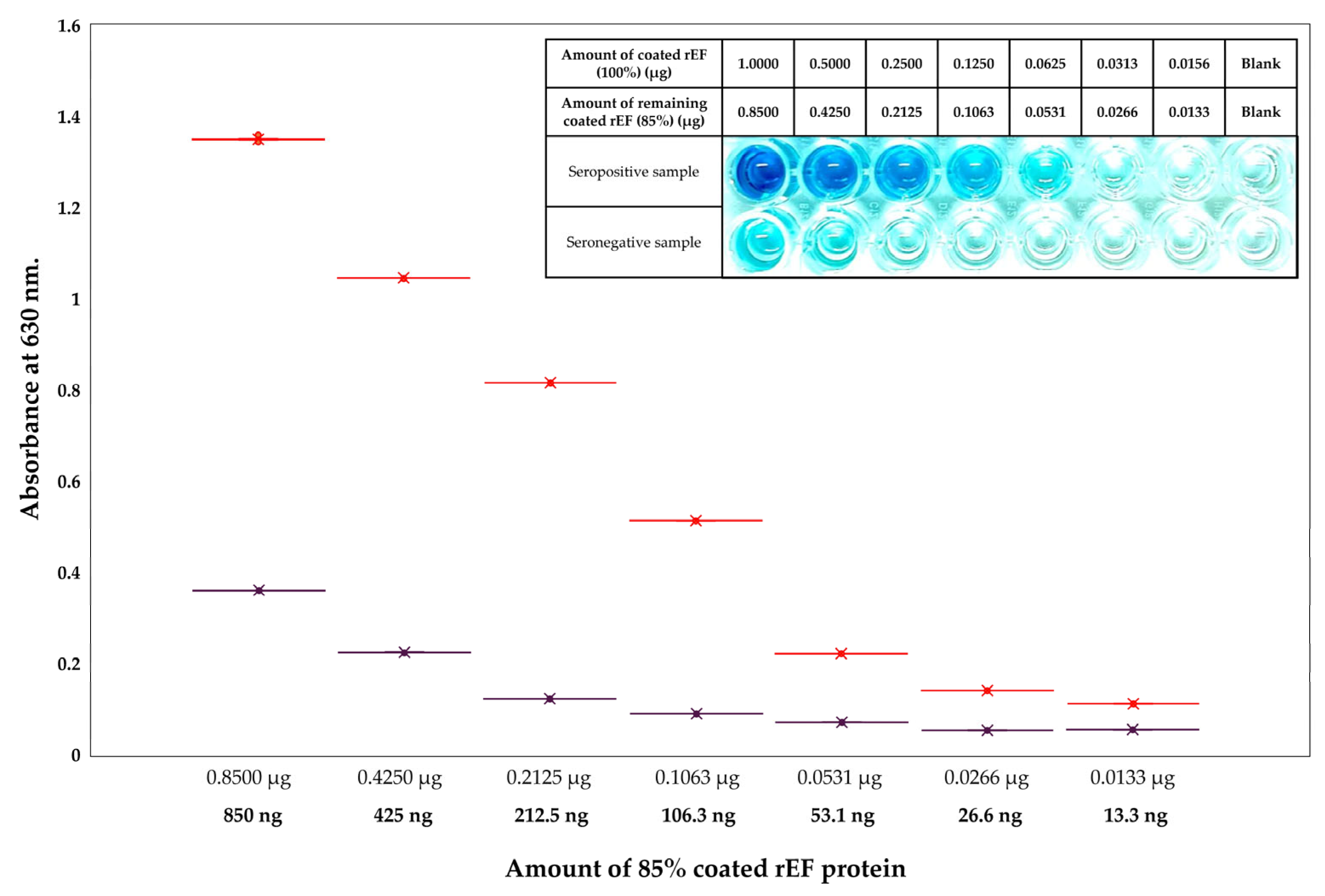
3.7. Sensitivity and Specificity Evaluations of Coated Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein Between Coated Whole S. suis Serotype 2 Cell Lysates
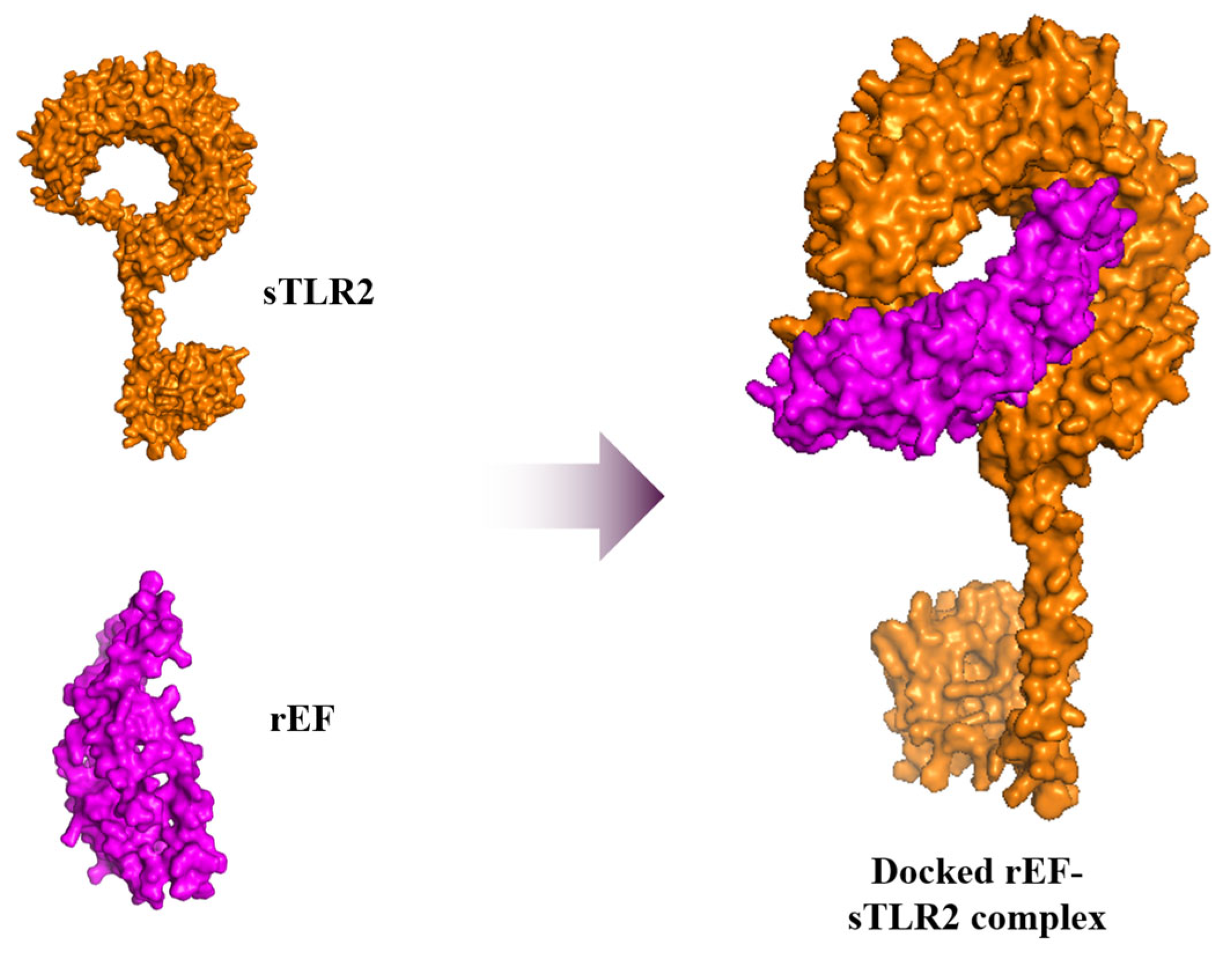
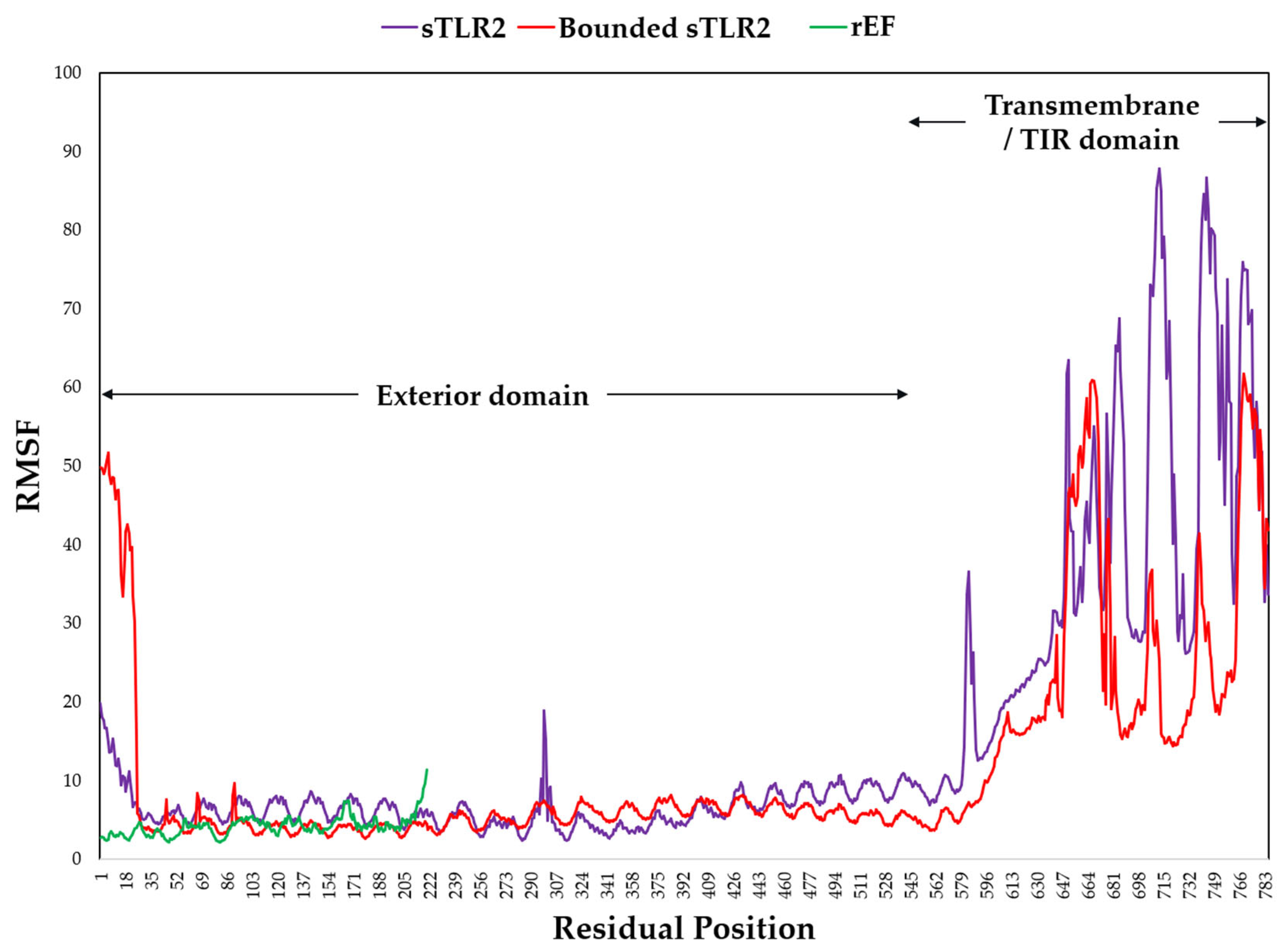
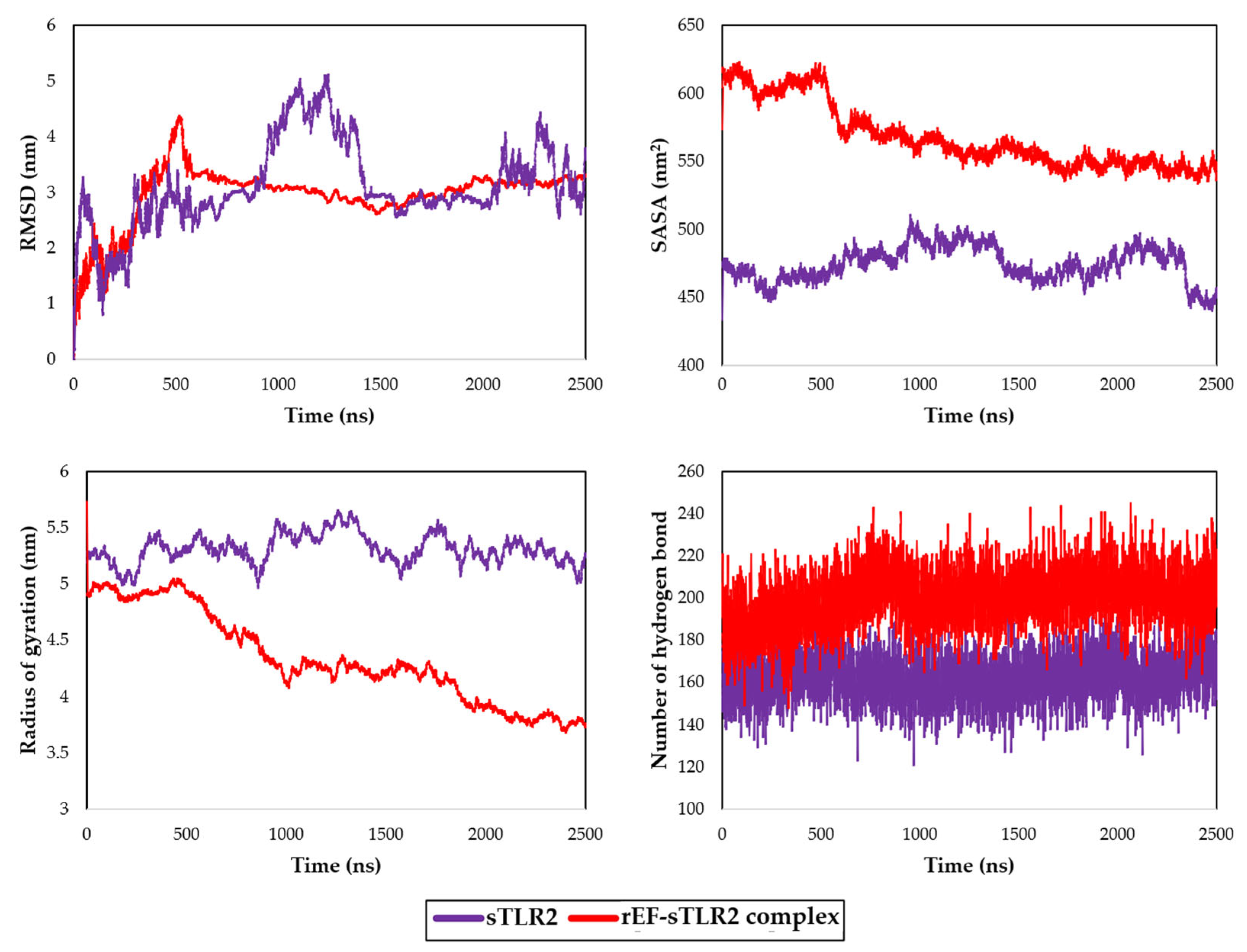
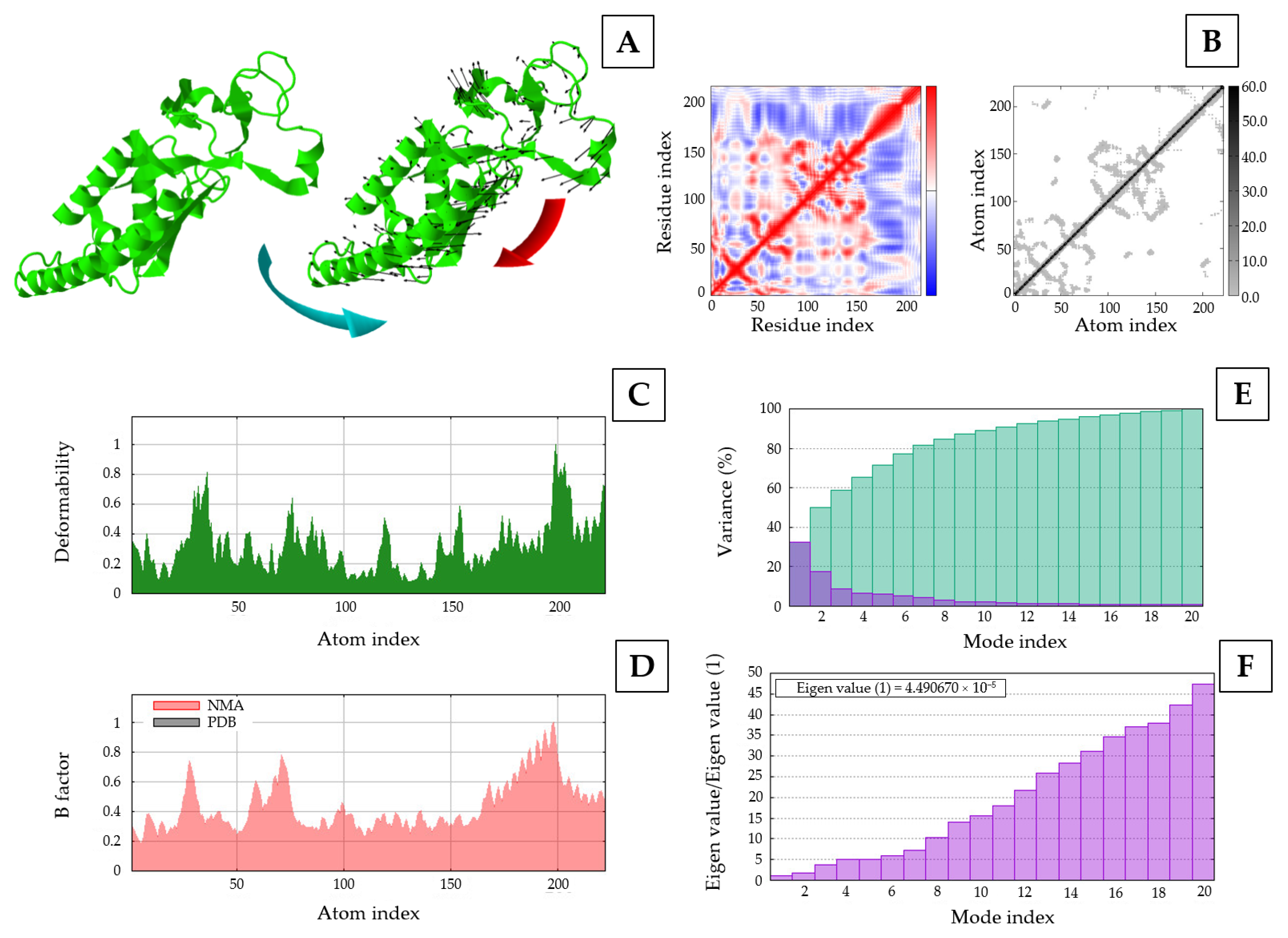
3.8. Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation
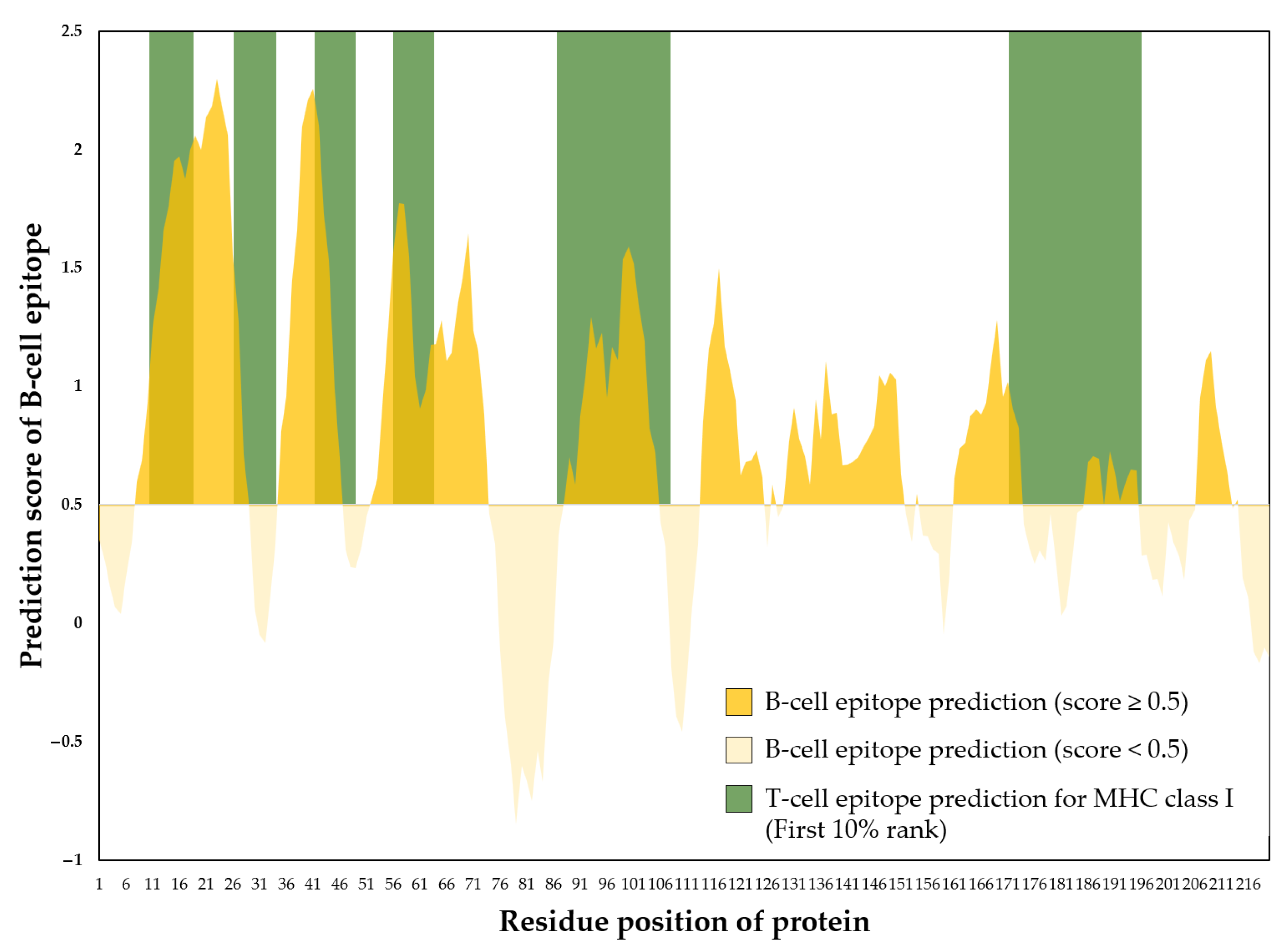
3.9. Prediction of B-Cell and T-Cell Epitope Regions of Recombinant EF Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EF | Extracellular factor protein |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| epf | Extracellular factor protein coding gene |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| rEF | Recombinant extracellular factor protein |
| Rg | Radius of gyration |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| RMSF | Root mean square fluctuation |
| SASA | Solvent accessible surface area |
| SLY | Suilysin or thiol activated cytolysin |
| sly | Suilysin coding gene |
| sTLR2 | Swine toll-like receptor 2 |
References
- Kerdsin, A. Human Streptococcus suis Infections in Thailand: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Genotypes, and Susceptibility. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis Virulence Factors: Are They All Really Critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.; Grenier, D. Understanding the Virulence of Streptococcus suis: A Veterinary, Medical, and Economic Challenge. Médecine Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.-P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an Important Pig Pathogen and Emerging Zoonotic Agent-an Update on the Worldwide Distribution Based on Serotyping and Sequence Typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntala, R.; Khamai, L.; Srisai, N.; Ounjaijean, S.; Khamduang, W.; Hongjaisee, S. Contamination of Streptococcus suis and S. suis Serotype 2 in Raw Pork and Edible Pig Organs: A Public Health Concern in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Foods 2024, 13, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijerink, M.; Ferrando, M.L.; Lammers, G.; Taverne, N.; Smith, H.E.; Wells, J.M. Immunomodulatory Effects of Streptococcus suis Capsule Type on Human Dendritic Cell Responses, Phagocytosis and Intracellular Survival. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. The Pathogenesis of the Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus suis: The Unresolved Questions. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, N.; Beineke, A.; de Buhr, N.; Lilienthal, S.; Merkel, J.; Waldmann, K.-H.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. Streptococcus suis Serotype 9 Bacterin Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 146, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M. Streptococcus Suis Vaccines: Candidate Antigens and Progress. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 1587–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Animal Health. Veterinary Autogenous Vaccine. Available online: https://niah.dld.go.th/webnew/images/newsletter/2564/news2564v5.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Gottschalk, M.G.; Lacouture, S.; Dubreuil, J.D. Characterization of Streptococcus suis Capsular Type 2 Haemolysin. Microbiology 1995, 141, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baums, C.G.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Surface-Associated and Secreted Factors of Streptococcus suis in Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esgleas, M.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Binding to Extracellular Matrix Proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Vecht, U.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smith, H.E. Protection of Pigs against Challenge with Virulent Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Strains by a Muramidase-Released Protein and Extracellular Factor Vaccine. Vet. Rec. 2001, 148, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, J.; Hu, J. Methods for the Detection and Characterization of Streptococcus suis: From Conventional Bacterial Culture Methods to Immunosensors. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.-J.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.-Q.; Qin, W.; Hu, J.; Jiang, S.-J.; Li, S.-G. Development of an Indirect Dot-PPA-ELISA Using Glutamate Dehydrogenase as a Diagnostic Antigen for the Rapid and Specific Detection of Streptococcus suis and Its Application to Clinical Specimens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecht, U.; Wisselink, H.J.; Anakotta, J.; Smith, H.E. Discrimination between Virulent and Nonvirulent Streptococcus suis Type 2 Strains by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Vet. Microbiol. 1993, 34, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasits, U.; Ahrens, C.H.; Müller, S.; Wollscheid, B. Protter: Interactive Protein Feature Visualization and Integration with Experimental Proteomic Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, R.; Zarebski, L.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Emami, H.; Hoof, I.; Salimi, N.; Damle, R.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. The Immune Epitope Database 2.0. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D854–D862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebditch, M.; Carballo-Amador, M.A.; Charonis, S.; Curtis, R.; Warwicker, J. Protein–Sol: A Web Tool for Predicting Protein Solubility from Sequence. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.W.A.; Moffat, L.; Lau, A.; Kandathil, S.M.; Jones, D.T. Deep Learning for the PSIPRED Protein Analysis Workbench. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W287–W293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Pearce, R.; Zhang, C.; Bell, E.W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER-MTD: A Deep-Learning-Based Platform for Multi-Domain Protein Structure and Function Prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 2326–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rathore, R.S. RamPlot: A Webserver to Draw 2D, 3D and Assorted Ramachandran (φ, ψ) Maps. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2025, 58, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A Server for Prediction of Protective Antigens, Tumour Antigens and Subunit Vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP—A Server for in Silico Prediction of Allergens. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14 (Suppl. 6), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools in the ExPASy Server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, Y.; Sugimoto, C.; Nakazawa, M.; Kashiwazaki, M. Detection of Streptococcus suis Type 2 in Tonsils of Slaughtered Pigs Using Improved Selective and Differential Media. Vet. Microbiol. 1991, 28, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwumabua, O.; O’Connor, M.; Shull, E. A Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay Specific for Streptococcus suis Based on the Gene Encoding the Glutamate Dehydrogenase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 218, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorato, R.V.; Trellet, M.E.; Jiménez-García, B.; Schaarschmidt, J.J.; Giulini, M.; Reys, V.; Koukos, P.I.; Rodrigues, J.P.G.L.M.; Karaca, E.; van Zundert, G.C.P.; et al. The HADDOCK2.4 Web Server for Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3219–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A Web Server for Predicting the Binding Affinity of Protein–Protein Complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; García, C.; Fraile, L.; Tommassen, J.; Arenas, J. How Streptococcus suis Escapes Antibiotic Treatments. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Harel, J.; D’Amours, B.; Lacouture, S.; Kobisch, M.; Gottschalk, M. Potential Use of an Unencapsulated and Aromatic Amino Acid-Auxotrophic Streptococcus suis Mutant as a Live Attenuated Vaccine in Swine. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3524–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cai, R.-J.; Li, C.-L.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Yang, D.-X. Deletion of SsnA Attenuates the Pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis and Confers Protection against Serovar 2 Strain Challenge. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, P.; Xu, J.; Tan, C.; Wang, X.; Bei, W.; Li, J. A Streptococcus suis Live Vaccine Suppresses Streptococcal Toxic Shock-Like Syndrome and Provides Sequence Type-Independent Protection. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F.; Chiers, K.; Maes, D.; Ducatelle, R.; Decostere, A. Efficacy of Vaccines against Bacterial Diseases in Swine: What Can We Expect? Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 100, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gan, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. An Ultrasensitive Peroxydisulfate Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Based on L-Cysteine Combined with Mimicking Bi-Enzyme Synergetic Catalysis to in Situ Generate Coreactant. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Hao, H.-J.; Xiong, G.-H.; Geng, H.-R.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.-H.; Cai, X.-H.; Jiang, Y.-Q. Development of Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Rapid Detection of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; et al. Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein. Anim. 2023, 13, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Yuan, F.; Fu, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Bei, W.; Chen, H. Vaccination with Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Recombinant 6PGD Protein Provides Protection against S. suis Infection in Swine. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 296, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shao, Z.-Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Hou, T.; Hu, D.; Zheng, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; et al. The Type II Histidine Triad Protein HtpsC Is a Novel Adhesion with the Involvement of Streptococcus suis Virulence. Virulence 2015, 6, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandanici, F.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Garibaldi, M.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Luque, I.; Tarradas, C.; Mancuso, G.; Papasergi, S.; Bárcena, J.A.; Teti, G.; et al. A Surface Protein of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Identified by Proteomics Protects Mice against Infection. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, G.; Wang, C.; Pan, X.; Cong, Y.; Pan, Q.; Wang, J.; Zheng, F.; Hu, F.; Tang, J. Identification and Experimental Verification of Protective Antigens against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Based on Genome Sequence Analysis. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gottschalk, M.; Esgleas, M.; Lacouture, S.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Willson, P.; Harel, J. Immunization with Recombinant Sao Protein Confers Protection against Streptococcus suis Infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, K.-J.; Lee, J.-W.; Hou, S.-M.; Chen, H.-S.; Chang, T.-C.; Chu, C.-Y. Evaluation on a Streptococcus suis Vaccine Using Recombinant Sao-l Protein Manufactured by Bioreactors as the Antigen in Pigs. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, e35–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, L.; D’Allaire, S.; Lebrun, A.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Antibody Response to an Autogenous Vaccine and Serologic Profile for Streptococcus suis Capsular Type 1/2. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 66, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Baums, C.G.; Brüggemann, C.; Kock, C.; Beineke, A.; Waldmann, K.-H.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Immunogenicity of an Autogenous Streptococcus suis Bacterin in Preparturient Sows and Their Piglets in Relation to Protection after Weaning. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kock, C.; Beineke, A.; Seitz, M.; Ganter, M.; Waldmann, K.-H.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. Intranasal Immunization with a Live Streptococcus suis Isogenic Ofs Mutant Elicited Suilysin-Neutralization Titers but Failed to Induce Opsonizing Antibodies and Protection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 132, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quessy, S.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Higgins, R. Immunization of Mice against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Infections Using a Live Avirulent Strain. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1994, 58, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quessy, S.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Caya, M.; Létourneau, R.; Higgins, R. Comparison of Pig, Rabbit and Mouse IgG Response to Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Proteins and Active Immunization of Mice against the Infection. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1994, 58, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Smith, H.E.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Peperkamp, K.; Vecht, U. Distribution of Capsular Types and Production of Muramidase-Released Protein (MRP) and Extracellular Factor (EF) of Streptococcus suis Strains Isolated from Diseased Pigs in Seven European Countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Fuller, T.E.; Teel, J.F.; Wilson, T.L.; Wolfram, T.J.; Lowery, D.E.; Gottschalk, M. Serotype Distribution and Production of Muramidase-Released Protein, Extracellular Factor and Suilysin by Field Strains of Streptococcus suis Isolated in the United States. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.E.; Reek, F.H.; Vecht, U.; Gielkens, A.L.; Smits, M.A. Repeats in an Extracellular Protein of Weakly Pathogenic Strains of Streptococcus suis Type 2 Are Absent in Pathogenic Strains. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3318–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot-Hérault, F.; Morvan, H.; Kéribin, A.M.; Gottschalk, M.; Kobisch, M. Production of Muraminidase-Released Protein (MRP), Extracellular Factor (EF) and Suilysin by Field Isolates of Streptococcus suis Capsular Types 2, 1/2, 9, 7 and 3 Isolated from Swine in France. Vet. Res. 2000, 31, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yan, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Yu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jin, M. A Novel Pro-Inflammatory Protein of Streptococcus suis 2 Induces the Toll-like Receptor 2-Dependent Expression of pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Activation of ERK1/2 Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Sun, L.; Yin, Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, B.; et al. Assessment of the Pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis Type 2 Infection in Piglets for Understanding Streptococcal Toxic Shock-like Syndrome, Meningitis, and Sequelae. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachance, C.; Segura, M.; Gerber, P.P.; Xu, J.; Gottschalk, M. Toll-like Receptor 2-Independent Host Innate Immune Response against an Epidemic Strain of Streptococcus suis That Causes a Toxic Shock-like Syndrome in Humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzas, C.; Lemire, P.; Auray, G.; Gerdts, V.; Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. Antibody Response Specific to the Capsular Polysaccharide Is Impaired in Streptococcus suis Serotype 2-Infected Animals. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwandner, R.; Dziarski, R.; Wesche, H.; Rothe, M.; Kirschning, C.J. Peptidoglycan- and Lipoteichoic Acid-Induced Cell Activation Is Mediated by Toll-like Receptor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17406–17409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzas, C.; Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Lemire, P.; Gagnon, F.; Lachance, C.; Van Calsteren, M.-R.; Segura, M. Group B Streptococcus and Streptococcus suis Capsular Polysaccharides Induce Chemokine Production by Dendritic Cells via Toll-like Receptor 2- and MyD88-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3106–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Chavda, V.P. Chapter 4—Subunit Protein-Based Vaccines. In Developments in Immunology; Chavda, V.P., Vora, L.K., Apostolopoulos, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 51–62. ISBN 978-0-443-18564-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pu, W.; Pan, X.; Li, P.; Bai, Q.; Liang, S.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. A Multi-Epitope Subunit Vaccine Providing Broad Cross-Protection against Diverse Serotypes of Streptococcus suis. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

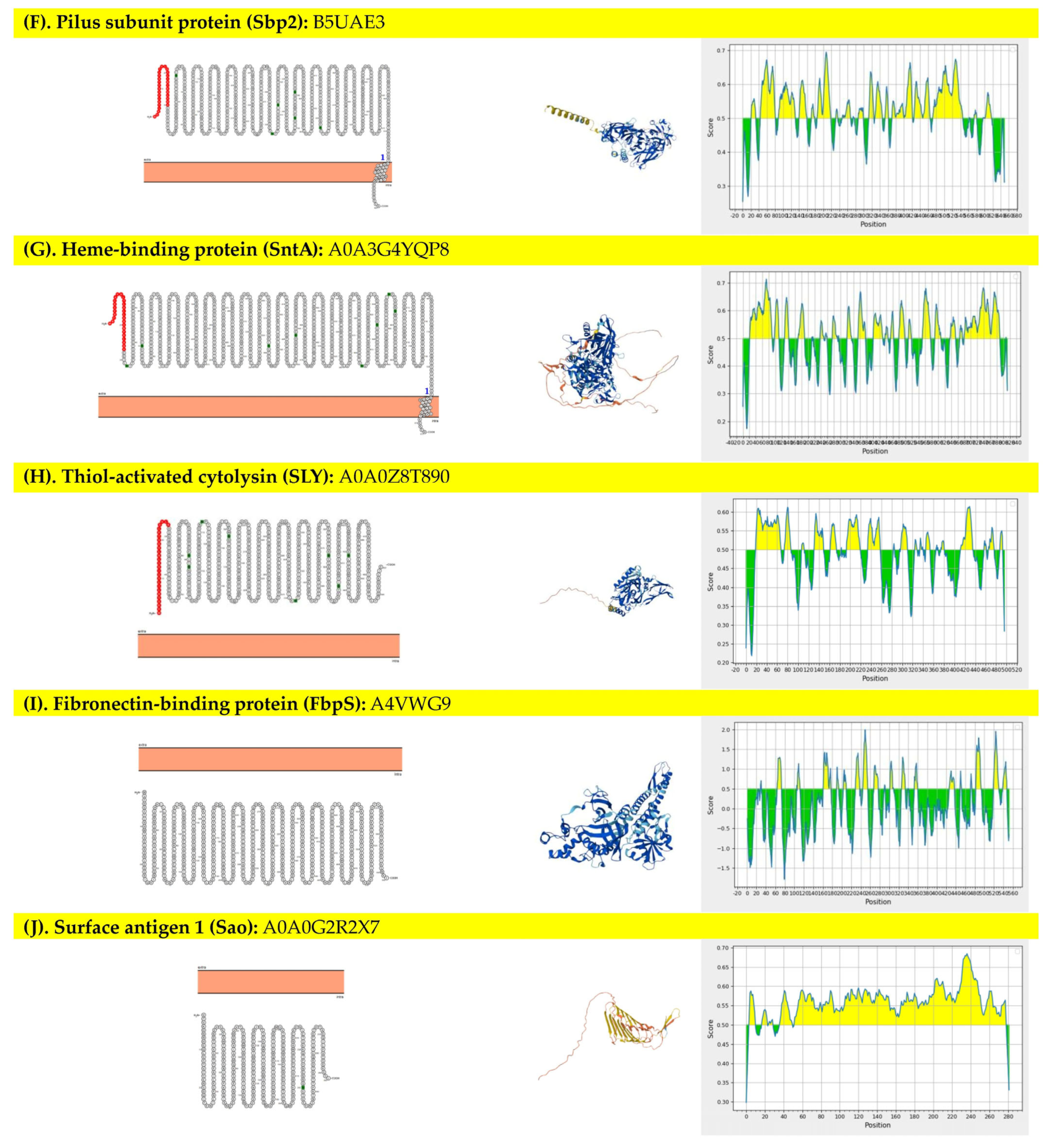


| Protein | Predicted Scaled Solubility | pI | Ratio of Candidate Protein to Population Average Solubility | At Least One Available Restriction Enzyme * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF | 0.795 | 4.830 | 1.77 | BamHI, BglI, HindIII, KpnI, PstI |
| SadP | 0.777 | 4.510 | 1.73 | NA |
| MRP | 0.726 | 4.870 | 1.61 | NA |
| SrtA | 0.435 | 5.930 | 0.97 | NA |
| Ofs | 0.435 | 5.930 | 0.97 | NA |
| Sbp2 | 0.616 | 5.410 | 1.37 | NA |
| SntA | 0.700 | 4.650 | 1.56 | NA |
| SLY | 0.469 | 4.910 | 1.04 | BglI, HindIII, KpnI |
| Physicochemical Property | Value of the rEF |
|---|---|
| Number of amino acids | 220 |
| Molecular weight | 23.30 kDa |
| Theoretical pI | 5.75 |
| Extinction coefficients | 4470 |
| Estimated half-life | |
| 30 h |
| >20 h |
| >10 h |
| Instability index | 17.72 (stable) |
| Aliphatic index | 68.36 |
| Grand average of hydropathicity | −0.709 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitsuwan, W.; Saengsawang, P.; Boripun, R.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Nwabor, O.F. Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein of Streptococcus suis as Potential Candidate Protein for Antibodies Against S. suis Detection and Subunit Vaccine Development: In Silico and In Vitro Approaches. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111128
Mitsuwan W, Saengsawang P, Boripun R, Rodríguez-Ortega MJ, Nwabor OF. Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein of Streptococcus suis as Potential Candidate Protein for Antibodies Against S. suis Detection and Subunit Vaccine Development: In Silico and In Vitro Approaches. Vaccines. 2025; 13(11):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111128
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitsuwan, Watcharapong, Phirabhat Saengsawang, Ratchadaporn Boripun, Manuel J. Rodríguez-Ortega, and Ozioma F. Nwabor. 2025. "Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein of Streptococcus suis as Potential Candidate Protein for Antibodies Against S. suis Detection and Subunit Vaccine Development: In Silico and In Vitro Approaches" Vaccines 13, no. 11: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111128
APA StyleMitsuwan, W., Saengsawang, P., Boripun, R., Rodríguez-Ortega, M. J., & Nwabor, O. F. (2025). Recombinant Extracellular Factor Protein of Streptococcus suis as Potential Candidate Protein for Antibodies Against S. suis Detection and Subunit Vaccine Development: In Silico and In Vitro Approaches. Vaccines, 13(11), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111128









