Immunogenicity and Safety of Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Booster Dose Administered Separately or Concomitantly with Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine or Measles–Mumps–Rubella Combined Attenuated Live Vaccine: An Open-Labelled, Randomized, Controlled, Phase 4 Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Randomization and Masking
2.4. Outcomes and Endpoints
2.5. Sample Size Determination
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
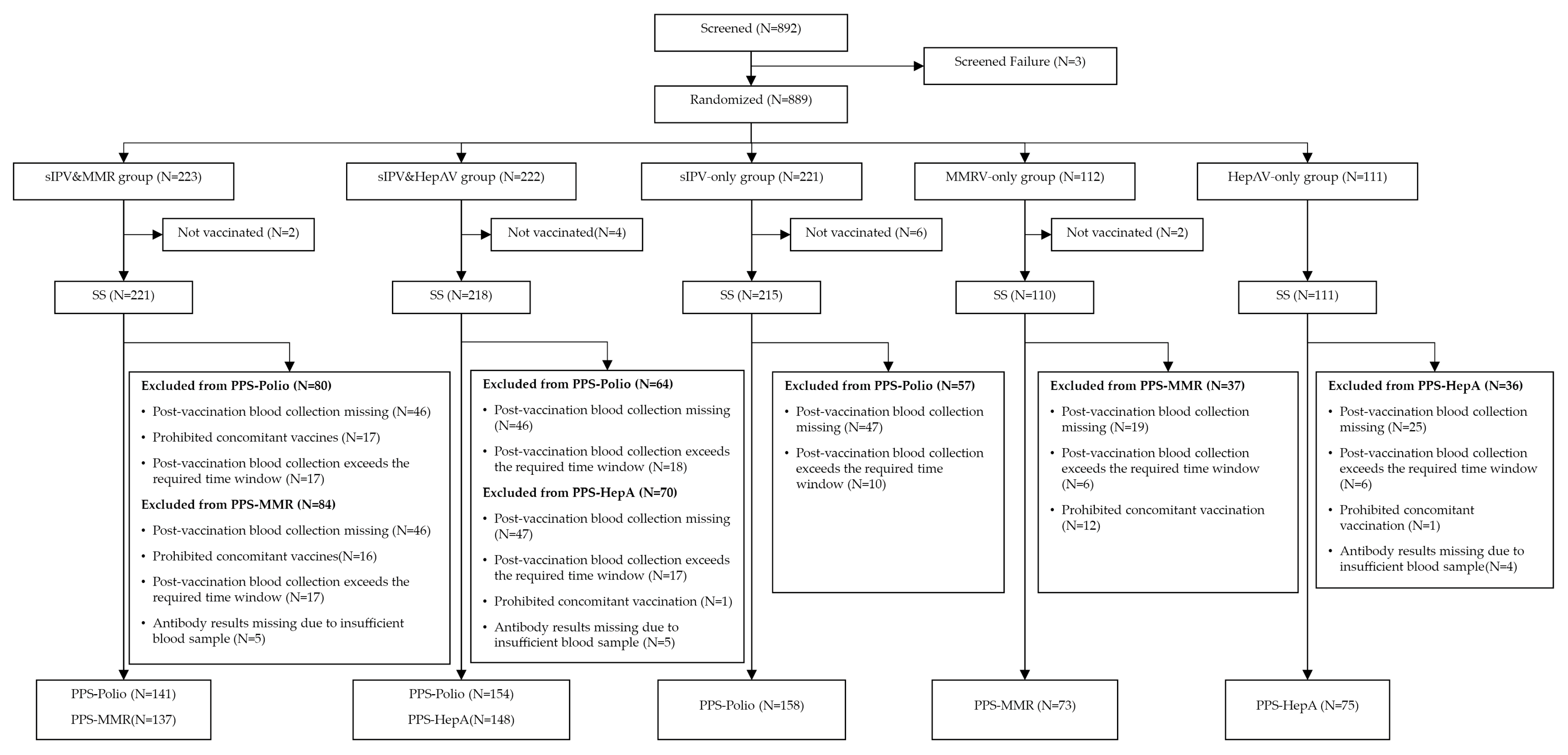
3.1. Participants Disposition and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Immunogenicity: Polioviruses
3.3. Immunogenicity: Hepatitis A and MMR Antigens
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Adverse Event |
| ANCOVA | Analysis of Covariance |
| AR | Adverse Reaction |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| cVDPV | Circulating Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus |
| DTaP | Diphtheria–Tetanus–acellular Pertussis Vaccine |
| ECLIA | Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EPI | Expanded Programme on Immunization |
| GCP | Good Clinical Practice |
| GMC | Geometric Mean Concentration |
| GMT | Geometric Mean Titer |
| GPEI | Global Polio Eradication Initiative |
| HAV/HepA | Hepatitis A Virus / Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine* |
| IM | Intramuscular |
| IPV | Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine |
| MMR | Measles–Mumps–Rubella Vaccine |
| MMRV | Measles–Mumps–Rubella–Varicella Vaccine |
| NAb | Neutralizing Antibody |
| OPV | Oral Poliovirus Vaccine |
| PPS | Per-Protocol Set |
| PV | Poliovirus |
| SAE | Serious Adverse Event |
| SCR | Seroconversion Rate |
| SC | Subcutaneous |
| SPoR | Seropositivity Rate |
| SPrR | Seroprotection Rate |
| SS | Safety Set |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| wIPV/sIPV | Wild strain IPV / Sabin strain IPV |
References
- Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI). Factsheet (1 April 2025). Available online: https://polioeradication.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/GPEI-general-factsheet-20250401.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Initiative for Vaccine Research; Executive Agency (IDEA). Current Status of Global Polio Eradication—June 2025. Available online: https://id-ea.org/current-status-of-global-polio-eradication-june-2025/ (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Bricks, L.F.; Macina, D.; Vargas-Zambrano, J.C. Polio Epidemiology: Strategies and Challenges for Polio Eradication Post the COVID-19 Pandemic. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, K.; Stehling-Ariza, T.; Bigouette, J.P.; Bennett, S.D.; Burns, C.C.; Quddus, A.; Wassilak, S.G.; Bolu, O. Progress Toward Poliomyelitis Eradication—Worldwide, January 2022–December 2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Poliovirus Containment: Guidance to Minimize Risks for Facilities Collecting, Handling or Storing Materials Potentially Infec-tious for Polioviruses. Second Edition. Web Annex A: Country- and Area-Specific Poliovirus Data, June 2024 Update (WHO/POLIO/24.02). Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/380037 (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- World Health Organization. Global Polio Eradication Initiative: Annual Report 2023. 2024. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/379270 (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Namageyo-Funa, A.; Greene, S.A.; Henderson, E.; Traoré, M.A.; Shaukat, S.; Bigouette, J.P.; Jorba, J.; Wiesen, E.; Bolu, O.; Diop, O.M.; et al. Update on Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus Outbreaks—Worldwide, January 2023–June 2024. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (on Behalf of GPEI). Polio Eradication Strategy 2022–2026. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/341938/9789240024830-eng.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Lewis, I.; Ottosen, A.; Rubin, J.; Blanc, D.C.; Zipursky, S.; Wootton, E. A Supply and Demand Management Perspective on the Accelerated Global Introductions of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine in a Constrained Supply Market. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216 (Suppl. 1), S33–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNICEF Supply Division. Inactivated Polio Vaccine: Supply and Demand Update. February 2025. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/supply/media/23146/file/IPV-Market%20Note-February-2025.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Kreeftenberg, H.; van der Velden, T.; Kersten, G.; van der Heuvel, N.; de Bruijn, M. Technology Transfer of Sabin-IPV to New Developing Country Markets. Biologicals 2006, 34, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, G.; Chu, K.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, F.; Ying, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Sabin Strain-Based Inactivated Polio Vaccine: A Phase 3 Clinical Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, K.; Han, W.; Chu, K.; Jiang, D.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Ying, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Compared with Salk Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine in Different Sequential Schedules with Bivalent Oral Poliovirus Vaccine: Randomized Controlled Noninferiority Clinical Trials in China. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Zheng, M.; Wu, F.; Sun, J.; Tuo, L.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Wei, L.; Xia, Z.; et al. Safety and 6-Month Immune Persistence of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine (Sabin Strains) Simultaneously Administered with Other Vaccines for Primary and Booster Immunization in Jiangxi Province, China. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Han, W.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Sequential Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine from Different Manufacturers in Infants: Randomized, Blinded, Controlled Trial. Vaccine 2025, 61, 127448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Polio vaccines: WHO position paper—June 2022. Wkly. Epidemiol. Record. 2022, 97, 277–300. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Measles vaccines: WHO position paper—April 2017. Wkly. Epidemiol. Record. 2017, 92, 205–228. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Fan, Q.; Tang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Immunogenicity Evaluation of Primary Polio Vaccination Schedule with Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccines and Bivalent Oral Poliovirus Vaccine. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.; Thuy, C.T.; Tam, N.H.; Nga, L.H.; Uyen, N.T.V.; Lan, T.T.T.; Tran, A.; Diem, L.T.K.; Khang, H.P.; Dung, D.T.X.; et al. Detection of Immunity Gap before Measles Outbreak, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2024. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2025, 31, e250234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis A Vaccines: WHO Position Paper—October 2022. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2022, 97, 493–512. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; He, H.; Deng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Du, Y.; et al. A Serological Survey of Measles and Rubella Antibodies among Different Age Groups in Eastern China. Vaccines 2024, 12, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Yao, K. One Single-Center Serological Survey on Measles, Rubella and Mumps Antibody Levels of People in Youyang, China. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 4203–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Zhu, X.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, R.; Liu, S.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Concomitant Administration of the Sabin-Strain-Based Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine, the Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis Vaccine, and Measles-Mumps-Rubella Vaccine to Healthy Infants Aged 18 Months in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 137, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, N.P.; Weston, W.M.; Kuriyakose, S.; Kolhe, D.; Howe, B.; Friedland, L.R.; Van Der Meeren, O. An Open-Label, Randomized, Multi-Center Study of the Immunogenicity and Safety of DTaP-IPV (Kinrix™) Co-Administered with MMR Vaccine with or without Varicella Vaccine in Healthy Pre-School Age Children. Vaccine 2012, 30, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, E.; Saidu, Y.; Adetifa, J.U.; Adigweme, I.; Hydara, M.B.; Bashorun, A.O.; Moneke-Anyanwoke, N.; Umesi, A.; Roberts, E.; Cham, P.M.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine When Given with Measles-Rubella Combined Vaccine and Yellow Fever Vaccine and When Given via Different Administration Routes: A Phase 4, Randomised, Non-Inferiority Trial in The Gambia. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e534–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Bai, Q.; Sun, X. Safety of Concomitant Administration of Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine with Other Vaccines in Children under 16 Years Old in Post-Marketing Surveillance. Vaccine 2023, 41, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Multiple Injections: Acceptability and Safety. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/essential-programme-on-immunization/implementation/multiple-injections (accessed on 25 September 2025).
| Indicators | sIPV&MMRV Group (n= 221) | sIPV& HepA Group (n = 218) | sIPV-Only Group (n = 215) | MMRV-Only Group (n = 110) | HepA-Only Group (n = 111) | Two-Side p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (months) | 18.2 (0.6) | 18.2 (0.4) | 18.2 (0.5) | 18.3 (0.6) | 18.3 (0.6) | 0.2075 |
| Height (cm) | 82.8 (3.1) | 82.7 (2.9) | 82.1 (2.9) | 82.6 (3.1) | 82.8 (3.4) | 0.0761 |
| Weight (kg) | 11.5 (1.2) | 11.5 (1.3) | 11.2 (1.5) | 11.6 (1.3) | 11.4 (1.4) | 0.1116 |
| Axillary temp | 36.5 (0.3) | 36.5 (0.3) | 36.5 (0.3) | 36.4 (0.3) | 36.5 (0.3) | 0.9568 |
| Han Chinese | 100% | 99.5% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 0.7474 |
| Boys | 49.3% | 48.6% | 52.1% | 56.4% | 55.0% | 0.6018 |
| Girls | 50.7% | 51.4% | 47.9% | 43.6% | 45.1% |
| Indicators | sIPV&MMRV Group (n = 141) | sIPV&HepA Group (n = 154) | sIPV-Only Group (n = 158) | Two-Side p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype 1 | ||||
| Pre-vaccination | ||||
| Sero-protection n (%) | 118 (83.7) | 130 (84.4) | 131 (82.9) | 0.9374 |
| 95%CI | (76.5, 89.4) | (77.7, 89.8) | (76.1, 88.4) | |
| GMT | 21.3 | 21.9 | 25.0 | 0.4612 |
| 95%CI | (17.6, 25.6) | (18.0, 26.6) | (20.5, 30.5) | |
| Post-vaccination | ||||
| Sero-protection n (%) | 141 (100.0) | 154 (100.0) | 158 (100.0) | 1.0000 |
| 95%CI | (97.4, 100.0) | (97.6, 100.0) | (97.7, 100.0) | |
| Seroconversion n (%) | 134 (95.0) | 143 (92.9) | 152 (96.2) | 0.4096 |
| 95%CI | (90.0, 98.0) | (87.6, 96.4) | (91.9, 98.6) | |
| GMT a | 750.5 | 662.7 | 841.6 | NA |
| 95%CI a | (617.9, 911.4) | (542.7, 809.1) | (706.4, 1002.6) | |
| GMT b | 767.6 | 671.2 | 814.5 | 0.2892 |
| 95%CI b | (639.2, 921.9) | (563.4, 799.7) | (685.0, 968.3) | |
| Serotype 2 | ||||
| Pre-vaccination | ||||
| Sero-protection n (%) | 133 (94.3) | 152 (98.7) | 152 (96.2) | 0.1147 |
| 95%CI | (89.1, 97.5) | (95.4, 99.8) | (91.9, 98.6) | |
| GMT | 56.3 | 66.5 | 71.7 | 0.2063 |
| 95%CI | (45.9, 69.2) | (55.8, 79.3) | (59.1, 87.0) | |
| Post-vaccination | ||||
| Sero-protection n (%) | 141 (100.0) | 154 (100.0) | 158 (100.0) | 1.0000 |
| 95%CI | (97.4, 100.0) | (97.6, 100.0) | (97.7, 100.0) | |
| Seroconversion n (%) | 137 (97.2) | 142 (92.2) | 151 (95.6) | 0.1380 |
| 95%CI | (92.9, 99.2) | (86.8, 95.9) | (91.1, 98.2) | |
| GMT a | 2641.9 | 2567.3 | 3074.8 | NA |
| 95%CI a | (2291.9, 3045.2) | (2172.1, 3034.5) | (2671.4, 3539.0) | |
| GMT b | 2692.3 | 2558.5 | 3033.4 | 0.2510 |
| 95%CI b | (2309.1, 3139.2) | (2209.6, 2962.6) | (2624.2, 3506.5) | |
| Serotype 3 | ||||
| Pre-vaccination | ||||
| Sero-protection n (%) | 117 (83.0) | 130 (84.4) | 134 (84.8) | 0.9032 |
| 95%CI | (75.7, 88.8) | (77.7, 89.8) | (78.23, 90.0) | |
| GMT | 23.2 | 29.1 | 29.7 | 0.2090 |
| 95%CI | (18.7, 28.7) | (23.5, 36.0) | (24.1, 36.6) | |
| Post-vaccination | ||||
| Sero-protection n (%) | 141 (100.0) | 154 (100.0) | 158 (100.0) | 1.0000 |
| 95%CI | (97.4, 100.0) | (97.6, 100.0) | (97.7, 100.0) | |
| Seroconversion n (%) | 137 (97.2) | 144 (93.5) | 154 (97.5) | 0.1422 |
| 95%CI | (92.9, 99.2) | (88.4, 96.8) | (93.7, 99.3) | |
| GMT a | 1627.8 | 1394.5 | 1851.8 | NA |
| 95%CI a | (1349.2, 1964.0) | (1156.5, 1681.4) | (1559.9, 2198.3) | |
| GMT b | 1695.5 | 1372.8 | 1813.2 | 0.0636 |
| 95%CI b | (1416.5, 2029.5) | (1156.2, 1629.9) | (1530.3, 2148.2) |
| Serotypes and Comparison Groups | SCR Difference (95%CI) | Two-Side p Value | One-Side p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype 1 | |||
| sIPV&MMRV vs. sIPV group | −1.2% (−6.6%, 3.8%) | 0.6213 | 0.3107 |
| sIPV&HepA vs. sIPV group | −3.4% (−9.0%, 1.9%) | 0.1931 | 0.0965 |
| sIPV&MMRV vs. sIPV&HepA group | 2.2% (−3.6%, 8.1%) | 0.4349 | 0.2175 |
| Serotype 2 | |||
| sIPV&MMRV vs. sIPV group | 1.6% (−3.2%, 6.4%) | 0.4650 | 0.2325 |
| sIPV&HepA vs. sIPV group | −3.4% (−9.3%, 2.1%) | 0.2144 | 0.1072 |
| sIPV&MMRV vs. sIPV&HepA group | 5.0% (−0.3%, 10.7%) | 0.0605 | 0.0303 |
| Serotype 3 | |||
| sIPV&MMRV vs. sIPV group | −0.3% (−4.8%, 3.9%) | 1.0000 | 0.5741 |
| sIPV&HepA vs. sIPV group | −4.0% (−9.3%, 0.7%) | 0.0910 | 0.0455 |
| sIPV&MMRV vs. sIPV&HepA group | 3.7% (−1.4%, 9.1%) | 0.1401 | 0.0700 |
| Indicators | sIPV&HepA/ MMRV Group | HepA/MMRV-Only Group | Two-Side p Value | sIPV&HepA/ MMRV Group | HepA/MMRV-Only Group | Two-Side p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatis A | Measles | |||||
| No. of participants | 148 | 75 | 137 | 73 | ||
| Pre-vaccination | ||||||
| Sero-positivity n (%) | 116 (78.4) | 68 (90.7) | 0.0225 | 134 (97.8) | 72 (98.6) | 1.0000 |
| 95%CI | (70.9, 84.7) | (81.7, 96.2) | (93.7, 99.6) | (92.6, 100.0) | ||
| GMC | 23.6 | 25.2 | 2025.7 | 1946.7 | 0.7892 | |
| 95%CI | (22.3, 24.9) | (24.0, 26.5) | 0.0749 | (1746.5, 2349.6) | (1507.4, 2513.9) | |
| Post-vaccination | ||||||
| Seroconversion n (%) | 143 (96.6) | 74 (98.7) | 0.6663 | NA | NA | |
| 95%CI | (92.3, 98.9) | (92.8, 100.0) | NA | NA | ||
| Sero-positivity n (%) | 147 (99.3) | 75 (100.0) | 1.0000 | 137 (100.0) | 73 (100.0) | 1.0000 |
| 95%CI | (96.3, 100.0) | (95.2, 100.0) | (97.3, 100.0) | (95.1, 100.0) | ||
| GMC a | 407.7 | 476.2 | NA | 3130.9 | 3238.9 | NA |
| 95%CI a | (359.2, 462.6) | (417.3, 543.6) | (2862.4, 3424.6) | (2871.6, 3653.1) | ||
| GMC b | 412.2 | 465.9 | 0.2224 | 3115.7 | 3268.6 | 0.4141 |
| 95%CI b | (367.8, 462.0) | (396.9, 546.9) | (2910.8, 3335.1) | (2977.7, 3587.9) | ||
| Mumps | Rubella | |||||
| No. of participants | 137 | 73 | 137 | 73 | ||
| Pre-vaccination | ||||||
| Sero-positivity n (%) | 115 (83.9) | 58 (79.5) | 0.4161 | 130 (94.9) | 72 (98.6) | 0.2665 |
| 95%CI | (76.7, 89.7) | (68.4, 88.0) | (89.8, 97.9) | (92.6, 100.0) | ||
| GMC | 259.3 | 237.9 | 0.5545 | 89.9 | 91.5 | 0.8558 |
| 95%CI | (218.1, 308.2) | (189.6, 298.4) | (79.1, 102.2) | (79.6, 105.2) | ||
| Post-vaccination | ||||||
| Sero-positivity n (%) | 136 (99.3) | 73 (100.0) | 1.0000 | 137 (100.0) | 73 (100.0) | 1.0000 |
| 95%CI | (96.0, 100.0) | (95.1, 100.0) | (97.3, 100.0) | (95.1, 100.0) | ||
| GMC a | 1716.7 | 1996.7 | NA | 139.7 | 148.6 | NA |
| 95%CI a | (1476.1, 1996.4) | (1707.5, 2334.9) | (127.8, 152.7) | (134.7, 164.0) | ||
| GMC b | 1697.6 | 2039.0 | 0.0871 | 134.0 | 148.0 | 0.3584 |
| 95%CI b | (1499.9, 1921.4) | (1720.7, 2416.0) | (130.5, 150.2) | (134.4, 163.0) | ||
| Indicators | sIPV&MMRV Group (n = 221) | sIPV&HepA Group (n = 218) | sIPV-Only Group (n = 215) | MMRV-Only Group (n = 110) | HepA-Only Group (n = 111) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 32 (14.5) | 38 (17.4) | 35 (16.3) | 8 (7.3) | 12 (10.8) |
| Grade 1 | 13 (5.9) | 26 (11.9) | 28 (13.0) | 4 (3.6) | 9 (8.1) |
| Grade 2 | 22 (10.0) | 14 (6.4) | 13 (6.1) | 4 (3.6) | 5 (4.5) |
| Grade 3 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) |
| Fever | 19 (8.6) | 20 (9.2) | 23 (10.7) | 5 (4.6) | 8 (7.2) |
| Irritability postvaccinal | 3 (1.4) | 6 (2.8) | 9 (4.2) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (1.8) |
| Decreased activity | 3 (1.4) | 3 (1.4) | 4 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Vaccination site erythema | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Vaccination site swelling | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Diarrhea | 3 (1.4) | 4 (1.8) | 7 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.8) |
| Vomiting | 1 (0.5) | 3 (1.4) | 5 (2.3) | 1 (0.9) | 3 (2.7) |
| Decreased appetite | 5 (2.2) | 1 (0.5) | 8 (3.7) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (1.8) |
| Cough | 3 (1.4) | 1 (0.5) | 2 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.8) |
| Rhinorrhea | 3 (1.4) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 3 (2.7) |
| Rash erythematous | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Rash | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Erythema | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Hypersensitivity | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Han, W.; Chu, K.; Zhang, H.; Tuo, L.; Duan, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Luan, C.; Pan, H.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Booster Dose Administered Separately or Concomitantly with Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine or Measles–Mumps–Rubella Combined Attenuated Live Vaccine: An Open-Labelled, Randomized, Controlled, Phase 4 Clinical Trial. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111087
Hu J, Han W, Chu K, Zhang H, Tuo L, Duan X, Li J, Yuan F, Luan C, Pan H, et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Booster Dose Administered Separately or Concomitantly with Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine or Measles–Mumps–Rubella Combined Attenuated Live Vaccine: An Open-Labelled, Randomized, Controlled, Phase 4 Clinical Trial. Vaccines. 2025; 13(11):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111087
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jialei, Weixiao Han, Kai Chu, Hengzhen Zhang, Ling Tuo, Xiaoqian Duan, Jun Li, Fang Yuan, Chunfang Luan, Hongxing Pan, and et al. 2025. "Immunogenicity and Safety of Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Booster Dose Administered Separately or Concomitantly with Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine or Measles–Mumps–Rubella Combined Attenuated Live Vaccine: An Open-Labelled, Randomized, Controlled, Phase 4 Clinical Trial" Vaccines 13, no. 11: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111087
APA StyleHu, J., Han, W., Chu, K., Zhang, H., Tuo, L., Duan, X., Li, J., Yuan, F., Luan, C., Pan, H., & Jiao, P. (2025). Immunogenicity and Safety of Sabin Strain Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Booster Dose Administered Separately or Concomitantly with Inactivated Hepatitis A Vaccine or Measles–Mumps–Rubella Combined Attenuated Live Vaccine: An Open-Labelled, Randomized, Controlled, Phase 4 Clinical Trial. Vaccines, 13(11), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111087






