Multi-Antigen Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) mRNA Vaccine Induces Humoral and Cell-Mediated Responses in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
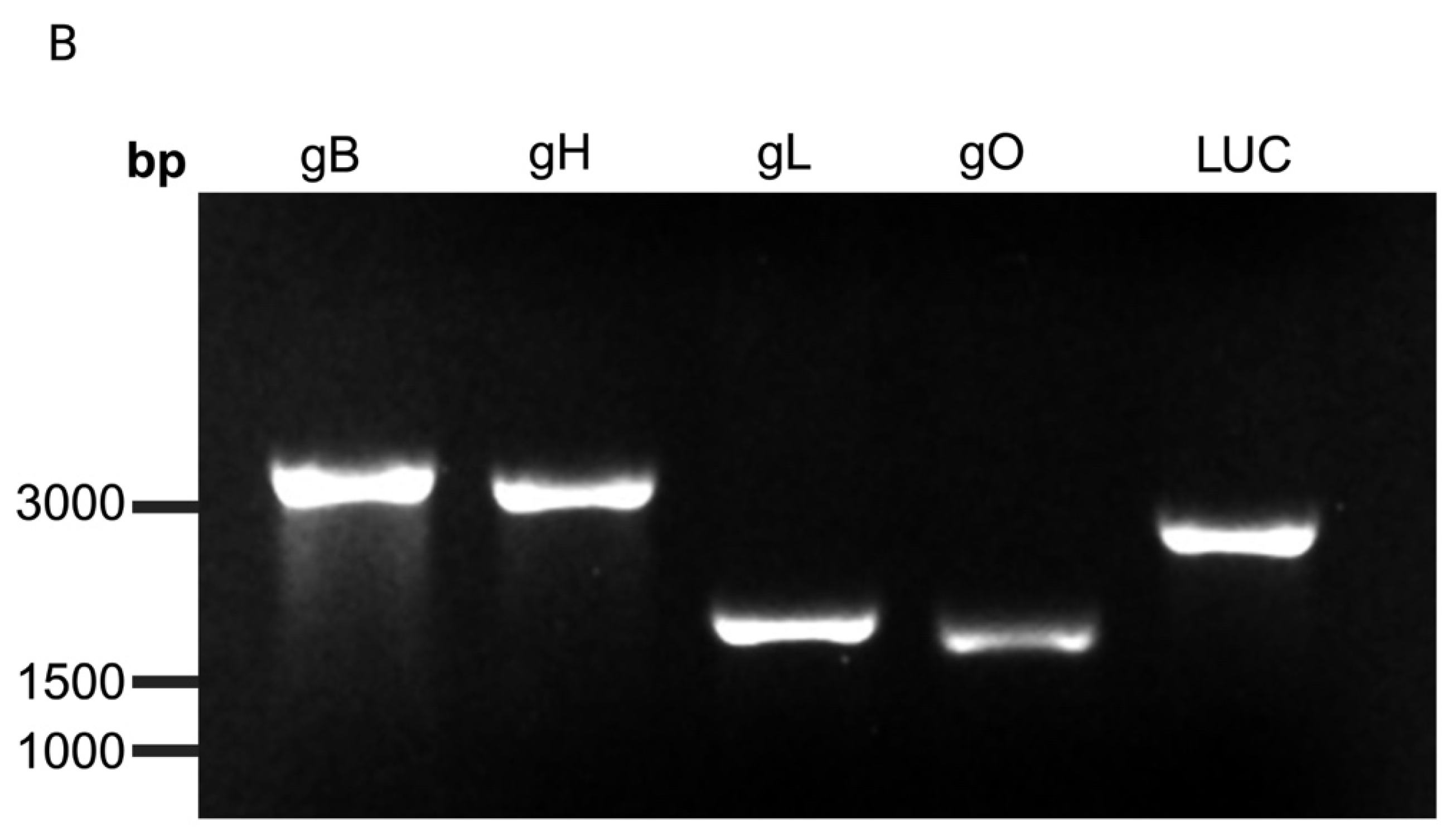
2.1. Generation of EEHV1A mRNA Transcripts and Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Encapsulation
2.2. Immunoblot
2.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
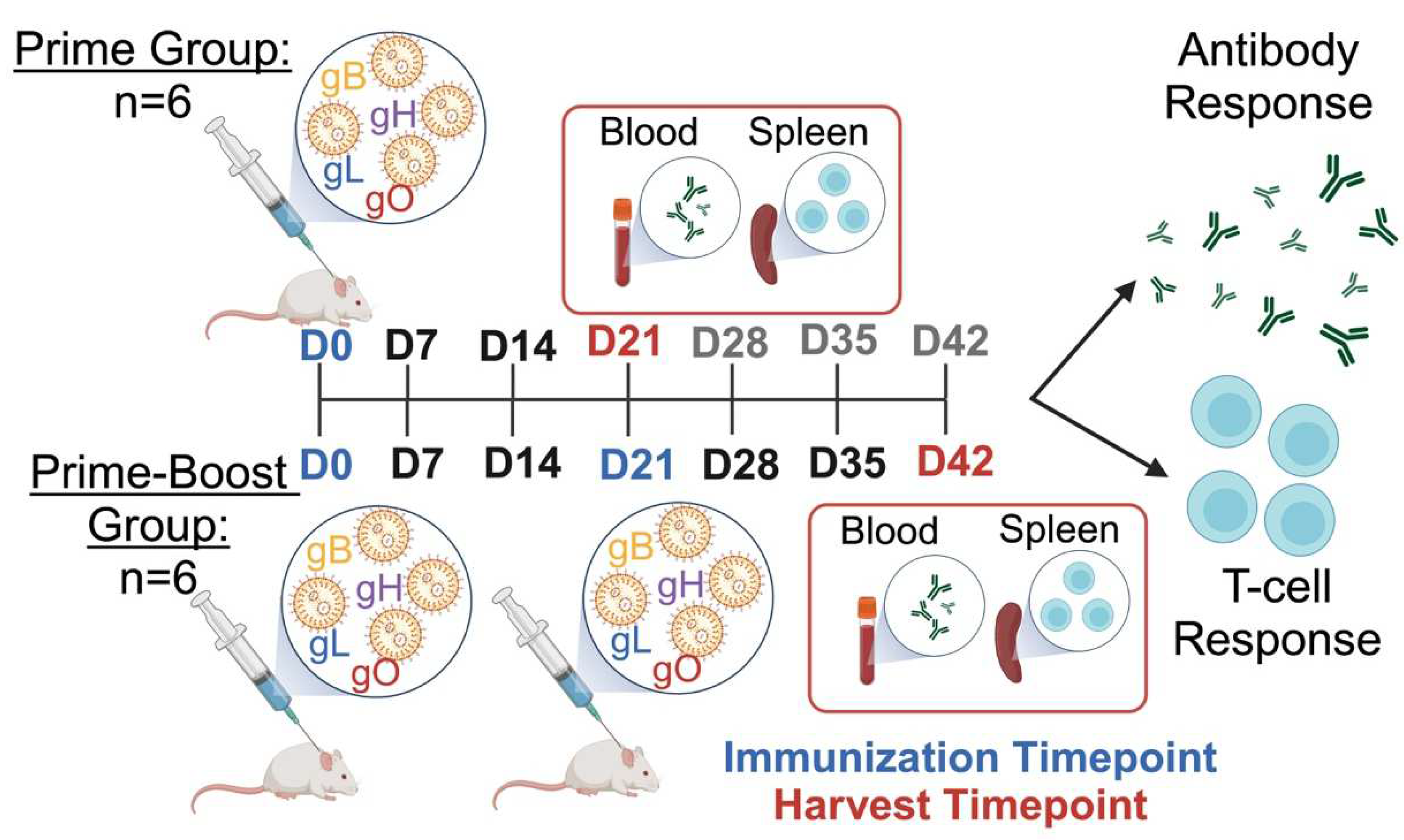
2.4. Mouse Immunizations
2.5. The Immunoassay to Evaluate the EEHV1A-Specific Antibody Response
2.6. The Immunoassay to Evaluate EEHV1A-Specific T-Cell Response
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protein Expression and Localization of Glycoproteins gB, gH, gL, and gO in the Transfected Cells
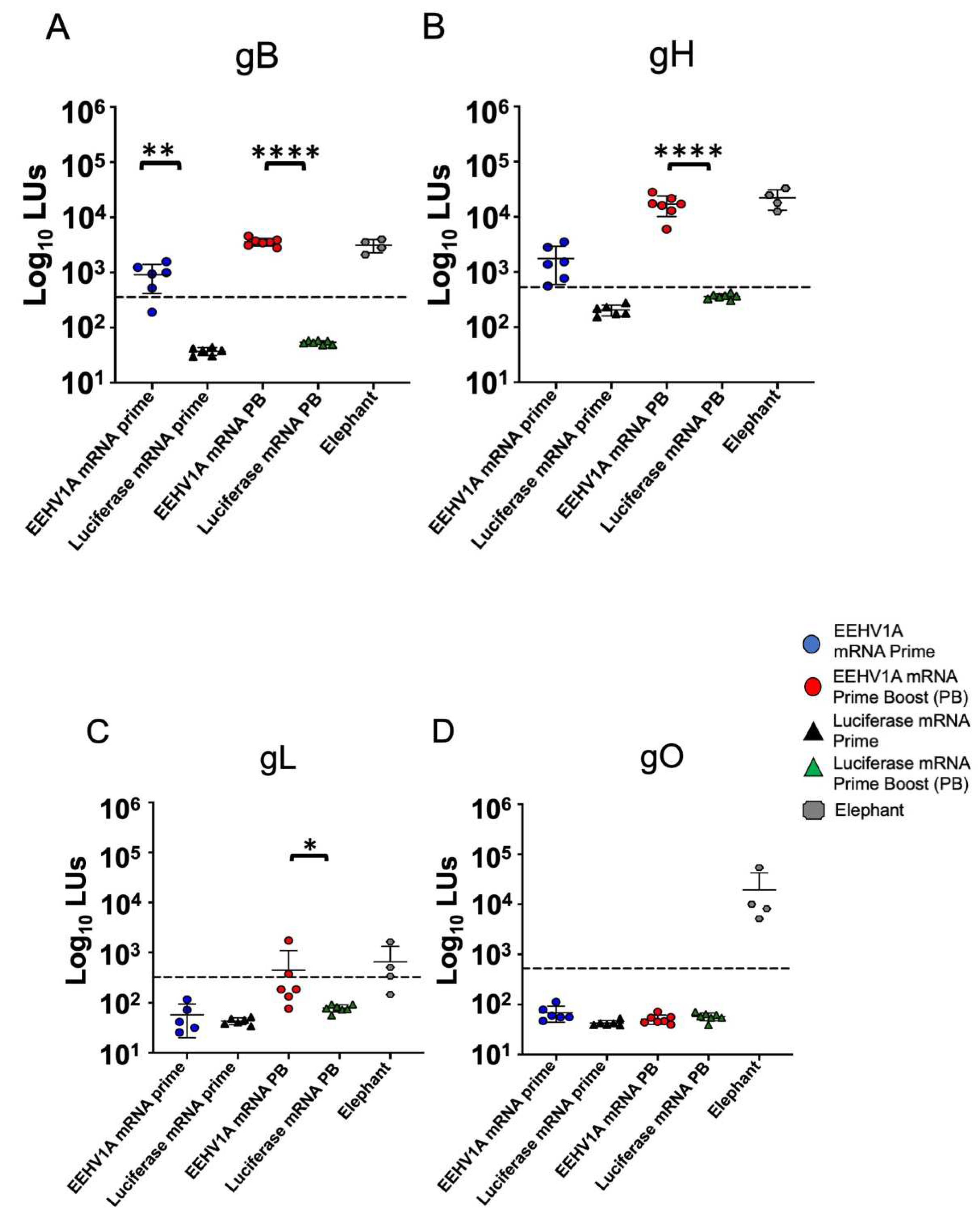
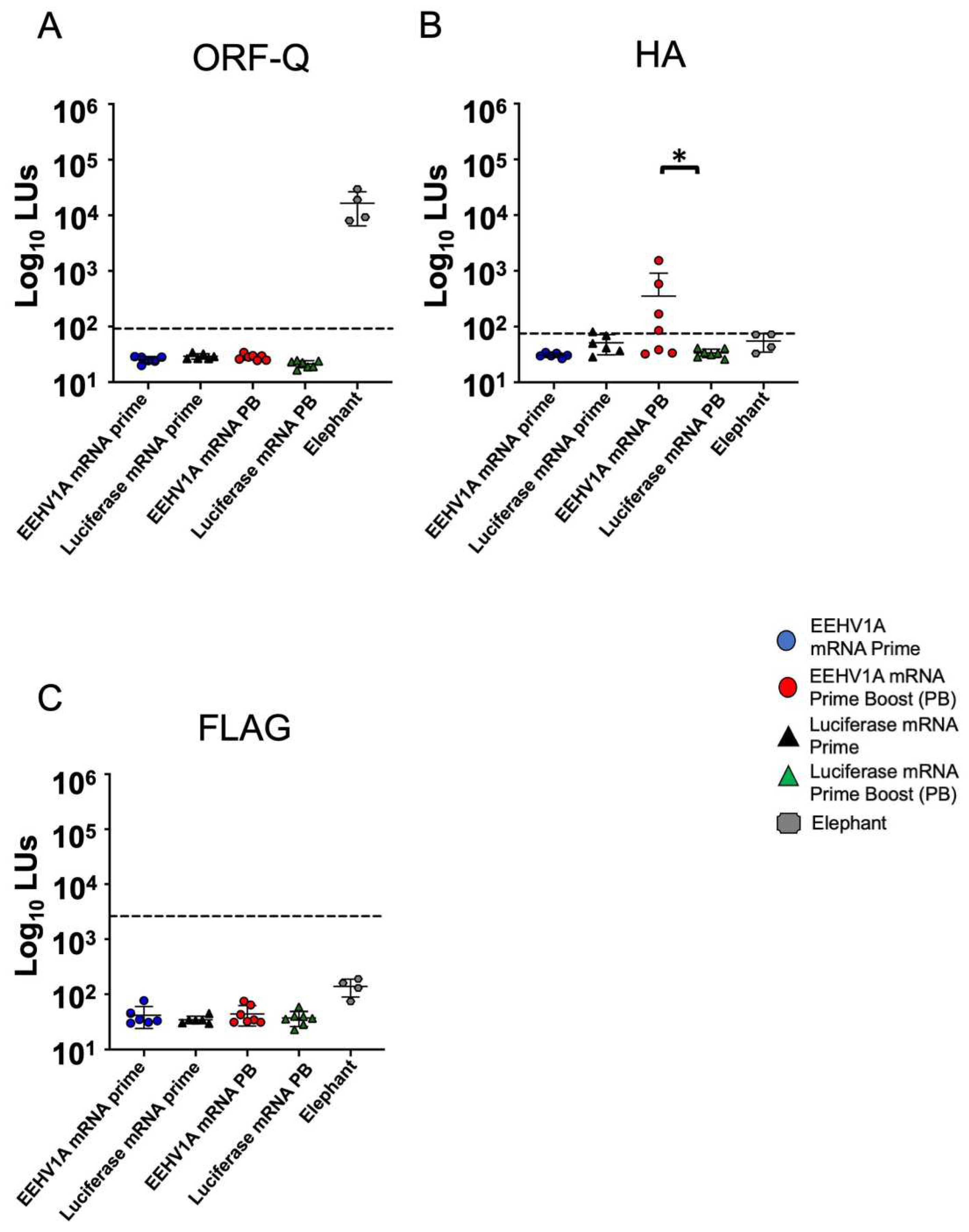
3.2. Multi-Antigen EEHV1A mRNA Vaccine Elicits Robust Antibody Responses in Mice
3.3. The EEHV1A gB, gH, gL, and gO mRNA Vaccine Elicits CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Responses in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, S.Y.; Latimer, E.M.; Hayward, G.S. Review of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses and Acute Hemorrhagic Disease. Ilar J. 2016, 56, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayette, M.A.; Brenner, E.E.; Garner, M.M.; Bowman, M.R.; Latimer, E.; Proudfoot, J.S. Acute Hemorrhagic Disease Due to Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 3a Infection in Five African Elephants (Loxodonta africana) at One North American Zoological Institution. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2021, 52, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, L.K.; Montali, R.J.; Garber, R.L.; Kennedy, M.A.; Lehnhardt, J.; Hildebrandt, T.; Schmitt, D.; Hardy, D.; Alcendor, D.J.; Hayward, G.S. Novel endotheliotropic herpesviruses fatal for Asian and African elephants. Science 1999, 283, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.C.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Long, S.Y.; Latimer, E.M.; Nofs, S.A.; Bronson, E.; Casares, M.; Fouraker, M.D.; Pearson, V.R.; Richman, L.K.; et al. Detection of Quiescent Infections with Multiple Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses (EEHVs), Including EEHV2, EEHV3, EEHV6, and EEHV7, within Lymphoid Lung Nodules or Lung and Spleen Tissue Samples from Five Asymptomatic Adult African Elephants. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 3028–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, E.; McClure, M.; Sohl, J.; Wiedner, E.; Cox, S.; Latimer, E.M.; Pearson, V.R.; Hayward, G.S.; Fuery, A.; Ling, P.D. Epidemiologic Evaluation of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 3b Infection in an African Elephant (Loxodonta africana). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2017, 48, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, J.C.; Latimer, E.M.; Long, S.Y.; Richman, L.K.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Hayward, G.S. Comparative genome analysis of four elephant endotheliotropic herpesviruses, EEHV3, EEHV4, EEHV5, and EEHV6, from cases of hemorrhagic disease or viremia. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13547–13569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, L.K.; Zong, J.C.; Latimer, E.M.; Lock, J.; Fleischer, R.C.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Hayward, G.S. Elephant endotheliotropic herpesviruses EEHV1A, EEHV1B, and EEHV2 from cases of hemorrhagic disease are highly diverged from other mammalian herpesviruses and may form a new subfamily. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13523–13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, J.J.; Nofs, S.A.; Peng, R.; Hayward, G.S.; Ling, P.D. Development and validation of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assays to detect elephant endotheliotropic herpesviruses-2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 186, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, J.J.; Nofs, S.A.; Zachariah, A.; Kalaivannan, N.; Ling, P.D. Detection of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus infection among healthy Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) in South India. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pursell, T.; Spencer Clinton, J.L.; Tan, J.; Peng, R.; Qin, X.; Doddapaneni, H.; Menon, V.; Momin, Z.; Kottapalli, K.; Howard, L.; et al. Primary Infection May Be an Underlying Factor Contributing to Lethal Hemorrhagic Disease Caused by Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 3 in African Elephants (Loxodonta africana). Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0098321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, L.K.; Montali, R.J.; Cambre, R.C.; Schmitt, D.; Hardy, D.; Hildbrandt, T.; Bengis, R.G.; Hamzeh, F.M.; Shahkolahi, A.; Hayward, G.S. Clinical and pathological findings of a newly recognized disease of elephants caused by endotheliotropic herpesviruses. J. Wildl. Dis. 2000, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khammesri, S.; Mathura, Y.; Boonprasert, K.; Ampasavate, C.; Hongwiset, D.; Brown, J.L.; Thitaram, C. Successful treatment of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus infection in an Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) calf by oral acyclovir medication: Case report. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, A.; Seilern-Moy, K.; Darpel, K.; Steinbach, F.; Molenaar, F. Surviving and fatal Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus-1A infections in juvenile Asian elephants—Lessons learned and recommendations on anti-herpesviral therapy. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuery, A.; Pursell, T.; Tan, J.; Peng, R.; Burbelo, P.D.; Hayward, G.S.; Ling, P.D. Lethal Hemorrhagic Disease and Clinical Illness Associated with Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 1 Are Caused by Primary Infection: Implications for the Detection of Diagnostic Proteins. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofs, S.A.; Atmar, R.L.; Keitel, W.A.; Hanlon, C.; Stanton, J.J.; Tan, J.; Flanagan, J.P.; Howard, L.; Ling, P.D. Prenatal passive transfer of maternal immunity in Asian elephants (Elephas maximus). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 153, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, T.E.; Perera, V.P.; Karunarathne, R.N.S.; Schaftenaar, W.; Mahakapuge, T.A.N.; Kalupahana, A.W.; Rutten, V.; de Haan, C.A.M. Young elephants in a large herd maintain high levels of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus-specific antibodies and do not succumb to fatal haemorrhagic disease. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3379–e3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jackson, J.O.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. Fusing structure and function: A structural view of the herpesvirus entry machinery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, M.J.; Dennis, M.; Stohr, D.; Valencia, S.M.; Rodgers, N.; Semmes, E.C.; Webster, H.S.; Jenks, J.A.; Barfield, R.; Pollara, J.; et al. Characterization of Plasma Immunoglobulin G Responses in Elite Neutralizers of Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciferri, C.; Chandramouli, S.; Donnarumma, D.; Nikitin, P.A.; Cianfrocco, M.A.; Gerrein, R.; Feire, A.L.; Barnett, S.W.; Lilja, A.E.; Rappuoli, R.; et al. Structural and biochemical studies of HCMV gH/gL/gO and Pentamer reveal mutually exclusive cell entry complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hara, K.; Kawabata, A.; Nishimura, M.; Wakata, A.; Tjan, L.H.; Poetranto, A.L.; Yamamoto, C.; Haseda, Y.; Aoshi, T.; et al. Tetrameric glycoprotein complex gH/gL/gQ1/gQ2 is a promising vaccine candidate for human herpesvirus 6B. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, W.; Krummenacher, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zeng, M.S.; Xia, N.; Zeng, Y.X.; Xu, M.; et al. Targeting herpesvirus entry complex and fusogen glycoproteins with prophylactic and therapeutic agents. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Knox, J.J.; Desmond, A.; Alameh, M.G.; Gaudette, B.T.; Lubinski, J.M.; Naughton, A.; Hook, L.M.; Egan, K.P.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. Trivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine yields durable memory B cell protection against genital herpes in preclinical models. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, P.D.; Long, S.Y.; Fuery, A.; Peng, R.S.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Qin, X.; Worley, K.C.; Dugan, S.; Hayward, G.S. Complete Genome Sequence of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 4, the First Example of a GC-Rich Branch Proboscivirus. mSphere 2016, 1, e00081-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, T.E.; Schaftenaar, W.; Maurer, G.; van den Doel, P.B.; Molenaar, F.M.; Chamouard-Galante, A.; Vercammen, F.; Rutten, V.; de Haan, C.A.M. Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus Is Omnipresent in Elephants in European Zoos and an Asian Elephant Range Country. Viruses 2021, 13, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuery, A.; Leen, A.M.; Peng, R.; Wong, M.C.; Liu, H.; Ling, P.D. Asian Elephant T Cell Responses to Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavulraj, S.; Eschke, K.; Prahl, A.; Flugger, M.; Trimpert, J.; van den Doel, P.B.; Andreotti, S.; Kaessmeyer, S.; Osterrieder, N.; Azab, W. Fatal Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus Infection of Two Young Asian Elephants. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursell, T.; Spencer Clinton, J.L.; Tan, J.; Peng, R.; Ling, P.D. Modified vaccinia Ankara expressing EEHV1A glycoprotein B elicits humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in mice. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer Clinton, J.L.; Hoornweg, T.E.; Tan, J.; Peng, R.; Schaftenaar, W.; Rutten, V.; de Haan, C.A.M.; Ling, P.D. EEHV1A glycoprotein B subunit vaccine elicits humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in mice. Vaccine 2022, 40, 5131–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer Clinton, J.L.; Hoornweg, T.E.; Tan, J.; Peng, R.; Schaftenaar, W.; Rutten, V.; de Haan, C.A.M.; Ling, P.D. The EEHV1A gH/gL complex elicits humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in mice. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.A. Immunologic basis of vaccine vectors. Immunity 2010, 33, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xia, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.T.; Zhu, J. RNA sensors of the innate immune system and their detection of pathogens. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.; Yuzhakov, O.; Woods, A.; Deterling, J.; Hassett, K.; Shaw, C.A.; Ciaramella, G. Multi-antigenic human cytomegalovirus mRNA vaccines that elicit potent humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.S.; Jenks, J.A.; Pardi, N.; Goodwin, M.; Roark, H.; Edwards, W.; McLellan, J.S.; Pollara, J.; Weissman, D.; Permar, S.R. Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Vaccine Elicits Antibody Responses with Greater Durability and Breadth than MF59-Adjuvanted gB Protein Immunization. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monslow, M.A.; Elbashir, S.; Sullivan, N.L.; Thiriot, D.S.; Ahl, P.; Smith, J.; Miller, E.; Cook, J.; Cosmi, S.; Thoryk, E.; et al. Immunogenicity generated by mRNA vaccine encoding VZV gE antigen is comparable to adjuvanted subunit vaccine and better than live attenuated vaccine in nonhuman primates. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5793–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Cai, Y.; Yan, J.; Fan, Y.; Lv, W.; Gong, S.; Yin, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, X.; et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy induced by an mRNA vaccine encoding gD antigen against pseudorabies virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 251, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Hook, L.M.; Pardi, N.; Wang, F.; Myles, A.; Cancro, M.P.; Cohen, G.H.; Weissman, D.; Friedman, H.M. Nucleoside-modified mRNA encoding HSV-2 glycoproteins C, D, and E prevents clinical and subclinical genital herpes. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaaw7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.J.; Bu, W.; Nguyen, L.A.; Batchelor, J.D.; Kim, J.; Pittaluga, S.; Fuller, J.R.; Nguyen, H.; Chou, T.H.; Cohen, J.I.; et al. A bivalent Epstein-Barr virus vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies that block infection and confer immunity in humanized mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabf3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Meng, S.; Gu, Q.; Zheng, R.; Gao, X.; Kim, J.D.; Chen, M.; Xia, B.; Zuo, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Epigenetic landscape reveals MECOM as an endothelial lineage regulator. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Walther, B.K.; Jiang, C.; Matrone, G.; Holgate, R.; Xu, Q.; Morales, E.; Wang, G.; Gu, J.; Wang, R.; et al. Telomerase therapy reverses vascular senescence and extends lifespan in progeria mice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4352–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Lin, P.J.C.; Sung, M.M.H.; Tam, Y.K.; Cullis, P.R. Influence of particle size on the in vivo potency of lipid nanoparticle formulations of siRNA. J. Control Release 2016, 235, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legere, R.M.; Poveda, C.; Ott, J.A.; Bray, J.M.; Villafone, E.G.; Silveira, B.P.D.; Kahn, S.K.; Martin, C.L.; Mancino, C.; Taraballi, F.; et al. Intramuscular but not nebulized administration of a mRNA vaccine against Rhodococcus equi stimulated humoral immune responses in neonatal foals. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Ching, K.H.; Klimavicz, C.M.; Iadarola, M.J. Antibody profiling by Luciferase Immunoprecipitation Systems (LIPS). J. Vis. Exp. 2009, e1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasiu, D.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Cairns, T.M.; Reilly, B.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Bimolecular complementation reveals that glycoproteins gB and gH/gL of herpes simplex virus interact with each other during cell fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18718–18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Natural and Synthetic Saponins as Vaccine Adjuvants. Vaccines 2021, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, N.B.; Swain, S.L. Cytotoxic CD4 T cells in antiviral immunity. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 954602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, S.; Mandaric, S.; Oxenius, A. CD4 T cell responses in latent and chronic viral infections. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. The structural basis of herpesvirus entry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Dong, J.; Yao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Fang, F.; Chen, Z. Complete protection of mice against lethal murine cytomegalovirus challenge by immunization with DNA vaccines encoding envelope glycoprotein complex III antigens gH, gL and gO. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.I.; Mozdzanowska, K.; Williams, K.L.; Singer, D.; Richter, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Caton, A.J.; Otvos, L.; Erikson, J. Vaccination with M2e-based multiple antigenic peptides: Characterization of the B cell response and protection efficacy in inbred and outbred mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz Cisneros, M.C.; Anderson, E.J.; Hampton, B.K.; Parotti, B.; Sarkar, S.; Taft-Benz, S.; Bell, T.A.; Blanchard, M.; Dillard, J.A.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; et al. Host Genetic Variation Impacts SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Response in the Diversity Outbred Mouse Population. Vaccines 2024, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, Y.; Lidenge, S.J.; Tran, T.; West, J.T.; Wood, C.; Tso, F.Y. The Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) gH/gL Complex Is the Predominant Neutralizing Antigenic Determinant in KSHV-Infected Individuals. Viruses 2020, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouts, A.E.; Chan, P.; Stephan, J.P.; Vandlen, R.; Feierbach, B. Antibodies against the gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL131 complex comprise the majority of the anti-cytomegalovirus (anti-CMV) neutralizing antibody response in CMV hyperimmune globulin. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7444–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, H.; Homad, L.J.; Wan, Y.H.; Poudel, B.; Fiala, B.; Borst, A.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Walkey, C.; Price, J.; Wall, A.; et al. Immunization with a self-assembling nanoparticle vaccine displaying EBV gH/gL protects humanized mice against lethal viral challenge. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraoka, M.; Aschner, C.B.; Windsor, I.W.; Mahant, A.M.; Garforth, S.J.; Kong, S.L.; Achkar, J.M.; Almo, S.C.; Kelsoe, G.; Herold, B.C. A non-neutralizing glycoprotein B monoclonal antibody protects against herpes simplex virus disease in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootz, A.; Karbach, A.; Spindler, J.; Kropff, B.; Reuter, N.; Sticht, H.; Winkler, T.H.; Britt, W.J.; Mach, M. Protective capacity of neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies against glycoprotein B of cytomegalovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, P.S.; Lai, L.; Samaha, H.; Feng, Y.; Hu, M.; Hui, H.S.; Wali, B.; Ellis, M.; Davis-Gardner, M.E.; Huerta, C.; et al. Durability of immune responses to mRNA booster vaccination against COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widge, A.T.; Rouphael, N.G.; Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Durability of Responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Roy, A.K.; Ahmed, R.; Kuddusi, R.U.; Sinha, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Vandenent, M.; Islam, M.Z.; Zaman, R.U.; Kibria, M.G.; et al. Antibody longevity and waning following COVID-19 vaccination in a 1-year longitudinal cohort in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korosec, C.S.; Farhang-Sardroodi, S.; Dick, D.W.; Gholami, S.; Ghaemi, M.S.; Moyles, I.R.; Craig, M.; Ooi, H.K.; Heffernan, J.M. Long-term durability of immune responses to the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines based on dosage, age and sex. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watts, J.R.; Clinton, J.L.S.; Pollet, J.; Peng, R.; Tan, J.; Ling, P.D. Multi-Antigen Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) mRNA Vaccine Induces Humoral and Cell-Mediated Responses in Mice. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121429
Watts JR, Clinton JLS, Pollet J, Peng R, Tan J, Ling PD. Multi-Antigen Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) mRNA Vaccine Induces Humoral and Cell-Mediated Responses in Mice. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121429
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatts, Jessica R., Jennifer L. Spencer Clinton, Jeroen Pollet, Rongsheng Peng, Jie Tan, and Paul D. Ling. 2024. "Multi-Antigen Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) mRNA Vaccine Induces Humoral and Cell-Mediated Responses in Mice" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121429
APA StyleWatts, J. R., Clinton, J. L. S., Pollet, J., Peng, R., Tan, J., & Ling, P. D. (2024). Multi-Antigen Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) mRNA Vaccine Induces Humoral and Cell-Mediated Responses in Mice. Vaccines, 12(12), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121429




