Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of a Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectored Vaccine Against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Heartland Bandavirus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, and Mice
2.2. Western Blot
2.3. rVSV-SFTSV Replication Kinetics Assay
2.4. Measurement of Plaque Area
2.5. Immunization
2.6. Intracranial Infection and Neurologic Sign Scoring
2.7. Blood Collection
2.8. Pseudovirus Neutralization Assay
2.9. Virus Titer Determination
2.10. Passive Transfer
2.11. Statistical and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. rVSV-SFTSV Is Attenuated in Ifnar−/− Mice and Exhibits a Favorable Safety Profile
3.2. Single Vaccination with rVSV-SFTSV Induces High Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies
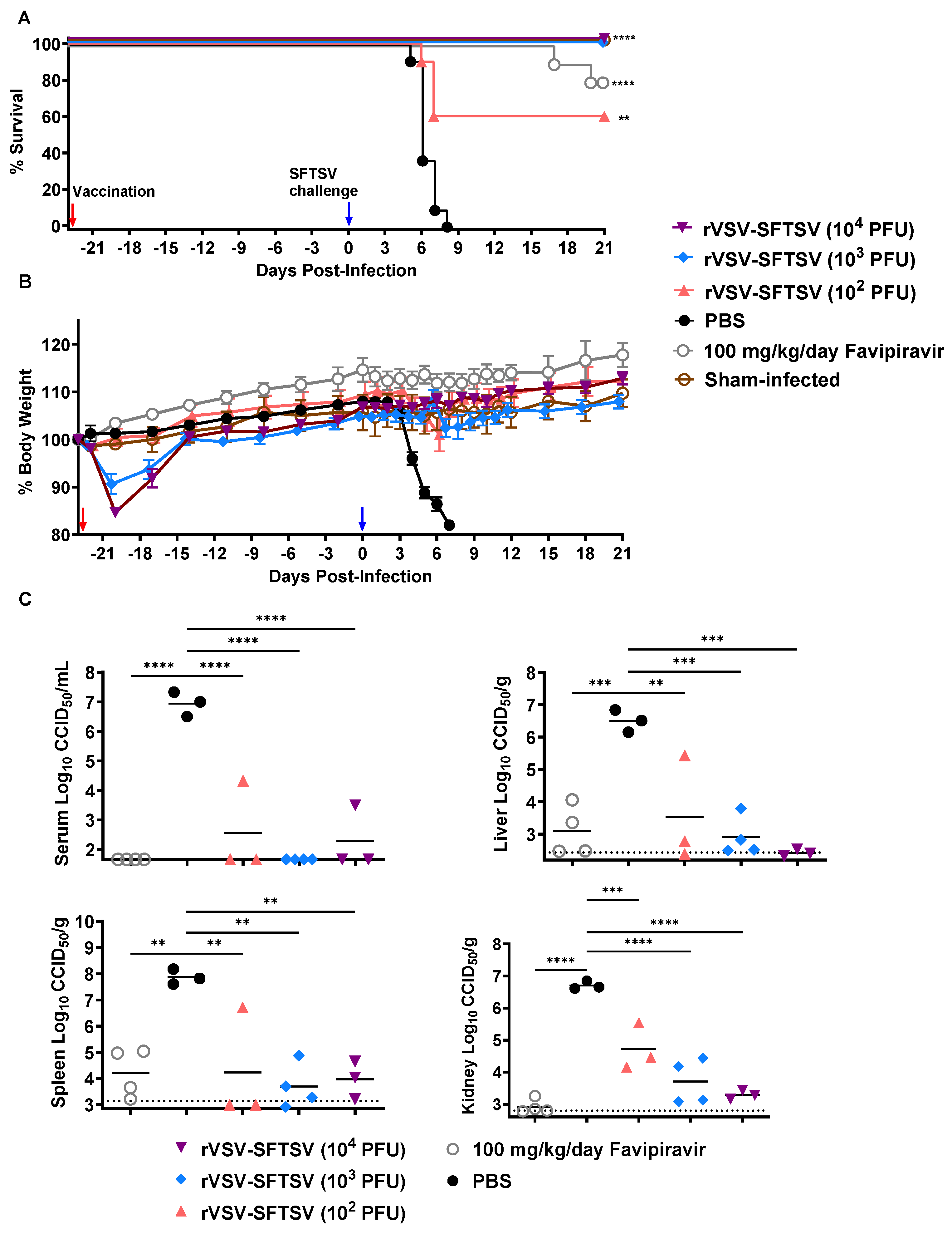
3.3. rVSV-SFTSV Protects Ifnar−/− Mice from Lethal SFTSV Challenge and Reduces Viral Titers in Tissues
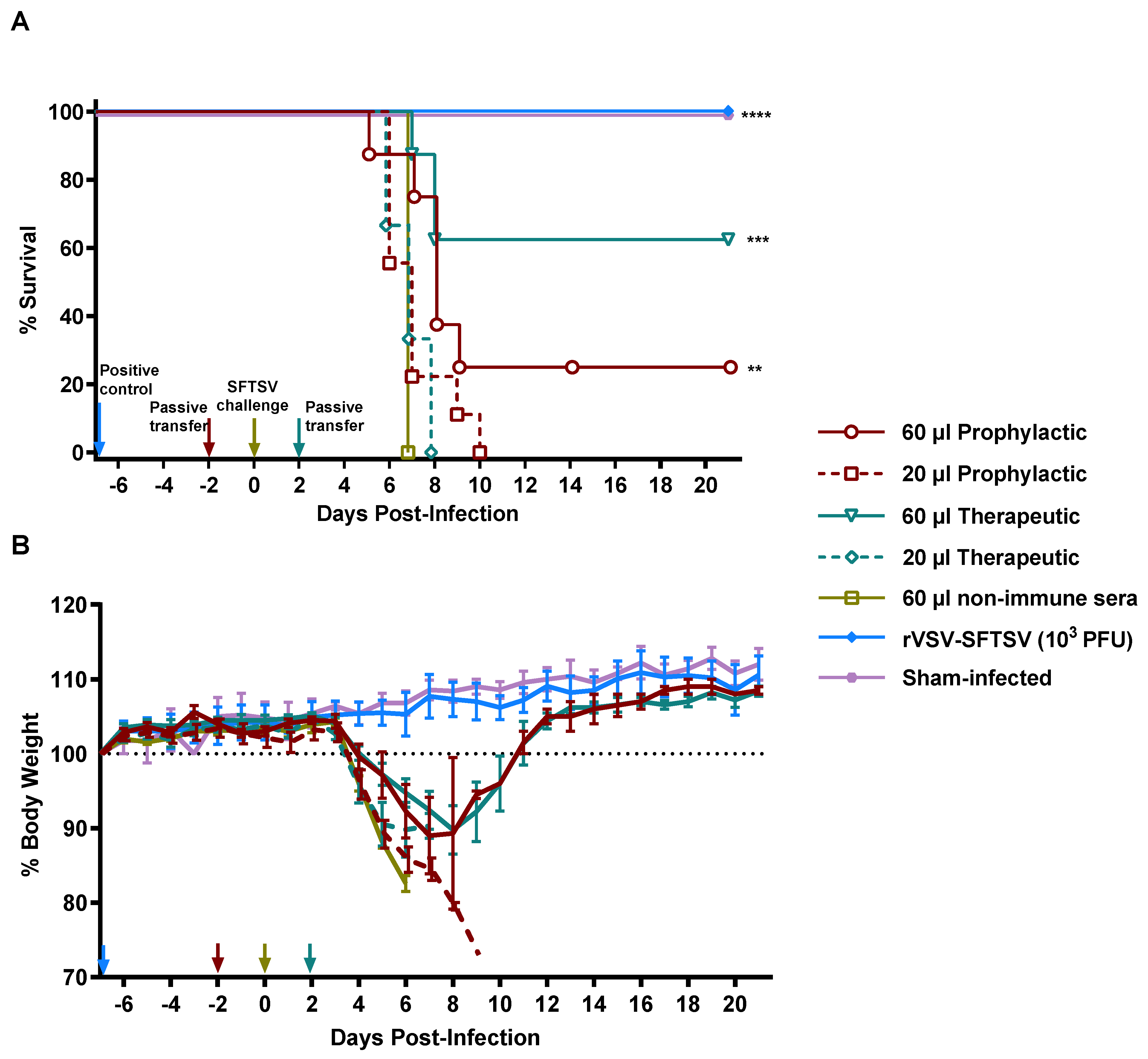
3.4. Passive Serum Transfer Imparts Protective Immunity to Naïve Mice
3.5. rVSV-SFTSV Vaccination Cross-Protects Against Lethal HRTV Challenge
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Shen, S.; Chen, L.; Fan, Z.; Wen, Q.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; La, B.; et al. Global epidemiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in human and animals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2024, 48, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.C.; Yun, Y.; Van An, L.; Kim, S.H.; Thao, N.T.P.; Man, P.K.C.; Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Cho, N.H.; Lee, K.H. Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.R.; Yun, Y.; Bae, S.G.; Park, D.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, N.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.H. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection, South Korea, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Maeda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishido, A.; Shigeoka, T.; Tominaga, T.; Kamei, T.; Honda, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Sakai, T.; et al. The first identification and retrospective study of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kato, H.; Yamagishi, T.; Shimada, T.; Matsui, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Shimojima, M.; Morikawa, S.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Japan, 2013–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Yi, J.; Kim, G.; Choi, S.J.; Jun, K.I.; Kim, N.H.; Choe, P.G.; Kim, N.J.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, M.D. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Han, M.G.; Yun, S.M.; Park, C.; Lee, W.J.; Ryou, J. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, South Korea, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1880–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.H.; Yang, S.L.; Tang, S.E.; Wang, T.C.; Hsu, T.C.; Su, C.L.; Chen, M.Y.; Shimojima, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shu, P.Y. Human Case of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection, Taiwan, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohaib, A.; Zhang, J.; Saqib, M.; Athar, M.A.; Hussain, M.H.; Chen, J.; Sial, A.U.; Tayyab, M.H.; Batool, M.; Khan, S.; et al. Serologic Evidence of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Related Viruses in Pakistan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, A.M.; Nguyen, Y.T.H.; Kim, Y.; Ha, N.Y.; Kang, J.G.; Kim, H.; San, B.; Kyaw, O.; Htike, W.W.; Choi, D.O.; et al. Genotypic Heterogeneity of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Scrub Typhus Patients and Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Co-infection, Myanmar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1878–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba Villarroel, P.M.; Chaiphongpachara, T.; Nurtop, E.; Laojun, S.; Pangpoo-Nga, T.; Songhong, T.; Supungul, D.; Baronti, C.; Thirion, L.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; et al. Seroprevalence study in humans and molecular detection in Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, P.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Kang, K.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia syndrome (FTLS) in Henan Province, China: Discovery of a new bunyavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.X. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A newly discovered emerging infectious disease. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casel, M.A.; Park, S.J.; Choi, Y.K. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: Emerging novel phlebovirus and their control strategy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bopp, N.E.; Kaiser, J.A.; Strother, A.E.; Barrett, A.D.T.; Beasley, D.W.C.; Benassi, V.; Milligan, G.N.; Preziosi, M.P.; Reece, L.M. Baseline mapping of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virology, epidemiology and vaccine research and development. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Liu, Q. The changing epidemiological characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–2016. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, L.K.; Folk, S.M.; Kelly, A.J.; MacNeil, A.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Batten, B.C.; Albarino, C.G.; Zaki, S.R.; Rollin, P.E.; et al. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantlo, E.K.; Haley, N.J. Heartland Virus: An Evolving Story of an Emerging Zoonotic and Vector-Borne Disease. Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 3, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Brown, K.; Adkins, S.; de la Torre, J.C.; Digiaro, M.; Ergunay, K.; Firth, A.E.; Hughes, H.R.; Junglen, S.; Lambert, A.J.; et al. Promotion of order Bunyavirales to class Bunyaviricetes to accommodate a rapidly increasing number of related polyploviricotine viruses. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.N.; Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M. Fields Virology; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lozach, P.Y.; Kuhbacher, A.; Meier, R.; Mancini, R.; Bitto, D.; Bouloy, M.; Helenius, A. DC-SIGN as a receptor for phleboviruses. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Kuhl, A.; Kaup, F.; Soldan, S.S.; Gonzalez-Scarano, F.; Weber, F.; He, Y.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia virus glycoproteins are targeted by neutralizing antibodies and can use DC-SIGN as a receptor for pH-dependent entry into human and animal cell lines. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4384–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halldorsson, S.; Behrens, A.J.; Harlos, K.; Huiskonen, J.T.; Elliott, R.M.; Crispin, M.; Brennan, B.; Bowden, T.A. Structure of a phleboviral envelope glycoprotein reveals a consolidated model of membrane fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7154–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Lv, S.; Han, S.; Zhang, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Xiao, G.; et al. CCR2 is a host entry receptor for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Qi, J.; Peng, R.; Feng, W.H.; Gao, G.F. The Postfusion Structure of the Heartland Virus Gc Glycoprotein Supports Taxonomic Separation of the Bunyaviral Families Phenuiviridae and Hantaviridae. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01558-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, M.J.; Brennan, B.; Briley, K., Jr.; Bart, S.M.; Sherman, E.; Szemiel, A.M.; Minutillo, M.; Bushman, F.D.; Bates, P. A role for glycolipid biosynthesis in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus entry. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qi, Y.; Liu, C.; Gao, W.; Chen, P.; Fu, L.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; Jing, Z.; Zhong, G.; et al. Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA is a critical factor contributing to the efficiency of early infection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Egawa, K.; Ozawa, T.; Kishi, H.; Shimojima, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Fukushi, S.; Fujii, H.; Yamada, H.; Tan, L.; et al. Characterization of pseudotyped vesicular stomatitis virus bearing the heartland virus envelope glycoprotein. Virology 2021, 556, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Wu, X.; Hong, E.; Jung, K.; Lai, C.J.; Kwak, M.J.; Seo, H.; Kim, S.; Jiang, Z.; Cha, I.; et al. Glucosylceramide is essential for Heartland and Dabie bandavirus glycoprotein-induced membrane fusion. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, F.; Jiao, Y.; Oladejo, B.O.; Chai, Y.; Bi, Y.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Zhang, C.; et al. Structures of phlebovirus glycoprotein Gn and identification of a neutralizing antibody epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7564–E7573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, N.; Xu, S.; Nawaz, W.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z. A single-domain antibody inhibits SFTSV and mitigates virus-induced pathogenesis in vivo. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e136855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.; Ko, M.; Chun, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Min, J.Y.; Park, W.B.; Oh, M.D.; Chung, J. An anti-Gn glycoprotein antibody from a convalescent patient potently inhibits the infection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Chi, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, X.; Qi, X.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Huang, M.; et al. Human antibody neutralizes severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, an emerging hemorrhagic Fever virus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, M.; Sugimoto, S.; Umekita, K.; Onodera, T.; Sano, K.; Tani, H.; Takamatsu, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Neutralizing mAbs against SFTS Virus Gn Protein Show Strong Therapeutic Effects in an SFTS Animal Model. Viruses 2022, 14, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Han, S.H.; Chong, S.T.; Klein, T.A.; Choi, C.Y.; Nam, H.Y.; Chae, H.Y.; Lee, H.; Ko, S.; Kang, J.G.; et al. Ticks collected from selected mammalian hosts surveyed in the Republic of Korea during 2008–2009. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.T.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, I.Y.; Kollars, T.M., Jr.; Sancho, A.R.; Sames, W.J.; Chae, J.S.; Klein, T.A. Seasonal distribution of ticks in four habitats near the demilitarized zone, Gyeonggi-do (Province), Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.G.; Noh, B.E.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, T.K.; Song, B.G.; Lee, H.I. Nationwide Temporal and Geographical Distribution of Tick Populations and Phylogenetic Analysis of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in Ticks in Korea, 2020. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Mekata, H.; Sudaryatma, P.E.; Kirino, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Ando, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Okabayashi, T. Isolation of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus from Various Tick Species in Area with Human Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Cases. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.K.; Barker, S.C.; Cobos, M.E.; Barker, D.; Teo, E.J.M.; Foley, D.H.; Nakao, R.; Lawrence, K.; Heath, A.C.G.; Peterson, A.T. Potential Spatial Distribution of the Newly Introduced Long-horned Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis in North America. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, C.B.; Occi, J.; Bonilla, D.L.; Egizi, A.M.; Fonseca, D.M.; Mertins, J.W.; Backenson, B.P.; Bajwa, W.I.; Barbarin, A.M.; Bertone, M.A.; et al. Multistate Infestation with the Exotic Disease-Vector Tick Haemaphysalis longicornis—United States, August 2017–September 2018. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A. Biology, ecology and distribution of the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2016, 64, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherst, R.W.; Bourne, A.S. Development, survival, fecundity and behaviour of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis (Ixodidae) at two locations in southeast Queensland. Int. J. Parasitol. 1991, 21, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.M.; Jeong, H.W.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.I.; Yu, M.A.; Kwon, H.I.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; et al. Shedding and Transmission Modes of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Phlebovirus in a Ferret Model. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.Y.; Choi, W.; Kim, J.; Wang, E.; Park, S.W.; Lee, W.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Uh, Y.; Kim, Y.K. Nosocomial person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 633.e1–633.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Chang, H.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.; Wang, E.; Kim, C.K.; Choi, E.; Lim, B.; Park, S.; Chae, H.; et al. Nosocomial outbreak of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome among healthcare workers in a single hospital in Daegu, Korea. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 119, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, M.; Bi, Z.Q.; Liang, M.F.; Ding, S.J.; Wang, S.W.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, S.Q.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. A cluster of person-to-person transmission cases caused by SFTS virus in Penglai, China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Choi, W.; Park, S.W.; Wang, E.B.; Lee, W.J.; Jee, Y.; Lim, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.O.; et al. Nosocomial transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Korea. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1681–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Fang, Y.; Cao, F.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, S.; Yu, Y.; Huang, R.; Ni, Z.; Li, J. A person-to-person transmission cluster of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome characterized by mixed viral infections with familial and nosocomial clustering. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, M.; Suzuki, T.; Murakami, T.; Matsui, K.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Shimojima, M.; Shimada, T.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Pathological Characteristics of a Patient with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS) Infected with SFTS Virus through a Sick Cat’s Bite. Viruses 2021, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuu, A.; Momoi, Y.; Nishiguchi, A.; Noguchi, K.; Yabuki, M.; Hamakubo, E.; Take, M.; Maeda, K. Natural severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection in domestic cats in Japan. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirino, Y.; Ishijima, K.; Miura, M.; Nomachi, T.; Mazimpaka, E.; Sudaryatma, P.E.; Yamanaka, A.; Maeda, K.; Sugimoto, T.; Saito, A.; et al. Seroprevalence of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in Small-Animal Veterinarians and Nurses in the Japanese Prefecture with the Highest Case Load. Viruses 2021, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, A.; Kirino, Y.; Fujimoto, S.; Ueda, N.; Himeji, D.; Miura, M.; Sudaryatma, P.E.; Sato, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mekata, H.; et al. Direct Transmission of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus from Domestic Cat to Veterinary Personnel. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2994–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brault, A.C.; Savage, H.M.; Duggal, N.K.; Eisen, R.J.; Staples, J.E. Heartland Virus Epidemiology, Vector Association, and Disease Potential. Viruses 2018, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raney, W.R.; Perry, J.B.; Hermance, M.E. Transovarial Transmission of Heartland Virus by Invasive Asian Longhorned Ticks under Laboratory Conditions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. 2018 Annual Review of Diseases Prioritized Under the Research and Development Blueprint. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2018/02/06/default-calendar/2018-annual-review-of-diseases-prioritized-under-the-research-anddevelopment-blueprint (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- NIAID. NIAID Biodefense Pathogens. 2018. Available online: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/niaid-biodefense-pathogens (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Kwak, J.E.; Kim, Y.I.; Park, S.J.; Yu, M.A.; Kwon, H.I.; Eo, S.; Kim, T.S.; Seok, J.; Choi, W.S.; Jeong, J.H.; et al. Development of a SFTSV DNA vaccine that confers complete protection against lethal infection in ferrets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Jeon, K.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.I.; Ro, H.J.; Seo, Y.B.; Shin, J.; Chung, J.; Jeon, Y.K.; et al. Vaccination with single plasmid DNA encoding IL-12 and antigens of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus elicits complete protection in IFNAR knockout mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jeon, K.; Park, S.I.; Bang, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Kwak, H.W.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, E.J.; Cho, N.H.; et al. mRNA vaccine encoding Gn provides protection against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in mice. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lai, C.J.; Cha, I.; Kang, S.; Yang, W.S.; Choi, Y.; Jung, J.U. SFTSV Gn-Head mRNA vaccine confers efficient protection against lethal viral challenge. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e29203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; He, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, G.; et al. A full-length glycoprotein mRNA vaccine confers complete protection against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, with broad-spectrum protective effects against bandaviruses. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0076924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Huang, D.D.; Bai, J.Y.; Zhuang, L.; Lu, Q.B.; Zhang, X.A.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.Y.; Cao, W.C. Immunization with recombinant SFTSV/NSs protein does not promote virus clearance in SFTSV-infected C57BL/6J mice. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, E.; Kim, S.; Chung, Y.; Lai, C.J.; Cha, I.; Cho, S.D.; Choi, Y.; Dai, X.; Kim, S.; et al. Self-assembling Gn head ferritin nanoparticle vaccine provides full protection from lethal challenge of Dabie bandavirus in aged ferrets. mBio 2023, 14, e0186823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.Q.; Dai, X.X.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Huang, X.X.; Li, J.D.; Wang, S.W.; et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of an inactivated SFTS vaccine candidate in mice. Biosaf. Health 2022, 4, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.M.; Park, S.J.; Yu, M.A.; Kim, Y.I.; Choi, Y.; Jung, J.U.; Brennan, B.; Choi, Y.K. Cross-genotype protection of live-attenuated vaccine candidate for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in a ferret model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26900–26908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, D.; Wen, D.; Li, S.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Jangra, R.K.; Wu, C.; Xia, D.; Zhang, X.; et al. Single dose of a rVSV-based vaccine elicits complete protection against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. NPJ Vaccines 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Kato, H.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Tani, H.; Kurosu, T.; Fujii, H.; Omura, N.; Shibamura, M.; Watanabe, S.; et al. A highly attenuated vaccinia virus strain LC16m8-based vaccine for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1008859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Yan, L.; Zheng, W.; Lei, X.; Fu, Q.; Xue, X.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Zheng, X. A rabies virus vectored severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) bivalent candidate vaccine confers protective immune responses in mice. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 257, 109076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jeon, K.; Hong, J.J.; Park, S.I.; Cho, H.; Park, H.J.; Kwak, H.W.; Park, H.J.; Bang, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. Heterologous vaccination utilizing viral vector and protein platforms confers complete protection against SFTSV. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Zheng, N.; Liu, Y.; Tian, C.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Zou, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; et al. Deficient humoral responses and disrupted B-cell immunity are associated with fatal SFTSV infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Griffiths, A.; Brackney, D.E.; Verardi, P.H. Generation of Multiple Arbovirus-like Particles Using a Rapid Recombinant Vaccinia Virus Expression Platform. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Buonocore, L.; Price, R.; Forman, J.; Rose, J.K. Attenuated vesicular stomatitis viruses as vaccine vectors. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.M.; Vogel, J.E.; Peralta, P.H. Clinical and serological response to laboratory-acquired human infection by Indiana type vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1966, 15, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, M.J.; Buonocore, L.; Kretzschmar, E.; Johnson, E.; Rose, J.K. Foreign glycoproteins expressed from recombinant vesicular stomatitis viruses are incorporated efficiently into virus particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11359–11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, I.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Jimenez, C.; Pauszek, S.J.; Wertz, G.W. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is a determinant of pathogenesis in swine, a natural host. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8039–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publicover, J.; Ramsburg, E.; Rose, J.K. Characterization of nonpathogenic, live, viral vaccine vectors inducing potent cellular immune responses. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9317–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Pol, A.N.; Dalton, K.P.; Rose, J.K. Relative neurotropism of a recombinant rhabdovirus expressing a green fluorescent envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, E.; Cataldi, M.; Marriott, I.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Understanding and altering cell tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virus Res. 2013, 176, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muik, A.; Kneiske, I.; Werbizki, M.; Wilflingseder, D.; Giroglou, T.; Ebert, O.; Kraft, A.; Dietrich, U.; Zimmer, G.; Momma, S.; et al. Pseudotyping vesicular stomatitis virus with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus glycoproteins enhances infectivity for glioma cells and minimizes neurotropism. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Feldmann, H. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-based vaccines against Ebola and Marburg virus infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204 (Suppl. S3), S1075–S1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Restrepo, A.M.; Camacho, A.; Longini, I.M.; Watson, C.H.; Edmunds, W.J.; Egger, M.; Carroll, M.W.; Dean, N.E.; Diatta, I.; Doumbia, M.; et al. Efficacy and effectiveness of an rVSV-vectored vaccine in preventing Ebola virus disease: Final results from the Guinea ring vaccination, open-label, cluster-randomised trial (Ebola Ca Suffit!). Lancet 2017, 389, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USFDA. First FDA-Approved Vaccine for the Prevention of Ebola Virus Disease, Marking a Critical Milestone in Public Health Preparedness and Response. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/first-fda-approved-vaccine-prevention-ebola-virus-disease-marking-critical-milestone-public-health (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Rupani, N.; Ngole, M.E.; Lee, J.A.; Aluisio, A.R.; Gainey, M.; Perera, S.M.; Ntamwinja, L.K.; Matafali, R.M.; Muhayangabo, R.F.; Makoyi, F.N.; et al. Effect of Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Zaire Ebola Virus Vaccination on Ebola Virus Disease Illness and Death, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, K.M.; Vande Burgt, N.H.; Francica, J.R.; Kaletsky, R.L.; Bates, P. Chinese hamster ovary cell lines selected for resistance to ebolavirus glycoprotein mediated infection are defective for NPC1 expression. Virology 2012, 432, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bart, S.M.; Cohen, C.; Dye, J.M.; Shorter, J.; Bates, P. Enhancement of Ebola virus infection by seminal amyloid fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7410–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westover, J.B.; Jung, K.H.; Alkan, C.; Boardman, K.M.; Van Wettere, A.J.; Martens, C.; Rojas, I.; Hicks, P.; Thomas, A.J.; Saindane, M.T.; et al. Modeling Heartland virus disease in mice and therapeutic intervention with 4′-fluorouridine. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0013224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrosovich, M.; Matrosovich, T.; Garten, W.; Klenk, H.D. New low-viscosity overlay medium for viral plaque assays. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowen, B.B.; Wong, M.H.; Jung, K.H.; Sanders, A.B.; Mendenhall, M.; Bailey, K.W.; Furuta, Y.; Sidwell, R.W. In vitro and in vivo activities of T-705 against arenavirus and bunyavirus infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3168–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Marzi, A.; Kercher, L.; Marceau, J.; York, A.; Callsion, J.; Gardner, D.J.; Geisbert, T.W.; Feldmann, H. Stat1-Deficient Mice Are Not an Appropriate Model for Efficacy Testing of Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Filovirus Vaccines. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212 (Suppl. S2), S404–S409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, I.L.; Kielczewski, J.L.; Ireland, D.D.C.; Sykes, J.S.; Lewkowicz, A.P.; Konduru, K.; Xu, B.C.; Chan, C.C.; Caspi, R.R.; Manangeeswaran, M.; et al. Pseudovirus rVSVDeltaG-ZEBOV-GP Infects Neurons in Retina and CNS, Causing Apoptosis and Neurodegeneration in Neonatal Mice. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1718–1726.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E.; Nasar, F.; Coleman, J.W.; Price, R.E.; Javadian, A.; Draper, K.; Lee, M.; Reilly, P.A.; Clarke, D.K.; Hendry, R.M.; et al. Neurovirulence properties of recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vectors in non-human primates. Virology 2007, 360, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunker, K.; Mollentze, N. Rabies Virus. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Ge, Z.; Cui, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Tian, D. Clinical manifestations of death with severe fever and thrombocytopenia syndrome: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3960–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.J. Correlates of protection to influenza virus, where do we go from here? Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, U.; Steinhoff, U.; Reis, L.F.; Hemmi, S.; Pavlovic, J.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Aguet, M. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science 1994, 264, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbin, J.E.; Hackenmiller, R.; Simon, M.C.; Levy, D.E. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell 1996, 84, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smee, D.F.; Jung, K.H.; Westover, J.; Gowen, B.B. 2′-Fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of bunyaviruses in vitro and in phleboviral disease mouse models. Antiviral Res. 2018, 160, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lai, C.J.; Cha, I.; Jung, J.U. Current Progress of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV) Vaccine Development. Viruses 2024, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisakov, D.N.; Belyakov, I.M.; Kisakova, L.A.; Yakovlev, V.A.; Tigeeva, E.V.; Karpenko, L.I. The use of electroporation to deliver DNA-based vaccines. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2024, 23, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Li, A.; Wang, S.; Li, D. Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome from 2010 to 2019 in Mainland China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, A. Two Point Mutations in the Glycoprotein of SFTSV Enhance the Propagation Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectors at Assembly Step. Viruses 2023, 15, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Duan, X.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Kou, C.; Liu, D.; et al. A novel tick-borne phlebovirus, closely related to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus and Heartland virus, is a potential pathogen. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muecksch, F.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Gaebler, C.; Ben Tanfous, T.; DaSilva, J.; Bednarski, E.; Ramos, V.; Zong, S.; Johnson, B.; et al. Increased memory B cell potency and breadth after a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA boost. Nature 2022, 607, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.N.; Roni, M.A. Challenges of Storage and Stability of mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazit, S.; Mizrahi, B.; Kalkstein, N.; Neuberger, A.; Peretz, A.; Mizrahi-Reuveni, M.; Ben-Tov, A.; Patalon, T. BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine Effectiveness Given Confirmed Exposure: Analysis of Household Members of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e734–e740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suder, E.; Furuyama, W.; Feldmann, H.; Marzi, A.; de Wit, E. The vesicular stomatitis virus-based Ebola virus vaccine: From concept to clinical trials. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulborn, R.M.; Bastard, M.; Peyraud, N.; Gignoux, E.; Luquero, F.; Guai, B.; Bateyi Mustafa, S.H.; Mukamba Musenga, E.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S. Case fatality risk among individuals vaccinated with rVSVDeltaG-ZEBOV-GP: A retrospective cohort analysis of patients with confirmed Ebola virus disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashkiw, J.A.; Mohamud, A.O.; Kazhdan, N.; Ameen, A.; Beecher, J.E.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Lichty, B.D. Improved thermal stabilization of VSV-vector with enhanced vacuum drying in pullulan and trehalose-based films. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundu, T.; Tsuda, Y.; Ito, R.; Shimizu, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Yoshii, K.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Arikawa, J.; Kariwa, H. Targeting of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus structural proteins to the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartment) and Golgi complex. Biomed. Res. 2018, 39, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnarajah, C.K.; Warrier, R.; Kuhn, R.J. Assembly of Viruses: Enveloped Particles; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Gao, D.; Liao, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Oladejo, B.O.; Li, S.; et al. Bispecific antibodies targeting two glycoproteins on SFTSV exhibit synergistic neutralization and protection in a mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2400163121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Fang, F.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The life cycle of a T cell after vaccination—Where does immune ageing strike? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 187, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Bevan, M.J. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahalom-Ronen, Y.; Tamir, H.; Melamed, S.; Politi, B.; Shifman, O.; Achdout, H.; Vitner, E.B.; Israeli, O.; Milrot, E.; Stein, D.; et al. A single dose of recombinant VSV-G-spike vaccine provides protection against SARS-CoV-2 challenge. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Publicover, J.; Ramsburg, E.; Rose, J.K. A single-cycle vaccine vector based on vesicular stomatitis virus can induce immune responses comparable to those generated by a replication-competent vector. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13231–13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlke, C.; Kasonta, R.; Lunemann, S.; Krahling, V.; Zinser, M.E.; Biedenkopf, N.; Fehling, S.K.; Ly, M.L.; Rechtien, A.; Stubbe, H.C.; et al. Dose-dependent T-cell Dynamics and Cytokine Cascade Following rVSV-ZEBOV Immunization. EBioMedicine 2017, 19, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hicks, P.; Manzoni, T.B.; Westover, J.B.; Petch, R.J.; Roper, B.; Gowen, B.B.; Bates, P. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of a Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectored Vaccine Against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Heartland Bandavirus. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121403
Hicks P, Manzoni TB, Westover JB, Petch RJ, Roper B, Gowen BB, Bates P. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of a Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectored Vaccine Against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Heartland Bandavirus. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121403
Chicago/Turabian StyleHicks, Philip, Tomaz B. Manzoni, Jonna B. Westover, Raegan J. Petch, Brianne Roper, Brian B. Gowen, and Paul Bates. 2024. "Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of a Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectored Vaccine Against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Heartland Bandavirus" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121403
APA StyleHicks, P., Manzoni, T. B., Westover, J. B., Petch, R. J., Roper, B., Gowen, B. B., & Bates, P. (2024). Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of a Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectored Vaccine Against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Heartland Bandavirus. Vaccines, 12(12), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121403






