Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
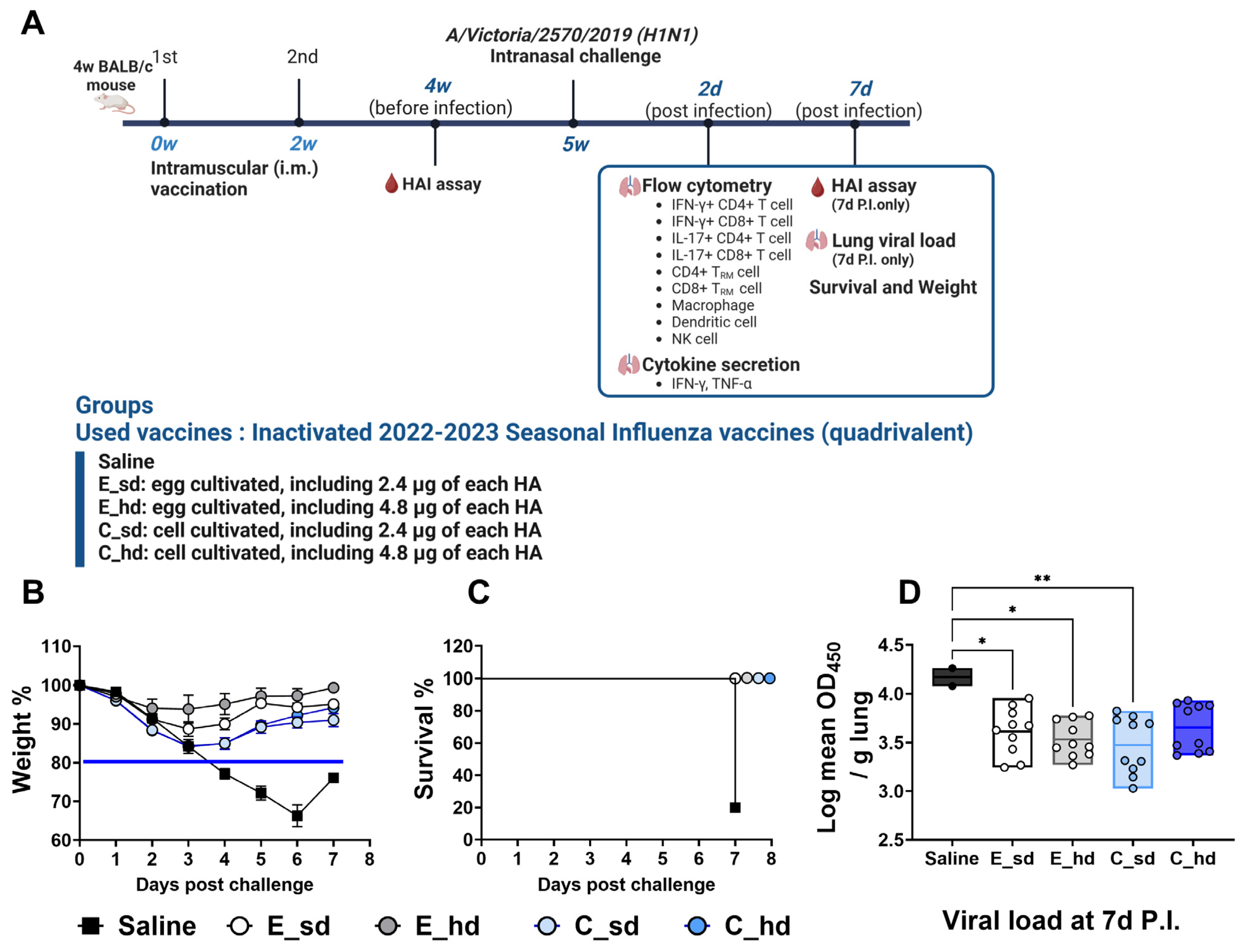
2.1. Vaccination and Challenges
2.2. Weight Loss, Survival, and Viral Titer
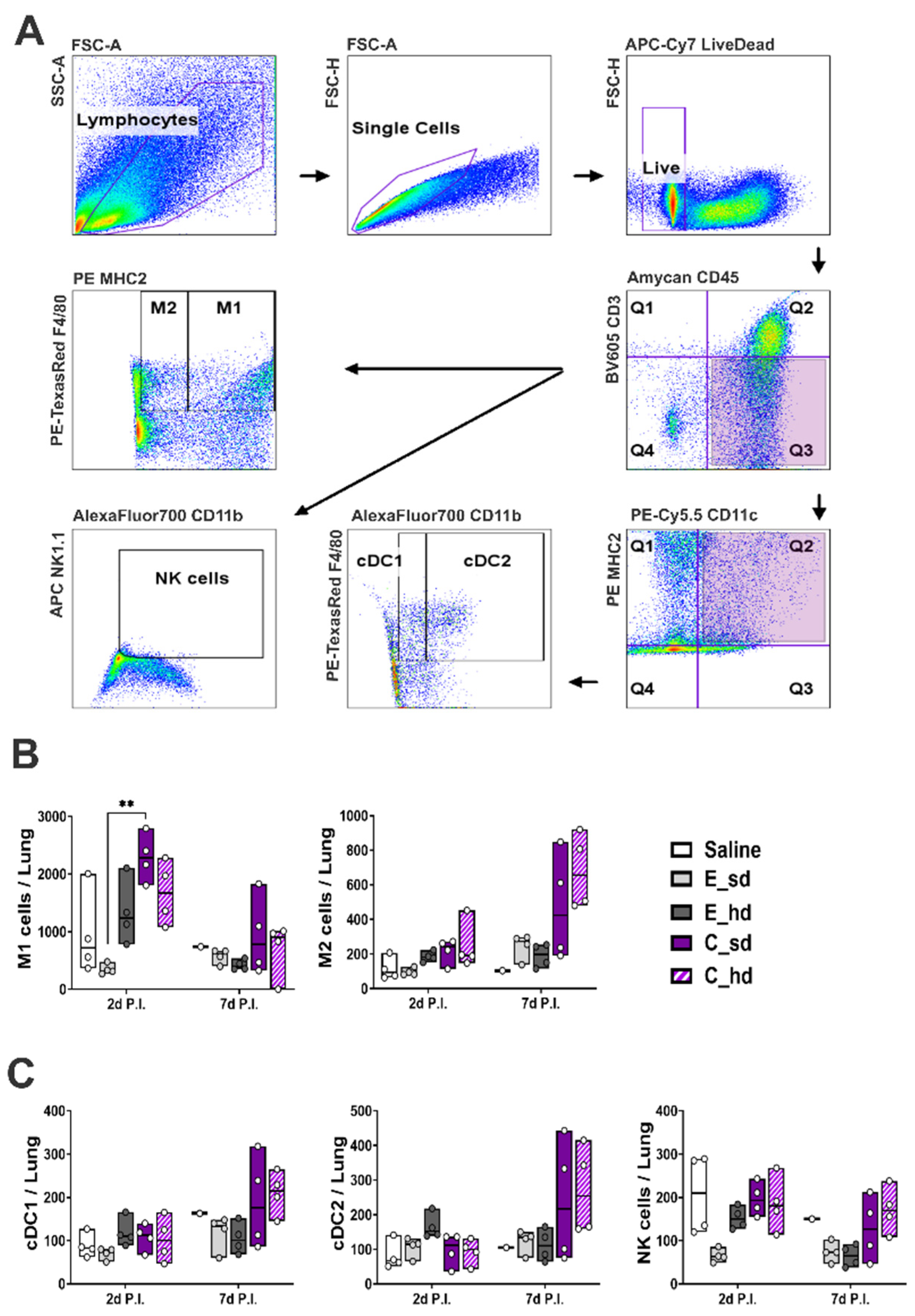
2.3. T Cell and Other Immune Cell Responses
2.4. Cytokine Secretion
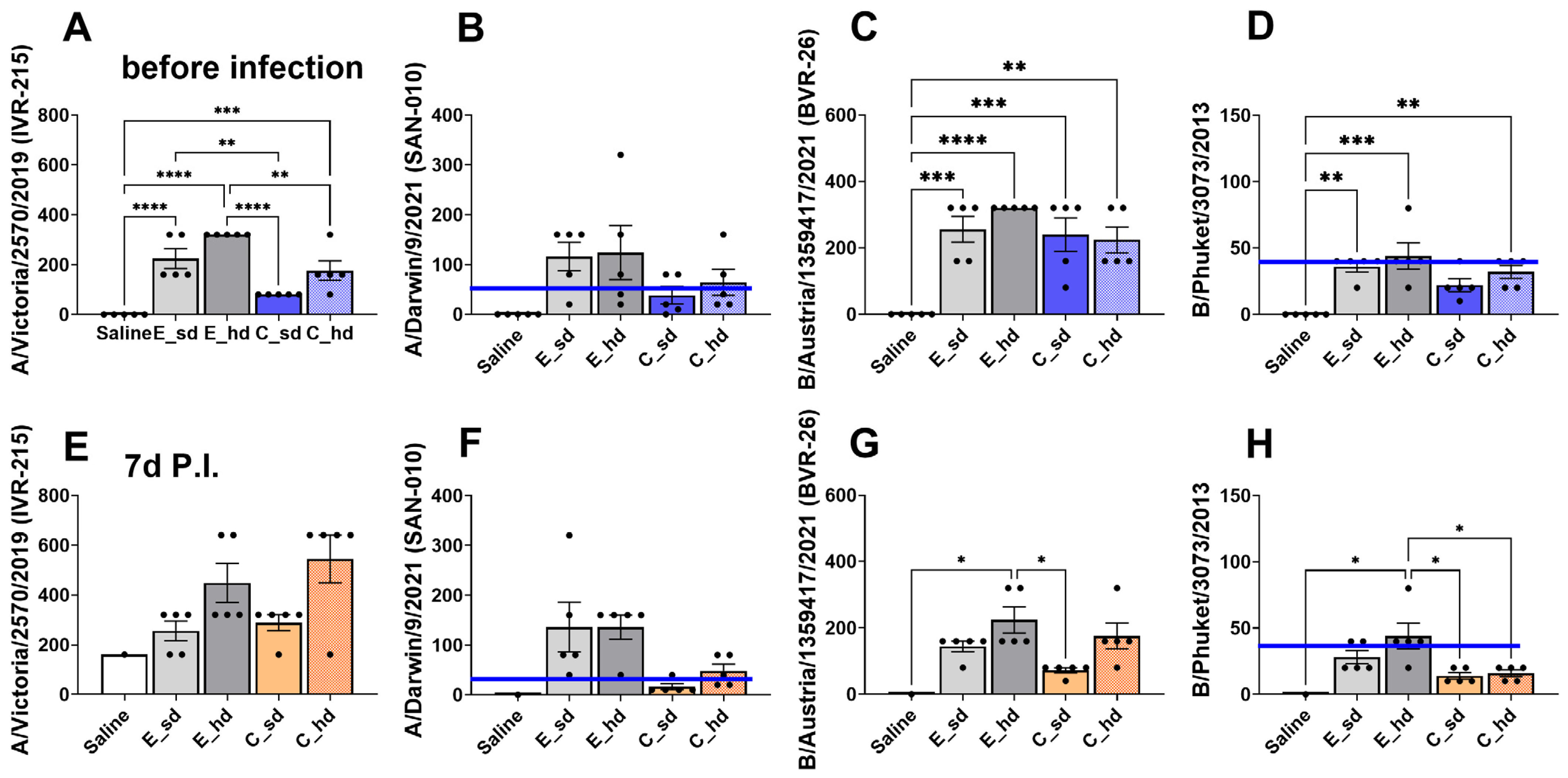
2.5. HAI Assay (Hemagglutinin Inhibition Assay)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The C_sd Group Showed Significantly Low Viral Titers Compared with the Saline Group
3.2. The C_sd Group Showed a High IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Count on Day 2 Post-Infection
3.3. The C_sd Group Showed a High Number of Macrophage 1 (M1) Cells on Day 2 Post-Infection
3.4. On Day 2 Post-Infection, the C_sd Group Showed High IFN-γ and TNF-α Secretion
3.5. The E_hd Group Showed over 40 HAI Titers Against Four 2022–2023 Seasonal Flu Virus Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dawood, F.S.; Iuliano, A.D.; Reed, C.; Meltzer, M.I.; Shay, D.K.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Bandaranayake, D.; Breiman, R.F.; Brooks, W.A.; Buchy, P.; et al. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Harvey, H.A.; Memoli, M.J. The 1918 influenza pandemic: Lessons for 2009 and the future. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38 (Suppl. S4), e10–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.W.; Sanford, J.C. A new look at an old virus: Patterns of mutation accumulation in the human H1N1 influenza virus since 1918. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2012, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, A.; Valour, F.; Vanhems, P. Burden of influenza in the elderly: A narrative review. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 36, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, N.-A.M.; Ortega-Sanchez, I.R.; Messonnier, M.L.; Thompson, W.W.; Wortley, P.M.; Weintraub, E.; Bridges, C.B. The annual impact of seasonal influenza in the US: Measuring disease burden and costs. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5086–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.M.; Antoon, J.W. Influenza in Children and Adolescents: Epidemiology, Management, and Prevention. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 44, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrico-Sánchez, A.; Valls-Arévalo, Á.; Garcés-Sánchez, M.; Álvarez Aldeán, J.; Ortiz de Lejarazu Leonardo, R. Efficacy and effectiveness of influenza vaccination in healthy children. A review of current evidence. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 41, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.Z.; Jiao, P.R.; Qi, W.B.; Fan, H.Y.; Liao, M. Development and strategies of cell-culture technology for influenza vaccine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Influenza (Flu) Vaccines Are Made. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/vaccine-process/?CDC_AAref_Val (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Robertson, J.S.; Bootman, J.S.; Newman, R.; Oxford, J.S.; Daniels, R.S.; Webster, R.G.; Schild, G.C. Structural changes in the haemagglutinin which accompany egg adaptation of an influenza A(H1N1) virus. Virology 1987, 160, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zost, S.J.; Parkhouse, K.; Gumina, M.E.; Kim, K.; Diaz Perez, S.; Wilson, P.C.; Treanor, J.J.; Sant, A.J.; Cobey, S.; Hensley, S.E. Contemporary H3N2 influenza viruses have a glycosylation site that alters binding of antibodies elicited by egg-adapted vaccine strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12578–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Aldeán, J.; Salamanca, I.; Ocaña, D.; Barranco, J.L.; Walter, S. Effectiveness of cell culture-based influenza vaccines compared with egg-based vaccines: What does the literature say? Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.; Vesikari, T.; Szymczakiewicz-Multanowska, A.; Lattanzi, M.; Izu, A.; Groth, N.; Holmes, S. Clinical efficacy of cell culture–derived and egg-derived inactivated subunit influenza vaccines in healthy adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.; Cheng, M.; Ko, K.; Mould, J.F.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Lee, P. Cost-effectiveness analysis of cell-based versus egg-based quadrivalent influenza vaccines in the pediatric population in Taiwan. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naleway, A.L.; Kim, S.S.; Flannery, B.; Levine, M.Z.; Murthy, K.; Sambhara, S.; Gangappa, S.; Edwards, L.J.; Ball, S.; Grant, L.; et al. Immunogenicity of High-Dose Egg-Based, Recombinant, and Cell Culture-Based Influenza Vaccines Compared with Standard-Dose Egg-Based Influenza Vaccine Among Health Care Personnel Aged 18–65 Years in 2019–2020. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y.-H.; Ha, D.L.A.; Simmons, C.; de Jong, M.D.; Chau, N.V.V.; Schumacher, R.; Peng, Y.C.; McMichael, A.J.; Farrar, J.J.; Smith, G.L.; et al. Memory T cells established by seasonal human influenza A infection cross-react with avian influenza A (H5N1) in healthy individuals. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3478–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.A.; Topham, D.; Chaves, F.A.; Sant, A.J. Cutting edge: CD4 T cells generated from encounter with seasonal influenza viruses and vaccines have broad protein specificity and can directly recognize naturally generated epitopes derived from the live pandemic H1N1 virus. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4998–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zens, K.D.; Farber, D.L. Memory CD4 T cells in influenza. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 386, 399–421. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, C.E.; Sample, C.J.; Kilburg-Basnyat, B.; Gabor, K.A.; Fessler, M.B.; Gowdy, K.M. Influenza-Mediated Lung Infection Models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1960, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broecker, F.; Liu, S.T.H.; Suntronwong, N.; Sun, W.; Bailey, M.J.; Nachbagauer, R.; Krammer, F.; Palese, P. A mosaic hemagglutinin-based influenza virus vaccine candidate protects mice from challenge with divergent H3N2 strains. NPJ Vaccines 2019, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T. Re-evaluation of the evolution of influenza H1 viruses using direct PCA. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Mishina, M.; Chung, J.R.; Cole, K.S.; Nowalk, M.P.; Martin, J.M.; Spencer, S.; Flannery, B.; Zimmerman, R.K.; Sambhara, S. Cell-Mediated Immunity Against Antigenically Drifted Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses in Children During a Vaccine Mismatch Season. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gärtner, B.C.; Beier, D.; Gosch, G.; Wahle, K.; Wendt, L.; Förster, L.C.; Schmidt, K.J.; Schwarz, T.F. Cell-based influenza vaccines: An effective vaccine option for under 60-year-olds. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2024, 19, Doc21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mould-Quevedo, J.F.; Pelton, S.I.; Nguyen, V.H. Vaccine Effectiveness of Cell-Based Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine in Children: A Narrative Review. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.N.; Mills, C.W.; McGovern, I.; McDermott, K.W.; Dean, A.; Bogdanov, A.N.; Sullivan, S.G.; Haag, M.D.M. Relative Vaccine Effectiveness of Cell- vs Egg-Based Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine Against Test-Confirmed Influenza Over 3 Seasons Between 2017 and 2020 in the United States. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Roy, B. Modelling the Economic Impact of lnfluenza Vaccine Programs with the Cell-Based Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine and Adjuvanted Trivalent Influenza Vaccine in Canada. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, R.; Triffon, C.; Mifsud, N.; Chen, W. Broad-Based Influenza-Specific CD8(+) T Cell Response without the Typical Immunodominance Hierarchy and Its Potential Implication. Viruses 2021, 13, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewes, R.; Kreijtz, J.H.; Hillaire, M.L.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Vaccination with whole inactivated virus vaccine affects the induction of heterosubtypic immunity against influenza virus A/H5N1 and immunodominance of virus-specific CD8+ T-cell responses in mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91 Pt 7, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Begom, S.; Bermingham, A.; Hoschler, K.; Adamson, W.; Carman, W.; Bean, T.; Barclay, W.; Deeks, J.J.; Lalvani, A. Cellular immune correlates of protection against symptomatic pandemic influenza. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhume, K.; Finn, C.M.; Devarajan, P.; Singh, A.; Tejero, J.D.; Prokop, E.; Strutt, T.M.; Sell, S.; Swain, S.L.; McKinstry, K.K. Bona Fide Th17 Cells without Th1 Functional Plasticity Protect against Influenza. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.K.; Lam, K.-T.; Liu, Y.; Fang, V.J.; Mu, X.; Leung, N.H.L.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Leung, G.M.; Cowling, B.J.; Tu, W. Investigation of CD4 and CD8 T cell-mediated protection against influenza A virus in a cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brühl, P.; Kerschbaum, A.; Kistner, O.; Barrett, N.; Dorner, F.; Gerencer, M. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity to vero cell-derived influenza vaccine. Vaccine 2000, 19, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, V.; Edmans, M.; Gubbins, S.; Jayaraman, S.; Paudyal, B.; Morgan, S.; McNee, A.; Morin, T.; Rijal, P.; Gerner, W.; et al. Spatial, temporal and molecular dynamics of swine influenza virus-specific CD8 tissue resident memory T cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.S.; Shin, H. CD8 tissue-resident memory T cells bridge the gap between humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2023, 16, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.; Sadarangani, S.; Jiang, L.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Chen, M.I. Duration of Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Meta-regression of Test-Negative Design Case-Control Studies. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Ahn, M.B.; Kang, H.M.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.W.; Chung, N.G.; Cho, B.; Jeong, D.C.; Kang, J.H. Shorter duration of protection and lower geometric mean titers against A/H3N2 antigen of the quadrivalent influenza vaccine in children post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022, 57, 1620–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Bao, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Hu, J.; Tang, R.; Yu, H.; Shan, J.; Li, Y.; et al. A broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody against the hemagglutinin of avian influenza virus H7N9. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomčíková, K.; Varečková, E. Different mechanisms of the protection against influenza A infection mediated by broadly reactive HA2-specific antibodies. Acta Virol. 2019, 63, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govorkova, E.A.; Kodihalli, S.; Alymova, I.V.; Fanget, B.; Webster, R.G. Growth and immunogenicity of influenza viruses cultivated in Vero or MDCK cells and in embryonated chicken eggs. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1999, 98, 39–51; discussion 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Reisinger, K.S.; Block, S.L.; Izu, A.; Groth, N.; Holmes, S.J. Subunit influenza vaccines produced from cell culture or in embryonated chicken eggs: Comparison of safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F. Diverse roles of lung macrophages in the immune response to influenza A virus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1260543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratsuchi, A.; Nakanishi, Y. [Elimination of influenza virus-infected cells by phagocytosis]. Yakugaku Zasshi 2006, 126, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, I.; Pan, J.; Takizawa, T.; Nakanishi, Y. Virus clearance through apoptosis-dependent phagocytosis of influenza A virus-infected cells by macrophages. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3399–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meischel, T.; Villalon-Letelier, F.; Saunders, P.M.; Reading, P.C.; Londrigan, S.L. Influenza A virus interactions with macrophages: Lessons from epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C.; He, Q.; Ye, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Prompt Antiviral Action of Pulmonary CD8+ T(RM) Cells Is Mediated by Rapid IFN-γ Induction and Its Downstream ISGs in the Lung. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 839455. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, D.A.; Rodríguez-Morales, P.; Mann, A.O.; Yu, S.; Lai, A.; Vazquez, A.B.; Pope, S.D.; Lim, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. Macrophages control pathological interferon responses during viral respiratory infection. bioRxiv 2023, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrich, A.; Dunsing, V.; Bobone, S.; Chiantia, S. Influenza A M2 recruits M1 to the plasma membrane: A fluorescence fluctuation microscopy study. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 5478–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Biernacka, Z.; Koper, M.; Struzik, J.; Gieryńska, M.; Schollenberger, A.; Lasocka, I.; Toka, F.N. Differential Activation of Splenic cDC1 and cDC2 Cell Subsets following Poxvirus Infection of BALB/c and C57BL/6 Mice. Cells 2023, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Kobinger, G.P. Evaluation of Mismatched Immunity Against Influenza Viruses. Future Virol. 2012, 7, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| T cells | |||
| Manufacturer | Cat No. | Marker | Fluorescence |
| BD | 564997 | Live/dead | APC-R700 (Alexa Fluor 700) |
| BD | 561100 | CD3 | PE-Cy7 |
| Invitrogen | MCD0417 | CD4 | PE-Texas red |
| Invitrogen | 35-5773-82 | Foxp3 | PE-Cy5.5 |
| Invitrogen | 15-0193-82 | CD19 | PE-Cy5 |
| BD | 563970 | CD44 | BV421_DAPI |
| Invitrogen | 11-0621-82 | CD62L | FITC |
| BD | 563290 | CD69 | BV605 |
| BD | 557495 | CD103 | PE |
| BD | 566409 | CD8 | BB700_PerCP Cy 5.5 |
| Invitrogen | 17-7177-81 | IL-17 | APC |
| Invitrogen | 11-7311-82 | IFN-γ | FITC |
| Immune cells | |||
| Manufacturer | Cat No. | Marker | Fluorescence |
| Biolegend | 423105 | Live/dead | APC Cy7 |
| Invitrogen | 406-0031-82 | CD3 | BV605 |
| Biolegend | 103138 | CD45 | Amcyan |
| Biolegend | 127615 | Ly6G | PerCP Cy5.5 |
| Invitrogen | 35-0114-82 | CD11c | PECy 5.5 |
| Biolegend | 101222 | CD11b | Alexa 700 |
| Biolegend | 107607 | MHC2 | PE |
| Invitrogen | MF48017 | F4 80 | PE Texas Red |
| Invitrogen | 17-5941-82 | NK1.1 | APC |
| Strains | NIBSC Code |
|---|---|
| A/Victoria/2570/2019 (IVR-215) (H1N1) | 22/100 |
| A/Darwin/9/2021 (SAN-010) antigen (H3N2) | 21/320 |
| B/Austria/1359417/2021 (BVR-26) (B Victoria lineage) | 21/316 |
| B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B Yamagata lineage) | 21/136 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, K.-R.; Kim, P.-K.; Jo, K.-M.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kang, H.M.; Kang, J.-H. Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121392
Kang K-R, Kim P-K, Jo K-M, Jang J-Y, Kang HM, Kang J-H. Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Kyu-Ri, Pan-Kyeom Kim, Kyung-Min Jo, Jin-Young Jang, Hyun Mi Kang, and Jin-Han Kang. 2024. "Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121392
APA StyleKang, K.-R., Kim, P.-K., Jo, K.-M., Jang, J.-Y., Kang, H. M., & Kang, J.-H. (2024). Cell-Cultured Influenza Vaccine Enhances IFN-γ+ T Cell and Memory T Cell Responses Following A/Victoria/2570/2019 IVR-215 (A/H1N1) Infection. Vaccines, 12(12), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121392







