Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
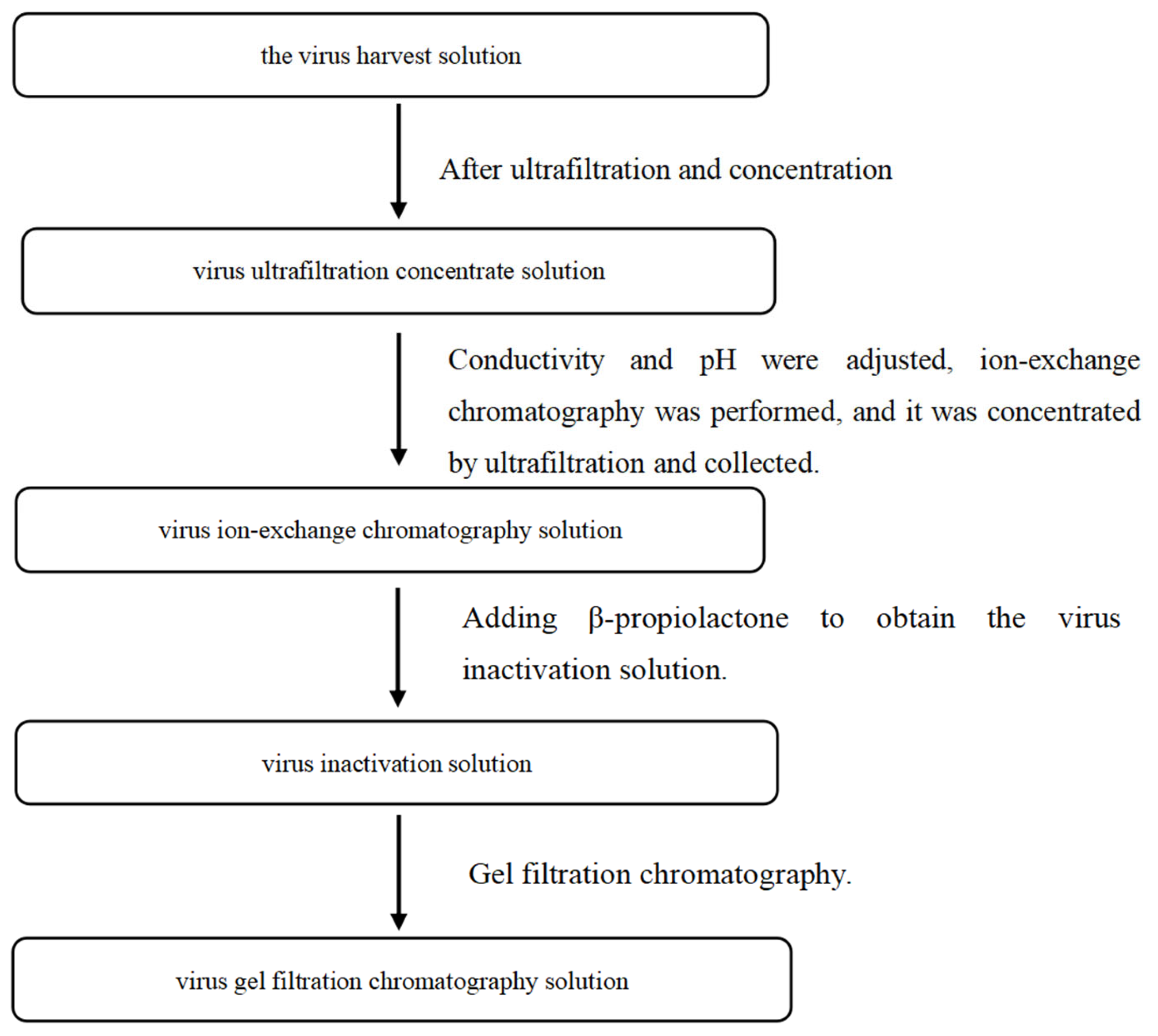
2.2. Preparation of Process Intermediates for Rabies Vaccine
2.3. Determination of Residual DNA Removal Efficiency and Antigen Recovery Rate in Various Steps of Human Rabies Vaccine Production
2.3.1. Determination of Residual HCD via qPCR
2.3.2. Distribution of Residual HCD Fragments Determined by CGE
2.3.3. Determination of the Rabies Virus Glycoprotein Antigen Content via ELISA
2.4. Evaluation of Process Stability
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Residual HCD in the Process Intermediates
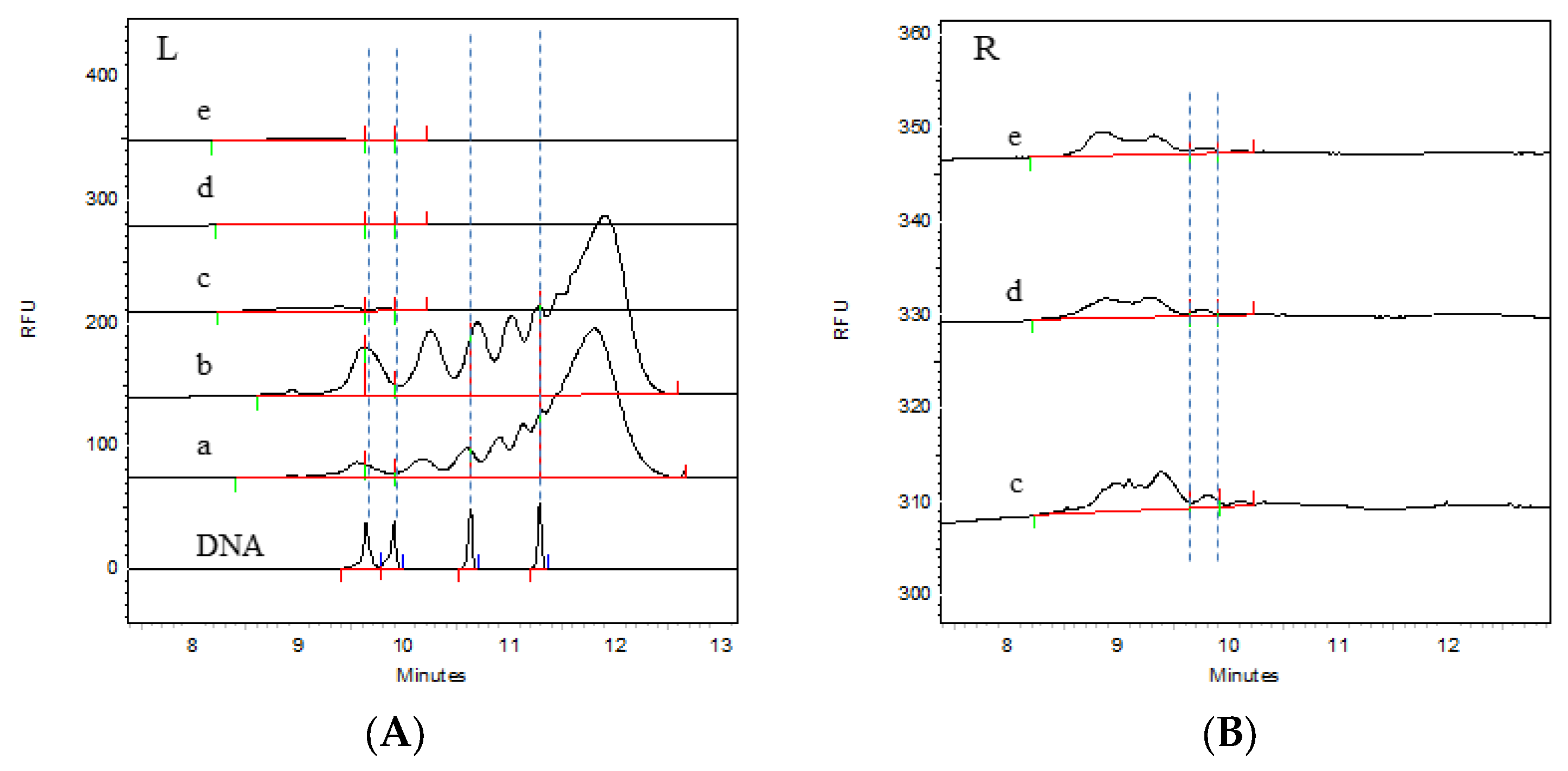
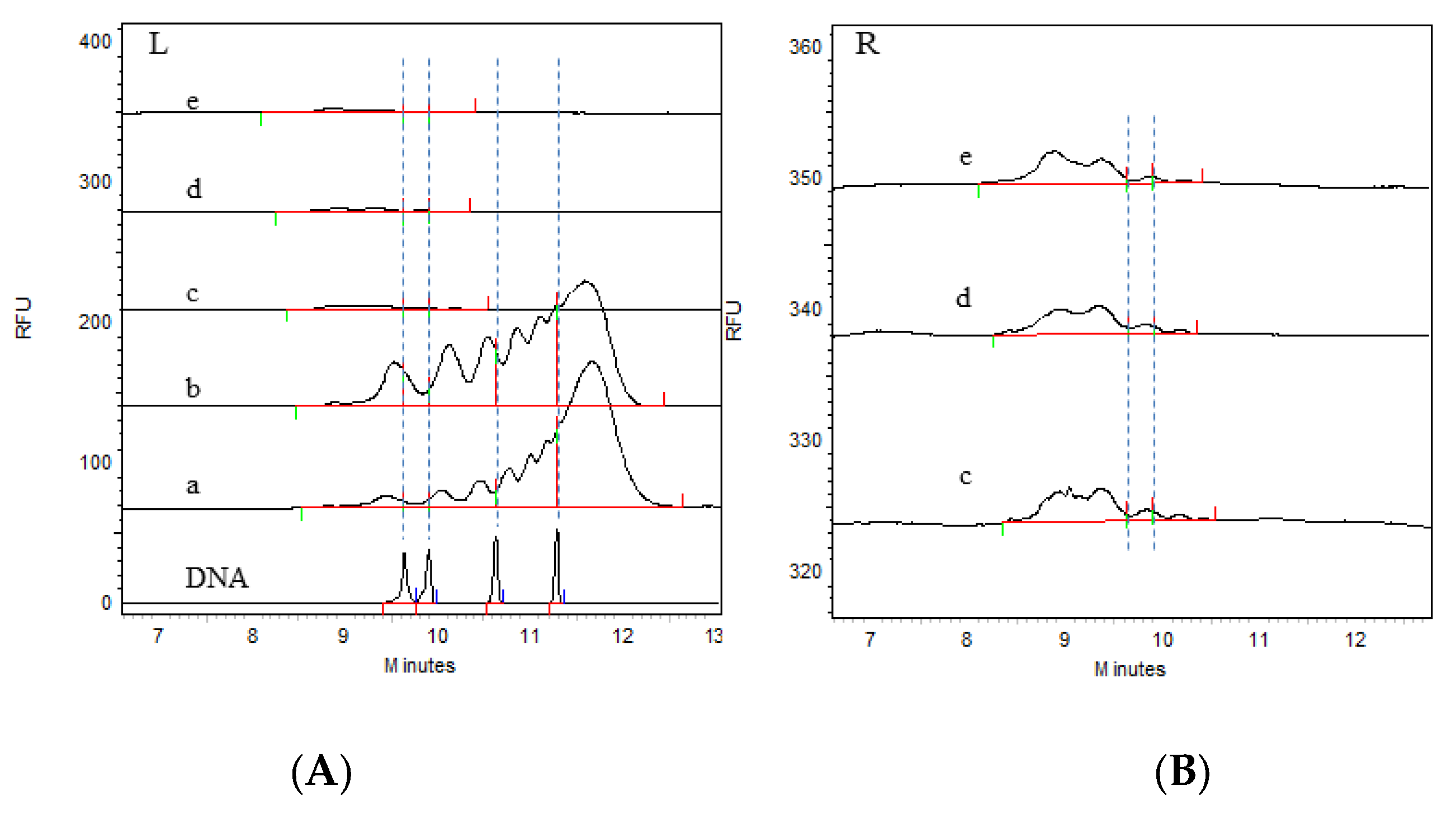
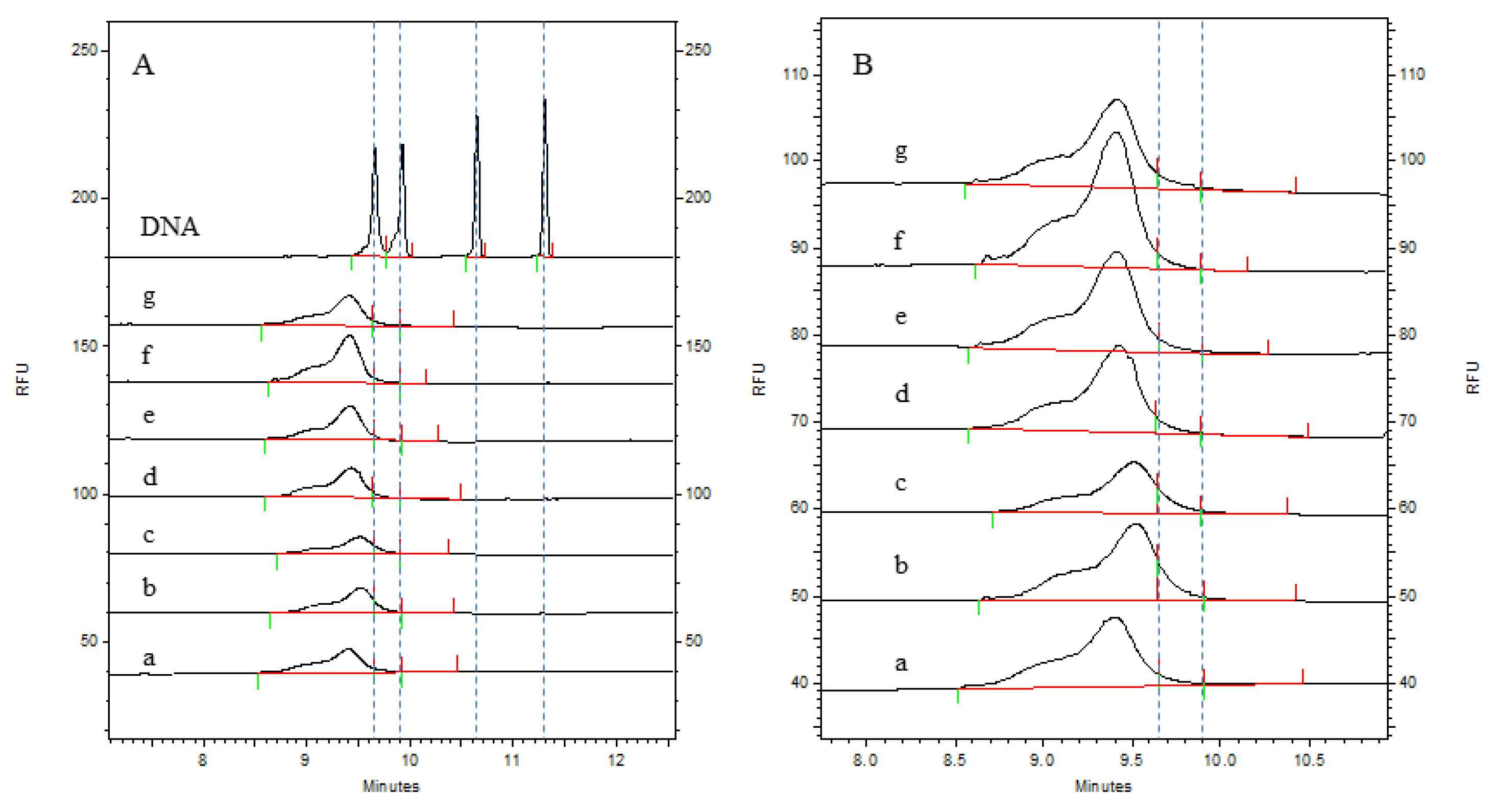
3.2. Detection of Residual HCD Fragment Size Distribution in the Process Intermediates
3.3. Detection of Rabies Virus Glycoprotein Antigen Content in the Process Intermediates
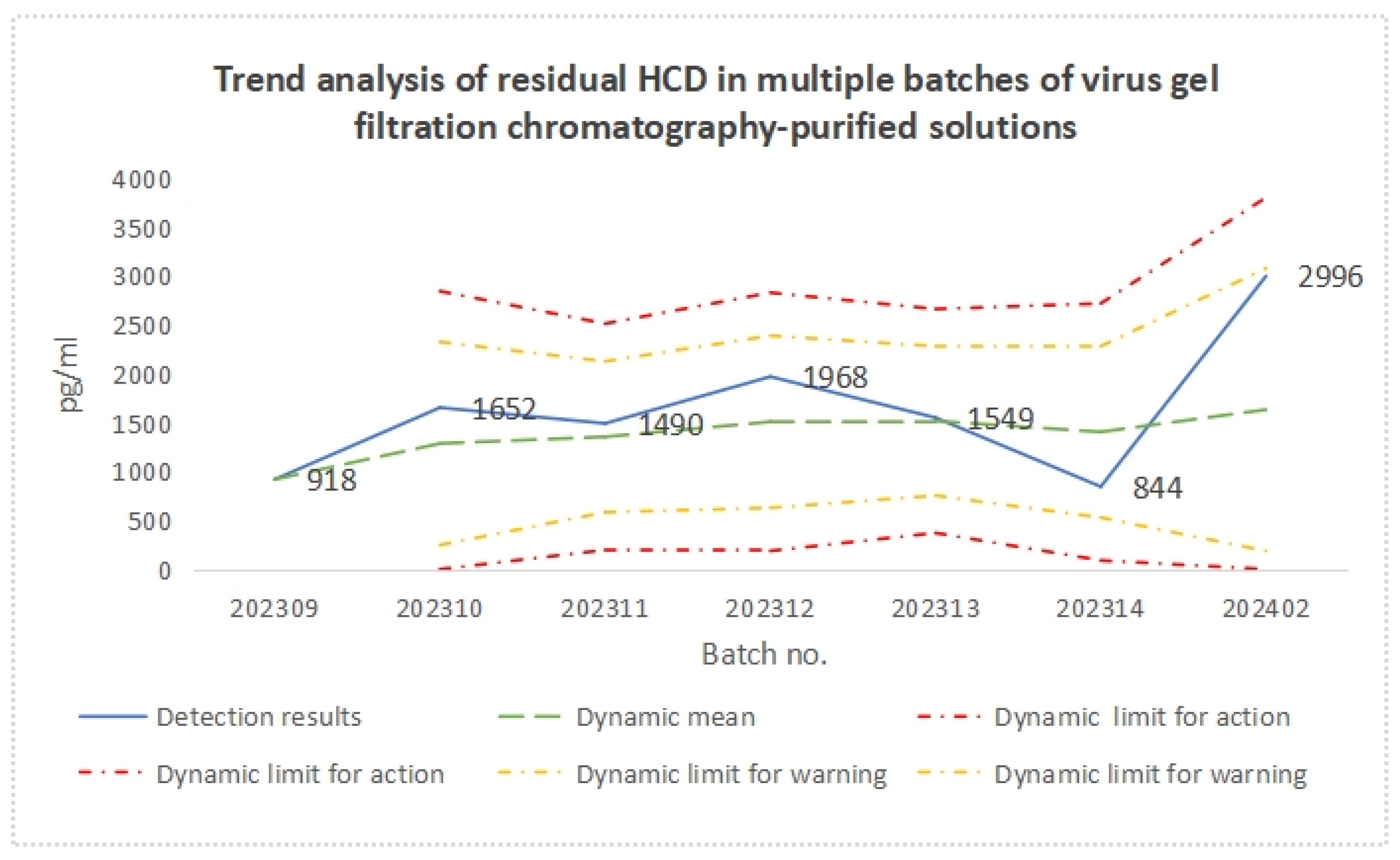
3.4. Process Stability
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, B.M.; Rall, G.F.; Schnell, M.J. Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Rabies Virus (But Were Afraid to Ask). Annu. Rev. Virol. 2015, 2, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumura, Y.; Kawakita, Y. Studies on SV40 in tissue culture: Preliminary step for cancer research in vitro. Nihon Rinsho 1963, 21, 1201–1215. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kiesslich, S.; Kamen, A.A. Vero cell upstream bioprocess development for the production of viral vectors and vaccines. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 44, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Lyu, J.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K. Application of bioreactor technology for cell culture-based viral vaccine production: Present status and future prospects. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 921755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Cai, F.; Zhu, Y.; Pal, A.; Athanasiou, M.; Orrison, B.; Blair, D.G.; Hughes, S.H.; Coffin, J.M.; Lewis, A.M.; et al. Oncogenicity of DNA in vivo: Tumor induction with expression plasmids for activated H-ras and c-myc. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2008, 36, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng-Fowler, L.; Lewis, A.M., Jr.; Peden, K. Quantitative determination of the infectivity of the proviral DNA of a retrovirus in vitro: Evaluation of methods for DNA inactivation. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2009, 37, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng-Fowler, L.; Tu, W.; Fu, H.; Murata, H.; Lanning, L.; Foseh, G.; Macauley, J.; Blair, D.; Hughes, S.H.; Coffin, J.M.; et al. A mouse strain defective in both T cells and NK cells has enhanced sensitivity to tumor induction by plasmid DNA expressing both activated H-Ras and c-Myc. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grachev, V.; Magrath, D.; Griffiths, E.; Petricciani, J. WHO requirements for the use of animal cells as in vitro substrates for the production of biologicals (requirements for biological substances No. 50). Biologicals 1998, 26, 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, P.; Allesø, M.; Bryder, M.C.; Holm, R. Q8 (R2) Pharmaceutical Development. In ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation Guide; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 535–577. [Google Scholar]
- 941 WT; Recommendations for Inactivated Rabies Vaccine for Human Use Produced in Cell Substrates and Embryonated Eggs, Annex 2, TRS No 941. 2007, pp. 102–103. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/inactivated-rabies-vaccine-for-human-use-annex-2-trs-no-941 (accessed on 1 January 2007).
- FDA. Guidance for Industry Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications; FDA: New Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peper, G.; Fankhauser, A.; Merlin, T.; Roscic, A.; Hofmann, M.; Obrdlik, P. Direct real-time quantitative PCR for measurement of host-cell residual DNA in therapeutic proteins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. Establishing acceptable limits of residual DNA. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cahill, J.D. Epidemiology of Rabies and Current US Vaccine Guidelines. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2020, 103, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rourou, S.; Ben Zakkour, M.; Kallel, H. Adaptation of Vero cells to suspension growth for rabies virus production in different serum free media. Vaccine 2019, 37, 6987–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.T.; Li, Y.H. Progress in Vero cell research and applications in rabies vaccines for human use. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2022, 38, 260–265. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Nie, F.; Chen, J.; Chai, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, M.; et al. A simulated, randomized study on the safety and immunogenicity of three consecutive commercial-scale batches of the CTN-1V strain human rabies vaccine to verify the inter-batch consistency. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2138049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Expert Committee on Biological Standardization; 56th Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yu, P.; Liu, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, W.; Peng, Y. Safety and efficacy assessment of an mRNA rabies vaccine in dogs, rodents, and cynomolgus macaques. npj Vaccines 2024, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Mu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yang, G.; Yu, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Study on immune persistence of the CTN-1V strain rabies vaccine in humans. J. Virus Erad. 2024, 10, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Xie, Z.Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wu, X.J.; Liu, D.M. Safety and immunogenicity of freeze-dried rabies vaccine (Vero-cells) for human use in healthy people aged 9–65 years. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi [Chin. J. Prev. Med.] 2023, 57, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Jin, Z.; Meng, Q.; Chai, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Phase III Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Immunogenicity and Safety of a Lyophilized Human Rabies Vaccine (Vero Cells) in Healthy Participants Aged 10–60 Years Following Essen and Zagreb Vaccination Procedures. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Luo, J. DNA Residue Control in Human Rabies Vaccine (Vero Cells). Chin. J. Biol. 2019, 32, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, K.; Ben Zakour, M.; Kallel, H. Purification of rabies virus produced in Vero cells grown in serum free medium. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7052–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Silva, C.A.T.; Farnos, O.; Venereo-Sanchez, A.; Toussaint, C.; Dash, S.; González-Domínguez, I.; Bernier, A.; Henry, O.; et al. Membrane Chromatography-Based Downstream Processing for Cell-Culture Produced Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaddeau, A.W.; Schneck, N.A.; Li, Y.; Ivleva, V.B.; Arnold, F.J.; Cooper, J.W.; Lei, Q.P. Development of a New Tandem Ion Exchange and Size Exclusion Chromatography Method To Monitor Vaccine Particle Titer in Cell Culture Media. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6430–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwardmann, L.S.; Nölle, V.; Elleuche, S. Bacterial non-specific nucleases of the phospholipase D superfamily and their biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-M.; Bai, F.-L.; Xu, W.-J.; Yang, Y.-B.; An, Y.; Li, T.-H.; Yu, Y.-H.; Li, D.-S.; Wang, W.-F. Removing residual DNA from Vero-cell culture-derived human rabies vaccine by using nuclease. Biologicals 2014, 42, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothert, K.; Pagallies, F.; Eilts, F.; Sivanesapillai, A.; Hardt, M.; Moebus, A.; Feger, T.; Amann, R.; Wolff, M.W. A scalable downstream process for the purification of the cell culture-derived Orf virus for human or veterinary applications. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 323, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Chen, X.; Tabor, D.E.; Liu, Y.; Albarghouthi, M.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Galinski, M.S. Size analysis of residual host cell DNA in cell culture-produced vaccines by capillary gel electrophoresis. Biologicals 2013, 41, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloyanova, S.; Trusova, V.M.; Gorbenko, G.P.; Deligeorgiev, T. Synthesis and fluorescence characteristics of novel asymmetric cyanine dyes for DNA detection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2011, 217, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Gao, T.; Luo, J.; Guo, L.H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.X. Size distribution analysis of residual host cell DNA fragments in lentivirus by CGE-LIF. Electrophoresis 2023, 44, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Goyon, A.; Zhang, K. Analysis of therapeutic nucleic acids by capillary electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 219, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnamkhasti, F.A.; Kia, V.; Shokri, R.; Mehdipour Moghaddam, M.J.; Paryan, M. Design and development of a simple method for the detection and quantification of residual host cell DNA in recombinant rotavirus vaccine. Mol. Cell. Probes 2021, 55, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Jiang, L.; Lei, Q.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, G. Development and Validation of Quantitative Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Residual CHO Host Cell DNA and Optimization of Sample Pretreatment Method in Biopharmaceutical Products. Biol. Proced. Online 2019, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, D.S. Arrangement of a highly repeated DNA sequence in the genome and chromatin of the African green monkey. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 5506–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tang, J.-r.; Liu, J.-h.; Qu, X.-s.; Dong, G.-m. The probe selection in Vero cells DNA residue detection by spot hybridization. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2008, 28, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Dong, G.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Development of a Vero cell DNA reference standard for residual DNA measurement in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Name | Batch Number | Nucleic Acid Residues (pg/mL) | Total Amount of Nucleic Acid (µg) | Nucleic Acid Removal Rate | Total Removal Rate % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus harvest solution | 202304 | 9.72 × 106 | 2.11 × 107 | / | 99.99% |
| Virus ultrafiltration concentrate solution | 1.23 × 107 | 3.23 × 106 | 84.69% | ||
| Virus ion-exchange chromatography | 1.48 × 104 | 3.07 × 102 | 99.99% | ||
| Virus inactivation solution | 6.17 × 103 | 1.25 × 102 | 59.17% | ||
| Virus gel chromatography solution | 4.27 × 103 | 1.19 × 102 | 4.75% | ||
| Virus harvest solution | 202305 | 8.31 × 106 | 1.77 × 107 | / | 99.99% |
| Virus ultrafiltration concentrate solution | 2.62 × 106 | 6.84 × 105 | 96.14% | ||
| Virus ion-exchange chromatography solution | 3.30 × 104 | 6.80 × 102 | 99.90% | ||
| Virus inactivation solution | 8.17 × 103 | 1.64 × 102 | 75.84% | ||
| Virus gel chromatography solution | 5.37 × 103 | 1.50 × 102 | 8.53% |
| Sample Name | Batch Number | Proportions of Residual HCD Fragments Sorted by Size (CA%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 bp | 100–200 bp | 200–500 bp | 500–1000 bp | >1000 bp | ||
| Virus harvest solution | 202304 | 4.15 | 1.77 | 8.41 | 17.77 | 67.9 |
| Virus ultrafiltration concentrate solution | 5.56 | 4.61 | 13.18 | 20.52 | 56.13 | |
| Virus ion-exchange chromatography solution | 89.5 | 7.69 | 2.81 | / | / | |
| Virus inactivation solution | 90.32 | 7.07 | 2.6 | / | / | |
| Virus gel chromatography solution | 91.62 | 6.03 | 2.35 | / | / | |
| Virus harvest solution | 202305 | 3.93 | 0.92 | 8.84 | 22.03 | 64.27 |
| Virus ultrafiltration concentrate solution | 8.77 | 3.39 | 20.23 | 27.27 | 40.34 | |
| Virus ion-exchange chromatography solution | 85.54 | 7.27 | 7.19 | / | / | |
| Virus inactivation solution | 87.38 | 8.13 | 4.49 | / | / | |
| Virus gel chromatography solution | 90.93 | 4.74 | 4.33 | / | / | |
| Sample Name | Batch Number | Antigen Content (IU/mL) | Total Antigen (IU) | Antigen Yield % | Total Yield % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus harvest solution | 202304 | 4 | 8.70 × 106 | / | 8.68% |
| Virus ultrafiltration concentrate solution | 14 | 3.67 × 106 | 42.22% | ||
| Virus ion-exchange chromatography solution | 45 | 9.34 × 105 | 25.44% | ||
| Virus inactivation solution | 44 | 8.94 × 105 | 95.71% | ||
| Virus gel chromatography solution | 27 | 7.55 × 105 | 84.47% | ||
| Virus harvest solution | 202305 | 4 | 8.53 × 106 | / | 8.53% |
| Virus ultrafiltration concentrate solution | 14 | 3.66 × 106 | 42.90% | ||
| Virus ion-exchange chromatography solution | 44 | 9.08 × 105 | 24.80% | ||
| Virus inactivation solution | 47 | 9.46 × 105 | 104.18% | ||
| Virus gel chromatography solution | 26 | 7.27 × 105 | 76.93% |
| Batch Number | HCD Residual Amount | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Results (pg/mL) | Trend Analysis | ||||||
| Dynamic Mean | Dynamic SD | Dynamic Lower Limit for Action | Dynamic Upper Limit for Action | Dynamic Lower Limit for Warning | Dynamic Upper Limit for Warning | ||
| 202309 | 918 | 918 | / | / | / | / | / |
| 202310 | 1652 | 1285 | 519 | 0 | 2842 | 247 | 2323 |
| 202311 | 1490 | 1353 | 386 | 196 | 2510 | 582 | 2125 |
| 202312 | 1968 | 1507 | 440 | 187 | 2827 | 627 | 2387 |
| 202313 | 1549 | 1515 | 381 | 371 | 2660 | 752 | 2278 |
| 202314 | 844 | 1404 | 438 | 90 | 2717 | 528 | 2279 |
| 202402 | 2996 | 1631 | 722 | 0 | 3798 | 186 | 3076 |
| Batch Number | Glycoprotein Antigen Content | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Results (IU/mL) | Trend Analysis | ||||||
| Dynamic Mean | Dynamic SD | Dynamic Lower Limit for Action | Dynamic Upper Limit for Action | Dynamic Lower Limit for Warning | Dynamic Upper Limit for Warning | ||
| 202309 | 33 | 33 | / | / | / | / | / |
| 202310 | 31 | 32 | 1 | 28 | 36 | 29 | 35 |
| 202311 | 32 | 32 | 1 | 29 | 35 | 30 | 34 |
| 202312 | 22 | 30 | 5 | 14 | 45 | 19 | 40 |
| 202313 | 29 | 29 | 4 | 16 | 43 | 21 | 38 |
| 202314 | 33 | 30 | 4 | 17 | 43 | 22 | 38 |
| 202402 | 25 | 29 | 4 | 16 | 42 | 21 | 38 |
| Batch Number | Residual HCD Fragment Content Sorted by Size (CA%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 bp | 100–200 bp | 200 bp–500 bp | >500 bp | |
| 202309(a) | 95.56 | 3.50 | 0.94 | / |
| 202310(b) | 89.84 | 8.77 | 1.40 | / |
| 202311(c) | 89.78 | 8.63 | 1.59 | / |
| 202312(d) | 95.48 | 4.13 | 0.39 | / |
| 202313(e) | 97.04 | 2.71 | 0.25 | / |
| 202314(f) | 97.47 | 2.41 | 0.11 | / |
| 202402(g) | 94.73 | 4.06 | 1.22 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Pan, R.; Yue, F.; Gao, T.; Wu, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Lan, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121379
Li J, Pan R, Yue F, Gao T, Wu X, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhao D, Lan Z, Chen H, et al. Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121379
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jia, Ruowen Pan, Fengyi Yue, Tie Gao, Xiaohong Wu, Leitai Shi, Yunpeng Wang, Danhua Zhao, Zhaohui Lan, Hongxu Chen, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121379
APA StyleLi, J., Pan, R., Yue, F., Gao, T., Wu, X., Shi, L., Wang, Y., Zhao, D., Lan, Z., Chen, H., Ye, Q., & Cao, S. (2024). Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine. Vaccines, 12(12), 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121379






