Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients: Data from the Dominican Republic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subjects Ethics Statement
2.2. Subject Data Analysis
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. mPlex-CoV Assay
2.5. Measurement of Hemoglobin (Hgb) and Adjustment of Antibody Concentration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
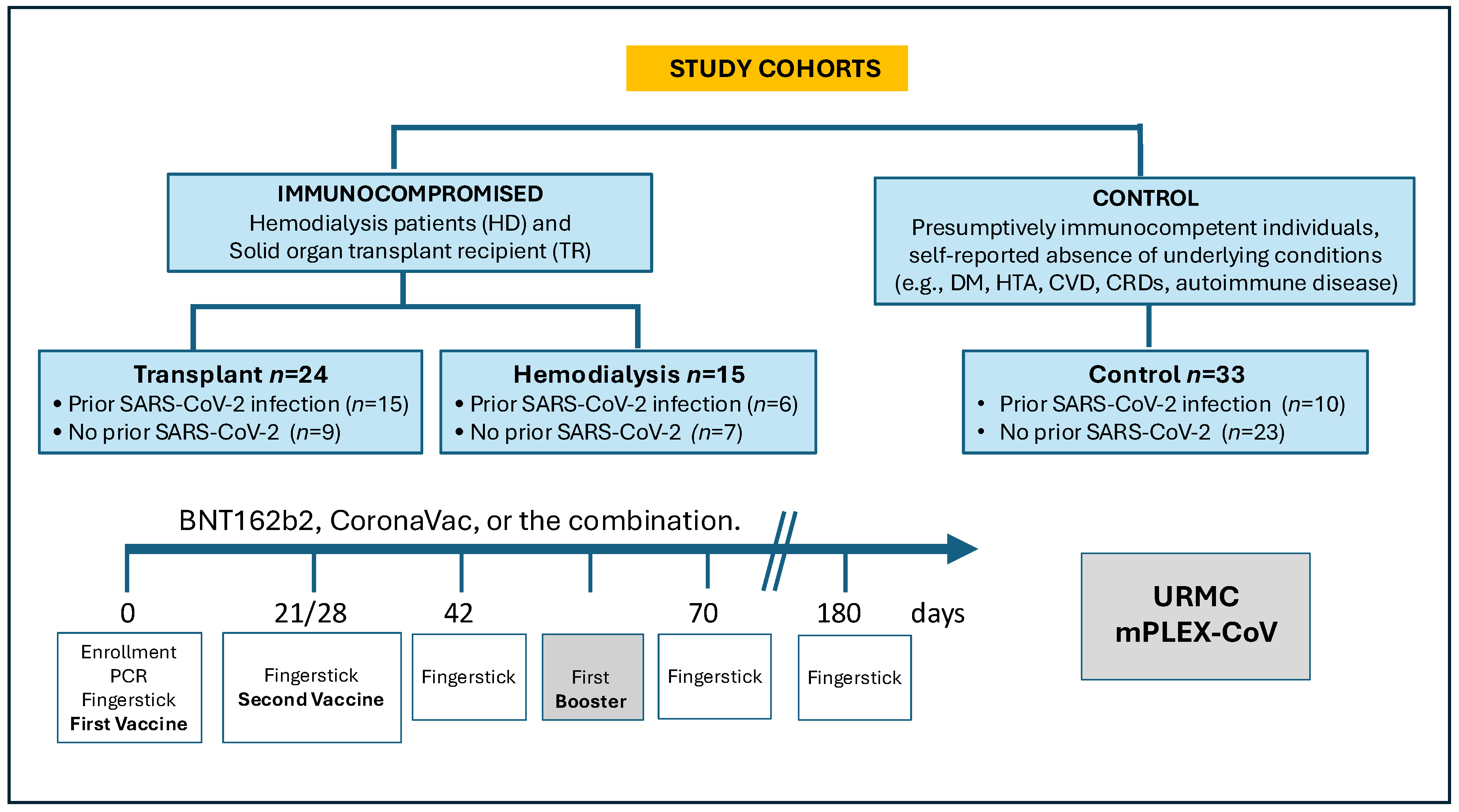
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Vaccination Characteristics and Prior COVID-19 Status
3.3. Generalized Linear Modeling
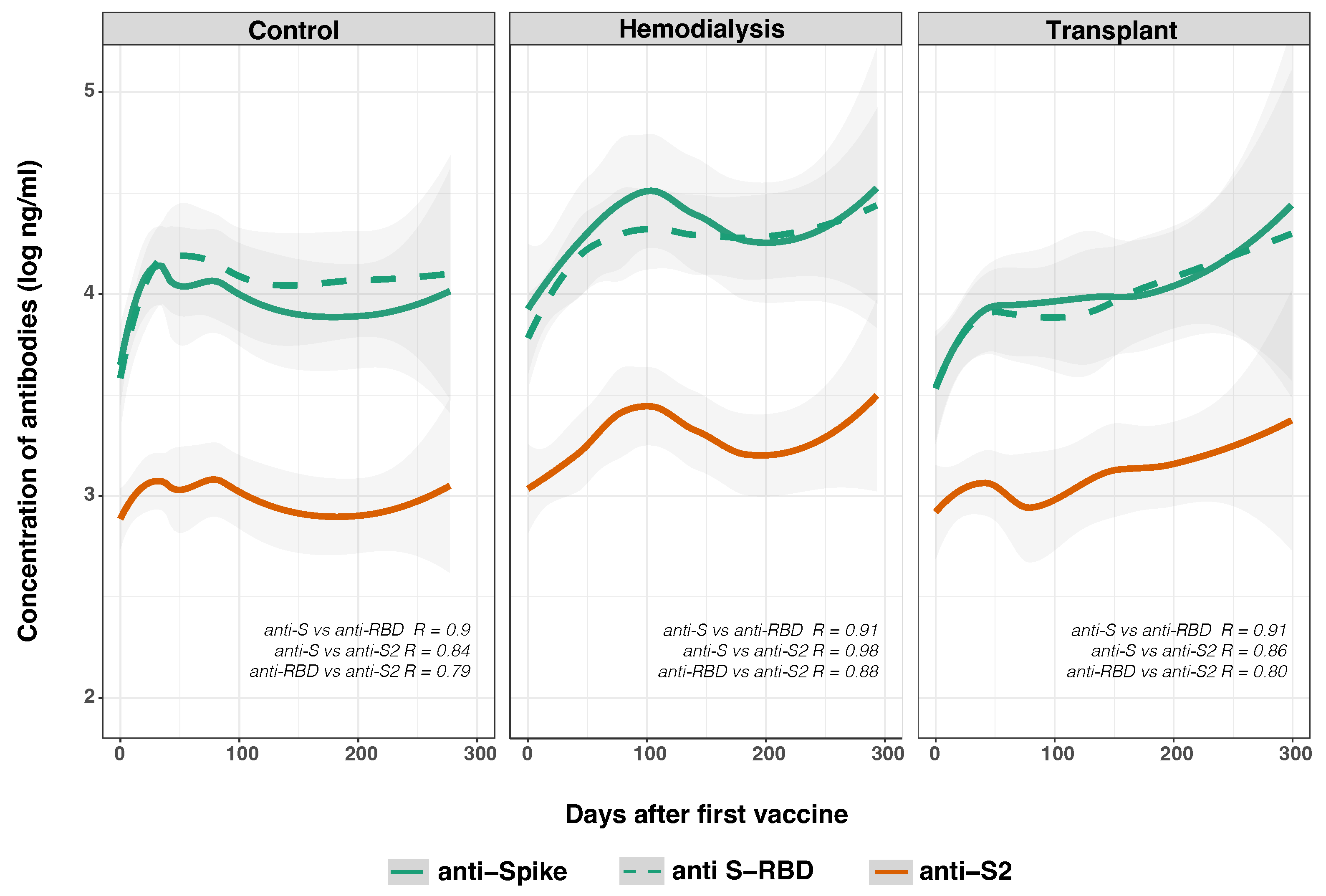
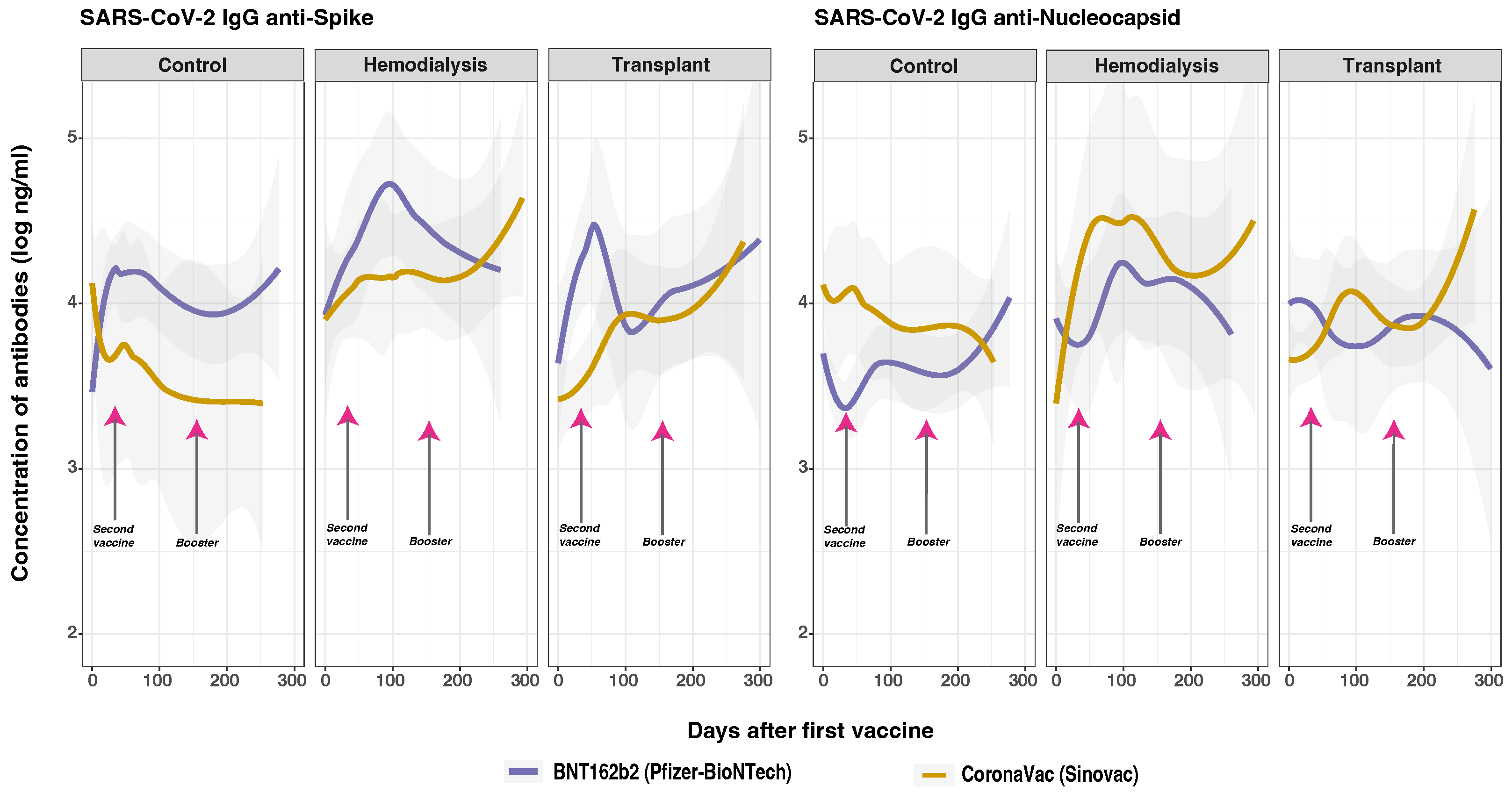
3.4. Time Varying Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Response
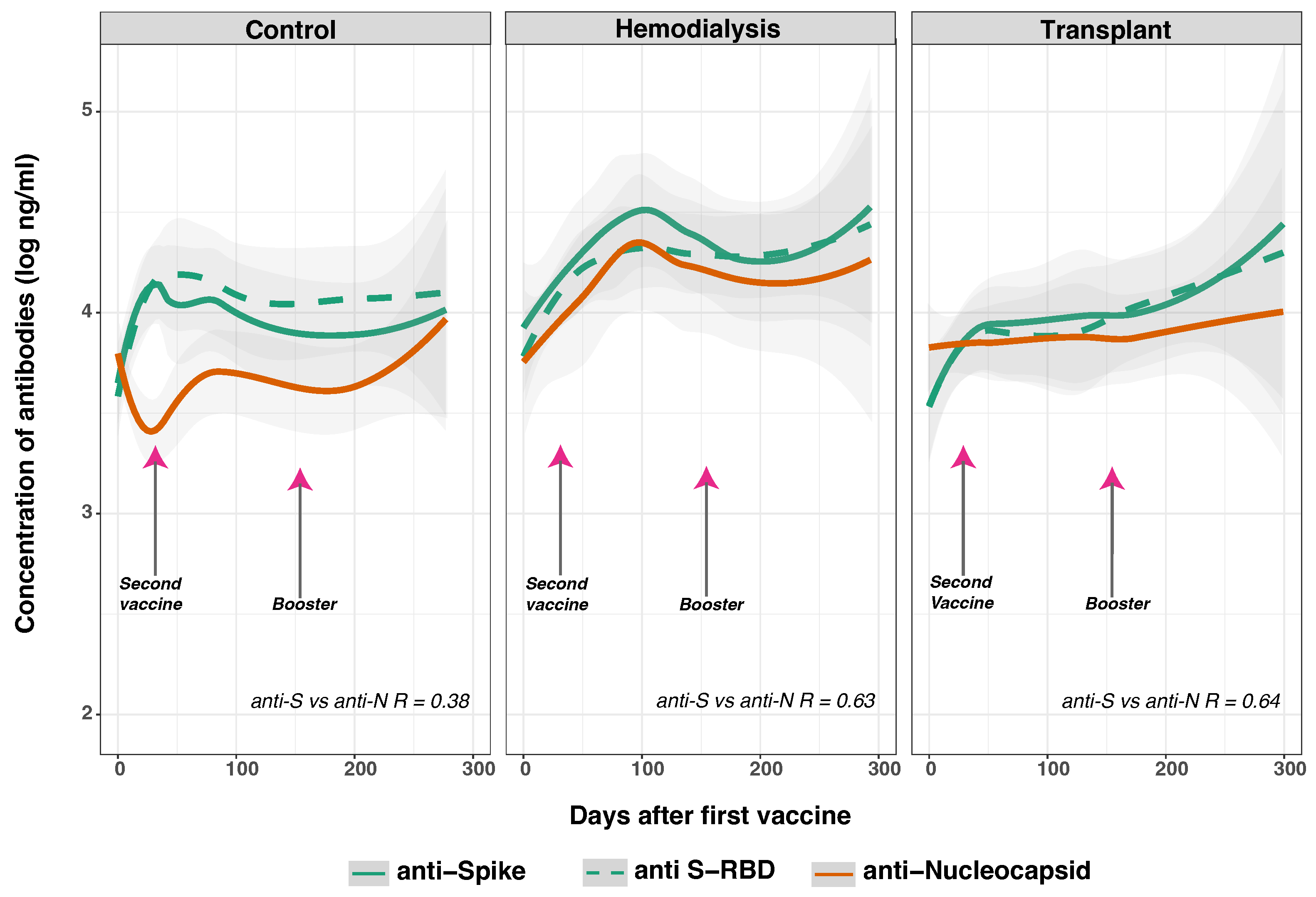
3.5. SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Spike and Anti-Nucleocapsid IgG Responses
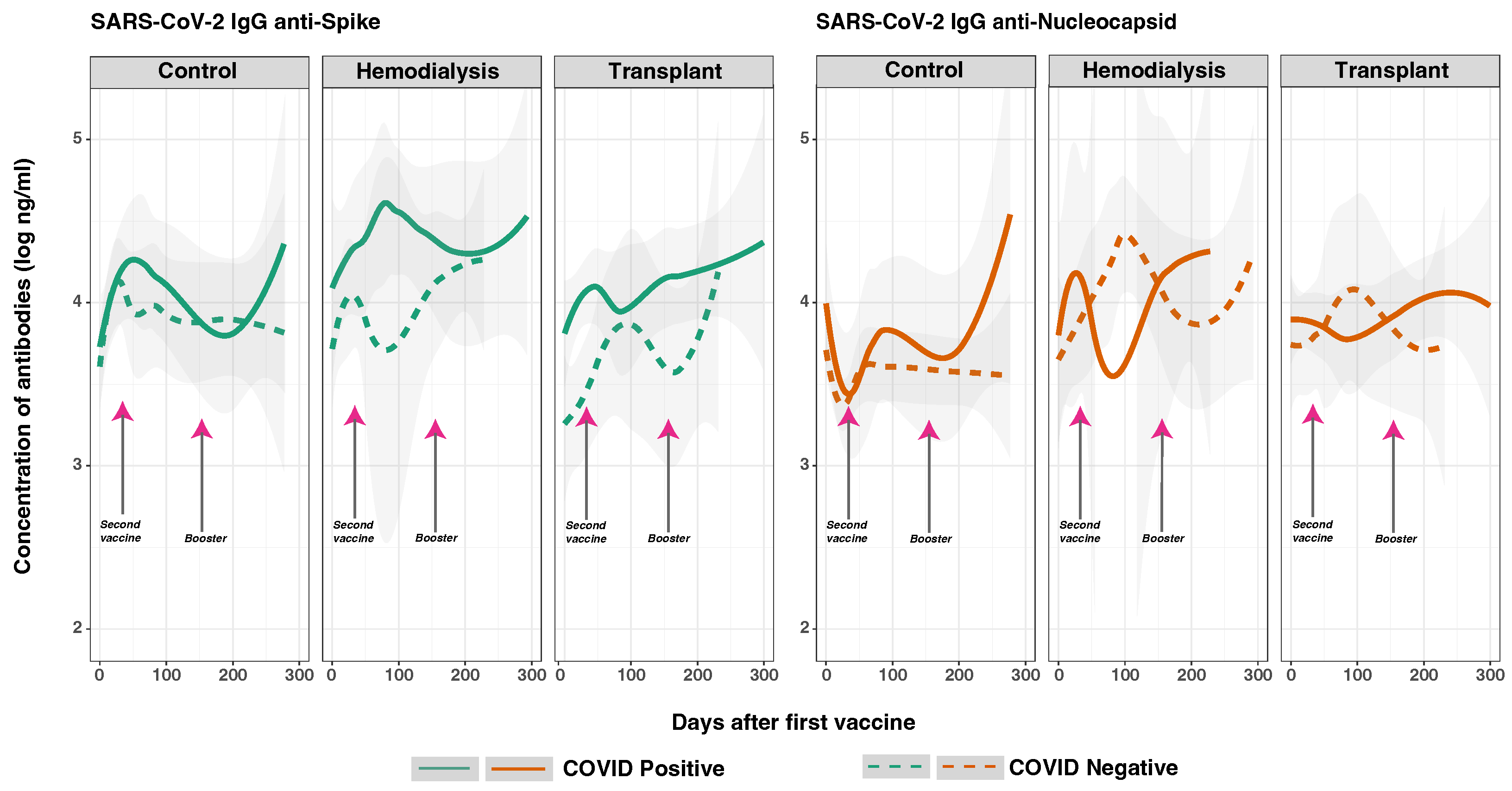
3.6. SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Spike and Anti-Nucleocapsid IgG Response in Previously Infected and Non-Infected Subjects
3.7. SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Spike and Anti-Nucleocapsid IgG Responses and Vaccine Type
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CO | Control group |
| CONABIOS | National Health Bioethics Committee of the Dominican Republic |
| (the Spanish acronym) | |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DOAJ | Directory of Open Access Journals |
| ESRD | End-Stage Renal Disease |
| GLMM | Generalized Linear Mixed Models |
| HD | Hemodialysis Patients |
| Hgb | Hemoglobin |
| IgG | Immunoglobin G |
| INCORT | Instituto Nacional de Coordinación de Trasplante |
| IRB | Institutional Review Boards |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| mPlex-CoV | Fluorescent Multiplex Assay |
| N | Nucleocapsid |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| S | Spike |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| TR | Transplant Recipients |
| VAMS | Volumetric Micro Sampling |
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Caronavirus Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- World Health Organization. Status of COVID-19 Vaccines Within WHO EUL/PQ Evaluation Process. 2023. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/prequal/sites/default/files/document_files/Status_COVID_VAX_08AUgust2023.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Carr, E.J.; Kronbichler, A.; Graham-Brown, M.; Abra, G.; Argyropoulos, C.; Harper, L.; Lerma, E.V.; Suri, R.S.; Topf, J.; Willicombe, M.; et al. Systematic Review of Early Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2292–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffin, E.; Candellier, A.; Vart, P.; Noordzij, M.; Arnol, M.; Covic, A.; Lentini, P.; Malik, S.; Reichert, L.J.; Sever, M.S.; et al. COVID-19 related mortality in kidney transplant and hemodialysis patients: A comparative, prospective registry based study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijewickrama, E.S.; Abdul Hafidz, M.I.; Robinson, B.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Liew, A.; Dreyer, G.; Caskey, F.J.; Bello, A.K.; Zaidi, D.; Damster, S.; et al. Availability and prioritisation of COVID-19 vaccines among patients with advanced chronic kidney disease and kidney failure during the height of the pandemic: A global survey by the International Society of Nephrology. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e065112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.; Porterfield, C.A.; Byron, L.; Wang, C.; Pearson, Z.; Bohrhunter, J.L.; Cardillo, A.B.; Ryan-Muntz, L.; Sorensen, R.A.; Caserta, M.; et al. A Multiplex Microsphere IgG Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Using ACE2-Mediated Inhibition as a Surrogate for Neutralization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, M.; Shashidhar, J.; Deepika, G.; Ravikanth, V.; Krishna, V.V.; Sadhana, Y.; Pragathi, K.; Reddy, D.N. Immunological memory and neutralizing activity to a single dose of COVID-19 vaccine in previously infected individuals. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisnivesky, J.P.; Stone, K.; Bagiella, E.; Doernberg, M.; Mendu, D.R.; Lin, J.J.; Kale, M. Long-term Persistence of Neutralizing Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Following Infection. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 3289–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Montez-Rath, M.E.; Han, J.; Garcia, P.; Cadden, L.; Hunsader, P.; Kerschmann, R.; Beyer, P.; Dittrich, M.; Block, G.A.; et al. Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients Receiving Dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2435–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windpessl, M.; Bruchfeld, A.; Anders, H.J.; Kramer, H.; Waldman, M.; Renia, L.; Ng, L.F.P.; Xing, Z.; Kronbichler, A. COVID-19 vaccines and kidney disease. Nat. Reviews. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, D.; Hamzaoui, M.; Lemée, V.; Lamulle, J.; Hanoy, M.; Laurent, C.; Lebourg, L.; Etienne, I.; Lemoine, M.; Le Roy, F.; et al. Antibody and T Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA BNT162b2 Vaccine in Kidney Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Couat, C.; Faguer, S.; Esposito, L.; Hebral, A.L.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Safety and Immunogenicity of Anti–SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccines in Recipients of Solid Organ Transplants. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, B.; Rubey, H.; Treipl, A.; Gromann, M.; Hemedi, B.; Zehetmayer, S.; Kirsch, B. Hemodialysis Patients Show a Highly Diminished Antibody Response after COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination Compared to Healthy Controls. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemba, R.; Campbell, K.N.; Yang, T.H.; Schaeffer, S.E.; Mayo, K.M.; McGann, P.; Quinn, S.; Roach, J.; Huff, E.D. Excess Death Estimates in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease—United States, February-August 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banham, G.D.; Godlee, A.; Faustini, S.E.; Cunningham, A.F.; Richter, A.; Harper, L.; Group, o.b.o.t.C.H.B.S. Hemodialysis Patients Make Long-Lived Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 that May Be Associated with Reduced Reinfection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2140–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Werbel, W.A.; Avery, R.K.; Tobian, A.A.R.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Antibody Response to 2-Dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine Series in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA 2021, 325, 2204–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Werbel, W.A.; Avery, R.K.; Tobian, A.A.R.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Immunogenicity of a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccine in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA 2021, 325, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotmane, I.; Gautier, G.; Perrin, P.; Olagne, J.; Cognard, N.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Caillard, S. Antibody Response After a Third Dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Minimal Serologic Response to 2 Doses. JAMA 2021, 326, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducloux, D.; Colladant, M.; Chabannes, M.; Yannaraki, M.; Courivaud, C. Humoral response after three doses of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Marion, O.; Couat, C.; Izopet, J.; Del Bello, A. Three Doses of an mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Min, S.; Jo, E.A.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Han, S.S.; Kang, H.G.; Ahn, Y.H.; Oh, I.; Song, E.Y.; et al. Association between Low Anti-spike Antibody Levels After the Third Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Hospitalization due to Symptomatic Breakthrough Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Ann. Lab. Med. 2023, 44, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Hendrickx, R.; Stensgaard, E.; Jellingsø, M.; Sommer, M.O. Kidney Transplant and Dialysis Patients Remain at Increased Risk for Succumbing to COVID-19. Transplantation 2023, 107, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, P.; Candel, F.J.; Carretero, M.M.; San Román, J. Risk of severe COVID in solid organ transplant recipient. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2023, 36 (Suppl. S1), 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, T.P.Y.; Abedon, A.T.; Alejo, J.L.; Segev, D.L.; Massie, A.B.; Werbel, W.A. Incident COVID-19 and Hospitalizations by Variant Era Among Vaccinated Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2329736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinchera, B.; Buonomo, A.R.; Trucillo, E.; Susini, S.; D’Agostino, A.; Di Filippo, I.; Tanzillo, A.; Villari, R.; Carrano, R.; Troisi, R.I.; et al. COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients after 2 years of pandemic: Outcome and impact of antiviral treatments in a single-center study. Front. Transplant. 2023, 2, 1095225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C. En República Dominicana, 5275 Pacientes Reciben Hemodiálisis y 500 Esperan un Riñón. Diario Libre. March 2023. Available online: https://www.diariolibre.com/actualidad/salud/2023/03/10/en-rd-5275-reciben-hemodialisis-y-500-esperan-un-rinon/2250175 (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Instituto Nacional de Coordinación de Trasplante (INCORT). Trasplantes de órganos y Tejidos de la República Dominicana 2008–2023. Incort. Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. 2024. Available online: https://incortrd.com/trasplantes-de-organos-y-tejidos-de-la-republica-dominicana-2008-2022/ (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Ministerio de Salud Pública de La República Dominicana. Gobierno Presenta Plan Nacional de Vacunación Contra COVID-19. 15 February 2021. Available online: https://dominicantoday.com/dr/health/2021/02/13/vaccines-that-the-country-will-use-are-very-effective/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Dominican Today. Vaccines That the Dominican Republic Will Use Are Very Effective. 13 February 2021. Available online: https://dominicantoday.com/dr/health/2021/02/13/vaccines-that-the-country-will-use-are-very-effective/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Pecora, N.D.; Zand, M.S. Measuring the Serologic Response to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Methods and Meaning. Clin. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wiltse, A.; Zand, M.S. Antibody Mediated Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and Human Coronaviruses: Multiplex Beads Assay and Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling to Generate Immune Repertoire Cartography. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompaniyets, L.; Pennington, A.F.; Goodman, A.B.; Rosenblum, H.G.; Belay, B.; Ko, J.Y.; Chevinsky, J.R.; Schieber, L.Z.; Summers, A.D.; Lavery, A.M.; et al. Underlying Medical Conditions and Severe Illness Among 540,667 Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020–March 2021. Prev. Chronic. Dis. 2021, 18, E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Wiltse, A.; Emo, J.; Hilchey, S.P.; Zand, M.S. Application of volumetric absorptive microsampling (VAMS) to measure multidimensional anti-influenza IgG antibodies by the mPlex-Flu assay. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2019, 3, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursac, Z.; Gauss, C.H.; Williams, D.K.; Hosmer, D.W. Purposeful selection of variables in logistic regression. Source Code Biol. Med. 2008, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). Encuesta Nacional de Autopercepción Racial y Étnica en República Dominicana. March 2022. Available online: https://dominicanrepublic.unfpa.org/es/publications/breve-encuesta-nacional-de-autopercepcion-racial-y-etnica-en-republica-dominicana (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Narongkiatikhun, P.; Noppakun, K.; Chaiwarith, R.; Winichakoon, P.; Vongsanim, S.; Suteeka, Y.; Pongsuwan, K.; Kusirisin, P.; Wongsarikan, N.; Fanhchaksai, K.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Homologous and Heterologous Prime-Boost of CoronaVac® and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 among Hemodialysis Patients: An Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Cardoso, M.J.; Ribeiro, L.; Guimarães, J.T. Assessing SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies after BNT162b2 Vaccination and Their Correlation with SARS-CoV-2 IgG Anti-S1, Anti-RBD and Anti-S2 Serological Titers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anichini, G.; Terrosi, C.; Gandolfo, C.; Gori Savellini, G.; Fabrizi, S.; Miceli, G.B.; Cusi, M.G. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response in Persons with Past Natural Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Dai, L.; Gao, G.F. Humoral and cellular immunity and the safety of COVID-19 vaccines: A summary of data published by 21 May 2021. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, J.; Siepmann, T.; Lindner, T.; Karger, C.; Schwöbel, J.; Anders, L.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Schewe, J.; Martin, H.; Schirutschke, H.; et al. Humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in renal transplant versus dialysis patients: A prospective, multicenter observational study using mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 9, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, N.; Bausch-Jurken, M. COVID-19 Vaccination Among Patients Receiving Maintenance Renal Replacement Therapy: Immune Response, Real-World Effectiveness, and Implications for the Future. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, S46–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlhelt, I.; Pérez-Alós, L.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Hansen, C.B.; Petersen, M.S.; Weihe, P.; Armenteros, J.J.A.; Madsen, J.R.; Nielsen, J.P.S.; Hilsted, L.M.; et al. Distinguishing SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine responses up to 18 months post-infection using nucleocapsid protein and receptor-binding domain antibodies. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01796-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Bretones, M.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; van Nierop, G.P. Impact of antigenic evolution and original antigenic sin on SARS-CoV-2 immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e162192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaqish, A.; Abbas, M.M.; Al-Tamimi, M.; Abbas, M.A.; Al-Omari, M.; Alqassieh, R. SARS-CoV-2 Antinucleocapsid Antibody Response of mRNA and Inactivated Virus Vaccines Compared to Unvaccinated Individuals. Vaccines 2022, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren Sadioğlu, R.; Demir, E.; Evren, E.; Aktar, M.; Şafak, S.; Artan, A.S.; Meşe, S.; Ağaçfidan, A.; Çınar, G.; Önel, M.; et al. Antibody response to two doses of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in kidney transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.Y.; Moreira, R.M.; Santos, C.F.D.; Strabelli, T.M.V.; Belizário, J.C.; Pinto, M.I.M.; Marinho, A.; Pereira, J.M.; Mello, L.S.; Ando, M.C.; et al. Immunogenicity of COVID-19 adsorbed inactivated vaccine (CoronaVac) and additional doses of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine in immunocompromised adults compared with immunocompetent persons. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2024, 66, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tu, P.; Beitsch, L.M. Confidence and Receptivity for COVID-19 Vaccines: A Rapid Systematic Review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, H.; Mount, P.F. COVID-19 beliefs and vaccination uptake in dialysis patients: Lessons from an anonymous patient survey. Intern. Med. J. 2022, 52, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.A.; Bloomstone, S.J.; Walder, J.; Crawford, S.; Fouayzi, H.; Mazor, K.M. Attitudes Toward a Potential SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: A Survey of U.S. Adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Control, n = 33 1 | Hemodialysis, n = 13 1 | Transplant, n = 24 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.150 | |||
| 18–24 | 6 (18%) | 1 (7.7%) | 3 (13%) | |
| 25–44 | 21 (64%) | 5 (38%) | 11 (46%) | |
| 45–65 | 6 (18%) | 7 (54%) | 10 (42%) | |
| Sex | 0.200 | |||
| Female | 19 (58%) | 4 (31%) | 10 (42%) | |
| Male | 14 (42%) | 9 (69%) | 14 (58%) | |
| Race | <0.001 | |||
| Asian | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Black | 15 (45%) | 10 (77%) | 24 (100%) | |
| White | 7 (21%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Not reported | 10 (30%) | 3 (23%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Ethnicity | 0.009 | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 19 (58%) | 10 (77%) | 19 (79%) | |
| Non-Hispanic or non-Latino | 4 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (21%) | |
| Not reported | 10 (30%) | 3 (23%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Education level | <0.001 | |||
| Less than high school | 1 (3.0%) | 5 (38%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| High school graduate | 4 (12%) | 3 (23%) | 7 (29%) | |
| Higher education | 9 (27%) | 0 (0%) | 15 (63%) | |
| Graduate education | 3 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Not reported | 16 (48%) | 5 (38%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| Underlying conditions | <0.001 | |||
| None | 27 (82%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| At least one | 6 (18%) | 2 (15%) | 6 (25%) | |
| Two or more | 0 (0%) | 11 (85%) | 17 (71%) | |
| COVID-19 positive before first fingerstick | 0.053 | |||
| Yes | 10 (30%) | 6 (46%) | 15 (63%) | |
| No | 23 (70%) | 7 (54%) | 9 (38%) |
| Characteristic | Control, n = 33 1 | Hemodialysis, n = 13 1 | Transplant, n = 24 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine doses | <0.001 | |||
| One dose | 11 (33%) | 5 (38%) | 2 (8.3%) | |
| Two doses | 20 (61%) | 4 (31%) | 11 (46%) | |
| Fully vaccinated and one booster | 2 (6.1%) | 2 (15%) | 10 (42%) | |
| Two or more boosters | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| Not reported | 0 (0%) | 2 (15%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Vaccine type (prime schedule) | 0.066 | |||
| BNT162b2 | 25 (76%) | 7 (64%) | 11 (46%) | |
| CoronaVac | 8 (24%) | 4 (36%) | 13 (54%) | |
| Booster schedule | 0.700 | |||
| Heterologous | 0 (0%) | 1 (50%) | 6 (55%) | |
| Homologous | 2 (100%) | 1 (50%) | 5 (45%) | |
| COVID-19 positive before first fingerstick | 0.053 | |||
| Yes | 10 (30%) | 6 (46%) | 15 (63%) | |
| No | 23 (70%) | 7 (54%) | 9 (38%) | |
| COVID-19 positive during the study | >0.900 | |||
| Yes | 8 (24%) | 2 (15%) | 5 (21%) | |
| Not reported | 25 (76%) | 11 (85%) | 19 (79%) |
| Variable | 95% CI 1 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time point | |||
| 1 | — | — | |
| 2 | 0.42 | −0.04, 0.89 | 0.076 |
| 3 | 0.63 | 0.17, 1.10 | 0.008 |
| 4 | 0.54 | 0.10, 0.98 | 0.018 |
| 5 | 0.90 | 0.43, 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Cohort | |||
| Control | — | — | |
| Hemodialysis | 1.30 | −0.13, 2.80 | 0.072 |
| Transplant | 0.34 | −0.53, 1.20 | 0.400 |
| Vaccine doses | 0.76 | 0.20, 1.30 | 0.008 |
| Age | |||
| 18–24 | — | — | |
| 25–44 | −0.52 | −1.4, 0.35 | 0.200 |
| 45–65 | 0.41 | −0.30, 1.1 | 0.300 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | — | — | |
| Male | −0.39 | −1.10, 0.31 | 0.300 |
| Underlying conditions | −0.98 | −1.60, −0.40 | 0.001 |
| COVID-19 positive before first fingerstick | |||
| No | — | — | |
| Yes | 1.10 | 0.23, 1.90 | 0.014 |
| Vaccine type (prime schedule) | |||
| BNT162b2 | — | — | |
| CoronaVac | 1.80 | 0.81, 2.80 | <0.001 |
| Booster schedule | |||
| Heterologous | — | — | |
| Homologous | 1.40 | 0.30, 2.50 | 0.014 |
| Education level | −0.01 | −0.68, 0.66 | >0.900 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcantara Sanchez, L.; Alvarez Guerra, E.; Li, D.; King, S.M.; Hilchey, S.P.; Zhou, Q.; Dewhurst, S.; Fiscella, K.; Zand, M.S. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121312
Alcantara Sanchez L, Alvarez Guerra E, Li D, King SM, Hilchey SP, Zhou Q, Dewhurst S, Fiscella K, Zand MS. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121312
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcantara Sanchez, Lisette, Eloy Alvarez Guerra, Dongmei Li, Samantha M. King, Shannon P. Hilchey, Qian Zhou, Stephen Dewhurst, Kevin Fiscella, and Martin S. Zand. 2024. "Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients: Data from the Dominican Republic" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121312
APA StyleAlcantara Sanchez, L., Alvarez Guerra, E., Li, D., King, S. M., Hilchey, S. P., Zhou, Q., Dewhurst, S., Fiscella, K., & Zand, M. S. (2024). Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines, 12(12), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121312







