4-1BBL-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Exerts Antitumor Effects in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Cells
2.3. Virus Construction
2.4. Viral Propagation, Purification, and Concentration
2.5. Plaque Formation Assay
2.6. 4-1BBL Expression Analysis by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Cytopathic Effect
2.8. Viral Growth Curve
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. Tumor Therapeutic Model
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
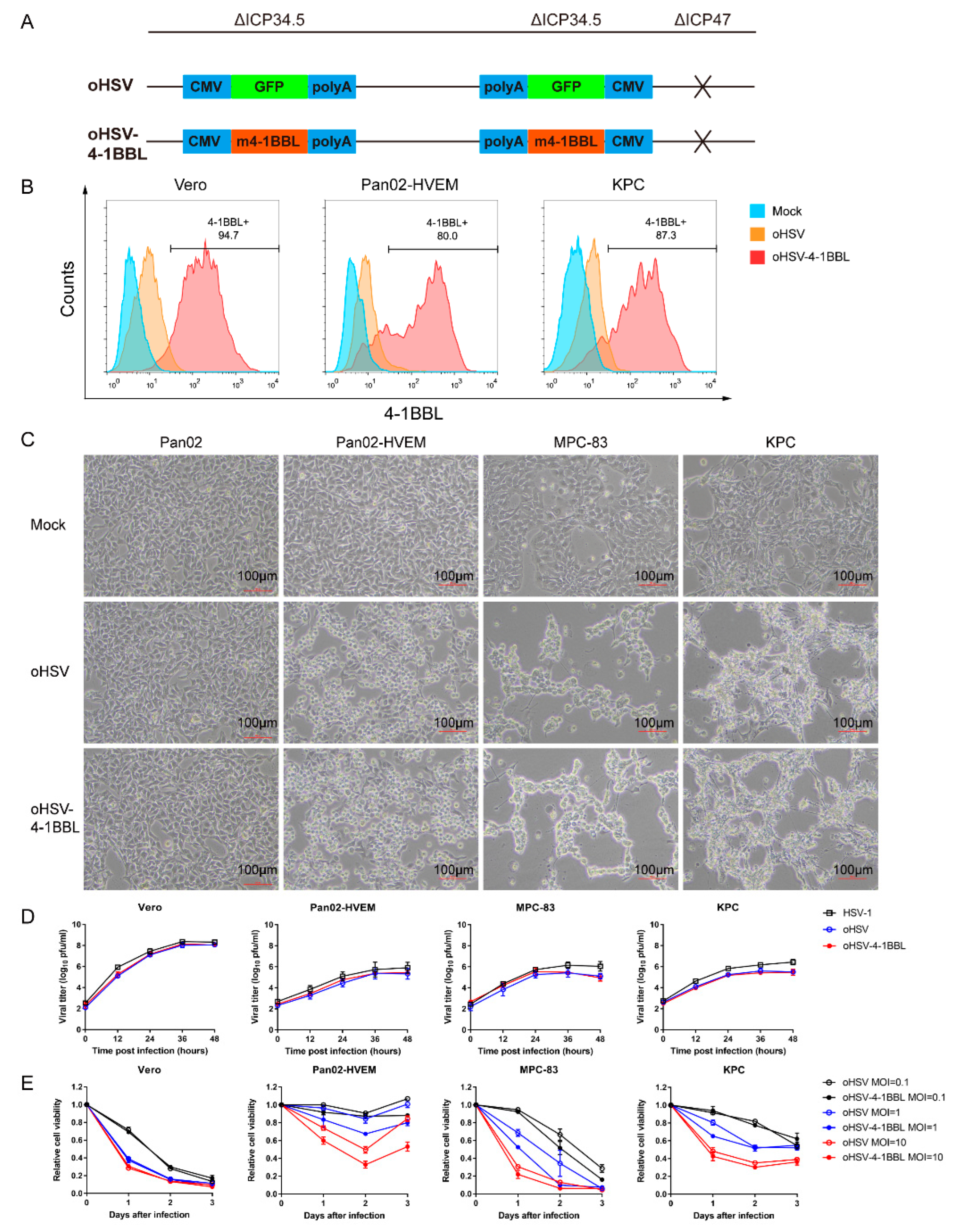
3.1. Construction and In Vitro Characteristics of the oHSV-4-1BBL Virus
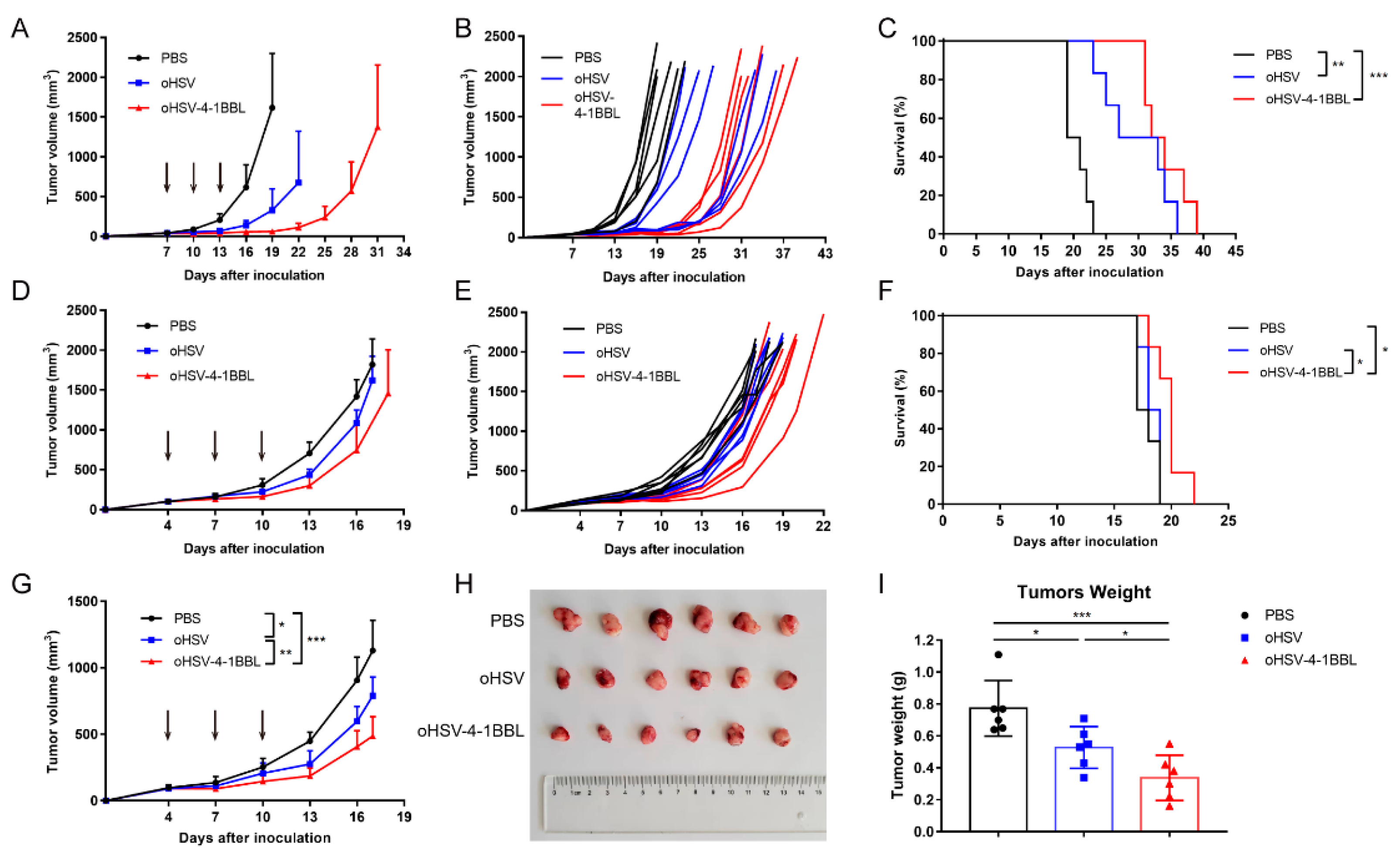
3.2. oHSV-4-1BBL Exhibits Superior Antitumor Activity Compared to oHSV
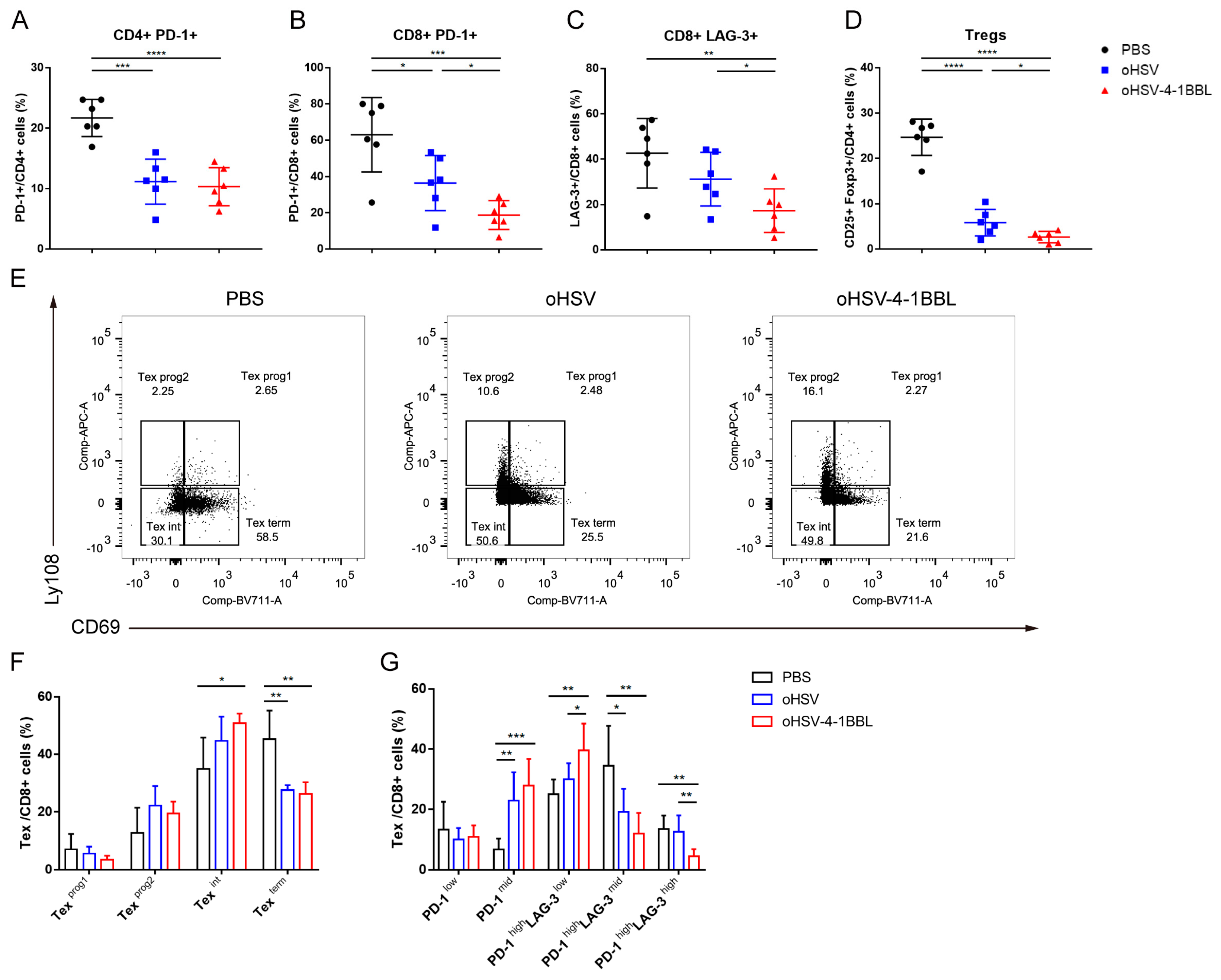
3.3. Impact of oHSV-4-1BBL Treatment on T Cells
3.4. oHSV-4-1BBL Alters Exhaustive CD8+ T-Cell Distribution
3.5. Combination Therapy with oHSV-4-1BBL and PD-1 Antibody
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ducreux, M.; Cuhna, A.S.; Caramella, C.; Hollebecque, A.; Burtin, P.; Goéré, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Haustermans, K.; Van Laethem, J.L.; Conroy, T.; et al. Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26 (Suppl. S5), v56–v68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teague, A.; Lim, K.-H.; Wang-Gillam, A. Advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A review of current treatment strategies and developing therapies. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2015, 7, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Zloza, A. Oncolytic viruses: A new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 642–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Wan, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, R.; et al. CD40L-armed oncolytic herpes simplex virus suppresses pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by facilitating the tumor microenvironment favorable to cytotoxic T cell response in the syngeneic mouse model. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2022, 10, e003809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, M.; Rabkin, S.D.; Kojima, H.; Martuza, R.L. Herpes simplex virus as an in situ cancer vaccine for the induction of specific anti-tumor immunity. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydova, J.; Gavrikova, T.; Brown, E.J.; Luo, X.; Curiel, D.T.; Vickers, S.M.; Yamamoto, M. In Vivo bioimaging tracks conditionally replicative adenoviral replication and provides an early indication of viral antitumor efficacy. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, V.; Ilett, E.; Scott, K.; West, E.; Vile, R.; Pandha, H.; Harrington, K.; Young, A.; Hall, G.; Coffey, M.; et al. Lymphokine-activated killer and dendritic cell carriage enhances oncolytic reovirus therapy for ovarian cancer by overcoming antibody neutralization in ascites. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 134, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledge, G.W.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. The Effect of Abemaciclib Plus Fulvestrant on Overall Survival in Hormone Receptor-Positive, ERBB2-Negative Breast Cancer That Progressed on Endocrine Therapy-MONARCH 2: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Gong, N.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; et al. An oncolytic HSV-1 armed with Visfatin enhances antitumor effects by remodeling tumor microenvironment against murine pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 718, 149931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.C.; Coffin, R.S.; Davis, C.J.; Graham, N.J.; Groves, N.; Guest, P.J.; Harrington, K.J.; James, N.D.; Love, C.A.; McNeish, I.; et al. A phase I study of OncoVEXGM-CSF, a second-generation oncolytic herpes simplex virus expressing granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6737–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Bines, S.D. OPTIM trial: A Phase III trial of an oncolytic herpes virus encoding GM-CSF for unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geevarghese, S.K.; Geller, D.A.; de Haan, H.A.; Hörer, M.; Knoll, A.E.; Mescheder, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Reid, T.R.; Sze, D.Y.; Tanabe, K.K.; et al. Phase I/II study of oncolytic herpes simplex virus NV1020 in patients with extensively pretreated refractory colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campadelli-Fiume, G.; De Giovanni, C.; Gatta, V.; Nanni, P.; Lollini, P.; Menotti, L. Rethinking herpes simplex virus: The way to oncolytic agents. Rev. Med. Virol. 2011, 21, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszthy, P.C.; Immervoll, H.; Wang, J.; Goplen, D.; Miletic, H.; Eide, G.E.; Bjerkvig, R. Cellular effects of oncolytic viral therapy on the glioblastoma microenvironment. Gene Ther. 2009, 17, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Robinson, M.; Han, Z.-Q.; Branston, R.H.; English, C.; Reay, P.; McGrath, Y.; Thomas, S.K.; Thornton, M.; Bullock, P.; et al. ICP34.5 deleted herpes simplex virus with enhanced oncolytic, immune stimulating, and anti-tumour properties. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.H.; Bouvier, M. MHC class I antigen presentation: Learning from viral evasion strategies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, J.; Kurozumi, K.; Dmitrieva, N.; Sayers, M.P.; Ahmad, S.; Waterman, P.; Weissleder, R.; Chiocca, E.A.; Kaur, B. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of vasculostatin (Vstat120) expressing oncolytic HSV-1. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, D.; Nawa, A.; Tanino, T.; Goshima, F.; Luo, C.H.; Iwaki, M.; Kajiyama, H.; Shibata, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Ino, K.; et al. Enhanced cytotoxicity with a novel system combining the paclitaxel-2’-ethylcarbonate prodrug and an HSV amplicon with an attenuated replication-competent virus, HF10 as a helper virus. Cancer Lett. 2010, 288, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, I.R.; Bustos-Villalobos, I.; Ichinose, T.; Matsumura, S.; Naoe, Y.; Miyajima, N.; Morimoto, D.; Mukoyama, N.; Zhiwen, W.; Tanaka, M.; et al. The Current Status and Future Prospects of Oncolytic Viruses in Clinical Trials against Melanoma, Glioma, Pancreatic, and Breast Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boagni, D.A.; Ravirala, D.; Zhang, S.X. Current strategies in engaging oncolytic viruses with antitumor immunity. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 22, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Eom, H.-S.; Choi, B.K. 4-1BB immunotherapy: Advances and hurdles. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, A.H.; Haso, W.M.; Shern, J.F.; Wanhainen, K.M.; Murgai, M.; Ingaramo, M.; Smith, J.P.; Walker, A.J.; Kohler, M.E.; Venkateshwara, V.R.; et al. 4-1BB costimulation ameliorates T cell exhaustion induced by tonic signaling of chimeric antigen receptors. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, E.; Milenova, I.; Wenthe, J.; Ståhle, M.; Leja-Jarblad, J.; Ullenhag, G.; Dimberg, A.; Moreno, R.; Alemany, R.; Loskog, A. Shaping the Tumor Stroma and Sparking Immune Activation by CD40 and 4-1BB Signaling Induced by an Armed Oncolytic Virus. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5846–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Li, F.; Wang, R.; Cen, T.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, R.; Xu, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; et al. An armed oncolytic virus enhances the efficacy of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy by converting tumors to artificial antigen-presenting cells in situ. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3658–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltra, J.-C.; Manne, S.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.S.; Kurachi, M.; Giles, J.R.; Chen, Z.; Casella, V.; Ngiow, S.F.; Khan, O.; Huang, Y.J.; et al. Developmental Relationships of Four Exhausted CD8(+) T Cell Subsets Reveals Underlying Transcriptional and Epigenetic Landscape Control Mechanisms. Immunity 2020, 52, 825–841.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, H.; Hao, M.; Xiong, D.; Luo, Y.; Huang, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N. Increasing the Efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Precise Genome Editing of HSV-1 Virus in Human Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Park, S.; Jeong, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, K.H.; Hong, S.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.; et al. 4-1BB Delineates Distinct Activation Status of Exhausted Tumor-Infiltrating CD8(+) T Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 71, 955–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menk, A.V.; Scharping, N.E.; Rivadeneira, D.B.; Calderon, M.J.; Watson, M.J.; Dunstane, D.; Watkins, S.C.; Delgoffe, G.M. 4-1BB costimulation induces T cell mitochondrial function and biogenesis enabling cancer immunotherapeutic responses. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Shen, H.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Han, C.; Yi, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; et al. The efficacy and safety of a novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody cadonilimab (AK104) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter retrospective observational study. Thorac. Cancer 2024, 15, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Kang, K.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Y. Dual blockade immunotherapy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, Y.; Liang, T. Oncolytic virotherapy: Basic principles, recent advances and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazaios, K.; van Berkum, R.E.; Calkoen, F.G.; van der Lugt, J.; Hulleman, E. OV Modulators of the Paediatric Brain TIME: Current Status, Combination Strategies, Limitations and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanivelu, L.; Liu, C.-H.; Lin, L.-T. Immunogenic cell death: The cornerstone of oncolytic viro-immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1038226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, W.; Zhao, Z.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, N.; Zhang, C.; Pan, S.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y. 4-1BBL-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Exerts Antitumor Effects in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121309
Gao W, Zhao Z, Bi Y, Li J, Tian N, Zhang C, Pan S, Deng L, Zhang Y. 4-1BBL-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Exerts Antitumor Effects in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121309
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Wenrui, Zhuoqian Zhao, Ying Bi, Jinghua Li, Na Tian, Cuizhu Zhang, Shuyuan Pan, Li Deng, and Yuntao Zhang. 2024. "4-1BBL-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Exerts Antitumor Effects in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121309
APA StyleGao, W., Zhao, Z., Bi, Y., Li, J., Tian, N., Zhang, C., Pan, S., Deng, L., & Zhang, Y. (2024). 4-1BBL-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Exerts Antitumor Effects in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Vaccines, 12(12), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121309



