Intranasal HBsAg/HBcAg-Containing Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Anti-HBs Production in Hepatitis B Vaccine Non-Responders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
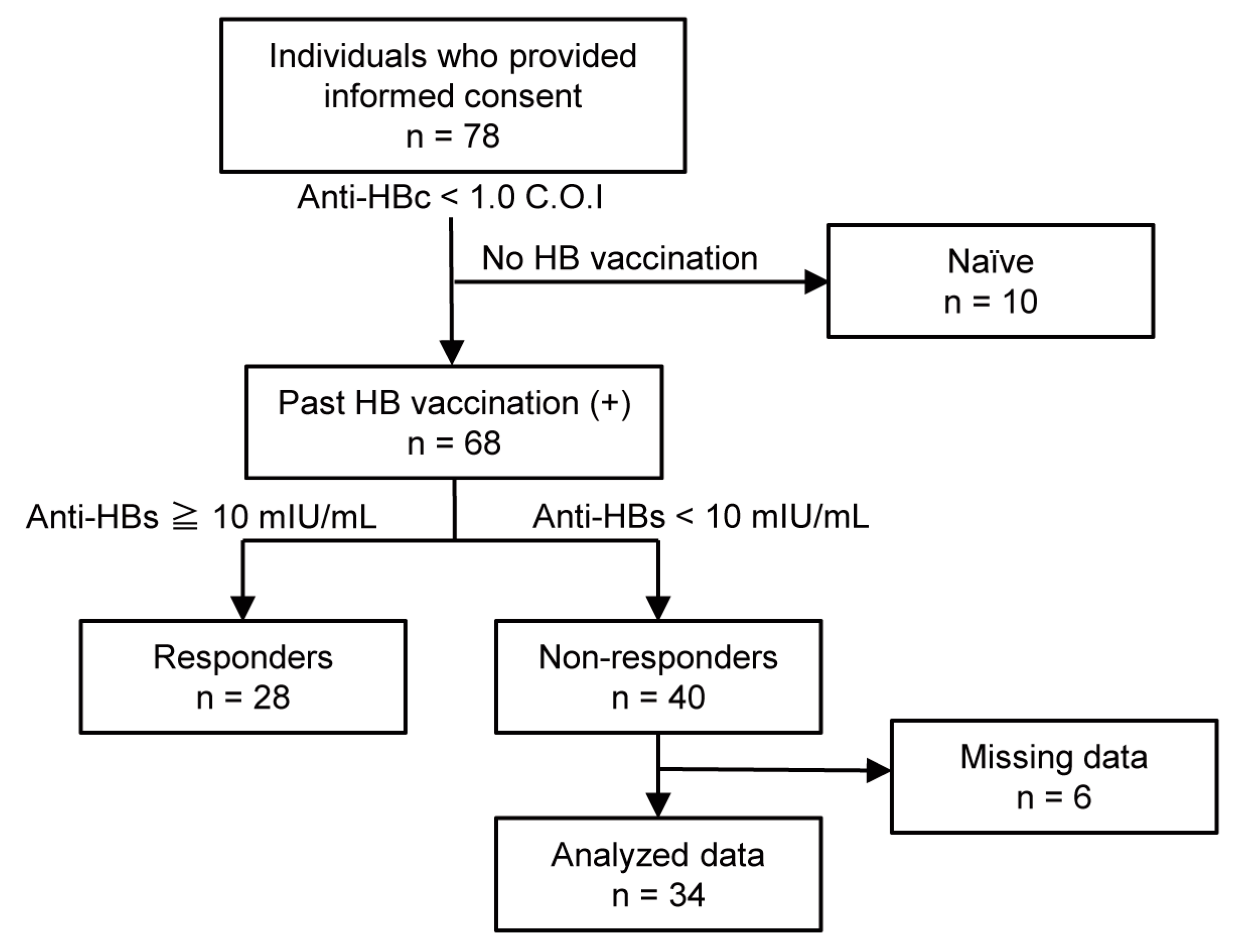
2.1. Study Population and Protocol
2.2. IgG-Type Anti-HBs and IgG-Type Anti-HBc and Anti-HBe Measurements
2.3. IgA-Type Anti-HBs and Anti-HBc Detection Using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.4. HBV-Neutralization Test
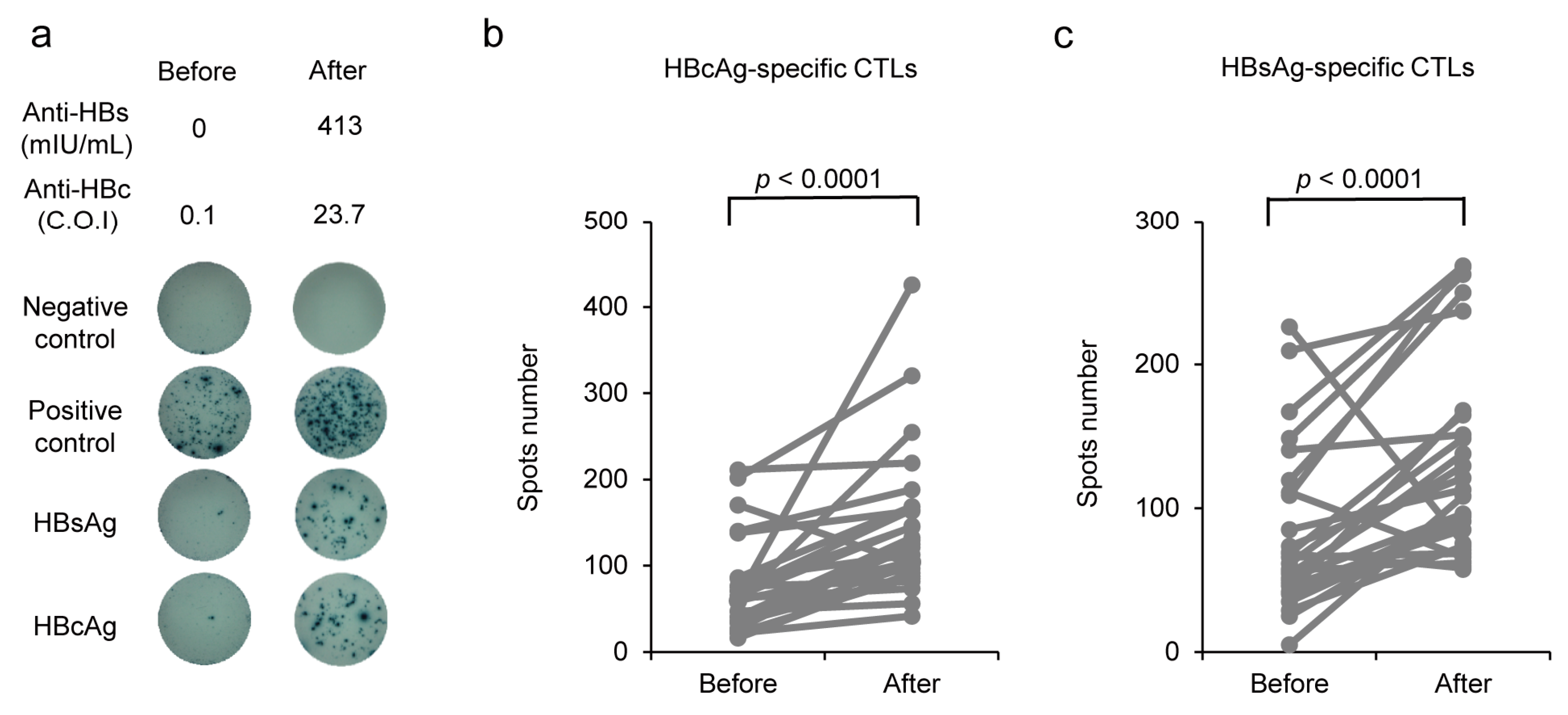
2.5. HBV-Specific CTL Detection Using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Spot Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Profile and Participant Demographics
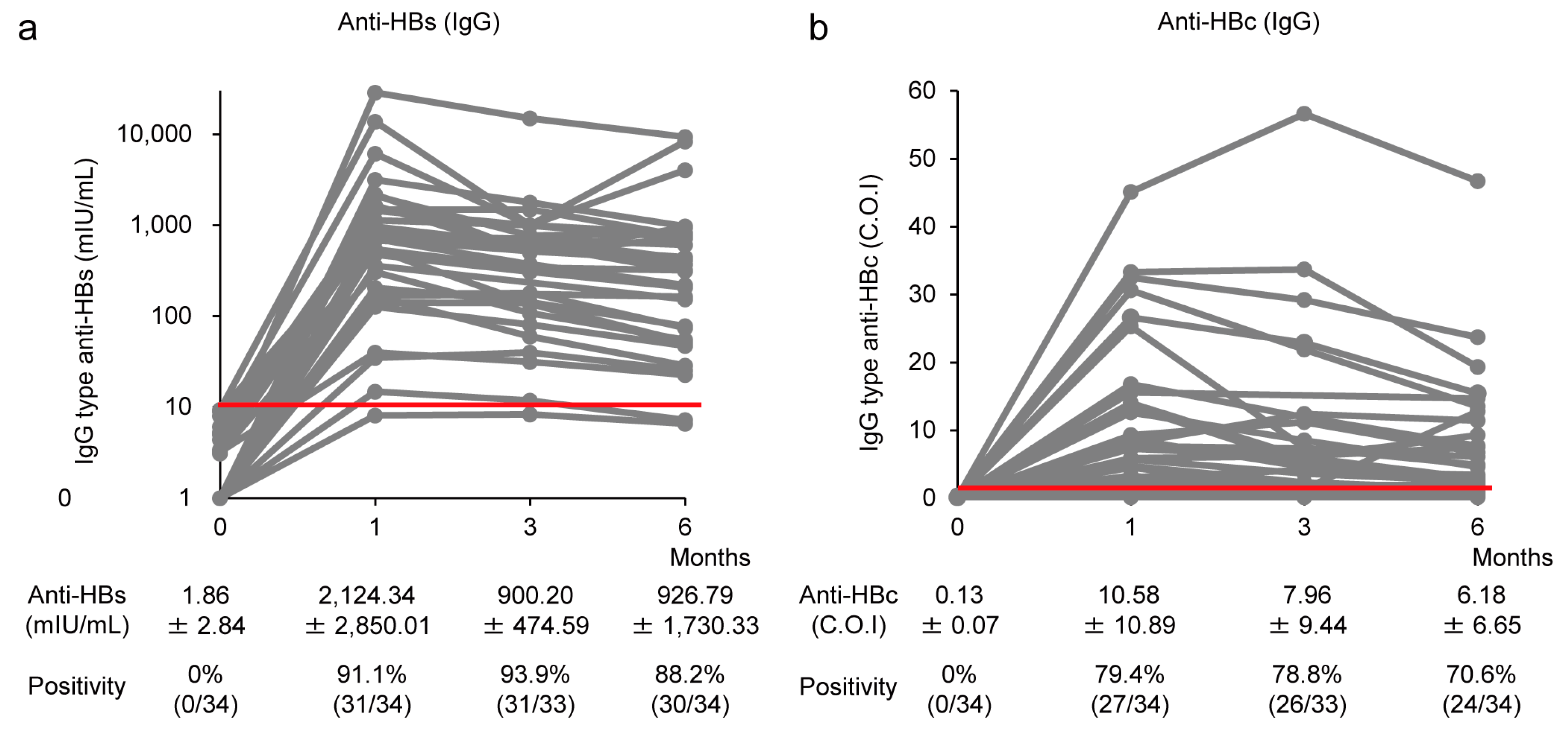
3.2. Induction of IgG-Type Anti-HBs and Anti-HBc Production by CVP-NASVAC in HB Vaccine Non-Responders
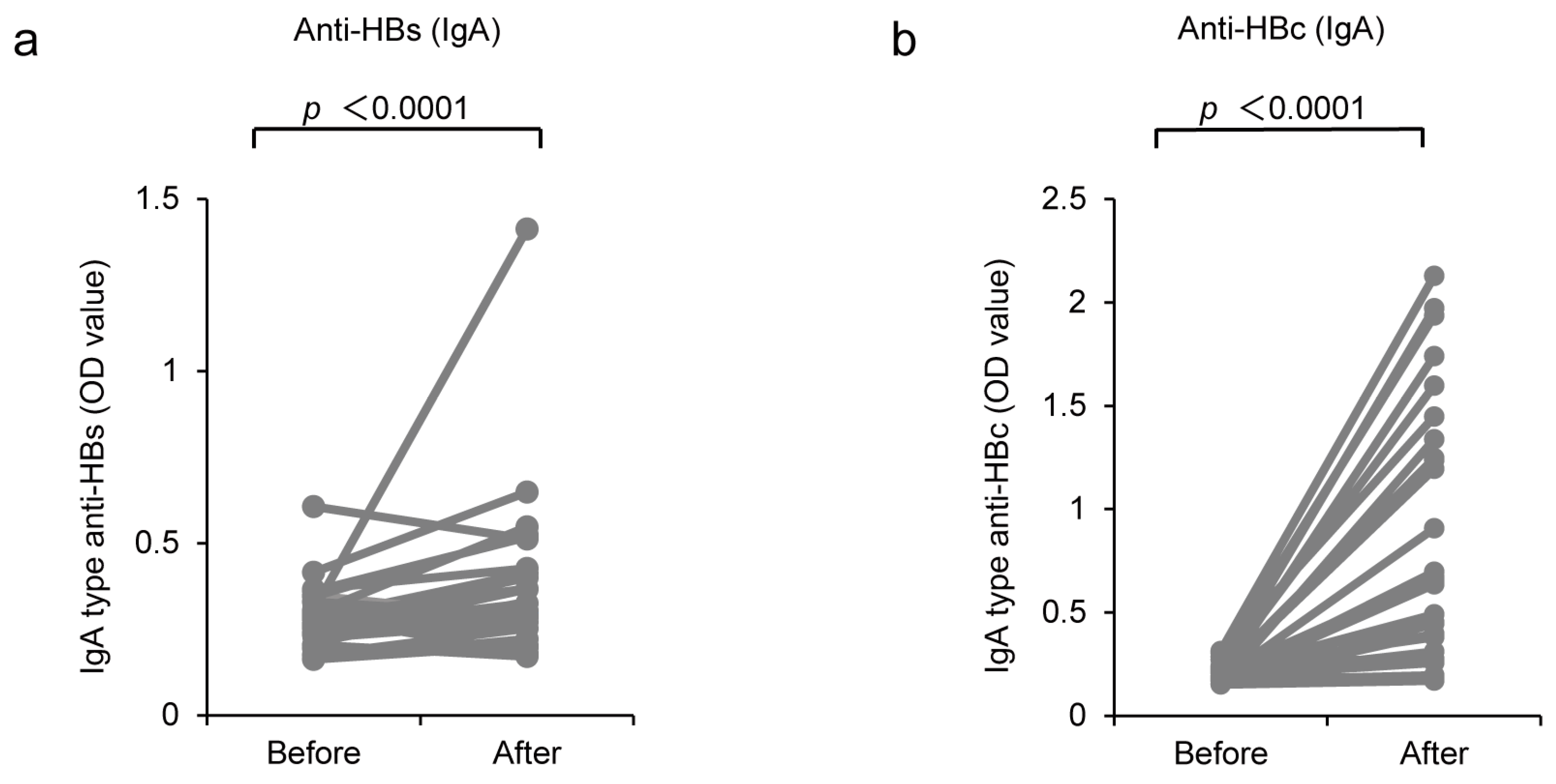
3.3. Induction of IgA-Type Antibody Production by CVP-NASVAC
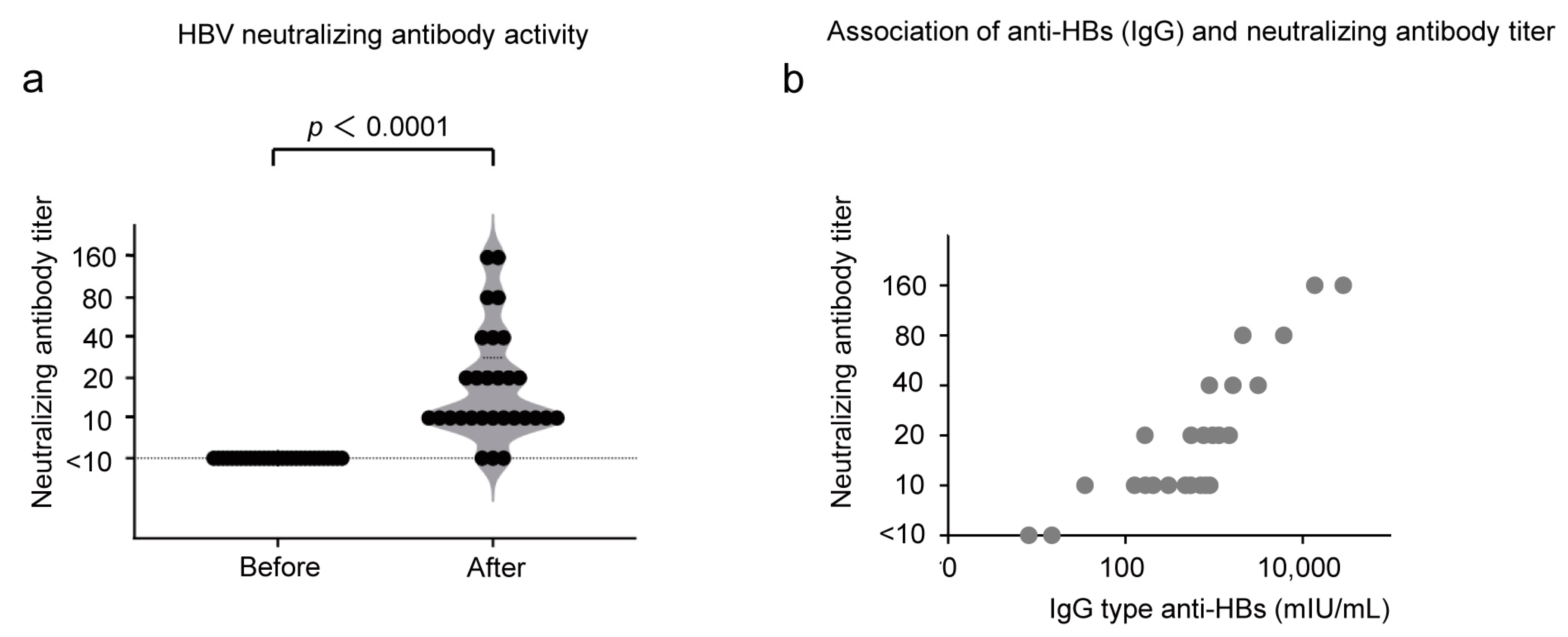
3.4. HBV Neutralization by the Antibody in the Sera of CVP-NASVAC-Immunized HB Vaccine Non-Responders
3.5. Induction of HBcAg-Specific CTL Production by CVP-NASVAC
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565455 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.H. Hepatitis B vaccine development and implementation. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2020, 16, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, L.; Albarran, B.; Salmen, S.; Borges, L.; Fields, H.; Montes, H.; Soyano, A.; Diaz, Y.; Berrueta, L. The nonresponse to hepatitis B vaccination is associated with impaired lymphocyte activation. Virology 2004, 326, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walayat, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Martin, D.; Puli, S.; Cashman, M.; Dhillon, S. Recent advances in vaccination of non-responders to standard dose hepatitis B virus vaccine. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, K.; Shimizu, Y. Unsolved problems and future perspectives of hepatitis B virus vaccination. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7074–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghasadeghi, M.R.; Banifazl, M.; Aghakhani, A.; Eslamifar, A.; Vahabpour, R.; Ramezani, A. No evidence for occult HBV infection in hepatitis B vaccine non-responders. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Gao, Y.; Cao, J.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, T.Y.; Yang, C.L.; Xiong, H.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Ou, S.H.; Cheng, T.; et al. Robust in vitro assay for analyzing the neutralization activity of serum specimens against hepatitis B virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, J.C.; Lobaina, Y.; Muzio, V.; García, D.; Pentón, E.; Iglesias, E.; Pichardo, D.; Urquiza, D.; Rodríguez, D.; Silva, D.; et al. Development of a nasal vaccine for chronic hepatitis B infection that uses the ability of hepatitis B core antigen to stimulate a strong Th1 response against hepatitis B surface antigen. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Diaz-Arévalo, D.; Guan, H.; Zeng, M. Noninvasive vaccination against infectious diseases. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobaina, Y.; García, D.; Abreu, N.; Muzio, V.; Aguilar, J.C. Mucosal immunogenicity of the hepatitis B core antigen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Ainai, A.; Suzuki, T.; Harada, N.; Ami, Y.; Yuki, Y.; Takeyama, H.; Kiyono, H.; Tsukada, H.; Hasegawa, H. The effect of mucoadhesive excipient on the nasal retention time of and the antibody responses induced by an intranasal influenza vaccine. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Kayesh, M.E.H.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Takano, J.I.; Shiogama, Y.; Yasutomi, Y.; Goh, Y.; et al. Intranasal vaccination with HBs and HBc protein combined with carboxyl vinyl polymer induces strong neutralizing antibody, anti-HBs IgA, and IFNG response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 520, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, O.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Imai, Y.; Sanada, T.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Kamishita, T.; Miyake, T.; Tokumoto, Y.; Hikita, H.; et al. Intranasal therapeutic vaccine containing HBsAg and HBcAg for patients with chronic hepatitis B; 18 months follow-up results of phase IIa clinical study. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, H.; Ichimiya, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. Mucosal immune response in nasal-associated lymphoid tissue upon intranasal administration by adjuvants. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, P. The Immune System, 4th ed.; Medical Sciences International: Tokyo, Japan, 2007; pp. 265–288. [Google Scholar]
- Kakisaka, K.; Sakai, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Miyasaka, A.; Takahashi, F.; Sumazaki, R.; Takikawa, T. Hepatitis B surface antibody titers at one and two years after hepatitis B virus vaccination in healthy young Japanese adults. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stramer, S.L.; Wend, U.; Candotti, D.; Foster, G.A.; Hollinger, F.B.; Dodd, R.Y.; Allain, J.P.; Gerlich, W.G. Nucleic acid testing to detect HBV infection in blood donors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Boni, C.; Lee, C.K.; Larrubia, J.R.; Reignat, S.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.S.; Herberg, J.; Gilson, R.; Alisa, A.; et al. The role of virus-specific CD8(+) cells in liver damage and viral control during persistent hepatitis B virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, G.J.M.; Reignat, S.; Brown, D.; Ogg, G.S.; Jones, L.; Seneviratne, S.L.; Williams, R.; Dusheiko, G.; Bertoletti, A. Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Implications for immunotherapy. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5707–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, P.J.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T. Cell and animal models for studying hepatitis B virus infection and drug development. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainai, A.; Tamura, S.; Suzuki, T.; van Riet, E.; Ito, R.; Odagiri, T.; Tashiro, M.; Kurata, T.; Hasegawa, H. Intranasal vaccination with an inactivated whole influenza virus vaccine induces strong antibody responses in serum and nasal mucus of healthy adults. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of participants | 34 |
| Age (years) | 23 (22–25) |
| Male: Female | 31: 3 |
| AST (U/L) | 22 (19–26) |
| ALT (U/L) | 19.5 (15–25) |
| Platelet count (×10⁴/µL) | 23.8 (21.5–27.9) |
| Anti-HBs (mIU/mL) | 0 (0–3.3) |
| Anti-HBc (C.O.I.) | 0.1 (0.1–0.1) |
| Anti-HBe positivity (%) | 0 (0%) |
| Duration from the last vaccination (years) | 2 (2–3) |
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| All AEs | 9 (26.5%) |
| Increase in CRP level | 3 (8.8%) |
| Nasal mucus formation | 2 (5.9) |
| Sneezing | 2 (5.9) |
| Fever | 2 (5.9) |
| General fatigue | 2 (5.9) |
| Stuffy nose | 1 (2.9) |
| Pruritus | 1 (2.9) |
| Increase in WBC count | 1 (2.9) |
| Increase in ALT level | 1 (2.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiraishi, K.; Yoshida, O.; Imai, Y.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Sanada, T.; Kohara, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Kamishita, T.; Miyake, T.; Hirooka, M.; et al. Intranasal HBsAg/HBcAg-Containing Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Anti-HBs Production in Hepatitis B Vaccine Non-Responders. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091479
Shiraishi K, Yoshida O, Imai Y, Akbar SMF, Sanada T, Kohara M, Miyazaki T, Kamishita T, Miyake T, Hirooka M, et al. Intranasal HBsAg/HBcAg-Containing Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Anti-HBs Production in Hepatitis B Vaccine Non-Responders. Vaccines. 2023; 11(9):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091479
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiraishi, Kana, Osamu Yoshida, Yusuke Imai, Sheikh Mohammad Fazle Akbar, Takahiro Sanada, Michinori Kohara, Takashi Miyazaki, Taizou Kamishita, Teruki Miyake, Masashi Hirooka, and et al. 2023. "Intranasal HBsAg/HBcAg-Containing Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Anti-HBs Production in Hepatitis B Vaccine Non-Responders" Vaccines 11, no. 9: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091479
APA StyleShiraishi, K., Yoshida, O., Imai, Y., Akbar, S. M. F., Sanada, T., Kohara, M., Miyazaki, T., Kamishita, T., Miyake, T., Hirooka, M., Tokumoto, Y., Abe, M., Rubido, J. C. A., Nieto, G. G., & Hiasa, Y. (2023). Intranasal HBsAg/HBcAg-Containing Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Anti-HBs Production in Hepatitis B Vaccine Non-Responders. Vaccines, 11(9), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091479







