Assessment of Safety and Prophylactic Efficacy of the EpiVacCorona Peptide Vaccine for COVID-19 Prevention (Phase III)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Vaccine and Placebo
2.3. Physical Examination and Clinical Laboratory Procedures
2.4. Safety Assessment
2.5. Detecting Coronavirus RNA in Nasopharyngeal Swabs
2.6. ELISA Kits for Quantifying Serum Antibodies
2.7. Quantification of Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in the Neutralization Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
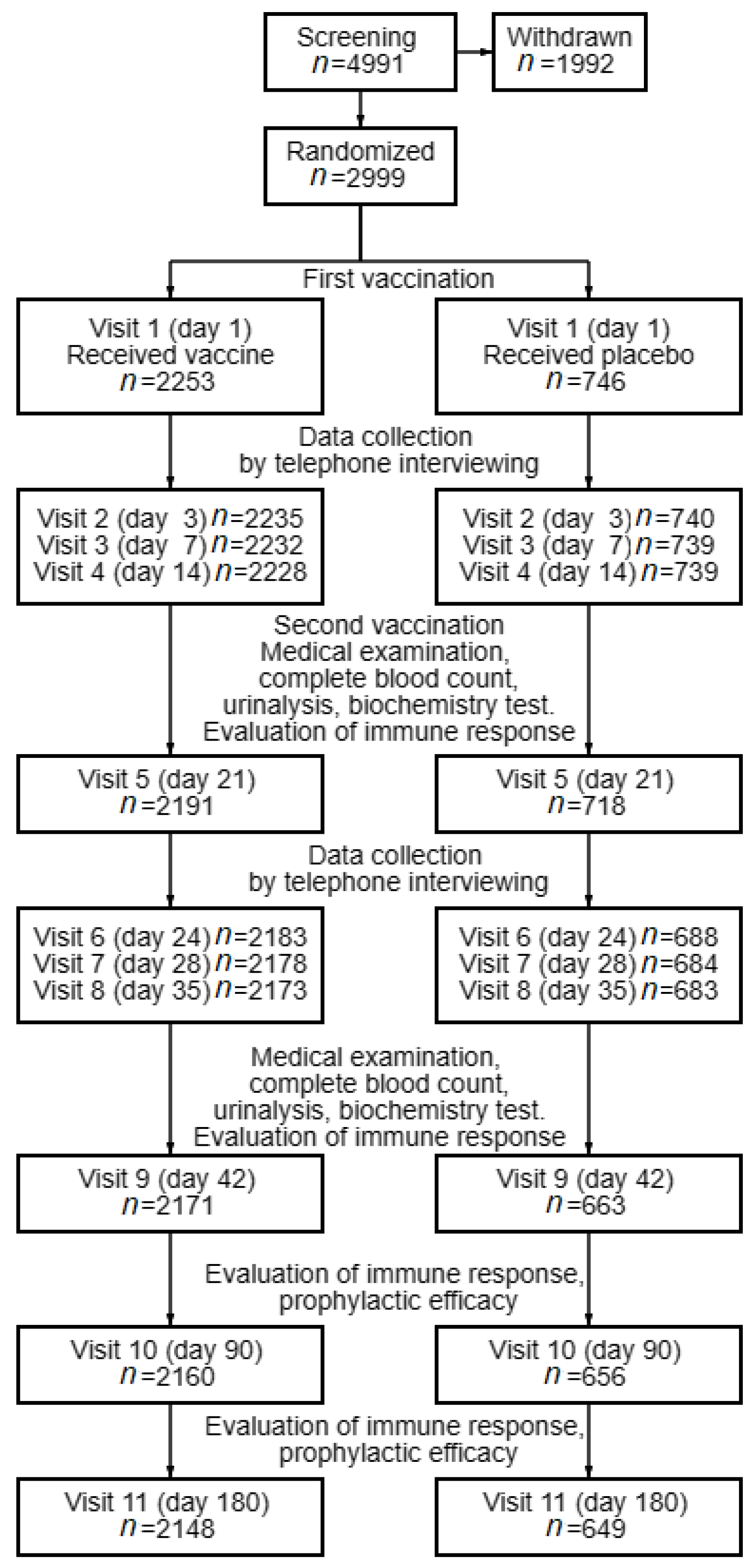
3.1. Information about the Study Subjects
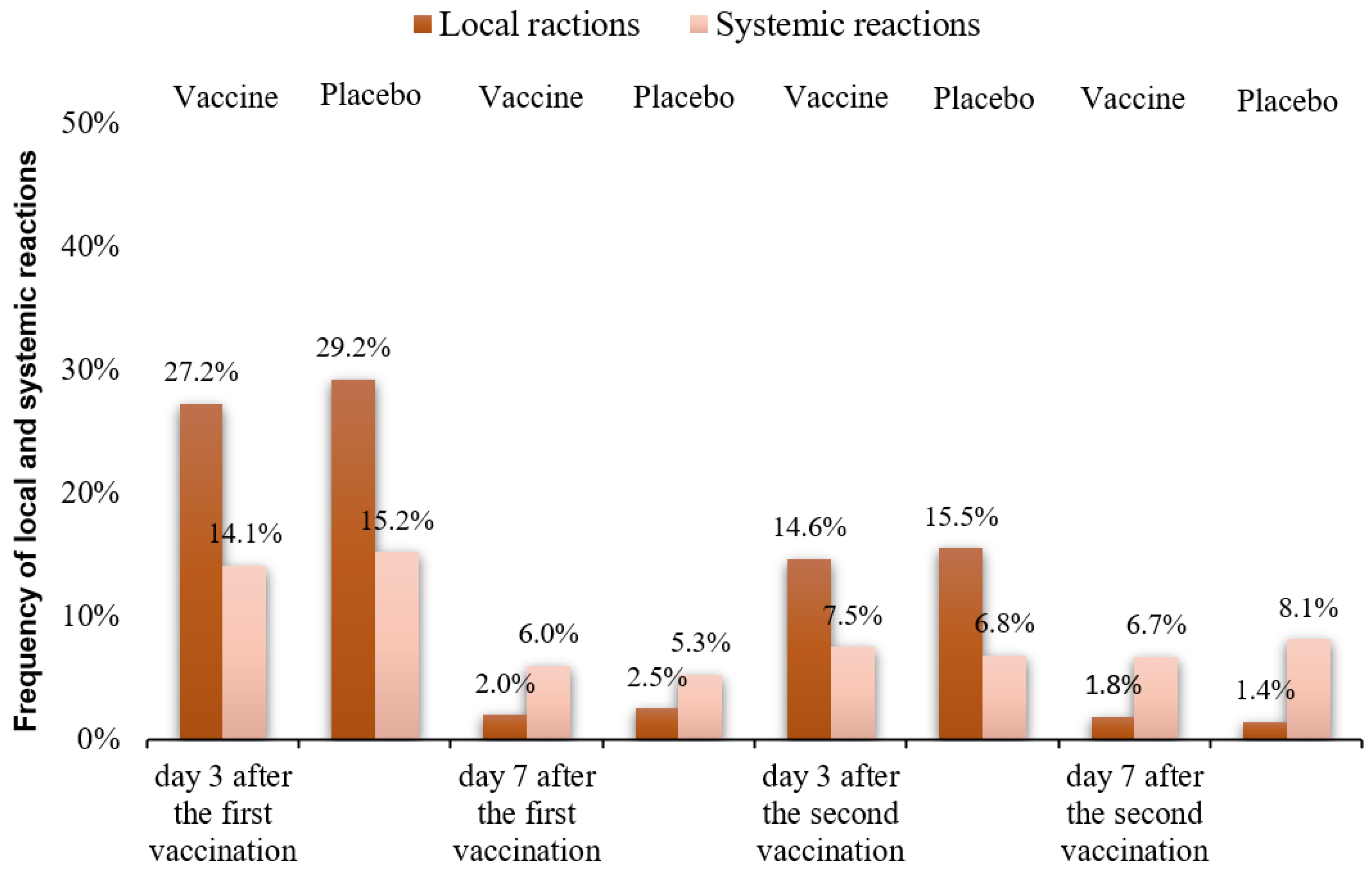
3.2. Safety and Reactogenicity of the EpiVacCorona Vaccine
3.3. Immunologic Effectiveness of the EpiVacCorona Vaccine
3.4. Prophylactic Efficacy of the EpiVacCorona Vaccine
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyrrell, D.A.J.; Bynoe, M.A. Cultivation of novel type of common cold virus in organ culture. Br. Med. J. 1965, 1, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, B.N.; Knipe, D.M. Virology; Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell, D.A.J.; Almeida June, D. Direct electron microscopy of organ cultures for the detection and characterization of viruses. Arch. Ges Vir Forsch 1967, 22, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddell, S.G.; Wege, H.; Meulen, V. The biology of coronaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1983, 64, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risri, H.; Hovi, T. Coronavirus infections of man associated with diseases other than the common cold. J. Med. Virol. 1980, 6, 385–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kiseleva, O.; Marinich, I.; Sominina, A. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viral Infections: Epidemiology, Prevention, Diagnostics, and Treatment; Borges: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sturman, L.; Holmes, K. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 1983, 28, 35–112. [Google Scholar]
- Enserink, M. SARS: Chronology of the epidemic. Science 2013, 339, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Guan, Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Novel Coronavirus, Wuhan, China; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, D.S.I.; Azhar, E.; Madani, T.A.; Ntoumi, F.; Kock, R.; Dar, O.; Ippolito, G.; Mchugh, T.D.; Memish, Z.A.; Drosten, C.; et al. The Continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, H.; Siddell, S.; Meulen, V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1982, 99, 165–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wunderink, R. MERS, SARS and other coronaviruses as causes of pneumonia. Respirology 2018, 23, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callegos, A. WHO Declares Public Health Emergency for novel coronavirus. Medscape Medical News, 30 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzy, A.; McNeil, D.G. W.H.O. Declares Global Emergency as Wuhan Coronavirus Spreads. The New York Times, 16 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus Landscape; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, A.B.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Bogryantseva, M.P.; Gavrilova, E.V.; Danilenko, E.D.; Imatdinov, I.R.; Maksyutov, R.A.; Nechaeva, E.A.; Popova, A.Y.; Pyankov, O.V.; et al. Peptide Immunogens and Vaccine Composition against Coronavirus Infection COVID-19 Using Peptide Immunogens. RU Patent No. 2738081 C1, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, A.B.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Bogryantseva, M.P.; Gavrilova, E.V.; Danilenko, E.D.; Imatdinov, I.R.; Maksyutov, R.A.; Nechaeva, E.A.; Popova, A.Y.; Pyankov, O.V.; et al. Vaccine Composition against COVID-19. RU Patent No. 2743595 C1, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, A.B.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Bogryantseva, M.P.; Gavrilova, E.V.; Danilenko, E.D.; Imatdinov, I.R.; Maksyutov, R.A.; Nechaeva, E.A.; Popova, A.Y.; Pyankov, O.V.; et al. Peptide Immunogens Used as Components of Vaccine Composition against COVID-19. RU Patent No. 2743594 C1, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, A.B.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Bogryantseva, M.P. A single blind, placebo-controlled randomized study of the safety, reactogencity and immunogencity of the “EPIVACCORONA” vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19, in volunteers aged 18–60 years (PHASE I–II). Infect. Immun. 2021, 11, 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Evaluation of COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness. Interim Guidance; WHO/2019-nCoV/vaccine_effectiveness/measurement/2021.1; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Clinical Evaluation of Vaccines: Regulatory Requirements; Ap-pendix 9, TRS No. 1004. Replacement of Appendix 1 of WHO Technical Report Series No. 924. WHO Technical Report Series, No. 1004, 11 January 2017, Meeting Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fleiss, J.L. Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, 2nd ed.; Wiley, John and Sons Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Goncharova, E.; Ryzhikov, E.; Poryvaev, V.; Bulychev, L.; Karpyshev, N.; Maksyutov, A.; Ryzhikov, A. Intranasal immunization with inactivated tick-borne encephalitis virus and the antigenic peptide 89-119 protects mice against intraperitoneal challenge. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksyutov, A.Z.; Bachinskii, A.G.; Bazhan, S.I.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Zaki, A. Exclusion of HIV epitopes shared with human proteins is prerequisite for designing safer AIDS vaccines. J Clin Virol. 2004, 1, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksyutov, A.Z.; Ryzhikov, A.B.; Kolobov, A.A.; Maksyutov, Z.A. Antigenic peptides. Patent, State Scientific Center of Virusology and Biotekhnologii “Vector” Rospotrebnadzora (GNII VB “Vector”). Patent No. WO 2004/031212, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhikov, A.B.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Bogryantseva, M.P.; Danilenko, E.D.; Imatdinov, I.R.; Nechaeva, E.A.; Pyankov, O.V.; Pyankova, O.G.; Susloparov, I.M.; Taranov, O.S.; et al. Immunogenicity and Protectivity of the Peptide Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Russ. Acad. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, E.; Kapur, V.; Musser, J.M. Convalescent plasma anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike protein ectodomain and receptor-binding domain IgG correlate with virus neutralization. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 6728–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Tytun, A.; Ury, H.K. A Simple Approximation for Calculating Sample Size for Comparing Independent Proportions. Biometrics 1980, 36, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittes, J. Sample size calculations for randomized controlled trials. Epidemiology 2002, 24, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Questions and Answers Regarding MMF and Results of Recent Research. Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- MedCalc. MedCalc Software. 2023. Available online: https://www.medcalc.org/calc/odds_ratio.php (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Chen, Y.; Ullah, I.; Prevost, J.; Tolbert, W.D.; Symmes, K.; Ding, S.; Benlarbi, M.; Gong, S.Y.; Tauzin, A.; et al. A Fc-ehanced NTD-binding non-neutralizing antibody delays virus spread and synergizes with a nAb to protect mice from lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell. Rep. 2022, 38, 110368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Strych, U.; Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E. The SARS-CoV-2 vaccine pipeline: An overview. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2020, 7, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahase, E. COVID-19: Novavax vaccine efficacy is 86% against UK variant and 60% against South African variant. BMJ 2021, 372, n296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, P.T.; Galiza, E.P.; Baxter, D.N.; Boffito, M.; Browne, D.; Burns, F.; Chadwick, D.R.; Clark, R.; Cosgrove, C.A.; Galloway, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndwandwe, D.; Wiysonge, C.S. COVID-19 vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 71, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Background Document on the Inactivated Vaccine Sinovac-CoronaVac against COVID-19: Background Document to the WHO Interim Recommendations for Use of the Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine, CoronaVac, Developed by Sinovac, 24 May 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tanriover, M.D.; Doğanay, H.L.; Akova, M.; Guner, H.R.; Azap, A.; Akhan, S.; Köse, Ş.; Erdinç, F.Ş.; Akalın, E.H.; Tabak, Ö.F.; et al. Efficacy and safety of an inactivated whole virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac): Interim results of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in Turkey. Lancet 2021, 398, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, C. What do we know about China’s COVID-19 vaccines? BMJ 2021, 373, n912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group C-VTW. Technical vaccination recommendations for COVID-19 vaccines in China. China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, D.K. Safety Monitoring of the Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) COVID-19 vaccine—United States, March–April 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emergency use Authorization (EUA) of the Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine to Prevent Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/146304/download (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine Overview and Safety. 1 June 2021. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/106729 (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Dutta, A.K. Vaccine against COVID-19 disease–present status of development. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J. COVID-19: New data on Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine backs 12 week dosing interval. Br. Med. J. 2021, 372, n326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallapaty, S. India’s DNA COVID vaccine is a world first–more are coming. Nature 2021, 597, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samal, K.C.; Sahoo, J.P.; Yadav, N.S.; Pradhan, P. ZyCoV-D: World’s first needle-free DNA vaccine’s emergency approval in India. Biot. Res. Today 2021, 3, 714–716. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, B.F. A new vaccine to battle COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 470–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Gaspar, P.D.; de Souza, H.J. Refrigeration of COVID-19 vaccines: Ideal storage characteristics, energy efficiency and environmental impacts of various vaccine options. Energies 2021, 14, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, E.H.; Malani, P.N.; Creech, C.B. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine for COVID-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 1575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malayala, S.V.; Mohan, G.; Vasireddy, D.; Atluri, P. Purpuric rash and thrombocytopenia after the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) COVID-19 vaccine. Cureus 2021, 13, e14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, S.E.; Gargano, J.W.; Marin, M.; Wallace, M.; Curran, K.G.; Chamberland, M.; McClung, N.; Campos-Outcalt, D.; Morgan, R.L.; Mbaeyi, S.; et al. The advisory committee on immuniza-tion practices’ interim recommendation for use of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine—United States, December 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiani, A.; Patel, J.; Ziolkowski, K.; Nielsen, F. Pfizer: The miracle vaccine for COVID-19? Public Health Pract. 2020, 1, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriss, J.L.; Reynolds, L.E.; Wang, A.; Stokley, S.; Cole, M.M.; Harris, L.Q.; Shaw, L.K.; Black, C.L.; Singleton, J.A.; Fitter, D.L.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine second-dose completion and interval between first and second doses among vaccinated per-sons—United States, December 14, 2020−February 14, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolgin, E. CureVac COVID vaccine let-down spotlights mRNA design challenges. Nature 2021, 594, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crommelin, D.J.; Anchordoquy, T.J.; Volkin, D.B.; Jiskoot, W.; Mastrobattista, E. Addressing the cold reality of mRNA vaccine stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Steain, M.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P.; Khoury, D.S. Relating in vitro neutralisation level and protection in the CVnCoV (CUREVAC) trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 878–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsahin, D.U.; Gelisen, M.I.; Taiwo, M.; Agachan, Y.; Rahi, D.; Uzun, B. Decision Analysis of the COVID-19 Vaccines. Eurobiotech. J. 2021, 5, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Visits | V2 Day 3 after the First Vaccine Dose | V3 Day 7 after the First Vaccine Dose | V6 Day 3 after the Second Vaccine Dose | V7 Day 7 after the Second Vaccine Dose | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body’s Responses | Vaccine n = 2235 | Placebo n = 740 | Vaccine n = 2232 | Placebo n = 739 | Vaccine n = 2183 | Placebo n = 688 | Vaccine n = 2178 | Placebo n = 684 |
| Soreness at the injection site | 500 (22.4%) | 183 (24.7%) | 31 (1.4%) | 10 (1.4%) | 271 (12.4%) | 89 (12.9%) | 31 (1.4%) | 9 (1.3%) |
| Hyperemia | 58 (2.6%) | 16 (2.2%) | 8 (0.4%) | 3 (0.4%) | 22 (1.0%) | 9 (1.3%) | 5 (0.2%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Swelling | 50 (2.2%) | 17 (2.3%) | 5 (0.2%) | 5 (0.7%) | 26 (1.2%) | 9 (1.3%) | 4 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) |
| Elevated body temperature | 57 (2.6%) | 21 (2.8%) | 32 (1.4%) | 11 (1.5%) | 33 (1.5%) | 15 (2.2%) | 30 (1.4%) | 10 (1.5%) |
| Headache | 122 (5.5%) | 46 (6.2%) | 57 (2.6%) | 15 (2.0%) | 60 (2.7%) | 12 (1.7%) | 37 (1.7%) | 11 (1.6%) |
| Fatigue | 133 (6.0%) | 46 (6.2%) | 44 (2.0%) | 13 (1.8%) | 71 (3.3%) | 20 (2.9%) | 79 (3.6%) | 34 (5.0%) |
| Groups | EpiVacCorona Vaccine | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| The number of volunteers included in assessment of the prophylactic effectiveness of the vaccine | 2148 | 649 |
| The number of volunteers not having COVID-19 on days 42 through 180 | 2090 b | 560 d |
| The number of volunteers having COVID-19 on days 42 through 180 | 58 a | 89 c |
| Calculated prophylactic effectiveness | ||
| OR | 0.175 | |
| Symptomatic diseases preventive efficacy, % | 82.5 | |
| CI 95+, % | 87.5 | |
| CI 95−, % | 75.3 | |
| Z-score | 9.954 | |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryzhikov, A.B.; Ryzhikov, E.A.; Bogryantseva, M.P.; Usova, S.V.; Nechaeva, E.A.; Danilenko, E.D.; Pyankov, S.A.; Gudymo, A.S.; Moiseeva, A.A.; Onkhonova, G.S.; et al. Assessment of Safety and Prophylactic Efficacy of the EpiVacCorona Peptide Vaccine for COVID-19 Prevention (Phase III). Vaccines 2023, 11, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050998
Ryzhikov AB, Ryzhikov EA, Bogryantseva MP, Usova SV, Nechaeva EA, Danilenko ED, Pyankov SA, Gudymo AS, Moiseeva AA, Onkhonova GS, et al. Assessment of Safety and Prophylactic Efficacy of the EpiVacCorona Peptide Vaccine for COVID-19 Prevention (Phase III). Vaccines. 2023; 11(5):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050998
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyzhikov, Alexander B., Evgeny A. Ryzhikov, Marina P. Bogryantseva, Svetlana V. Usova, Elena A. Nechaeva, Elena D. Danilenko, Stepan A. Pyankov, Andrey S. Gudymo, Anastasiya A. Moiseeva, Galina S. Onkhonova, and et al. 2023. "Assessment of Safety and Prophylactic Efficacy of the EpiVacCorona Peptide Vaccine for COVID-19 Prevention (Phase III)" Vaccines 11, no. 5: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050998
APA StyleRyzhikov, A. B., Ryzhikov, E. A., Bogryantseva, M. P., Usova, S. V., Nechaeva, E. A., Danilenko, E. D., Pyankov, S. A., Gudymo, A. S., Moiseeva, A. A., Onkhonova, G. S., Pyankov, O. V., Sleptsova, E. S., Lomakin, N. V., Vasilyeva, V. S., Tulikov, M. V., Gusarov, V. G., Pulin, A. A., Balalaeva, M. A., Erofeeva, S. B., ... Maksyutov, R. A. (2023). Assessment of Safety and Prophylactic Efficacy of the EpiVacCorona Peptide Vaccine for COVID-19 Prevention (Phase III). Vaccines, 11(5), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11050998





