Feeding Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma to Pigs Reduces African Swine Fever Virus Load in Infected Pigs and Delays Virus Transmission—Study 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
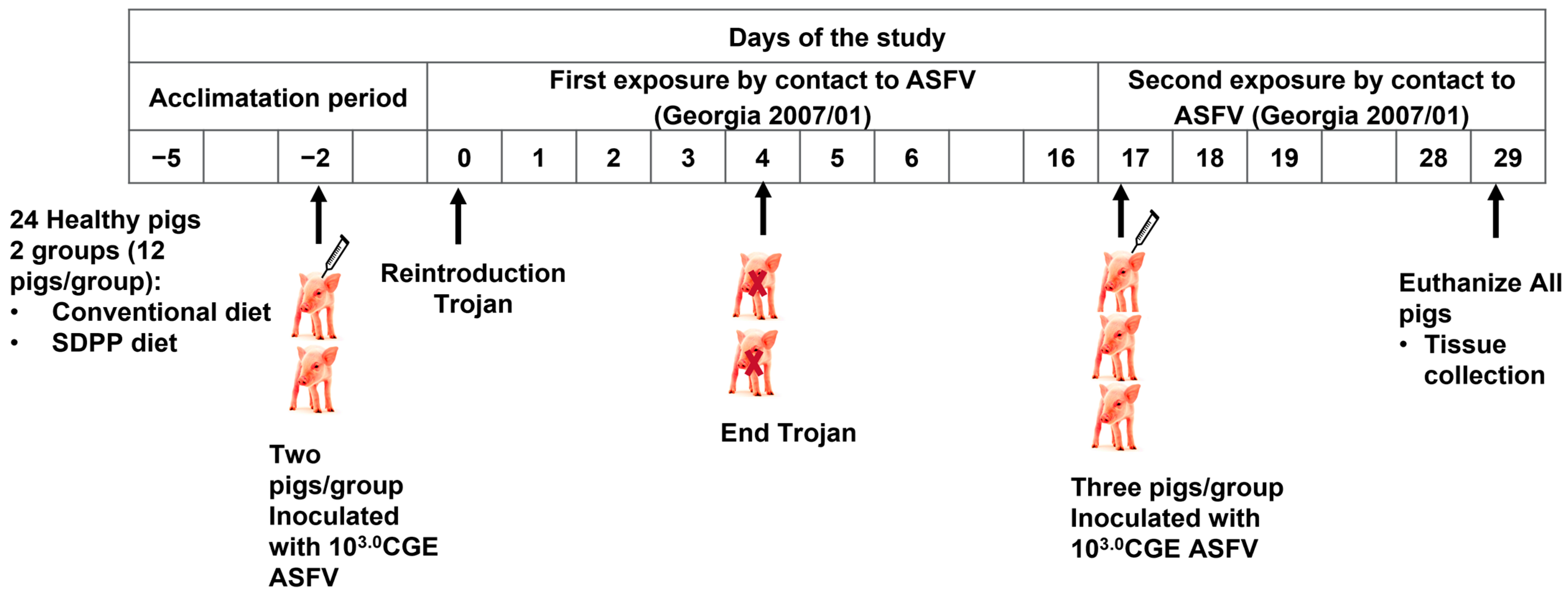
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
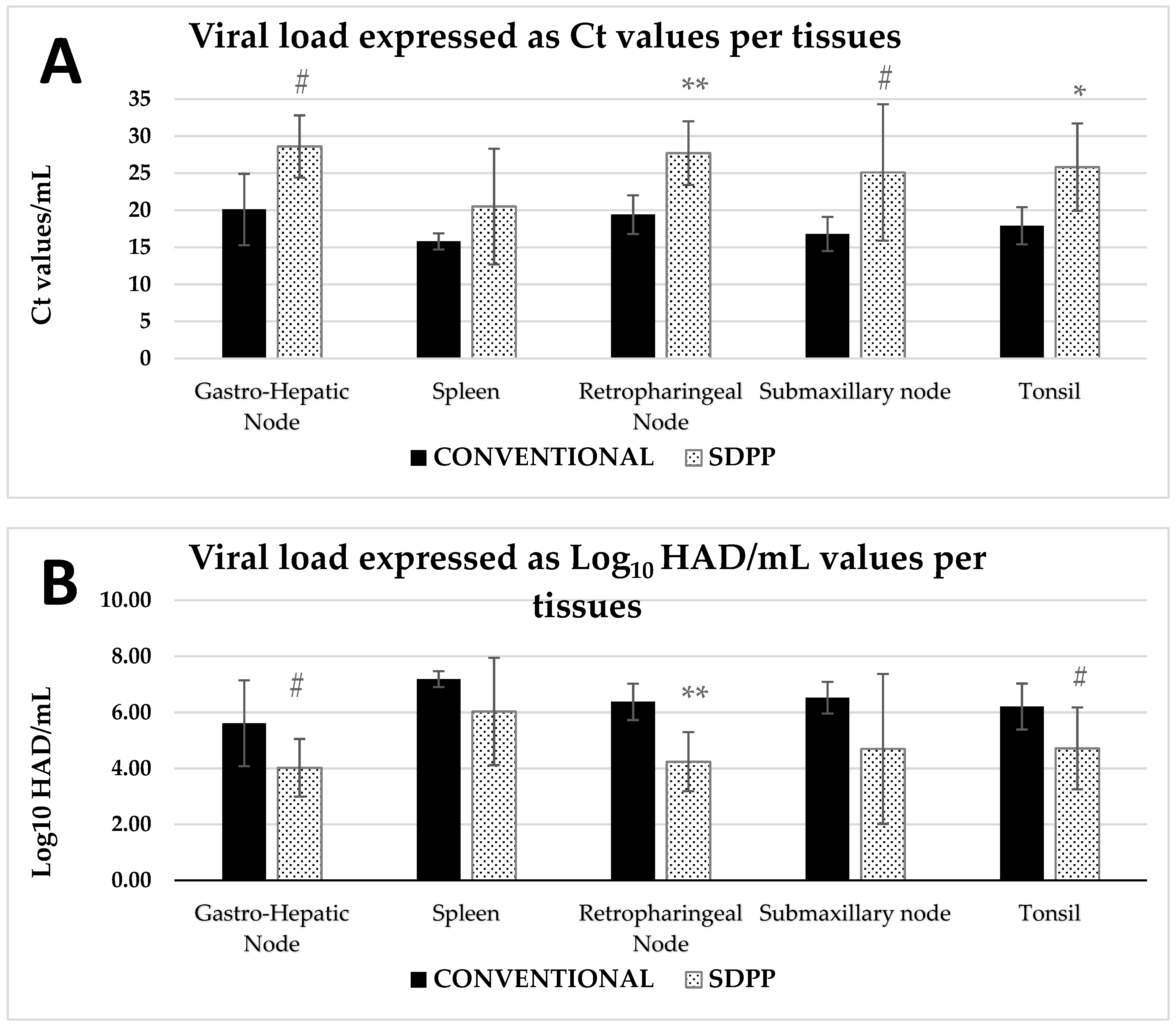
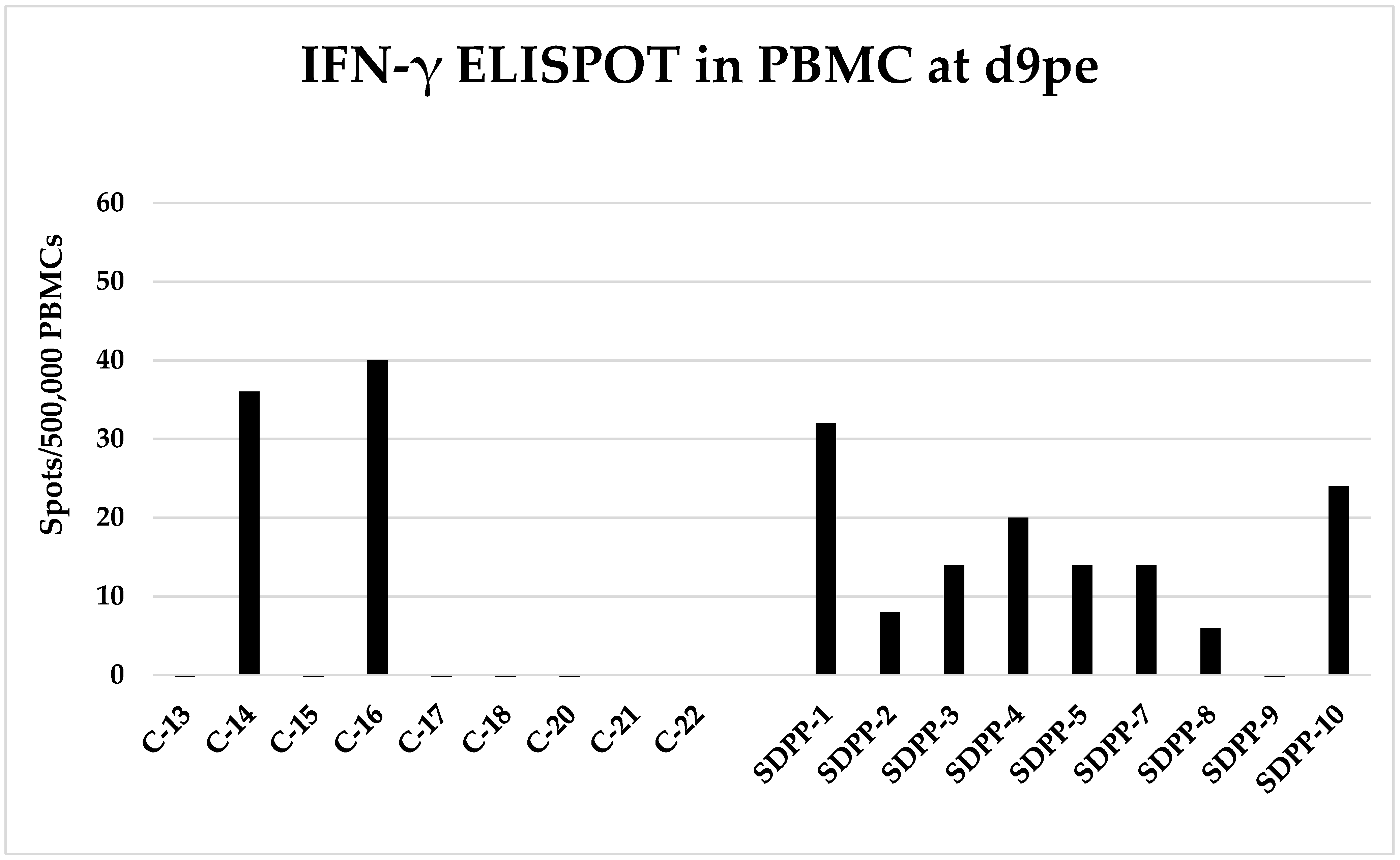
3. Results
3.1. First Exposure
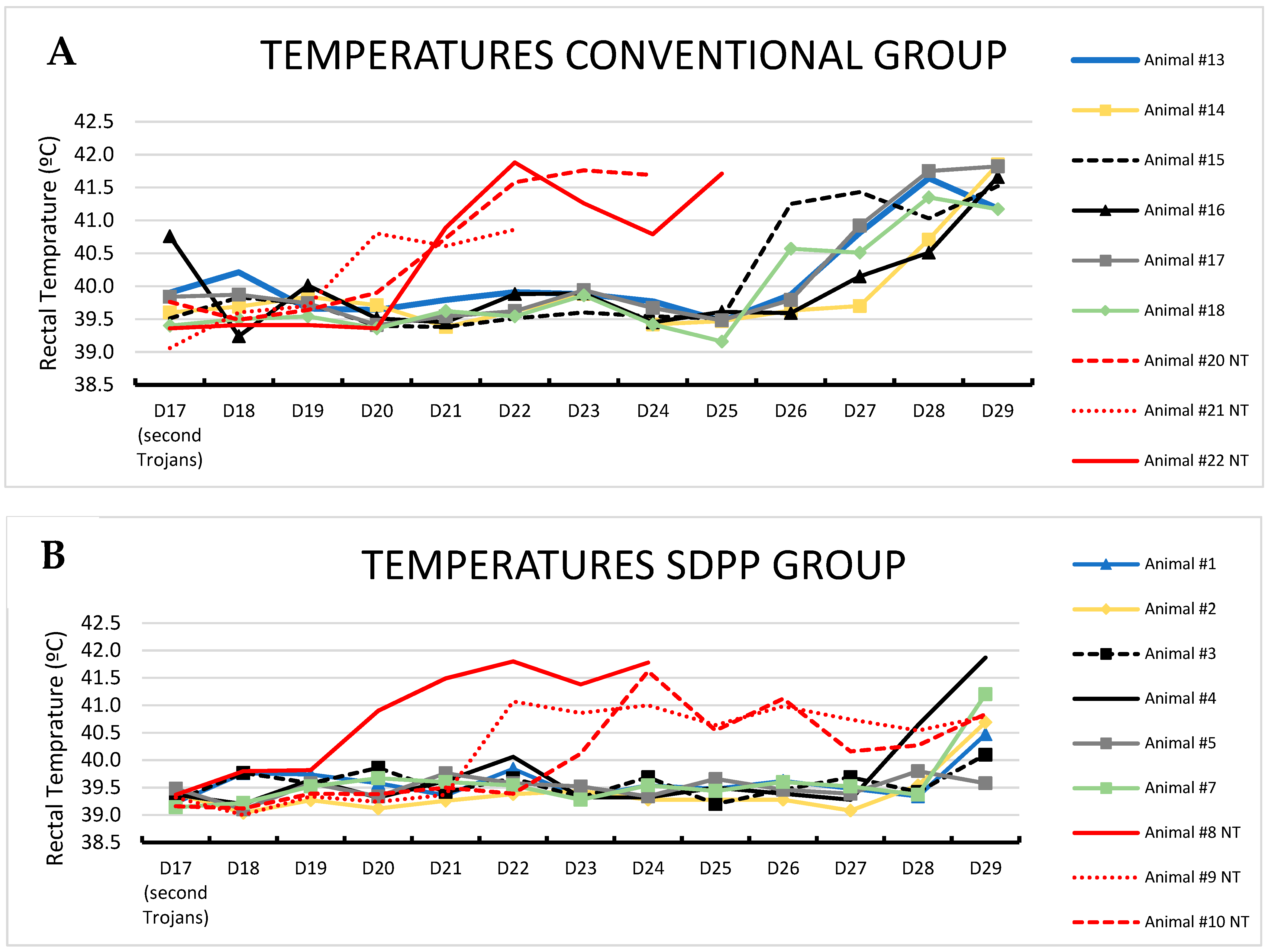
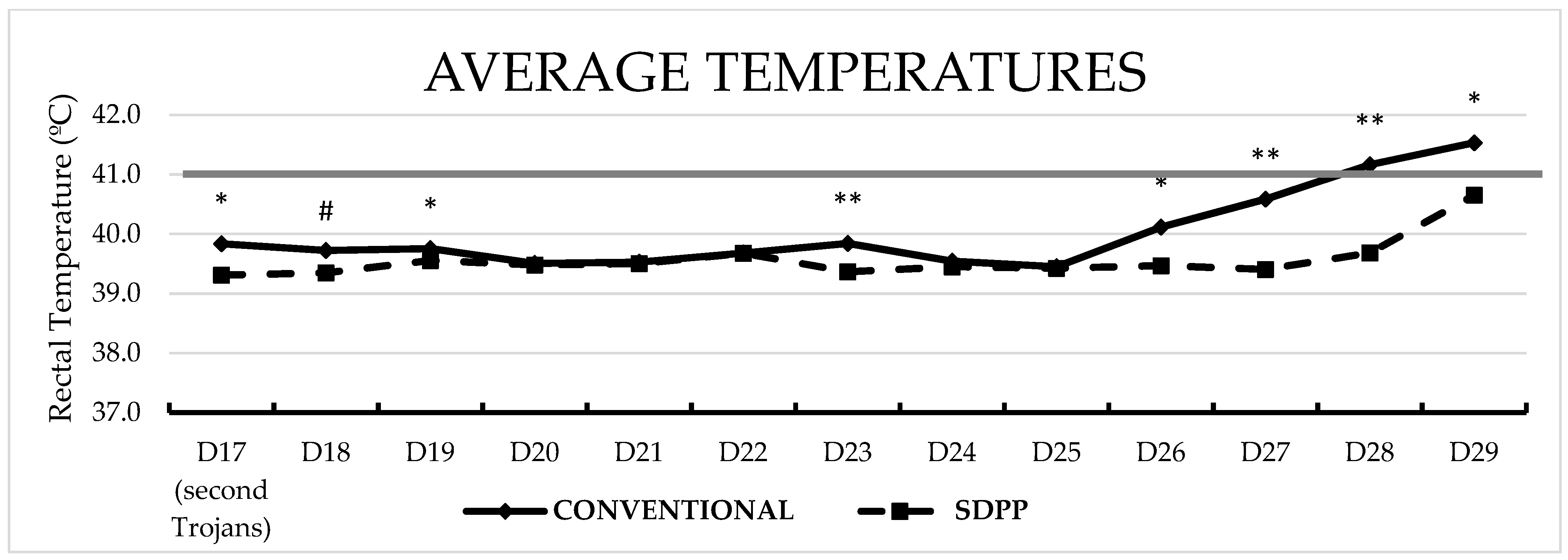
3.2. Second Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Śmietanka, K.; Woźniakowski, G.; Kozak, E.; Niemczuk, K.; Frączyk, M.; Bocian, Ł.; Kowalczyk, A.; Pejsak, Z. African Swine Fever Epidemic, Poland, 2014–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). African Swine Fever Situation Report. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2022/10/asf-report22.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Pietschmann, J.; Guinat, C.; Beer, M.; Pronin, V.; Tauscher, K.; Petrov, A.; Keil, G.; Blome, S. Course and transmission characteristics of oral low-dose infection of domestic pigs and European wild boar with a Caucasian African swine fever virus isolate. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulovic, E.; Mehinagic, K.; Wüthrich, T.; Hilty, M.; Posthaus, H.; Summerfield, A.; Ruggli, N.; Benarafa, C. The baseline immunological and hygienic status of pigs impact disease severity of African swine fever. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Chang, X.; Stoll, B.; Fan, M.Z.; Burrin, D.G.; Arthington, J.; Weaver, E.; Campbell, J. Dietary Plasma Protein Reduces Small Intestinal Growth and Lamina Propria Cell Density in Early Weaned Pigs. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, A.; Everts, H.; Nabuurs, M.; Margry, R.J.C.F.; Beynen, A.C. Growth performance of weanling pigs fed spray-dried animal plasma: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2001, 68, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, P.; Han, I.K.; Jung, H.J.; Heo, K.N.; Perini, S.; Castellazzi, A.M.; Casini, L.; Creston, D.; Gremokolini, C. Effect of Different Spray Dried Plasmas on Growth, Ileal Digestibility, Nutrient Deposition, Immunity and Health of Early-Weaned Pigs Challenged with E. coli K88. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.A.; Touchette, K.J.; Matteri, R.L.; Dyer, C.J.; Allee, G.L. Effect of spray-dried plasma and lipopolysaccharide exposure on weaned pigs: II. Effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchette, K.J.; Carroll, J.A.; Allee, G.L.; Matteri, R.L.; Dyer, C.J.; Beausang, L.A.; Zannelli, M.E. Effect of spray-dried plasma and lipopolysaccharide exposure on weaned pigs: I. Effects on the immune axis of weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrallardona, D.; Conde, R.; Esteve-García, E.; Brufau, J. Use of spray dried animal plasma as an alternative to antimicrobial medication in weanling pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2002, 99, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Chirlaque, C.; Aranda, C.; Ocón, B.; Polo, J.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; de Medina, F.S. Immunoregulatory Effects of Porcine Plasma Protein Concentrates on Rat Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Splenocytes. Animals 2021, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrallardona, D. Spray Dried Animal Plasma as an Alternative to Antibiotics in Weanling Pigs—A Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bosque, A.; Polo, J.; Torrallardona, D. Spray dried plasma as an alternative to antibiotics in piglet feeds, mode of action and biosafety. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.; Anderson, C.L.; Bundy, J.W.; Fernando, S.C.; Miller, P.S.; Burkey, T.E. Effects of spray-dried porcine plasma on fecal microbiota in nursery pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretó, M.; Miró, L.; Amat, C.; Polo, J.; Manichanh, C.; Pérez-Bosque, A. Dietary supplementation with spray-dried porcine plasma has prebiotic effects on gut microbiota in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Balebona, M.D.C.; Firmino, J.P.; Rodríguez, C.; Polo, J.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Gisbert, E. The effect of spray-dried porcine plasma on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) intestinal microbiota. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretó, M.; Pérez-Bosque, A. Dietary plasma proteins, the intestinal immune system, and the barrier functions of the intestinal mucosa1. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, E92–E100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofrarías, M.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Pujols, J.; Gibert, X.; Majo, N.; Segalés, J.; Gasa, J. Effects of spray-dried porcine plasma and plant extracts on intestinal morphology and on leukocyte cell subsets of weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maijó, M.; Miró, L.; Polo, J.; Campbell, J.; Russell, L.; Crenshaw, J.; Weaver, E.; Moretó, M.; Pérez-Bosque, A. Dietary Plasma Proteins Modulate the Adaptive Immune Response in Mice with Acute Lung Inflammation. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maijó, M.; Miró, L.; Polo, J.; Campbell, J.; Russell, L.; Crenshaw, J.; Weaver, E.; Moretó, M.; Pérez-Bosque, A. Dietary plasma proteins attenuate the innate immunity response in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, C.E.; Johnston, W.T.; Gould, L.; Whiting, T.L. Postweaning mortality in Manitoba swine. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 70, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Bosque, A.; Amat, C.; Polo, J.; Campbell, J.M.; Crenshaw, J.; Russell, L.; Moretó, M. Spray-Dried Animal Plasma Prevents the Effects of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxin B on Intestinal Barrier Function in Weaned Rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peace, R.M.; Campbell, J.; Polo, J.; Crenshaw, J.; Russell, L.; Moeser, A. Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma Influences Intestinal Barrier Function, Inflammation, and Diarrhea in Weaned Pigs. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Navas, M.J.; Costa-Hurtado, M.; Almagro, V.; Bosch-Camós, L.; López, E.; Cuadrado, R.; Accensi, F.; Pina-Pedrero, S.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation from warthog to pig confirms the influence of the gut microbiota on African swine fever susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onisk, D.V.; Borca, M.V.; Kutish, S.; Kramer, E.; Irusta, P.; Rock, D.L. Passively Transferred African Swine Fever Virus Antibodies Protect Swine against Lethal Infection. Virology 1994, 198, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, C.A.L.; Denyer, M.S.; Takamatsu, H.; Parkhouse, R.M.E. In vivo depletion of CD8+ T lymphocytes abrogates protective immunity to African swine fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, H.-H.; Denyer, M.S.; Lacasta, A.; Stirling, C.M.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Netherton, C.L.; Oura, C.A.L.; Martins, C.; Rodríguez, F. Cellular immunity in ASFV responses. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch-Camós, L.; López, E.; Rodriguez, F. African swine fever vaccines: A promising work still in progress. Porc. Health Manag. 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska-Daniel, I.; Szczotka, A.; Bednarek, D.; Pejsak, Z. Preliminary study of the influence of plasma proteins on immunological and production parameters in pigs. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2003, 6, 275–277. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, I.; Lorca, C.; Galindo, I.; Campbell, J.; Barranco, L.; Kuzemtseva, L.; Rodríguez-Gómez, I.-M.; Crenshaw, J.; Russell, L.; Polo, J.; et al. Potential positive effect of commercial spray-dried porcine plasma on pigs challenged with PRRS virus. In Proceedings of the 21st International Pig Veterinary Society (IPVA), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–21 July 2010; p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo-Cardiel, I.; Ballester, M.; Solanes, D.; Nofrarías, M.; López-Soria, S.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Lacasta, A.; Accensi, F.; Rodríguez, F.; Segalés, J. Standardization of pathological investigations in the framework of experimental ASFV infections. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Camós, L.; Alonso, U.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Chang, C.-Y.; Martín-Mur, B.; Accensi, F.; Muñoz, M.; Navas, M.J.; Dabad, M.; Vidal, E.; et al. Cross-protection against African swine fever virus upon intranasal vaccination is associated with an adaptive-innate immune crosstalk. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goatley, L.C.; Reis, A.L.; Portugal, R.; Goldswain, H.; Shimmon, G.L.; Hargreaves, Z.; Ho, C.-S.; Montoya, M.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Taylor, G.; et al. A Pool of Eight Virally Vectored African Swine Fever Antigens Protect Pigs against Fatal Disease. Vaccines 2020, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.A.; Darby, A.; Da Silva, M.; Upton, C.; Radford, A.; Dixon, L.K. Genomic Analysis of Highly Virulent Georgia 2007/1 Isolate of African Swine Fever Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pinero, J.; Gallardo, C.; Elizalde, M.; Robles, A.; Gómez, C.; Bishop, R.; Heath, L.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Fasina, F.O.; Pelayo, V.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of African Swine Fever by a New Real-Time PCR Using Universal Probe Library. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, I.; Darwich, L.; Pappaterra, G.; Pujols, J.; Mateu, E. Immune responses of pigs after experimental infection with a European strain of Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, K.; Conraths, F.J.; Blome, S.; Staubach, C.; Sauter-Louis, C. African Swine Fever: Fast and Furious or Slow and Steady? Viruses 2019, 11, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, E.; Pujols, J.; Segalés, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Crenshaw, J.; Rodríguez, C.; Ródenas, J.; Polo, J. Commercial feed containing porcine plasma spiked with African swine fever virus is not infective in pigs when administered for 14 consecutive days. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederwerder, M.C.; Stoian, A.M.M.; Rowland, R.R.R.; Dritz, S.S.; Petrovan, V.; Constance, L.A.; Gebhardt, J.T.; Olcha, M.; Jones, C.K.; Woodworth, J.C.; et al. Infectious Dose of African Swine Fever Virus When Consumed Naturally in Liquid or Feed. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, M.; Tran, H.T.T.; Lannoo, K.; Bruggeman, G.; Dang, H.V. Medium chain fatty acids show potential to mitigate ASFv in feed. In Proceedings of the 26th International Pig Veterinary Society Congress (IPVS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 21–24 June 2022; p. 704. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.; Truong, D.; Ly, V.; Hoang, T.; Chu, N.; Nguyen, H.; Dang, A.; Vos, M.; Lannoo, K.; Bruggeman, G.; et al. The potential anti- African swine fever virus effects of medium chain fatty acids on in vitro feed model: An evaluation study using a field ASFV strain isolated in Vietnam. Open Vet. J. 2021, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujols, J.; Lorca-Oró, C.; Díaz, I.; Russell, L.E.; Campbell, J.M.; Crenshaw, J.D.; Polo, J.; Mateu, E.; Segalés, J. Commercial spray-dried porcine plasma does not transmit porcine circovirus type 2 in weaned pigs challenged with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. J. 2011, 190, e16–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretó, M.; Pérez-Bosque, A.; Pelegrí, C.; Vicario, M.; Castell, M.; Amat, C.; Russell, L.; Campbell, J.M.; Quigley, J.D.; Polo, J. Dietary Plasma Protein Affects the Immune Response of Weaned Rats Challenged with S. aureus Superantigen B. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2667–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bosque, A.; Miró, L.; Amat, C.; Polo, J.; Moretó, M. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Spray-Dried Plasma Is Mediated by a Reduction in Mucosal Lymphocyte Activation and Infiltration in a Mouse Model of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2016, 8, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S.; Feng, B.; et al. Microbial insight into dietary protein source affects intestinal function of pigs with intrauterine growth retardation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasta, A.; Ballester, M.; Monteagudo, P.L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Salas, M.L.; Accensi, F.; Pina-Pedrero, S.; Bensaid, A.; Argilaguet, J.; López-Soria, S.; et al. Expression Library Immunization Can Confer Protection against Lethal Challenge with African Swine Fever Virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13322–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, E.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huo, H.; Wang, W.; Huangfu, H.; et al. Genotype I African swine fever viruses emerged in domestic pigs in China and caused chronic infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Bosch, J.; Martínez-Avilés, M.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. The Evolution of African Swine Fever in China: A Global Threat? Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 828498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujols, J.; Blázquez, E.; Segalés, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Chang, C.-Y.; Argilaguet, J.; Bosch-Camós, L.; Rosell, R.; Pailler-García, L.; Gavrilov, B.; et al. Feeding Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma to Pigs Improves the Protection Afforded by the African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) BA71ΔCD2 Vaccine Prototype against Experimental Challenge with the Pandemic ASFV—Study 2. Vaccines 2023, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | Conventional Diet | SDPP Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Barley | 298.7 | 313.3 |
| Maize | 295.7 | 303.4 |
| Sweet milk whey | 137.2 | 137.2 |
| Soy protein concentrate | 100.9 | - |
| Spray-dried porcine plasma (SDPP) | - | 80.0 |
| Soybean meal (48% CP) | 107.4 | 110.6 |
| Animal fat | 26.7 | 30.0 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 14.4 | 16.1 |
| Calcium carbonate | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Salt | 4.7 | 0.2 |
| L-Lysine-HCl | 4.2 | 2.3 |
| L-Threonine | 1.9 | 0.5 |
| DL-Methionine | 2.1 | 1.4 |
| L-Tryptophan | 0.7 | 0.2 |
| L-Valine | 0.3 | - |
| Noxyfeed * | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Vitamin-Mineral complex ** | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Nutritive composition | ||
| Crude Protein | 195.0 | 195.0 |
| Crude Fiber | 28.0 | 25.2 |
| Fat | 45.5 | 50.3 |
| Ash | 58.2 | 56.6 |
| Energy (kcal ME/kg) | 3340 | 3340 |
| Total sodium | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| Total chlorine | 6.7 | 4.5 |
| Total calcium | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Total phosphorous | 6.7 | 7.4 |
| Digestible phosphorous | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Lysine (SID) | 12.50 | 12.50 |
| Threonine (SID) | 8.13 | 8.13 |
| Methionine (SID) | 4.62 | 3.75 |
| Met + Cys (SID) | 7.38 | 7.78 |
| Tryptophan (SID) | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Isoleucine (SID) | 7.36 | 6.75 |
| Valine (SID) | 8.50 | 9.26 |
| Leucine (SID) | 13.52 | 14.89 |
| Phenylalanine (SID) | 8.02 | 8.52 |
| Phe + Tyr (SID) | 13.41 | 14.60 |
| Histidine (SID) | 4.25 | 4.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blázquez, E.; Pujols, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Segalés, J.; Rosell, R.; Campbell, J.; Polo, J. Feeding Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma to Pigs Reduces African Swine Fever Virus Load in Infected Pigs and Delays Virus Transmission—Study 1. Vaccines 2023, 11, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040824
Blázquez E, Pujols J, Rodríguez F, Segalés J, Rosell R, Campbell J, Polo J. Feeding Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma to Pigs Reduces African Swine Fever Virus Load in Infected Pigs and Delays Virus Transmission—Study 1. Vaccines. 2023; 11(4):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040824
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlázquez, Elena, Joan Pujols, Fernando Rodríguez, Joaquim Segalés, Rosa Rosell, Joy Campbell, and Javier Polo. 2023. "Feeding Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma to Pigs Reduces African Swine Fever Virus Load in Infected Pigs and Delays Virus Transmission—Study 1" Vaccines 11, no. 4: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040824
APA StyleBlázquez, E., Pujols, J., Rodríguez, F., Segalés, J., Rosell, R., Campbell, J., & Polo, J. (2023). Feeding Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma to Pigs Reduces African Swine Fever Virus Load in Infected Pigs and Delays Virus Transmission—Study 1. Vaccines, 11(4), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040824







