Toll-Like Receptors and the Response to Radiotherapy in Solid Tumors: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Activation and Inhibition of TLRs in Cancer
2.1. TLR1 and TLR2—Pro and Anti-Tumoral Roles
2.2. TLR3—Mostly Anti-Tumoral Effects Mediated by Dendritic Cells and CD8 T Cells
2.3. TLR4—Pro-Tumoral—Cancer Cell Intrinsic Activation
2.4. TLR5—Anti-Tumoral—Action Primarily Mediated by Neutrophils
2.5. TLR7 and TLR8—Primarily Anti-Tumoral
2.6. TLR9—Pro-Tumoral and Anti-Tumoral—Action Mediated through APCs
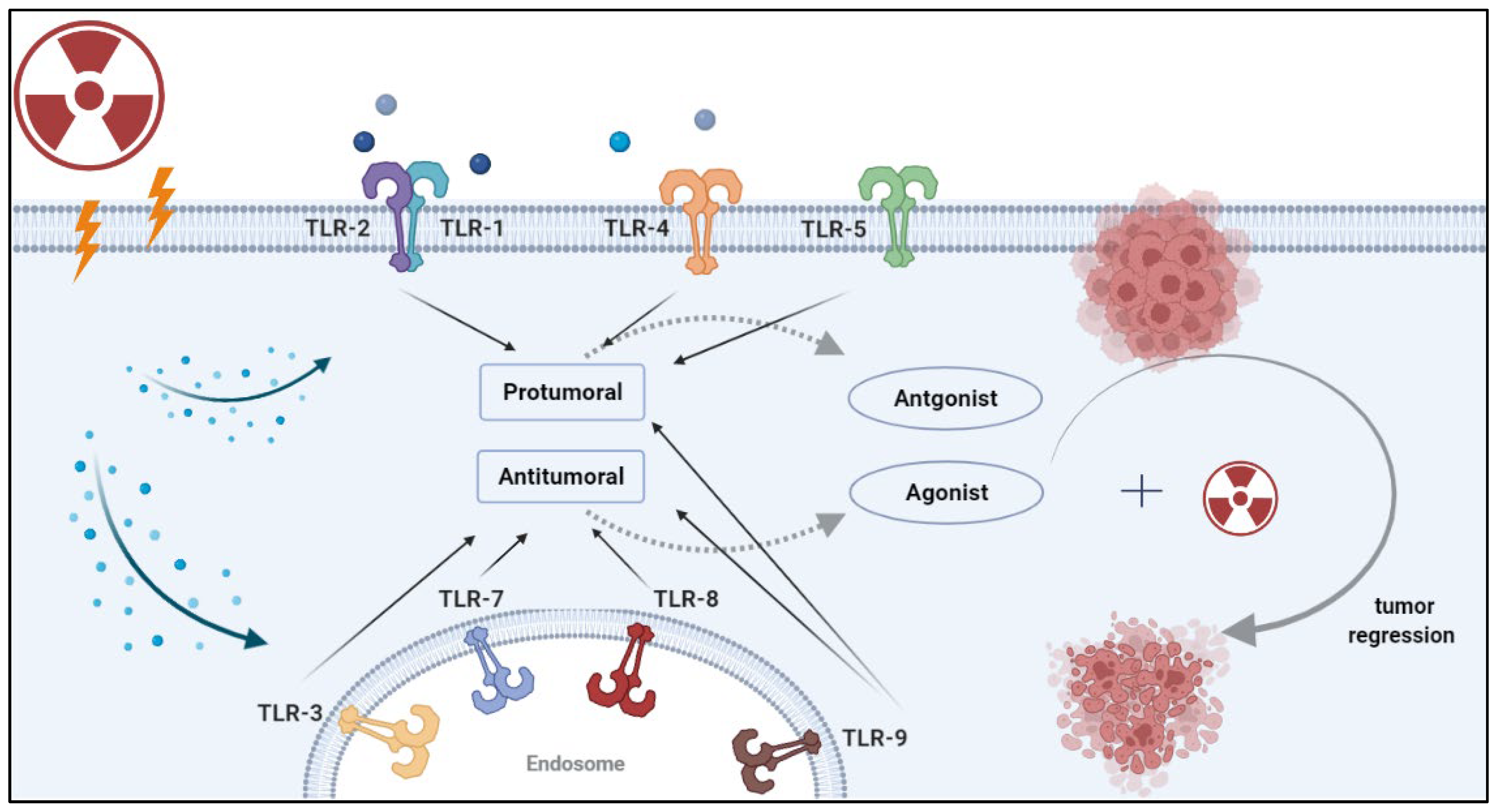
3. The Effects of Radiation on TLRs
4. Combining Radiotherapy and TLR-Based Therapy
4.1. Radiotherapy and TLR Agonist-Based Therapies: TLR3, TLR7/8 and TLR9
4.2. Radiotherapy and Antagonist-Based Therapies: TLR1, TLR2, TLR4
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wallet, S.; Puri, V.; Gibson, F. Linkage of Infection to Adverse Systemic Complications: Periodontal Disease, Toll-Like Receptors, and Other Pattern Recognition Systems. Vaccines 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.J.; Symmons, M.F.; Gangloff, M.; Bryant, C.E. Assembly and Localization of Toll-like Receptor Signalling Complexes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.L. Important Aspects of Toll-like Receptors, Ligands and Their Signaling Pathways. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Cang, H.; Guo, B. Crosstalk between Cancer and Immune Cells: Role of Tumor-associated Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4709–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, C.; Giovannetti, E.; Martinez, P.; McCue, S.; Naing, A. Applications and Clinical Trial Landscape Using Toll-like Receptor Agonists to Reduce the Toll of Cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Batool, M.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S. Toll-Like Receptors as a Therapeutic Target in the Era of Immunotherapies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 756315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavanneshan, S.; Sayadmanesh, A.; Ebrahimiyan, H.; Basiri, M. Toll-Like Receptor-Based Strategies for Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9912188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Han, C.; Liu, J. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Oncotherapy. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Naour, J.; Kroemer, G. Trial Watch: Toll-like Receptor Ligands in Cancer Therapy. Oncoimmunology 2023, 12, 2180237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-Like Receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 335–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like Receptors and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukata, M.; Chen, A.; Vamadevan, A.S.; Cohen, J.; Breglio, K.; Krishnareddy, S.; Hsu, D.; Xu, R.; Harpaz, N.; Dannenberg, A.J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor-4 Promotes the Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Tumors. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, K. Expression Profiles of Toll-like Receptors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Xu, D.; Brint, E.K.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Negative Regulation of Toll-like Receptor-Mediated Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefetz, I.; Alvero, A.; Holmberg, J.; Lebowitz, N.; Craveiro, V.; Yang-Hartwich, Y.; Yin, G.; Squillace, L.; Gurrea Soteras, M.; Aldo, P.; et al. TLR2 Enhances Ovarian Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Promotes Tumor Repair and Recurrence. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Li, Y.; Zang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ning, H.; Li, J. Effect of TLR2 on the Proliferation of Inflammation-Related Colorectal Cancer and Sporadic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, H.; Kennedy, C.L.; Najdovska, M.; McLeod, L.; McCormack, W.; Hughes, N.; Dev, A.; Sievert, W.; Ooi, C.H.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. STAT3-Driven Upregulation of TLR2 Promotes Gastric Tumorigenesis Independent of Tumor Inflammation. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Qian, G.; Ge, S.; Zhang, J. The Regulation of Toll-like Receptor 2 by MiR-143 Suppresses the Invasion and Migration of a Subset of Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, J.; Qian, J.; Liu, R.; Huang, E.; Wang, Y.; Luo, F.; Chu, Y. TLR1/TLR2 Signaling Blocks the Suppression of Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell by Promoting Its Differentiation into M1-Type Macrophage. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, F.; Cai, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, L.; Xu, D.; Chu, Y. TLR1/TLR2 Agonist Induces Tumor Regression by Reciprocal Modulation of Effector and Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belani, C.P.; Chakraborty, B.C.; Modi, R.I.; Khamar, B.M. A Randomized Trial of TLR-2 Agonist CADI-05 Targeting Desmocollin-3 for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Yang, H. Roles of Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Human Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 667454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeljic, K.; Supic, G.; Jovic, N.; Kozomara, R.; Brankovic-Magic, M.; Obrenovic, M.; Magic, Z. Association of TLR2, TLR3, TLR4 and CD14 Genes Polymorphisms with Oral Cancer Risk and Survival. Oral Dis. 2014, 20, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.-M.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X.-Y.; Qin, J.; Shen, Y. TLR3 Expression Correlates with Apoptosis, Proliferation and Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Predicts Prognosis. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zheng, Z. Toll-like Receptor 3 Genetic Variants and Susceptibility to Hepatocellular Carcinoma and HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.A.; Försti, A.; Buch, S.; Kalthoff, H.; Krauss, C.; Bauer, M.; Egberts, J.; Schniewind, B.; Broering, D.C.; Schreiber, S.; et al. TLR-3 Polymorphism Is an Independent Prognostic Marker for Stage II Colorectal Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.L.; Herrick, J.S.; Bondurant, K.L.; Wolff, R.K. Toll-like Receptor Genes and Their Association with Colon and Rectal Cancer Development and Prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2974–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.-M.; Huang, C.-C.; Wu, P.-Y.; Lee, H.; Huang, M.-C.; Tai, M.-H.; Chuang, J.-H. Toll-like Receptor 3 Expression Inhibits Cell Invasion and Migration and Predicts a Favorable Prognosis in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2013, 336, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Alexiadis, S.; Camisaschi, C.; Truini, M.; Centonze, G.; Milione, M.; Balsari, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Sfondrini, L. TLR3 Expression Induces Apoptosis in Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, V.; Tow, C.; Huang, C.; Bard-Chapeau, E.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Weber, A.; Lim, K.H.; Toh, H.C.; Heikenwalder, M.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 3 Expressing Tumor Parenchyma and Infiltrating Natural Killer Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, C.-J. Is Knowledge of Hemodynamics Really Dangerous? J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2016, 30, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-O.; Yu, Q. Systemic Administration of TLR3 Agonist Induces IL-7 Expression and IL-7-Dependent CXCR3 Ligand Production in the Lung. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.B.; Evers, G.; Görlich, D.; Mohr, M.; Marra, A.; Hillejan, L.; Rehkämper, J.; Schmidt, L.H.; Heitkötter, B. Tumor Infiltrating T Cells Influence Prognosis in Stage I-III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-C.; Zhang, B.-X.; Su, E.C.-Y.; Wu, W.-C.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Salazar, A.M.; Lin, Y.-K.; Ding, J.L. Hiltonol Cocktail Kills Lung Cancer Cells by Activating Cancer-Suppressors, PKR/OAS, and Restraining the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Poly I: C Enhances Cycloheximide-Induced Apoptosis of Tumor Cells through TLR3 Pathway. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Kume, H.; Ota, S.; Kashima, T.; Tomita, K.; Kitamura, T.; Kodama, T.; Fukayama, M.; Aburatani, H. Identification of Toll-like Receptor 3 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5703–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaun, B.; Coste, I.; Rissoan, M.-C.; Lebecque, S.J.; Renno, T. TLR3 Can Directly Trigger Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4894–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaun, B.; Lebecque, S.; Matikainen, S.; Rimoldi, D.; Romero, P. Toll-like Receptor 3 Expressed by Melanoma Cells as a Target for Therapy? Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4565–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, M.; Fares, N.; Testoni, B.; Estornes, Y.; Weber, K.; Vanbervliet, B.; Lefrançois, L.; Garcia, A.; Kfoury, A.; Pez, F.; et al. Toll-like Receptor 3 Downregulation Is an Escape Mechanism from Apoptosis during Hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheyhidin, I.; Nabi, G.; Hasim, A.; Zhang, R.-P.; Ainiwaer, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, H. Overexpression of TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Reyes, S.; Marín, L.; González, L.; González, L.O.; del Casar, J.M.; Lamelas, M.L.; González-Quintana, J.M.; Vizoso, F.J. Study of TLR3, TLR4 and TLR9 in Breast Carcinomas and Their Association with Metastasis. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Eiró, N.; González-Reyes, S.; González, L.; Aguirre, A.; González, L.O.; Del Casar, J.M.; García-Muñiz, J.L.; Vizoso, F.J. Clinical Significance of Toll-like Receptor 3, 4, and 9 in Gastric Cancer. J. Immunother. 2014, 37, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Chien, C.-Y.; Chuang, J.-H. Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Tumor Invasion in Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.; Xie, X.; Cao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Fan, H.; Liu, Z. Autophagy Facilitates TLR4- and TLR3-Triggered Migration and Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells through the Promotion of TRAF6 Ubiquitination. Autophagy 2014, 10, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Gai, X.; Jia, T.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y. FOXP3 and TLR4 Protein Expression Are Correlated in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Tumor Progression and Escape. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; He, F.L.; Fang, M.; Hua, T.F.; Hu, B.D.; Zhang, Z.H.; Cao, Q.; Liu, R.Y. Increased Expression of Toll-like Receptors 4 and 9 in Human Lung Cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, F.; Yu, L.; Chen, X. TLR4/MyD88 Signaling Determines the Metastatic Potential of Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, N.; Cao, X. TLR4 Signaling Promotes Immune Escape of Human Lung Cancer Cells by Inducing Immunosuppressive Cytokines and Apoptosis Resistance. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2850–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Xu, L.; He, C.; Wen, H.; Yan, J.; Su, H.; Zhu, X. Toll-Like Receptor 4 Prompts Human Breast Cancer Cells Invasiveness via Lipopolysaccharide Stimulation and Is Overexpressed in Patients with Lymph Node Metastasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Liu, D.; Chen, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, B.; Wu, H. Soluble B7-H3 Promotes the Invasion and Metastasis of Pancreatic Carcinoma Cells through the TLR4/NF-KappaB Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk-Draper, L.; Hall, K.; Griggs, C.; Rajput, S.; Kohio, P.; DeNardo, D.; Ran, S. Paclitaxel Therapy Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis in a TLR4-Dependent Manner. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5421–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, S.; Volk-Draper, L.D.; Ran, S. TLR4 Is a Novel Determinant of the Response to Paclitaxel in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, R.P.; Jordan, K.R.; Kapoor, P.; Spongberg, E.; Davis, D.; Vorwald, V.M.; Couts, K.L.; Gao, D.; Smith, D.E.; Borgers, J.S.W.; et al. IL-6 and IL-8 Are Linked With Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Accumulation and Correlate With Poor Clinical Outcomes in Melanoma Patients. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; Feng, P.; Zhou, X.; Wen, H.; Xie, X.; Shen, H.; Zhu, X. Reduced Expression of Toll-like Receptor 4 Inhibits Human Breast Cancer Cells Proliferation and Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, E.A.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Warren, S.E.; Aderem, A. TLR5 and Ipaf: Dual Sensors of Bacterial Flagellin in the Innate Immune System. Semin. Immunopathol 2007, 29, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, S.; Akira, S. Immune Responses of TLR5+ Lamina Propria Dendritic Cells in Enterobacterial Infection. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D. Activation of Toll-like Receptor 5 on Breast Cancer Cells by Flagellin Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2466–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaußer, B.; Andrulis, M.; Endrich, S.; Müller-Hermelink, H.-K.; Eck, M. Toll-like Receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on Gastric Carcinoma Cells: An Implication for Interaction with Helicobacter Pylori. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.H.; Im, E.; Pothoulakis, C. Toll-Like Receptor 5 Engagement Modulates Tumor Development and Growth in a Mouse Xenograft Model of Human Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 518–528.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Yao, Y.; Han, F.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. MAP1S Controls Breast Cancer Cell TLR5 Signaling Pathway and Promotes TLR5 Signaling-Based Tumor Suppression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Siegler, K.L.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Vera, P.L. Inhibition of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor or Its Receptor (CD74) Attenuates Growth and Invasion of DU-145 Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8730–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Park, C.-S.; Lee, Y.-R.; Im, S.-A.; Song, S.; Lee, C.-K. Resiquimod, a TLR7/8 Agonist, Promotes Differentiation of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells into Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, M.P.; Schön, M. TLR7 and TLR8 as Targets in Cancer Therapy. Oncogene 2008, 27, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimmig, T.; Matthes, N.; Hoeland, K.; Tripathi, S.; Chandraker, A.; Grimm, M.; Moench, R.; Moll, E.-M.; Friess, H.; Tsaur, I.; et al. TLR7 and TLR8 Expression Increases Tumor Cell Proliferation and Promotes Chemoresistance in Human Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherfils-Vicini, J.; Platonova, S.; Gillard, M.; Laurans, L.; Validire, P.; Caliandro, R.; Magdeleinat, P.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.-C.; Fridman, W.-H.; et al. Triggering of TLR7 and TLR8 Expressed by Human Lung Cancer Cells Induces Cell Survival and Chemoresistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahm, C.D.; Colluru, V.T.; McIlwain, S.J.; Ong, I.M.; McNeel, D.G. TLR Stimulation during T-Cell Activation Lowers PD-1 Expression on CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, K.A.; Norgard, M.A.; Zhu, X.; Levasseur, P.R.; Sivagnanam, S.; Liudahl, S.M.; Burfeind, K.G.; Olson, B.; Pelz, K.R.; Angeles Ramos, D.M.; et al. The TLR7/8 Agonist R848 Remodels Tumor and Host Responses to Promote Survival in Pancreatic Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Mei, T.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. The TLR7/8 Agonist R848 Optimizes Host and Tumor Immunity to Improve Therapeutic Efficacy in Murine Lung Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 61, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinetti, T.; Spagnuolo, L.; Mottas, I.; Secondini, C.; Treinies, M.; Rüegg, C.; Hotz, C.; Bourquin, C. TLR7-Based Cancer Immunotherapy Decreases Intratumoral Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Blocks Their Immunosuppressive Function. OncoImmunology 2016, 5, e1230578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Ma, C.; Hsueh, E.C.; Dou, J.; Mo, W.; Liu, S.; Han, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Varvares, M.A.; et al. TLR 8 Signaling Enhances Tumor Immunity by Preventing Tumor-induced T-cell Senescence. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1294–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Campos, C.; Burguete-García, A.I.; Madrid-Marina, V. Role of TLR9 in Oncogenic Virus-Produced Cancer. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, B.D.; López González, M.; van den Hout, M.F.; Turksma, A.W.; Sluijter, B.J.; Molenkamp, B.G.; van Leeuwen, P.A.; Vosslamber, S.; Scheper, R.J.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.; et al. T Cell Infiltration on Local CpG-B Delivery in Early-Stage Melanoma Is Predominantly Related to CLEC9A + CD141 + CDC1 and CD14 + Antigen-Presenting Cell Recruitment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Guery, L.; Brighouse, D.; Lemeille, S.; Hugues, S. Intratumoral CpG-B Promotes Antitumoral Neutrophil, CDC, and T-Cell Cooperation without Reprograming Tolerogenic PDC. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3280–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Karakousis, C.P.; Takita, H.; Shin, K.; Brooks, S.P. Cytokines and Chemokines Are Expressed at Different Levels in Small and Large Murine Colon-26 Tumors Following Intratumoral Injections of CpG ODN. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratesi, G.; Petrangolini, G.; Tortoreto, M.; Addis, A.; Belluco, S.; Rossini, A.; Selleri, S.; Rumio, C.; Menard, S.; Balsari, A. Therapeutic Synergism of Gemcitabine and CpG-Oligodeoxynucleotides in an Orthotopic Human Pancreatic Carcinoma Xenograft. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6388–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Takahashi, K.; Yaku, H.; Kobiyama, K.; Iwaisako, K.; Zhao, X.; Shiokawa, M.; Uza, N.; Kodama, Y.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. In Situ Vaccination Using Unique TLR9 Ligand K3-SPG Induces Long-Lasting Systemic Immune Response and Synergizes with Systemic and Local Immunotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambirinis, C.P.; Levie, E.; Nguy, S.; Avanzi, A.; Barilla, R.; Xu, Y.; Seifert, L.; Daley, D.; Greco, S.H.; Deutsch, M.; et al. TLR9 Ligation in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Promotes Tumorigenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2077–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.A.; Fu, A.; Onishko, H.; Hallahan, D.E.; Geng, L. Radiation Induces an Antitumour Immune Response to Mouse Melanoma. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Yin, L.; Vidyasagar, S.; Maguire, D.; Swarts, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Alteration of Circulating Mitochondrial DNA Concentration after Irradiation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 765, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, S.; Themelis, G.; Friedrich, L.; Ntziachristos, V.; Sarantopoulos, A.; Molls, M.; Skerra, A.; Multhoff, G. Detection of Irradiation-Induced, Membrane Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70) in Mouse Tumors Using Hsp70 Fab Fragment. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 99, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, M.; Panaretakis, T.; Joza, N.; Tufi, R.; Tesniere, A.; van Endert, P.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Calreticulin Exposure Is Required for the Immunogenicity of Gamma-Irradiation and UVC Light-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1848–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, J.F.; Liu, N.; Candolfi, M.; Xiong, W.; Assi, H.; Yagiz, K.; Edwards, M.R.; Michelsen, K.S.; Kroeger, K.M.; Liu, C.; et al. HMGB1 Mediates Endogenous TLR2 Activation and Brain Tumor Regression. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.-K.; Lee, M.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.-W.; Jang, S.-J.; Kang, J.-H.; Moon, E.-Y. γ-Irradiated Cancer Cells Promote Tumor Growth by Activation of Toll-like Receptor 1-Mediated Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatz, M.; Menendez, D.; Resnick, M.A. The Human TLR Innate Immune Gene Family Is Differentially Influenced by DNA Stress and P53 Status in Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3948–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-C.; Chan, M.W.Y.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chiou, W.-Y.; Lin, R.-I.; Chen, C.-A.; Lee, M.-S.; Chi, C.-L.; Chen, L.-C.; Huang, L.-W.; et al. IRAK2, an IL1R/TLR Immune Mediator, Enhances Radiosensitivity via Modulating Caspase 8/3-Mediated Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 647175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerich, L.; Marron, T.U.; Upadhyay, R.; Svensson-Arvelund, J.; Dhainaut, M.; Hussein, S.; Zhan, Y.; Ostrowski, D.; Yellin, M.; Marsh, H.; et al. Systemic Clinical Tumor Regressions and Potentiation of PD1 Blockade with in Situ Vaccination. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, T.; Kajihara, R.; Yokoi, T.; Repasky, E.A.; Ito, F. Neoadjuvant In Situ Immunomodulation Enhances Systemic Antitumor Immunity against Highly Metastatic Tumors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 6183–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulandra, M.; Kobescak, A.; Verillaud, B.; Busson, P.; Matijevic Glavan, T. Radio-Sensitization of Head and Neck Cancer Cells by a Combination of Poly(I:C) and Cisplatin through Downregulation of Survivin and c-IAP2. Cell Oncol. 2019, 42, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Shime, H.; Takeda, Y.; Nam, J.; Takashima, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Shirato, H.; Kasahara, M.; Seya, T. Toll-like Receptor 3 Signal Augments Radiation-induced Tumor Growth Retardation in a Murine Model. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, M.R.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Grossman, S.A.; Peereboom, D.M.; Lesser, G.J.; Batchelor, T.T.; Desideri, S.; Salazar, A.M.; Ye, X. A Multi-Institution Phase II Study of Poly-ICLC and Radiotherapy with Concurrent and Adjuvant Temozolomide in Adults with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butowski, N.; Chang, S.M.; Junck, L.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Abrey, L.; Fink, K.; Cloughesy, T.; Lamborn, K.R.; Salazar, A.M.; Prados, M.D. A Phase II Clinical Trial of Poly-ICLC with Radiation for Adult Patients with Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial Glioblastoma: A North American Brain Tumor Consortium (NABTC01-05). J. Neurooncol. 2009, 91, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Ko, H.-J.; Yoon, B.-I.; Choe, J.; Kim, K.-C.; Hahn, T.-W.; Han, J.A.; Choi, S.S.; Jung, Y.M.; et al. The TLR7 Agonist Imiquimod Induces Anti-Cancer Effects via Autophagic Cell Death and Enhances Anti-Tumoral and Systemic Immunity during Radiotherapy for Melanoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24932–24948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schölch, S.; Rauber, C.; Tietz, A.; Rahbari, N.N.; Bork, U.; Schmidt, T.; Kahlert, C.; Haberkorn, U.; Tomai, M.A.; Lipson, K.E.; et al. Radiotherapy Combined with TLR7/8 Activation Induces Strong Immune Responses against Gastrointestinal Tumors. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4663–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, S.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Formenti, S.C.; Adams, S. The TLR7 Agonist Imiquimod as an Adjuvant for Radiotherapy-Elicited in Situ Vaccination against Breast Cancer. OncoImmunology 2013, 2, e25997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shirota, Y.; Bayik, D.; Shirota, H.; Tross, D.; Gulley, J.L.; Wood, L.V.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Klinman, D.M. Effect of TLR Agonists on the Differentiation and Function of Human Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Su, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, P.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages by TLR7/8 Conjugated Radiosensitive Peptide Hydrogel for Overcoming Tumor Radioresistance. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; et al. A Three-In-One Assembled Nanoparticle Containing Peptide–Radio-Sensitizer Conjugate and TLR7/8 Agonist Can Initiate the Cancer-Immunity Cycle to Trigger Antitumor Immune Response. Small 2022, 18, 2107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yu, D.; Kandimalla, E.R.; Sun, H.B.; Agrawal, S.; Guha, C. An in Situ Autologous Tumor Vaccination with Combined Radiation Therapy and TLR9 Agonist Therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.I.; Barsoumian, H.B.; Sezen, D.; Verma, V.; Patel, R.; Wasley, M.; Hu, Y.; Dunn, J.D.; He, K.; Chen, D.; et al. Addition of TLR9 Agonist Immunotherapy to Radiation Improves Systemic Antitumor Activity. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boss, M.K.; Watts, R.; Harrison, L.G.; Hopkins, S.; Chow, L.; Trageser, E.; Easton, C.; LaRue, S.M.; Regan, D.; Dewhirst, M.W.; et al. Immunologic Effects of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Dogs with Spontaneous Tumors and the Impact of Intratumoral OX40/TLR Agonist Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Qiao, T.; Li, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Toll-like Receptor 9 Activation by CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide 7909 Enhances the Radiosensitivity of A549 Lung Cancer Cells via the P53 Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5271–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhuang, X.; Xu, G.; Qaio, T. High-Dose Irradiation in Combination with Toll-like Receptor 9 Agonist CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide 7909 Downregulates PD-L1 Expression via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. OTT 2016, 9, 6511–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Yue, X.; Ren, G.; Li, H.; Ping, L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, T. MiR-15a/16 Enhances Radiation Sensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Targeting the TLR1/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, M.; Murgueitio, M.S.; Bermudez, M.; Wolber, G.; Weindl, G. The Novel Small-Molecule Antagonist MMG-11 Preferentially Inhibits TLR2/1 Signaling. Biochem Pharm. 2020, 171, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Song, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Fan, X.; Cao, X.; Gong, A.; Wang, D.; et al. Radiotherapy-Induced Cell Death Activates Paracrine HMGB1-TLR2 Signaling and Accelerates Pancreatic Carcinoma Metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, B.; Zandi, Z.; Bashash, D.; Zaghal, A.; Momeny, M.; Poursani, E.M.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Mousavi, S.A.; Ghaffari, S.H. Small Molecule Inhibitor of TLR4 Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation: New Insight into the Anticancer Effect of TAK-242 (Resatorvid). Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastille, E.; Faßnacht, T.; Adamczyk, A.; Ngo Thi Phuong, N.; Buer, J.; Westendorf, A.M. Inhibition of TLR4 Signaling Impedes Tumor Growth in Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 669747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, Z.; Kashani, B.; Bashash, D.; Poursani, E.M.; Mousavi, S.A.; Chahardoli, B.; Ghaffari, S.H. The Anticancer Effect of the TLR4 Inhibition Using TAK-242 (Resatorvid) Either as a Single Agent or in Combination with Chemotherapy: A Novel Therapeutic Potential for Breast Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Liang, P. Development of a Toll-Like Receptor-Based Gene Signature That Can Predict Prognosis, Tumor Microenvironment, and Chemotherapy Response for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 729789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Receptor | Ligand | Pro-Tumoral Effect (# of Studies) | Anti-Tumoral Effect (# of Studies) | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR1/2 | BLP | Colorectal (2); Gastric (1); Ovarain (1) | Lung (3); Melanoma (1) | Effects are modulated through cancer-intrinsic mechanisms which vary depending on tumor type |
| TLR3 | Poly (I:C) | Esophageal (1); Breast (1); Gastric (1); HNSCC (1) | Lung (6); HNSCC (2); HCC (5); CRC (2); Neuroblastoma (1); Clear cell carcinoma (1); Breast (1); Cervical (1); Prostate (1); Melanoma (1) | Primarily anti-tumorigenic effects that are cancer-intrinsic and/or involve dendritic cells and CD8 T cells. Few correlative and in vitro studies suggest a pro-tumoral effect. |
| TLR4 | LPS | Lung (3); Breast (5); PDAC (1) | - | Pro-tumorigenic effect that is primarily cancer-cell intrinsic with limited immune involvement. |
| TLR5 | Flagellin | - | Gastric (1); CRC (1); Breast (3); Prostate (1) | Anti-tumorigenic effect mediated through neutrophils (likely N1). |
| TLR7/8 | ssRNA | PDAC (1) | Sarcoma (1); PDAC (1); Lung (1); CRC (1); Melanoma (1) | Anti-tumorigenic effect mediated through NK and CD8 T cells and decreasing MDSCs and Tregs |
| TLR9 | CpG | PDAC (1) | Melanoma (2); CRC (1); PDAC (2) | Mainly anti-tumorigenic effects mediated through recruitment of cDCs and priming of CTLs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haroun, R.; Naasri, S.; Oweida, A.J. Toll-Like Receptors and the Response to Radiotherapy in Solid Tumors: Challenges and Opportunities. Vaccines 2023, 11, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040818
Haroun R, Naasri S, Oweida AJ. Toll-Like Receptors and the Response to Radiotherapy in Solid Tumors: Challenges and Opportunities. Vaccines. 2023; 11(4):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040818
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaroun, Ryma, Sahar Naasri, and Ayman J. Oweida. 2023. "Toll-Like Receptors and the Response to Radiotherapy in Solid Tumors: Challenges and Opportunities" Vaccines 11, no. 4: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040818
APA StyleHaroun, R., Naasri, S., & Oweida, A. J. (2023). Toll-Like Receptors and the Response to Radiotherapy in Solid Tumors: Challenges and Opportunities. Vaccines, 11(4), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11040818







