A DNA Vaccine Encoding the Full-Length Spike Protein of Beta Variant (B.1.351) Elicited Broader Cross-Reactive Immune Responses against Other SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Design, Construction, and Identification of DNA Vaccines
2.3. Western Blot
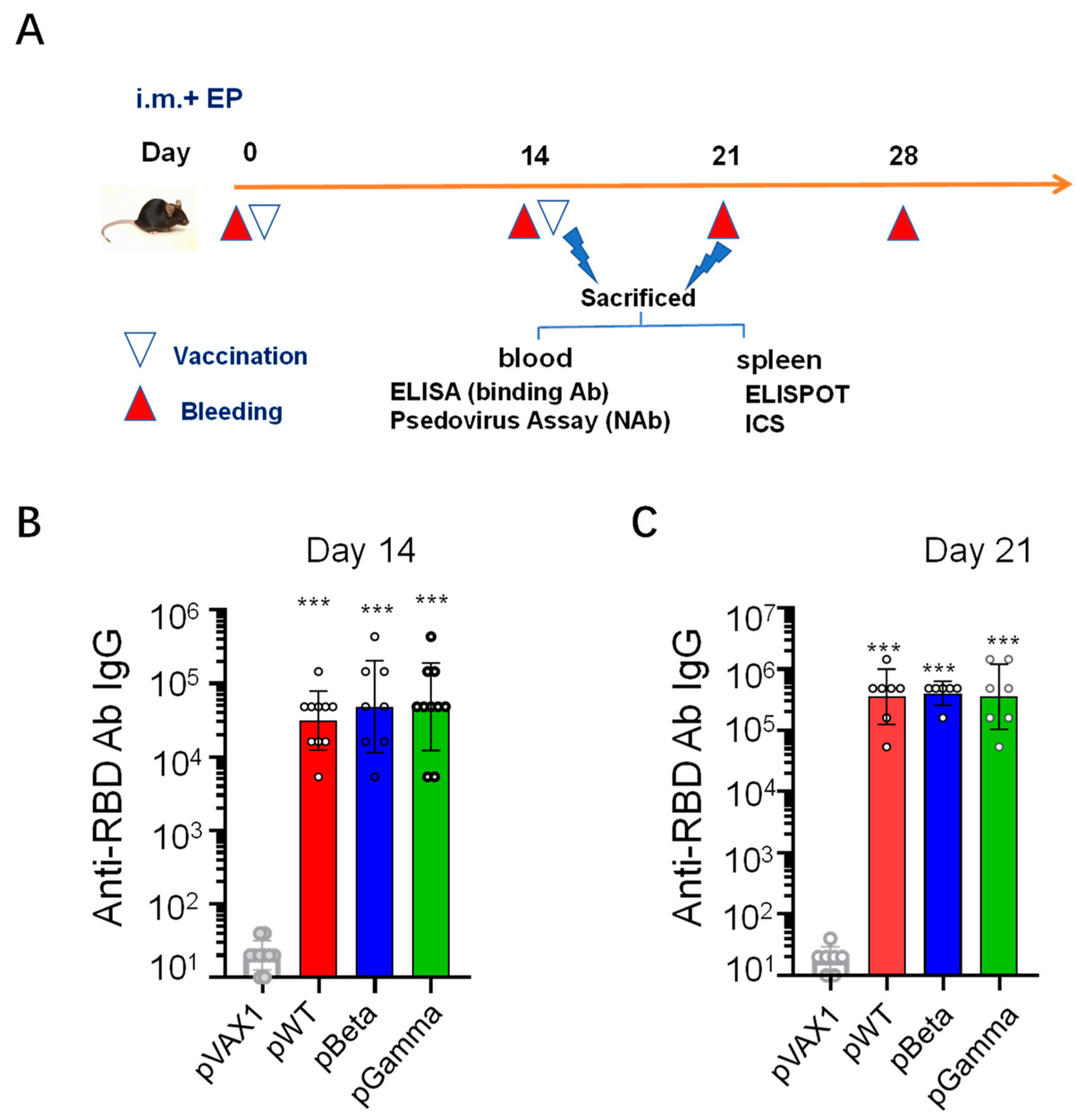
2.4. Immunization
2.5. Binding Antibody Detection by ELISA
2.6. Neutralization Antibody Detection
2.7. ELISpot
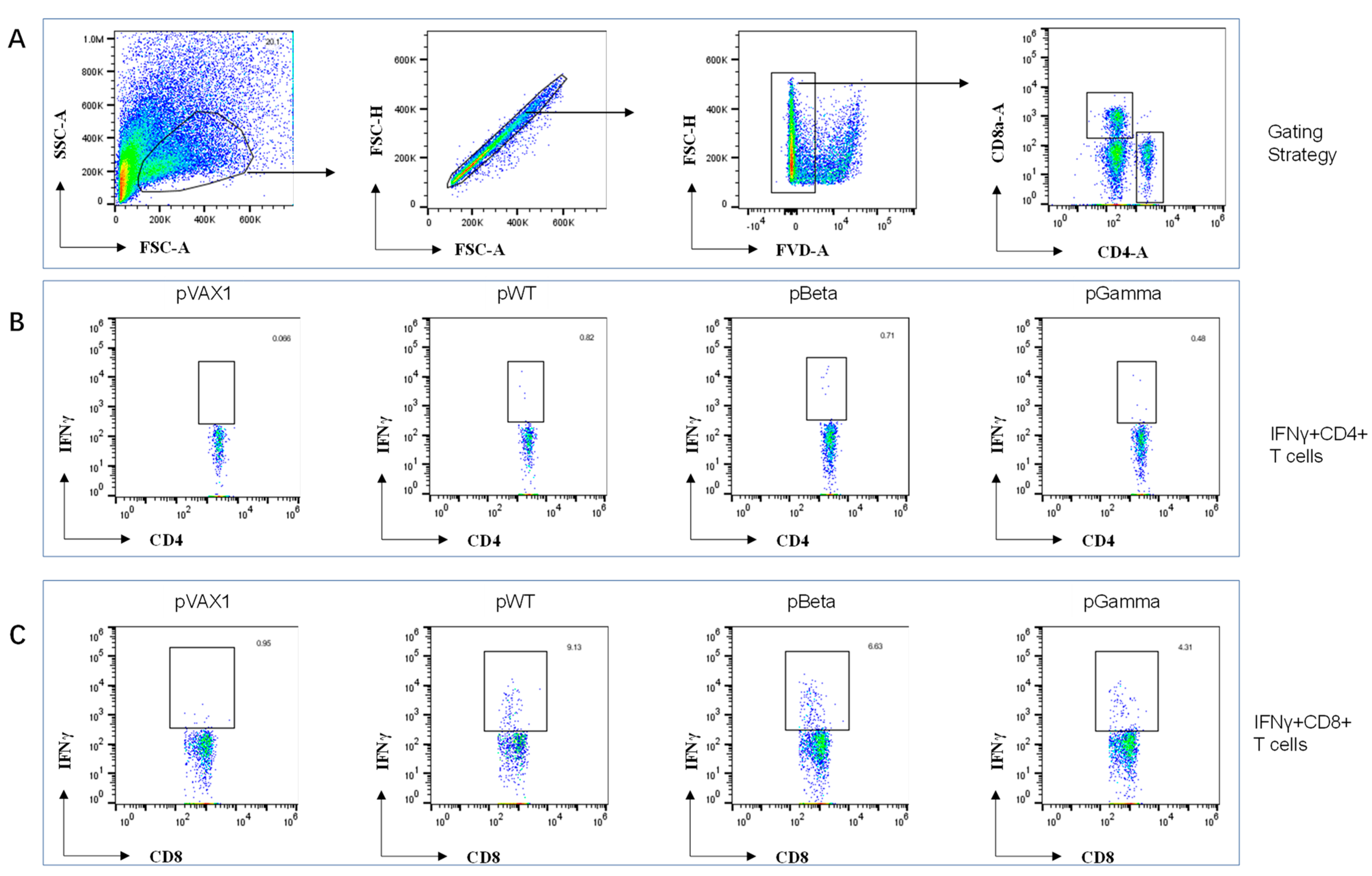
2.8. Intracellular Staining (ICS)
2.9. In Vivo CTL Assay
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
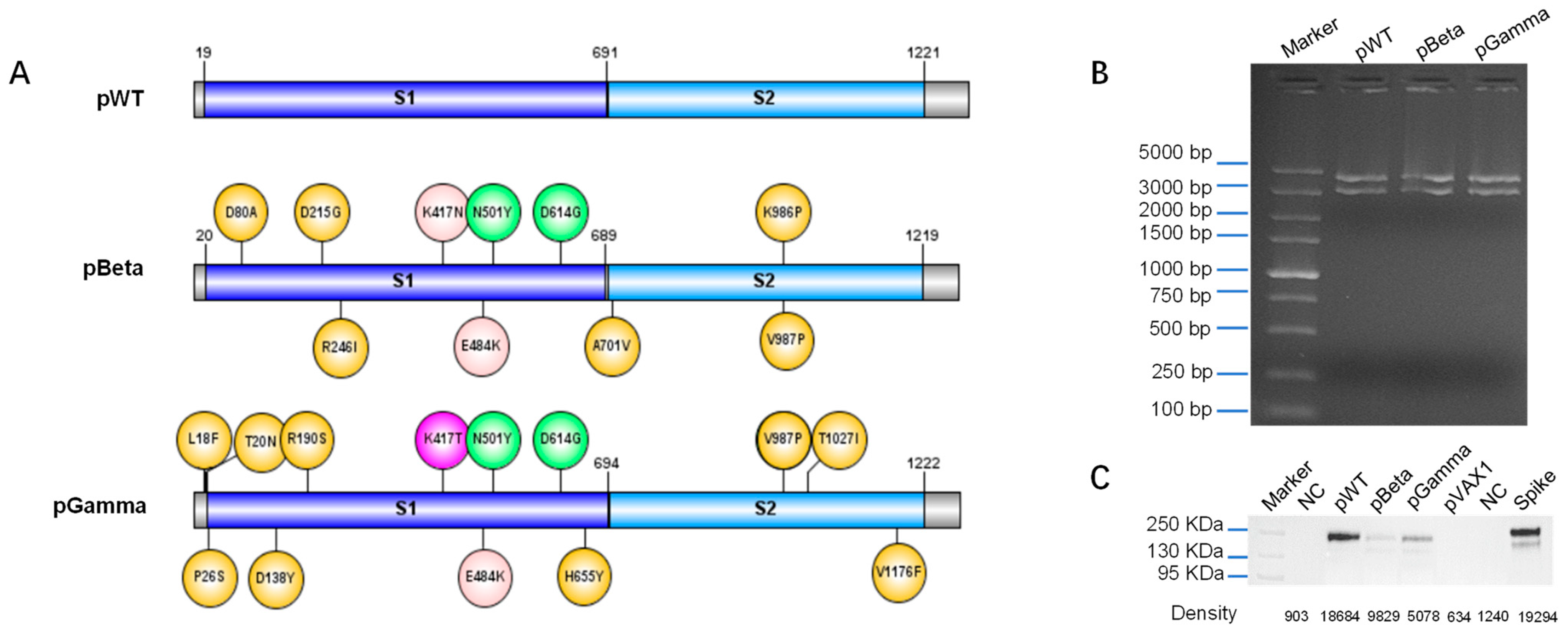
3.1. Design DNA Vaccine against Various SARS-CoV-2 Variants
3.2. DNA Vaccines pWT, pBeta, and pGamma Elicited High Binding Antibody Levels to Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2
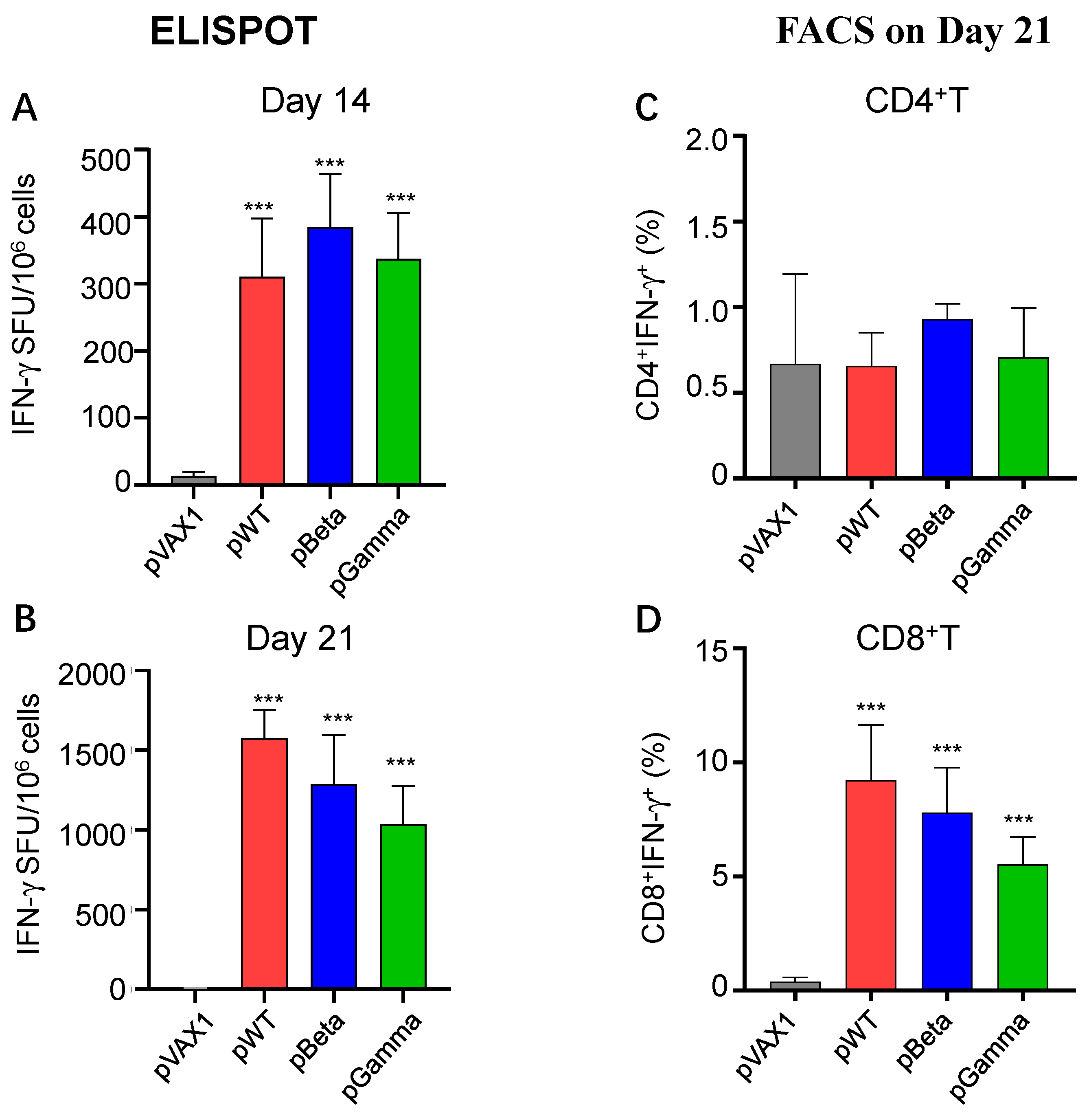
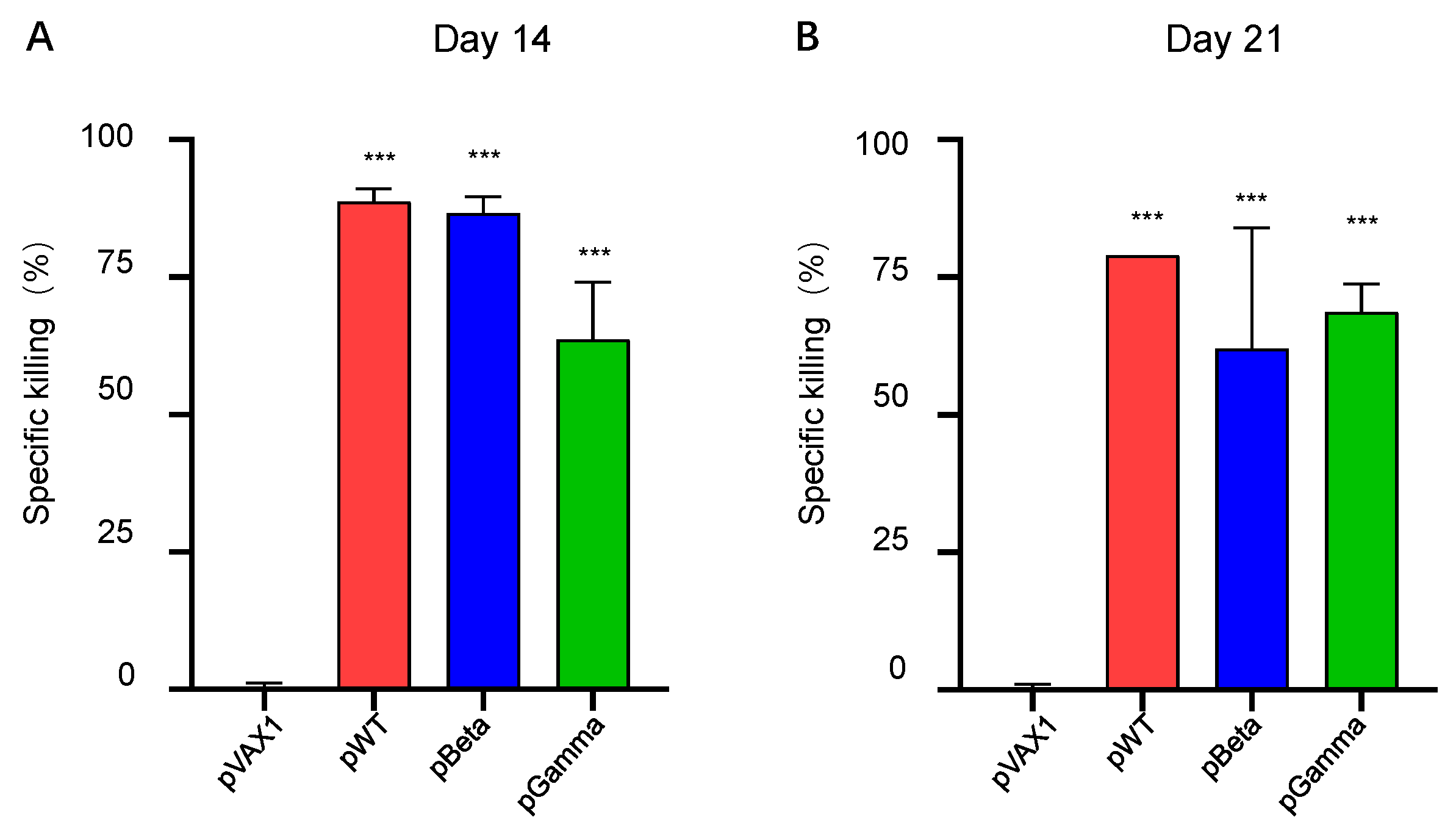
3.3. DNA Vaccines pWT, pBeta, and pGamma Elicited Robust Cellular Immune Responses
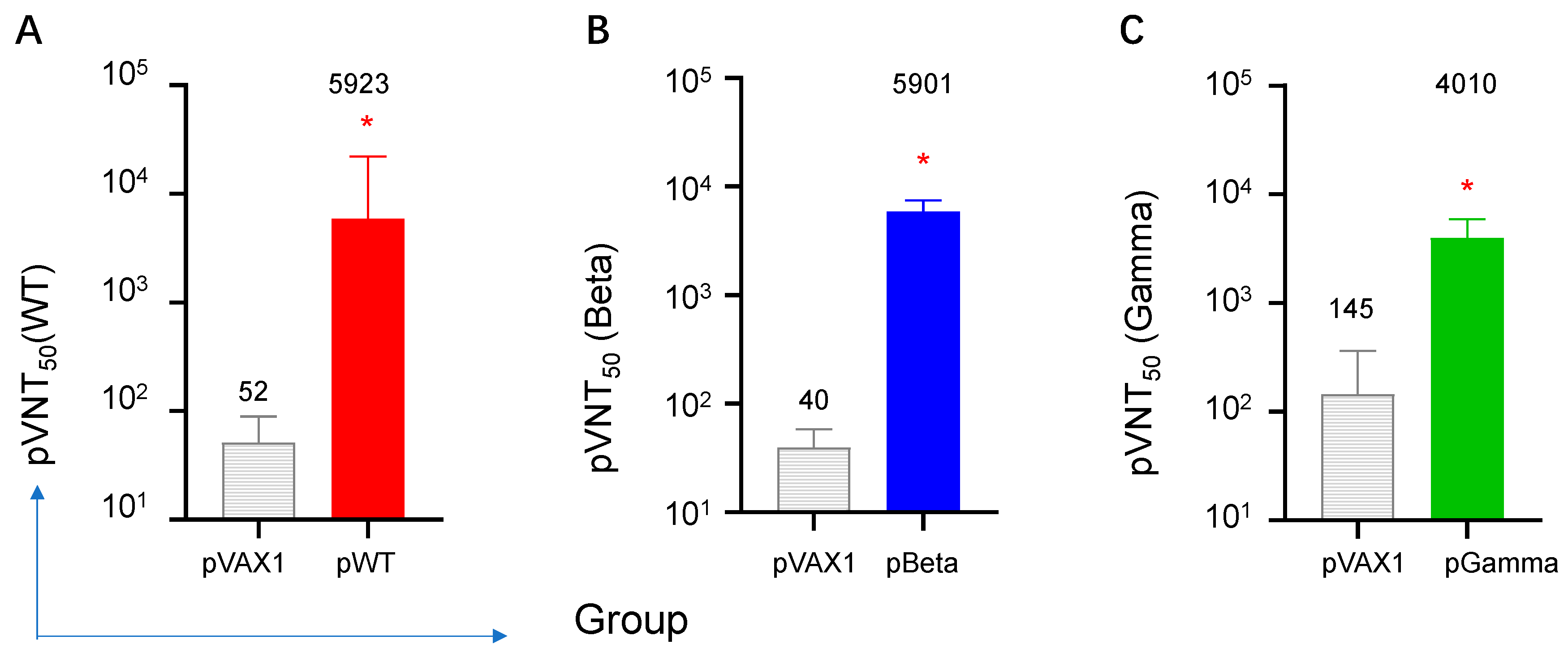
3.4. DNA Vaccines Induced the Highest Neutralizing Antibody for Each Variant, but Diverse Cross-Reactive Neutralizing Antibodies for Other VOCs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.I.; Manamela, N.P.; Motsoeneng, B.M.; Kaldine, H.; Ayres, F.; Makhado, Z.; Mennen, M.; Skelem, S.; Williams, N.; Sullivan, N.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Beta and Delta variants trigger Fc effector function with increased cross-reactivity. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; Walls, A.C.; Sprouse, K.R.; Bowen, J.E.; Rosen, L.E.; Dang, H.V.; De Marco, A.; Franko, N.; Tilles, S.W.; Logue, J.; et al. Molecular basis of immune evasion by the Delta and Kappa SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2021, 374, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S.A.; Baillie, V.; Cutland, C.L.; Voysey, M.; Koen, A.L.; Fairlie, L.; Padayachee, S.D.; Dheda, K.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 COVID-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lee, A.; Grigoryan, L.; Arunachalam, P.S.; Scott, M.K.D.; Trisal, M.; Wimmers, F.; Sanyal, M.; Weidenbacher, P.A.; Feng, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity to the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Hwang, K.P.; Kuo, H.K.; Peng, W.J.; Shen, Y.H.; Kuo, B.S.; Huang, J.H.; Liu, H.; Ho, Y.H.; Lin, F.; et al. A multitope SARS-CoV-2 vaccine provides long-lasting B cell and T cell immunity against Delta and Omicron variants. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e157707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Sellers, D.; Barrett, J.; Jacob-Dolan, C.; Lifton, M.; McMahan, K.; Sciacca, M.; VanWyk, H.; Wu, C.; et al. Vaccines elicit highly conserved cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Nature 2022, 603, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Peter, L.; Mercado, N.B.; McMahan, K.; Mahrokhian, S.H.; Nkolola, J.P.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chandrashekar, A.; et al. DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 369, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Duan, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. A novel DNA and protein combination COVID-19 vaccine formulation provides full protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, B.; Nuwarda, R.F.; Ramzan, I.; Kayser, V. A Narrative Review of COVID-19 Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wambani, J.; Okoth, P. Scope of SARS-CoV-2 variants, mutations, and vaccine technologies. Egypt J. Intern. Med. 2022, 34, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Karim, F.; Ganga, Y.; Bernstein, M.; Jule, Z.; Reedoy, K.; Cele, S.; Lustig, G.; Amoako, D.; Wolter, N.; et al. Omicron BA.4/BA.5 escape neutralizing immunity elicited by BA.1 infection. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, Y.; Jiao, S. Neutralization heterogeneity of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants to sera elicited by a vaccinee or convalescent. Future Virol. 2022, 17, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Silva, I.T.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Z.; et al. Enhancement versus neutralization by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from a convalescent donor associates with distinct epitopes on the RBD. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; O’Connell, S.E.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; Talana, C.A.; Lai, L.; Albert, J.; Anderson, E.; Bennett, H.; Corbett, K.S.; et al. Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2021, 373, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Single-dose administration and the influence of the timing of the booster dose on immunogenicity and efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine: A pooled analysis of four randomised trials. Lancet 2021, 397, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, G.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Borducchi, E.N.; Tostanoski, L.H.; McMahan, K.; Jacob-Dolan, C.; Martinez, D.R.; Chang, A.; et al. Immunogenicity of Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants in humans. Nature 2021, 596, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.-C.; Guan, X.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-Y.; Jiang, T.; Hou, L.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Yang, B.-F.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.-J.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18 years or older: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Gao, L.; Tao, L.; Hadinegoro, S.R.; Erkin, M.; Ying, Z.; He, P.; Girsang, R.T.; Vergara, H.; Akram, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the RBD-Dimer–Based COVID-19 Vaccine ZF2001 in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, P.T.; Galiza, E.P.; Baxter, D.N.; Boffito, M.; Browne, D.; Burns, F.; Chadwick, D.R.; Clark, R.; Cosgrove, C.A.; Galloway, J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the NVX-CoV2373 COVID-19 Vaccine at Completion of the Placebo-Controlled Phase of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 76, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Jin, H.; Cui, G.; Chen, P.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy adults aged 60 years and older: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: A randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraynyak, K.A.; Blackwood, E.; Agnes, J.; Tebas, P.; Giffear, M.; Amante, D.; Reuschel, E.L.; Purwar, M.; Christensen-Quick, A.; Liu, N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine INO-4800 Induces Durable Immune Responses Capable of Being Boosted in a Phase 1 Open-Label Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Faraone, J.; Evans, J.P.; Zou, X.; Zheng, Y.M.; Carlin, C.; Bednash, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Saif, L.J.; et al. Neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4/5 and BA.2.12.1 Subvariants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2526–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P.; Qu, P.; Zeng, C.; Zheng, Y.M.; Carlin, C.; Bednash, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Saif, L.J.; Oltz, E.M.; et al. Neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 Deltacron and BA.3 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2340–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo-Gwete, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Makhado, Z.; Ayres, F.; Mhlanga, D.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; Kgagudi, P.; Tegally, H.; Iranzadeh, A.; et al. Cross-Reactive Neutralizing Antibody Responses Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 (B.1.351). N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2161–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cai, C.; Grifoni, A.; Muller, T.R.; Niessl, J.; Olofsson, A.; Humbert, M.; Hansson, L.; Osterborg, A.; Bergman, P.; et al. Ancestral SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells cross-recognize the Omicron variant. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, Y. Booster COVID-19 vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: A systematic review. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2062983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Evans, J.P.; Chakravarthy, K.; Qu, P.; Reisinger, S.; Song, N.J.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Shields, P.G.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.L. COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccines elicit strong protection against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, T.K. Omicron variant and booster COVID-19 vaccines. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Peng, L.; Filler, R.; Suzuki, K.; McNamara, A.; Lin, Q.; Renauer, P.A.; Yang, L.; Menasche, B.; Sanchez, A.; et al. Omicron-specific mRNA vaccination alone and as a heterologous booster against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Patel, A.; Tursi, N.J.; Zhu, X.; Muthumani, K.; Kulp, D.W.; Weiner, D.B. Harnessing Recent Advances in Synthetic DNA and Electroporation Technologies for Rapid Vaccine Development Against COVID-19 and Other Emerging Infectious Diseases. Front. Med. Technol. 2020, 2, 571030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Martinez, D.R.; Schäfer, A.; Chen, H.; Barr, M.; Sutherland, L.L.; Lee, E.; Parks, R.; Mielke, D.; Edwards, W.; et al. Breadth of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization and Protection Induced by a Nanoparticle Vaccine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Wu, S.; Zhao, G.; He, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, J.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, B. Identification of a promiscuous conserved CTL epitope within the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wu, S.; Zhao, G.; He, Y.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Qin, C.; Hou, J.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, A.; et al. Comparison of Wild Type DNA Sequence of Spike Protein from SARS-CoV-2 with Optimized Sequence on The Induction of Protective Responses Against SARS-Cov-2 Challenge in Mouse Model. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2016201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Hao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Nie, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by a pseudotyped virus-based assay. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3699–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, Y.; Sutandhio, S.; Furukawa, K.; Tjan, L.H.; Iwata, S.; Sano, S.; Tohma, Y.; Ohkita, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Cross-Neutralizing Breadth and Longevity Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants After Infections. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 773652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; de Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalkias, S.; Harper, C.; Vrbicky, K.; Walsh, S.R.; Essink, B.; Brosz, A.; McGhee, N.; Tomassini, J.E.; Chen, X.; Chang, Y.; et al. A Bivalent Omicron-Containing Booster Vaccine against COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalkias, S.; Eder, F.; Essikn, B.; Khetan, S.; Nestorova, B.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Montefiori, D.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity and antibody persistence of a bivalent Beta-containing booster vaccine against COVID-19: A phase 2/3 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Hou, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Sui, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Gao, X.; et al. A DNA Vaccine Encoding the Full-Length Spike Protein of Beta Variant (B.1.351) Elicited Broader Cross-Reactive Immune Responses against Other SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines 2023, 11, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030513
Zhao G, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Hou J, Liu Y, Zhang M, Sui C, Wang L, Xu X, Gao X, et al. A DNA Vaccine Encoding the Full-Length Spike Protein of Beta Variant (B.1.351) Elicited Broader Cross-Reactive Immune Responses against Other SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030513
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Gan, Zhiyu Zhang, Yuan Ding, Jiawang Hou, Ying Liu, Mengying Zhang, Cheng Sui, Limei Wang, Xin Xu, Xiaoming Gao, and et al. 2023. "A DNA Vaccine Encoding the Full-Length Spike Protein of Beta Variant (B.1.351) Elicited Broader Cross-Reactive Immune Responses against Other SARS-CoV-2 Variants" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030513
APA StyleZhao, G., Zhang, Z., Ding, Y., Hou, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, M., Sui, C., Wang, L., Xu, X., Gao, X., & Kou, Z. (2023). A DNA Vaccine Encoding the Full-Length Spike Protein of Beta Variant (B.1.351) Elicited Broader Cross-Reactive Immune Responses against Other SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines, 11(3), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030513




