Epidemiological Analysis of Avian Reovirus in China and Research on the Immune Protection of Different Genotype Strains from 2019 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Samples
2.2. Major Reagents and Experimental Animals
2.3. Primers
2.4. Extraction of Viral RNA
2.5. RT-PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.6. Genetic Evolution Analysis
2.7. Isolation and Identification of ARV
2.8. Determination of the Embryonic Half Lethal Dose (ELD50)
2.9. Challenge Protection Test
2.10. Ethics Statements
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Typing of Chinese ARV Isolates and Homology Analysis of σC Genes from 2019 to 2020
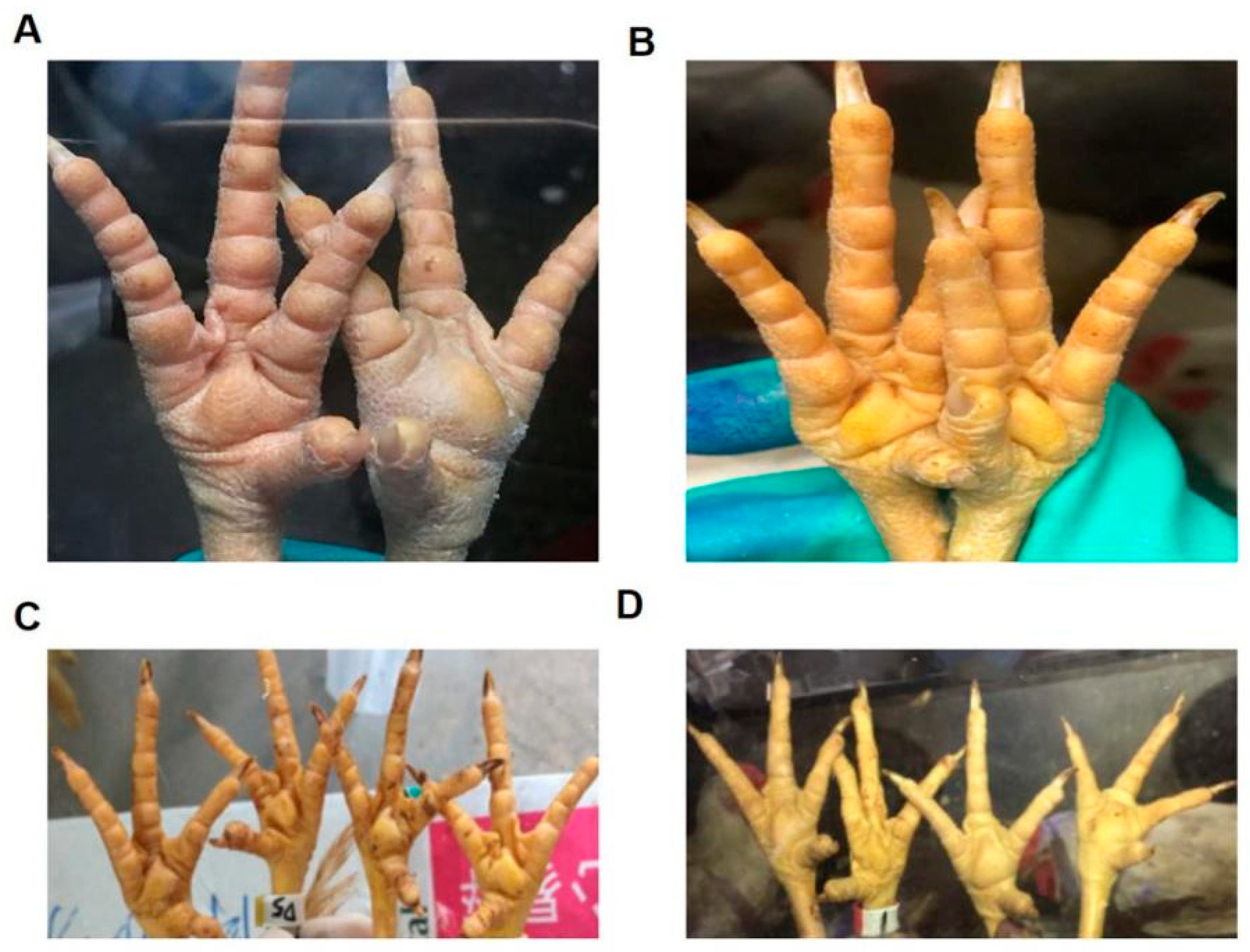
3.2. Isolation and Identification of ARV Strains
3.3. ELD50 of Challenge Strains ARV 1774, ARV 10415, TS18, and WF17
3.4. Results of the Challenge Protection Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberger, J.K.; Sterner, F.J.; Botts, S.; Lee, K.P.; Margolin, A. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian reoviruses. I. Pathogenicity and antigenic relatedness of several avian reovirus isolates. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, P. The dsRNA viruses. Virus Res. 2004, 101, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, K.N.; Glisson, J.R. Economic impact of a documented case of reovirus infection in broiler breeders. Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heide, L. The history of avian reovirus. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffels-Redmann, U.; Muller, H.; Kaleta, E.F. Structural and biological characteristics of reoviruses isolated from Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata). Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palya, V.; Glavits, R.; Dobos-Kovacs, M.; Ivanics, E.; Nagy, E.; Banyai, K.; Reuter, G.; Szucs, G.; Dan, A.; Benko, M. Reovirus identified as cause of disease in young geese. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heide, L.; Kalbac, M.; Brustolon, M.; Lawson, M.G. Pathogenicity for chickens of a reovirus isolated from turkeys. Avian Dis. 1980, 24, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.D.; Villegas, P.; Dawe, D.L.; Brown, J. Effect of avian reoviruses on lymphoid organ weights and antibody response in chickens. Avian Dis. 1985, 29, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lei, X.; Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Bao, E. Genetic and pathogenic characteristics of newly emerging avian reovirus from infected chickens with clinical arthritis in China. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5321–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yan, M.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Pathogenicity and genomic characterization of a novel avian orthoreovius variant isolated from a vaccinated broiler flock in China. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomino-Tapia, V.; Mitevski, D.; Inglis, T.; van der Meer, F.; Abdul-Careem, M.F. Molecular characterization of emerging avian reovirus variants isolated from viral arthritis cases in Western Canada 2012–2017 based on partial sigma (σ)C gene. Virology 2018, 522, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, S.L.; Marton, S.; Dandar, E.; Kugler, R.; Gal, B.; Jakab, F.; Balint, A.; Kecskemeti, S.; Banyai, K. Lineage diversification, homo-and heterologous reassortment and recombination shape the evolution of chicken orthoreoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandar, E.; Balint, A.; Kecskemeti, S.; Szentpali-Gavaller, K.; Kisfali, P.; Melegh, B.; Farkas, S.L.; Banyai, K. Detection and characterization of a divergent avian reovirus strain from a broiler chicken with central nervous system disease. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2583–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Lu, H. Whole genome alignment based one-step real-time RT-PCR for universal detection of avian orthoreoviruses of chicken, pheasant and turkey origins. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Lim, T.H.; Lee, J.H.; Day, J.M.; Song, C.S. Isolation and genomic characterization of a novel avian orthoreovirus strain in Korea, 2014. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, S.O.; De Carli, S.; Lunge, V.R.; Ikuta, N.; Canal, C.W.; Pavarini, S.P.; Driemeier, D. Pathological and molecular findings of avian reoviruses from clinical cases of tenosynovitis in poultry flocks from Brazil. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Tang, Y.; Dunn, P.A.; Wallner-Pendleton, E.A.; Lin, L.; Knoll, E.A. Isolation and molecular characterization of newly emerging avian reovirus variants and novel strains in Pennsylvania, USA, 2011–2014. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayalew, L.E.; Gupta, A.; Fricke, J.; Ahmed, K.A.; Popowich, S.; Lockerbie, B.; Tikoo, S.K.; Ojkic, D.; Gomis, S. Phenotypic, genotypic and antigenic characterization of emerging avian reoviruses isolated from clinical cases of arthritis in broilers in Saskatchewan, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Lu, H. Genomic characterization of a broiler reovirus field strain detected in Pennsylvania. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 31, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, M.; Qi, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X. Genetic and pathogenic characterisation of 11 avian reovirus isolates from northern China suggests continued evolution of virulence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ARV strains isolated in 2019;
ARV strains isolated in 2019;  ARV strains isolated in 2020;
ARV strains isolated in 2020;  challenge virus.
challenge virus.
 ARV strains isolated in 2019;
ARV strains isolated in 2019;  ARV strains isolated in 2020;
ARV strains isolated in 2020;  challenge virus.
challenge virus.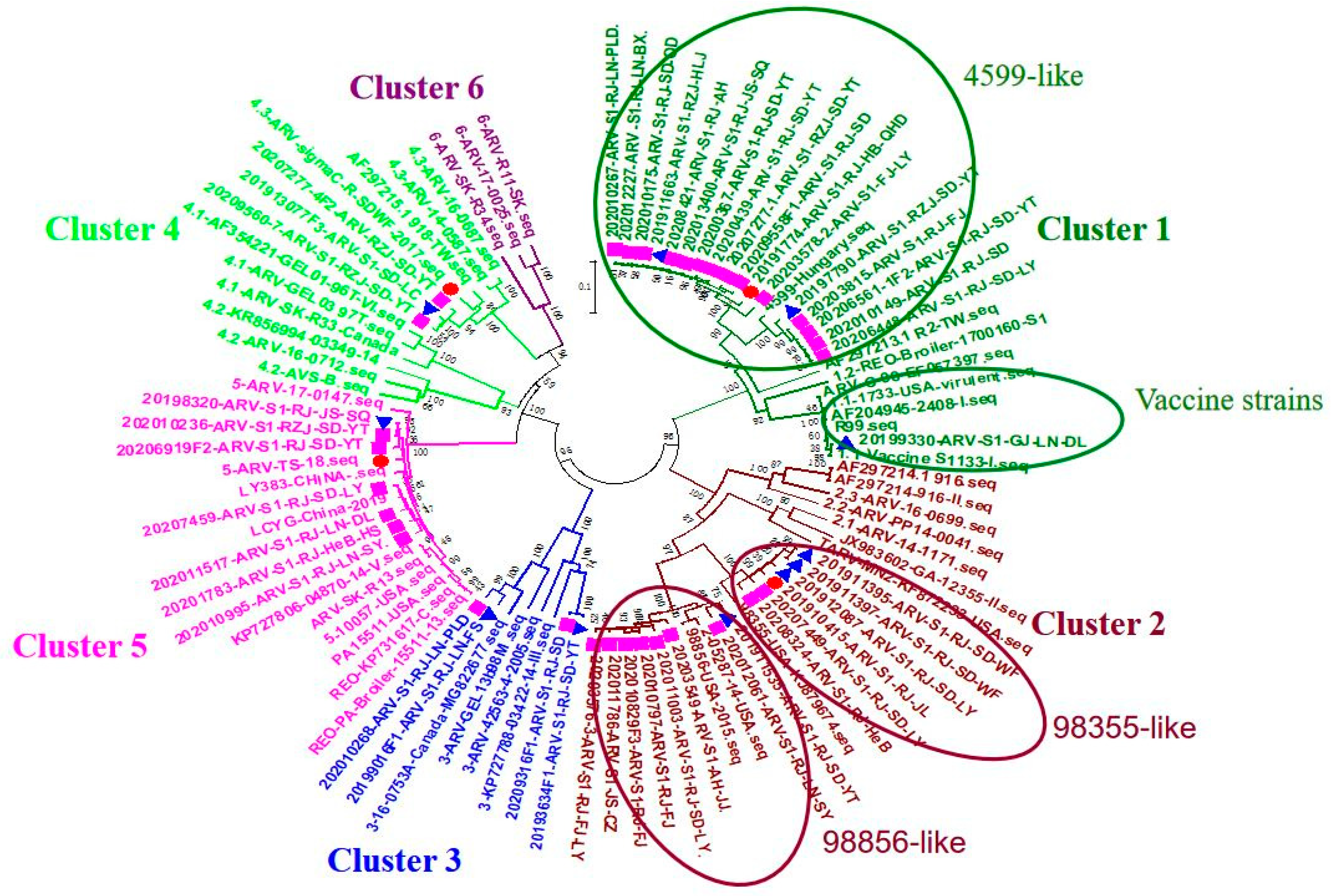

| Vaccinated Groups | Number | Days | Immunization Dosage | Challenge Virus | Challenge Dosage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccinated groups | 1 | 5 | 50 | 0.2 mL | ARV 1774 | 102.7 ELD50 |
| 2 | 5 | ARV 10415 | ||||
| 3 | 5 | ARV TS18 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | WF17 | ||||
| Challenge control groups | 5 | 5 | 50 | 0.2 mL | ARV 1774 | 102.7 ELD50 |
| 6 | 5 | ARV 10415 | ||||
| 7 | 5 | ARV TS18 | ||||
| 8 | 5 | WF17 | ||||
| Negative control group | 9 | 5 | 50 | 0.2 mL (Normal saline) | Normal saline | 0.1 mL |
| Isolates | Origin | Time of Isolation | Breed | σC Genotype | GenBank NO. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20191774 | The farm A※ in Hebei | 2019.3 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262159 |
| 20197790 | The farm B in Shangdong | 2019.8 | Broiler breeder | 1 | ON262154 |
| 20199330 | The farm C in Liaoning | 2019.10 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262153 |
| 20200367 | The farm D in Shandong | 2020.1 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262160 |
| 20200439 | The farm E in Shandong | 2020.1 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262161 |
| 20203578 | The farm F in Fujian | 2020.4 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262162 |
| 201911663 | The farm G in Heilongjiang | 2019.12 | Broiler breeder | 1 | ON262166 |
| 201910415 | The farm H in Jilin | 2019.11 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262181 |
| 201911395 | The farm I in Shandong | 2019.11 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262182 |
| 201911397 | The farm G in Shandong | 2019.11 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262183 |
| 201911535 | The farm K in Shandong | 2019.11 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262173 |
| 201912087 | The farm L in Shandong | 2019.12 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262184 |
| 20203549 | The farm M in Anhui | 2020.4 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262171 |
| 20203576 | The farm N in Fujian | 2020.4 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262172 |
| 20193634 | The farm O in Shandong | 2019.5 | White-feather broiler | 3 | ON262187 |
| 20199016 | The farm P in Liaoning | 2019.9 | Broiler breeder | 3 | ON262185 |
| 201913077 | The farm Q in Shandong | 2019.12 | White-feather broiler | 4 | ON262191 |
| 20198320 | The farm R in Jiangsu | 2019.9 | White-feather broiler | 5 | ON262192 |
| 20201783 | The farm S in Hebei | 2020.3 | White-feather broiler | 5 | ON262193 |
| 20203815 | The farm T in Fujian | 2020.4 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262155 |
| 20206448 | The farm U in Shandong | 2020.6 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262156 |
| 20206561 | The farm V in Shandong | 2020.6 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262157 |
| 20206919 | The farm W in Shandong | 2020.7 | White-feather broiler | 5 | ON262194 |
| 20207277-1 | The farm X1 in Shandong | 2020.7 | Broiler breeder | 1 | ON262163 |
| 20207277-4 | The farm X2 in Shandong | 2020.7 | Broiler breeder | 4.3 | ON262189 |
| 20207449 | The farm Y in Shandong | 2020.7 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262179 |
| 20207459 | The farm Z in Shandong | 2020.7 | White-feather broiler | 5 | ON262195 |
| 20208324 | The farm AB in Hebei | 2020.7 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262180 |
| 20208421 | The farm AC in Anhui | 2020.7 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262164 |
| 20209316 | The farm AD in Shandong | 2020.8 | White-feather broiler | 3 | ON262188 |
| 20209558 | The farm AE in Shandong | 2020.8 | Broiler breeder | 1 | ON262165 |
| 20209560 | The farm AF in Shandong | 2020.8 | Broiler breeder | 4 | ON262190 |
| 202010149 | The farm AG in Shandong | 2020.8 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262158 |
| 202010175 | The farm AH in Shandong | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262167 |
| 202010236 | The farm AI in Shandong | 2020.9 | Broiler breeder | 5 | ON262196 |
| 202010267 | The farm AJ in Liaoning | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262170 |
| 202010268 | The farm AK in Liaoning | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 3 | ON262186 |
| 202010797 | The farm AL in Fujian | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262174 |
| 202010829 | The farm AM in Fujian | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262175 |
| 202010995 | The farm AN in Liaoning | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 5 | ON262197 |
| 202011003 | The farm AO in Shandong | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262176 |
| 202011517 | The farm AP in Liaoning | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 5 | ON262198 |
| 202011786 | The farm AQ in Jiangsu | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262177 |
| 202012061 | The farm AR in Liaoning | 2020.9 | White-feather broiler | 2 | ON262178 |
| 202012227 | The farm AS in Liaoning | 2020.1 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262168 |
| 202013400 | The farm AT in Jiangsu | 2020.1 | White-feather broiler | 1 | ON262169 |
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 74–99.8% | 58.4–60.2% | 54.8–57.2% | 53.8–56% | 53.1–55.6% |
| 2 | 73.3–99.6% | 51.3–58.3% | 54.6–57.8% | 53–57.2% | |
| 3 | 68.7–98% | 56–56.6% | 55.2–58.7% | ||
| 4 | 97.1–97.4% | 61.6–62% | |||
| 5 | 94.9–100% |
| ARV1774 | ARV10415 | WF17 | TS18 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilution of Virus | Mortality Rate | Dilution of Virus | Mortality Rate | Dilution of Virus | Mortality Rate | Dilution of Virus | Mortality Rate |
| 10−3 | 100% | 10−3 | 100% | 10−3 | 100% | 10−3 | 100% |
| 10−4 | 100% | 10−4 | 100% | 10−4 | 100% | 10−4 | 50% |
| 10−5 | 83% | 10−5 | 83% | 10−5 | 100% | 10−5 | 0 |
| 10−6 | 17% | 10−6 | 17% | 10−6 | 50% | 10−6 | 0 |
| 10−7 | 0 | 10−7 | 0 | 10−7 | 0 | 10−7 | 0 |
| Vaccinated Groups | Challenge Virus | Challenge Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Day | 5-Day | 7-Day | |||
| Vaccinated groups | 1 | ARV 1774 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| 2 | ARV 10415 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 4/5 | |
| 3 | ARV TS18 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | |
| 4 | WF17 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | |
| Challenge control groups | 5 | ARV 1774 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 5/5 |
| 6 | ARV 10415 | 5/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 | |
| 7 | ARV TS18 | 3/5 | 4/5 | 5/5 | |
| 8 | WF17 | 3/5 | 3/5 | 5/5 | |
| Negative control group | 9 | \ | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Zou, Z.; Song, S.; Liu, H.; Gong, X.; Li, B.; Liu, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Luan, D.; et al. Epidemiological Analysis of Avian Reovirus in China and Research on the Immune Protection of Different Genotype Strains from 2019 to 2020. Vaccines 2023, 11, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020485
Liu D, Zou Z, Song S, Liu H, Gong X, Li B, Liu P, Wang Q, Liu F, Luan D, et al. Epidemiological Analysis of Avian Reovirus in China and Research on the Immune Protection of Different Genotype Strains from 2019 to 2020. Vaccines. 2023; 11(2):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020485
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dong, Zhong Zou, Shanshan Song, Hongxiang Liu, Xiao Gong, Bin Li, Ping Liu, Qunyi Wang, Fengbo Liu, Dongzu Luan, and et al. 2023. "Epidemiological Analysis of Avian Reovirus in China and Research on the Immune Protection of Different Genotype Strains from 2019 to 2020" Vaccines 11, no. 2: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020485
APA StyleLiu, D., Zou, Z., Song, S., Liu, H., Gong, X., Li, B., Liu, P., Wang, Q., Liu, F., Luan, D., Zhang, X., Du, Y., & Jin, M. (2023). Epidemiological Analysis of Avian Reovirus in China and Research on the Immune Protection of Different Genotype Strains from 2019 to 2020. Vaccines, 11(2), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020485




