Immune Activation Following Vaccination of Streptococcus iniae Bacterin in Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish and Husbandry
2.2. Preparation of Formalin-Killed S. iniae Bacterin
2.3. Vaccination and Challenge Protocol
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Immune-Related Gene Expression
2.5.1. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.5.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Challenge
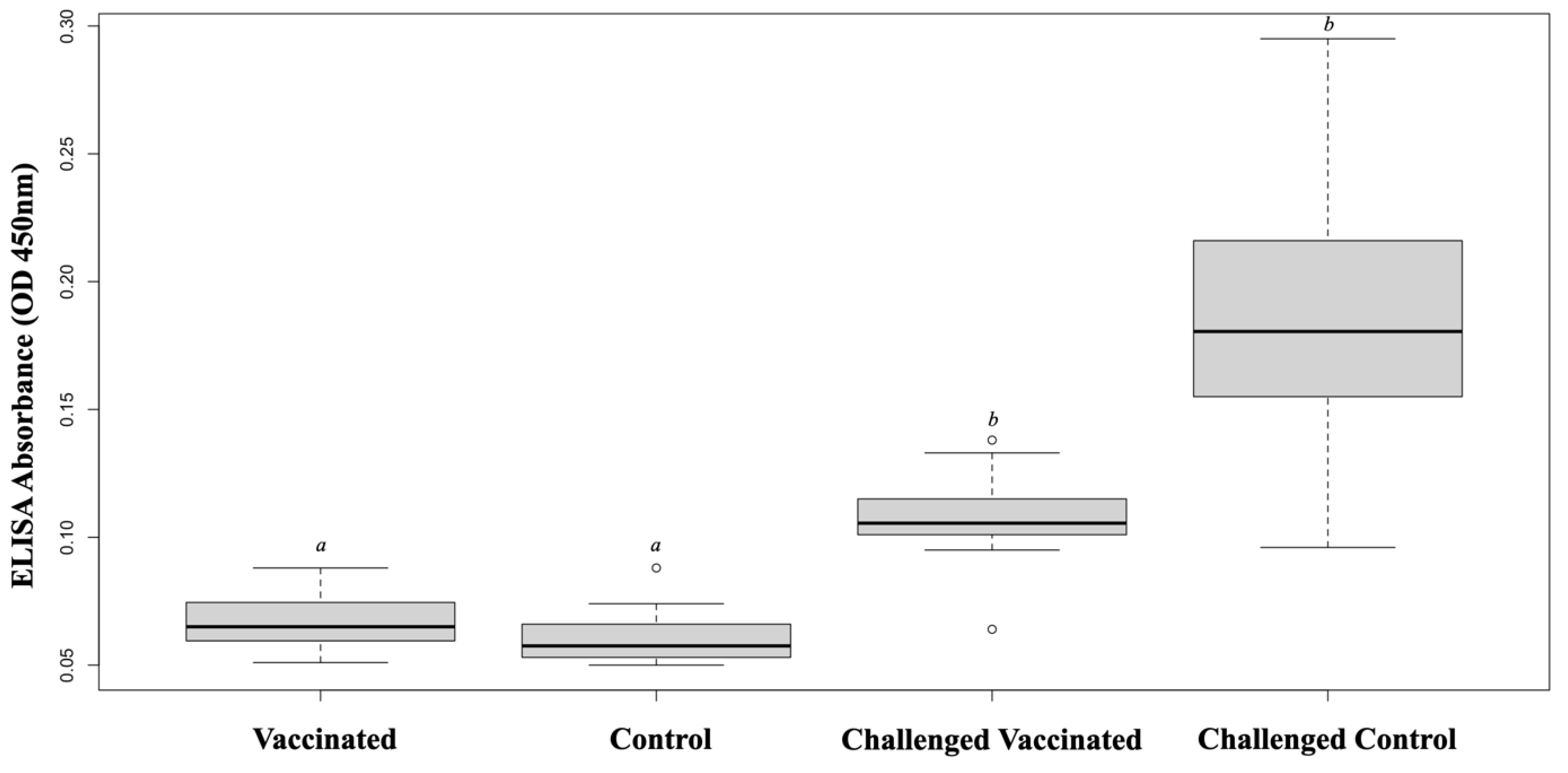
3.2. IgM Antibody Response
3.3. Immune-Related Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department of Fisheries Statistics of Marine Fish Farms SURVEY. 2020. Available online: https://www4.fisheries.go.th/local/pic_activities/202112281419571_pic.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- El-Noby, G.A.; Hassanin, M.; El-Hady, M.; Aboshabana, S. Streptococcus: A review article on an emerging pathogen of farmed fishes. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanyuk, N.; Sukkasame, N.; Tanmark, N.; Yoshida, T.; Itami, T.; Thune, R.L.; Tantikitti, C.; Supamattaya, K. Streptococcus iniae infection in cultured asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) and red tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) in southern Thailand. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 32, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bromage, E.S.; Thomas, A.; Owens, L. Streptococcus iniae, a bacterial infection in barramundi Lates calcarifer. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 36, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.H.; Bai, Z.Y.; Xia, J.H.; Liu, F.; Liu, P.; Yue, G.H. Analysis of two lysozyme genes and antimicrobial functions of their recombinant proteins in Asian seabass. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Khang, P.; Van Nha, V.; Nguyen, N.H. Resistance to Streptococcus iniae and its genetic associations with traits of economic importance in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfanmanesh, A.; Beikzadeh, B.; Mohseni, F.A.; Nikaein, D.; Mohajerfar, T. Ulcerative dermatitis in barramundi due to coinfection with Streptococcus iniae and Shewanella algae. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2019, 134, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckman, T.I.; Griffin, M.J.; Camus, A.C.; LaFrentz, B.R.; Morick, D.; Smirnov, R.; Ofek, T.; Soto, E. Multilocus sequence analysis of diverse Streptococcus iniae isolates indicates an underlying genetic basis for phenotypic heterogeneity. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2020, 141, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piamsomboon, P.; Thanasaksiri, K.; Murakami, A.; Fukuda, K.; Takano, R.; Jantrakajorn, S.; Wongtavatchai, J. Streptococcosis in freshwater farmed seabass Lates calcarifer and its virulence in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayansamruaj, P.; Dong, H.T.; Nguyen, V.V.; Le, H.D.; Pirarat, N.; Rodkhum, C. Susceptibility of freshwater rearing Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) to pathogenic Streptococcus iniae. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bruce, T.J.; Jones, E.M.; Cain, K.D. A review of fish vaccine development strategies: Conventional methods and modern biotechnological approaches. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Thu Nguyen, T.T.; Tsai, M.A.; Ya-Zhen, E.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. A formalin-inactivated vaccine provides good protection against Vibrio harveyi infection in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 65, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Salleh, A.; Mustaffa-Kamal, F.; Matori, M.F.; Azmai, M.N.A. Efficacy of whole cell inactivated vibrio harveyi vaccine against vibriosis in a marine red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus) model. Vaccines 2020, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Hong, S. Characterization of Aeromonas salmonicida and A. sobria isolated from cultured salmonid fish in Korea and development of a vaccine against furunculosis. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klesius, P.H.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Evans, J.J. Efficacy of single and combined Streptococcus iniae isolate vaccine administered by intraperitoneal and intramuscular routes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2000, 188, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Characterization of Streptococcus iniae ghost vaccine and its immunization in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.; Yusoff, M.S.M.; Samad, M.J.; Razak, I.S.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Thompson, K.D.; Hasni, K. Efficacy of feed-based formalin-killed vaccine of streptococcus iniae stimulates the gut-associated lymphoid tissues and immune response of red hybrid tilapia. Vaccines 2021, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, P.C.; Tsai, M.A.; Yeh, S.C.; Liang, H.J.; Chen, S.C. Efficacy of a formalin-inactivated vaccine against Streptococcus iniae infection in the farmed grouper Epinephelus coioides by intraperitoneal immunization. Vaccine 2014, 32, 7014–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Membrebe, J.D.; Yoon, N.K.; Hong, M.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Park, K.; Seo, S.H.; Yoon, I.; Yoo, S.; Kim, Y.C.; et al. Protective efficacy of Streptococcus iniae derived enolase against Streptococcal infection in a zebrafish model. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 170, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, M.; Alishahi, M.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Ghorbanpoor, M.; Tabandeh, M.R. High efficacy and economical procedure of oral vaccination against Lactococcus garvieae/Streptococcus iniae in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, M.; Alishahi, M.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Ghorbanpoor, M.; Tabandeh, M.R. Valuable method for production of oral vaccine by using alginate and chitosan against Lactococcus garvieae/Streptococcus iniae in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, A.; Horovitcz, A.; Bercovier, H. Development and efficacy of a vaccine against Streptococcus iniae infection in farmed rainbow trout. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 56, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, Y.; Mesbah, M.; Dezfoulnejad, M.C.; Mehrgan, M.S.; Islami, H.R. Growth performance, blood biochemical parameters, immune response, and antioxidant defense of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) fingerlings exposed to monovalent and bivalent vaccines against Streptococcus iniae and Vibrio harveyi. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 2751–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu Lan, N.G.; Salin, K.R.; Longyant, S.; Senapin, S.; Dong, H.T. Systemic and mucosal antibody response of freshwater cultured Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) to monovalent and bivalent vaccines against Streptococcus agalactiae and Streptococcus iniae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 108, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantrakajorn, S.; Lukkana, M.; Wongtavatchai, J. Serological and molecular characterization of Streptococcus iniae in cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Thailand. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2014, 44, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.M.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Xie, M.Q.; Li, A.X. Rapid identification of Streptococcus iniae by specific PCR assay utilizing genetic markers in ITS rDNA. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soonthonsrima, T.; Wangman, P.; Pengsuk, C.; Sithigorngul, P.; Longyant, S. Production of Monoclonal Antibody Specific to Immunoglobulin of Asian Sea Bass Lates calcarifer. Burapha Sci. J. 2019, 24, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Fu, T.; Li, X.; Luo, Q.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. Cross-immunity in Nile tilapia vaccinated with Streptococcus agalactiae and Streptococcus iniae vaccines. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaraj, S.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Karim, M.M.A.; Saad, M.Z. Elucidating the efficacy of vaccination against vibriosis in lates calcarifer using two recombinant protein vaccines containing the outer membrane protein k (R-ompk) of vibrio alginolyticus and the dna chaperone j (r-dnaj) of vibrio harveyi. Vaccines 2020, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Shaharuddin, N.; Mohd-Adnan, A.; Kua, B.C.; Nathan, S. Expression profile of immune-related genes in Lates calcarifer infected by Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, F.; Gerdol, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Stocchi, V.; Randelli, E.; Belardinelli, M.C.; Miccoli, A.; Saraceni, P.R.; Secombes, C.J.; Scapigliati, G.; et al. Identification, molecular characterization and functional analysis of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-2like (IL-2L) cytokines in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Cytokine 2020, 126, 154898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapigliati, G.; Buonocore, F.; Randelli, E.; Casani, D.; Meloni, S.; Zarletti, G.; Tiberi, M.; Pietretti, D.; Boschi, I.; Manchado, M.; et al. Cellular and molecular immune responses of the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) experimentally infected with betanodavirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bøgwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. Review on immersion vaccines for fish: An update 2019. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Christianus, A.; Ishak, Z.; Syed, M.A.; Courtenay, S.C. The effects of intramuscular and intraperitoneal injections of benzo[a]pyrene on selected biomarkers in Clarias gariepinus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piamsomboon, P.; Tanpichai, P.; Wongtavatchai, J. Enteritis associated with subclinical infection of Streptococcus iniae in juvenile Asian seabass Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790). J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.B.; Vicknair, M.R.; Ostland, V.E.; Nizet, V.; Buchanan, J.T. Evaluation of Streptococcus iniae killed bacterin and live attenuated vaccines in hybrid striped bass through injection and bath immersion. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2010, 89, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasaksiri, K.; Fukuda, K.; Tsubone, S.; Miyadai, H.; Murakami, T.; Murakami, A.; Takano, R. Efficacy of a bivalent inactivated vaccine against red seabream iridovirus and Streptococcus iniae in red seabream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2018, 492, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Múzquiz, J.L.; Royo, F.M.; Ortega, C.; De Blas, I.; Ruiz, I.; Alonso, J.L. Pathogenicity of streptococcosis in rainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mykiss): Dependence on age of diseased fish. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1999, 19, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, F.; Peyghan, R.; Alishahi, M.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Ahangarzadeh, M. Molecular and biochemical investigation of the role of streptococcus iniae in mortality of Lates calcarifer cages culturing in the Persian Gulf. Exp. Anim. Biol. 2021, 9, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, C.S.; Sun, L. A multivalent killed whole-cell vaccine induces effective protection against Edwardsiella tarda and Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Correlates of protective immunity for fish vaccines. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 85, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Cheng, T.C.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. Protective efficacy of four heat-shock proteins as recombinant vaccines against photobacteriosis in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 111, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Cerpa, S.; Maisey, K.; Reyes-López, F.; Toro-Ascuy, D.; Sandino, A.M.; Imarai, M. Fish Cytokines and Immune Response. In New Advances and Contributions to Fish Biology; Türker, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bedekar, M.K.; Kole, S. Fundamentals of Fish Vaccination. In Vaccine Design: Methods and Protocols, Volume 2. Vaccines for Veterinary Diseases; Thomas, S., Ed.; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 147–173. ISBN 978-1-0716-1888-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Liu, C.S.; Sun, L. Construction and comparative study of monovalent and multivalent DNA vaccines against Streptococcus iniae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.S.; Qiu, R.; Sun, L. A divalent DNA vaccine based on Sia10 and OmpU induces cross protection against Streptococcus iniae and Vibrio anguillarum in Japanese flounder. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Cao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Construction and characterization of a DNA vaccine encoding the SagH against Streptococcus iniae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankar, P.; John, K.R.; George, M.R.; Mansoor, M.M.; Kumar, P.M.; Selvamagheswaran, M.; Srinivasan, A.; Veerabhadran, K. Analysis of Immune Gene Expression in Seabass (Lates calcarifer) Immunized with Inactivated Vaccine against Similar Damselfish Virus. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2020, 55, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Silvera, D.; Guardiola, F.A.; Espinosa, C.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Esteban, M.Á.; Cuesta, A. Recombinant nodavirus vaccine produced in bacteria and administered without purification elicits humoral immunity and protects European sea bass against infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhujin, D.; Marana, M.H.; Dalsgaard, I.; Rzgar, J.; Heidi, M.; Asma, K.M.; Per, K.W.; Kurt, B. Immersion vaccines against Yersinia ruckeri infection in rainbow trout: Comparative effects of strain differences. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1937–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Genes | Target | Sequences (5′-3′) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal control | 18S rRNA | F: TGGTTAATTCCGATAACGAACGA R: CGCCACTTGTCCCTCTAAGAA | Wang et al. [28] |
| Innate immune genes | MHC I | F: GGCTGTTTTTGCCGCTCTG R: GTGGACAGGTCTGGATAAAG | Silvaraj et al. [29] |
| MHC II | F: GTTGGATACACTGAGTTTGG R: GTTGGATACACTGAGTTTGG | Mohd-Shaharuddin et al. [30] | |
| CCL4 | F: TCCTCGTCTACTCTGTCTGT R: GACCTGCCACTGTCTTCAGC | Silvaraj et al. [29] | |
| IL-1β | F: ATCTGGAGGTGGTGGACAAA R: AGGGTGCTGATGTTCAAACC | Silvaraj et al. [29] | |
| IL-4/13B | F: TCATGAAGACGCAAATCTGATGT R: CGAGACAGGAGAACTCTTTCACACA | Buonocore et al. [31] | |
| IL-10 | F: CGACCAGCTCAAGAGTGATG R: AGAGGCTGCATGGTTTCTGT | Silvaraj et al. [29] | |
| Adaptive immune genes | IgM | F: GAGCTGCAGAAGGACAGTG R: TCAGACTGGCCTCACAGCT | Scapigliati et al. [32] |
| CD4 | F: GTGATAACGCTGAAGATCGAGCC R: GAGGTGTGTCATCTTCCGTTG | ||
| CD8-α | F: CTAAGATTCGGCAAAATAACTCGA R: GATGAGGAGTAGAAGAGAAGGCC |
| Weeks Post-Vaccination (Bodyweight, g) | Group | Mortality (%) | Infection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Culture | PCR | Total (%) | |||
| 4 (10 0.7) | Vaccine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control | 13/30 (43.33) | 13 | 1 | 14/17 (82.35) | |
| 8 (48 3.5) | Vaccine | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4/30 (13.33) |
| Control | 3/30 (10.00) | 4 | 6 | 10/27 (37.03) | |
| 12 (70 5.8) | Vaccine | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3/30 (10.00) |
| Control | 8/30 (26.66) | 12 | 3 | 15/22 (68.18) | |
| 20 (97 9.4) | Vaccine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control | 12/30 (40.00) | 12 | 2 | 14/18 (77.78) | |
| 28 (130 12.6) | Vaccine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control | 0 | 0 | 9 | 9/30 (30.00) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanpichai, P.; Chaweepack, S.; Senapin, S.; Piamsomboon, P.; Wongtavatchai, J. Immune Activation Following Vaccination of Streptococcus iniae Bacterin in Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790). Vaccines 2023, 11, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020351
Tanpichai P, Chaweepack S, Senapin S, Piamsomboon P, Wongtavatchai J. Immune Activation Following Vaccination of Streptococcus iniae Bacterin in Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790). Vaccines. 2023; 11(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020351
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanpichai, Pornpawit, Surachart Chaweepack, Saengchan Senapin, Patharapol Piamsomboon, and Janenuj Wongtavatchai. 2023. "Immune Activation Following Vaccination of Streptococcus iniae Bacterin in Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790)" Vaccines 11, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020351
APA StyleTanpichai, P., Chaweepack, S., Senapin, S., Piamsomboon, P., & Wongtavatchai, J. (2023). Immune Activation Following Vaccination of Streptococcus iniae Bacterin in Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790). Vaccines, 11(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020351






