Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
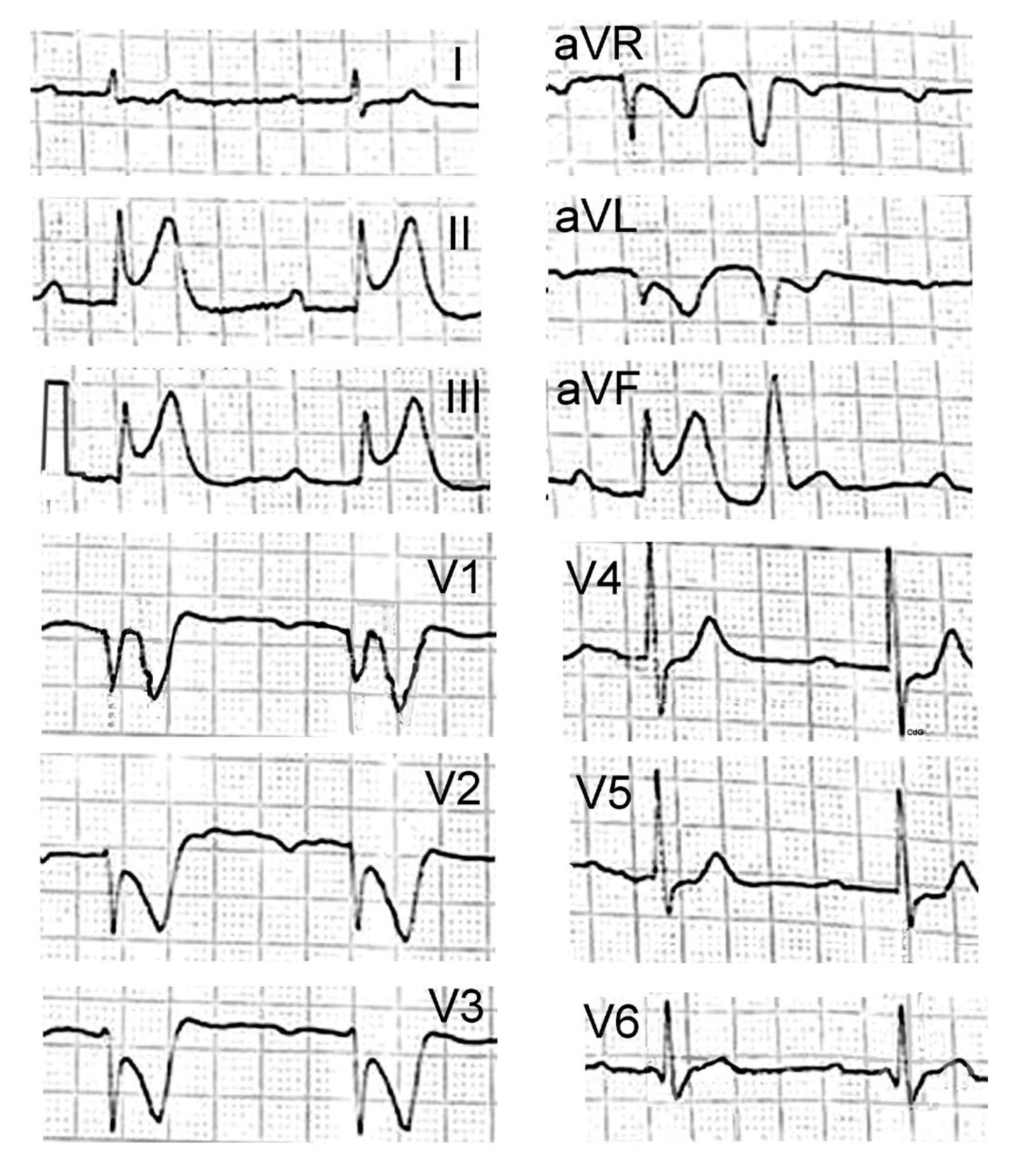
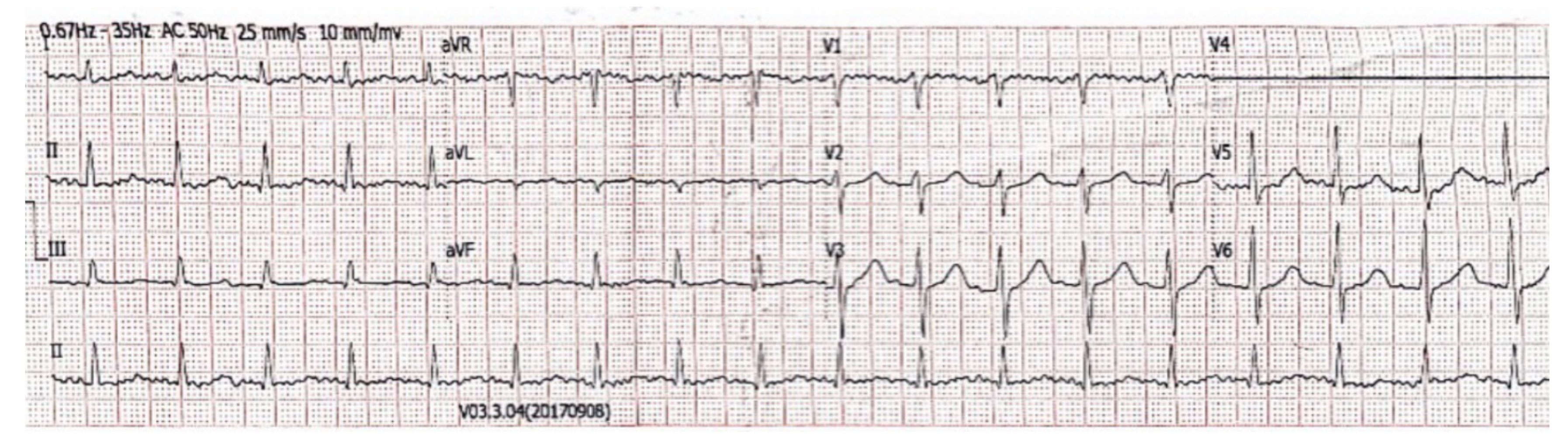
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
3.1. Types and Incidence of Blood Transfusion Reactions
- Allergic transfusion non-hemolytic reactions
- Altered oxygen affinity
- Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions
- Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions
- Delayed serologic transfusion reactions
- Hypotensive transfusion reactions
- Infections
- Post-transfusion purpura
- Transfusion-associated graft vs. host disease
- Transfusion-transmitted infection
- Transfusion-associated dyspnea
- Transfusion-associated circulatory overload
- Transfusion-related acute lung injury
- Metabolic reactions
3.2. Etiology of Platelet Transfusion Induced Allergy Reactions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warburton, K.G.; Chituku, M.; Ballard, K.; Al-Obaidi, M.J. Challenging blood transfusion practice: Effect of targeted behavioural intervention on red cell transfusion in a district general hospital. Future Hosp. J. 2016, 3, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadaksharappa, K.S.; Pillai, H.K.; Mohan, N.T.; Chandrasekhra Rao, A.S. Myocardial infarction following blood transfusion. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1963, 40, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuramoto, K.; Matsushita, S.; Ueda, K.; Mifune, J.; Sakai, M. Reversible myocardial infarction in the aged following blood transfusion. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 1976, 13, 400–405. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Nomura, M.; Nada, T.; Endo, J.; Yukinaka, M.; Saito, K.; Ichikawa, S.; Ito, S.; Nakaya, Y. Ischaemic electrocardiographic changes after massive blood transfusion: Findings based on myocardial scintigraphy using 99mTc-MIBI and 123I-MIBG. Acta Cardiol. 1998, 53, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Velibey, Y.; Erbay, A.; Ozkurt, E.; Usta, E.; Akin, F. Acute myocardial infarction associated with blood transfusion: Case report and literature review. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2014, 50, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadell, L.A. Egyptian Civilization it’s Sumerian Original and Real Chronology; Luzac & Co.: London, UK, 1930; pp. 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Krombach, J.W.; Kampe, S.; Keller, C.A.; Wright, P.M. Pharaoh Menes’ death after an anaphylactic reaction the end of a myth. Allergy 2004, 59, 1234–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.H. Contributions to Medical Research, Dedicated to Victor Clarence Vaughan; George Wahr: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1903; p. 51.
- Auer, J. Lethal cardiac anaphylaxis in the rabbit. J. Exp. Med. 1911, 14, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, E. Serum carditis: Morphologic cardiac alterations in man associated with serum disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1938, 110, 1098–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, G.M.; Brown, C.H. Serum reaction complicated by acute carditis. J. Pediatr. 1940, 17, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, A.R.; Gregory, J.E. Experimental evidence that lesions with basic characteristics of rheumatic carditis can result from anaphylactic hypersensitivity. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1943, 73, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Zavras, G.M. Histamine-induced coronary artery spasm: The concept of allergic angina. Br. J. Clin. Pract. 1991, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zavras, G.M.; Papadaki, P.J.; Kokkinis, C.E.; Kalokairinov, K.; Kouni, S.N.; Batsolaki, M.; Gouvelou-Deligianni, G.V.; Koutsojannis, C. Kounis syndrome secondary to allergic reaction following shellfish ingestion. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2003, 57, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rich, M.W. Is vasospastic angina an inflammatory disease? Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; Velissaris, D.; Tzanis, G.; Hahalis, G. Kounis Syndrome-not a single-organ arterial disorder but a multisystem and multidisciplinary disease. Balkan Med. J. 2019, 36, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; de Gregorio, C. COVID-19 and Kounis Syndrome: Deciphering Their Relationship. Balkan Med. J. 2021, 38, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S. Mast cell tryptase level should be checked in all patients with suspected Kounis syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C. The impact of psychological stress on mast cells. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, S.; Tashiro, N.; Matsubara, T.; Furukawa, S.; Ra, C. A comparison of Fcepsilon RI-mediated RANTES release from human platelets between allergic patients and healthy individuals. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 125 (Suppl. 1), 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, S.; Pawankar, R.; Suzuki, K.; Nakahata, T.; Furukawa, S.; Okumura, K.; Ra, C. Functional expression of the high affinity receptor for IgE (FcepsilonRI) in human platelets and its’ intracellular expression in human megakaryocytes. Blood 1999, 93, 2543–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G. Kounis syndrome: An update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic management. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Trinh, H.K.T.; Park, H.S.; Shin, Y.S. The blocking effect of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor in the mouse model of asthma. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2021, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodfolk, J.A.; Commins, S.P.; Schuyler, A.J.; Erwin, E.A.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Allergens, sources, particles, and molecules: Why do we make IgE responses? Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodnough, L.T. Blood management: Transfusion medicine comes of age. Lancet 2013, 381, 1791–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLisle, J. Is this a blood transfusion reaction? don’t hesitate; check it out. J. Infus. Nurs. 2018, 41, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Usman, M.; Khurshid, M. Acute transfusion reactions encountered in patients at a tertiary care center. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2010, 60, 832–836. [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama, F. Current understanding of allergic transfusion reactions: Incidence, pathogenesis, laboratory tests, prevention and treatment. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzik, W.H. Leukoreduced blood components: Laboratory and clinical aspects. In Principles of Transfusion Medicine; Rossi, E.C., Simon, T.L., Moss, G.S., Gould, S.A., Eds.; Williams &Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1996; pp. 353–373. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, W.J. Allergic Transfusion Reactions. In Transfusion Medicine and Hemostasis: Clinical and Laboratory Aspects, 2nd ed.; Shaz, B.H., Hillyer, C.D., Eds.; Newnes: London, UK, 2013; p. 395. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Gao, A.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Comparison of transfusion reactions in children and adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, L.; Colciago, A.; Castiglioni, S.; Maier, J.A. Platelets in Wound Healing: What Happens in Space? Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 716184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, K.; Ogasawara, M. The Role of Histamine in the Pathophysiology of Asthma and the Clinical Efficacy of Antihistamines in Asthma Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürk, T.; Duerschmied, D.; Müller, T.; Grimm, M.; Reuter, S.; Vieira, R.P.; Ayata, K.; Cicko, S.; Sorichter, S.; Walther, D.J.; et al. Production of serotonin by tryptophan hydroxylase 1 and release via platelets contribute to allergic airway inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.M.; Janssen, L.J. Revisiting the Usefulness of Thromboxane-A2 Modulation in the Treatment of Bronchoconstriction in Asthma. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palgan, K.; Bartuzi, Z. Platelet Activating Factor in Allergies. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idzko, M.; Hammad, H.; van Nimwegen, M.; Kool, M.; Willart, M.A.; Muskens, F.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Luttmann, W.; Ferrari, D.; Di Virgilio, F.; et al. Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, T.; Unno, H.; Morita, H.; Futamura, K.; Emi-Sugie, M.; Arae, K.; Shoda, T.; Okada, N.; Igarashi, A.; Inoue, E.; et al. Platelets constitutively express IL-33 protein and modulate eosinophilic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, M.; Hu, M.; Fu, F.; Ruan, H.; Wu, C. Emerging Roles of Platelets in Allergic Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 846055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Lee, J.; Tao, A. Platelets, Not an Insignificant Player in Development of Allergic Asthma. Cells 2021, 10, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefel, V. Reactions induced by platelet transfusions. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2008, 35, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Byun, J.M.; Kim, I.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, I.S.; Yang, M.S.; Park, H. Successful management of severe allergic reactions to platelet transfusion with omalizumab: A case report. Medicine 2021, 100, e27724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, S.G.; Mallory, D.; Malamut, D.; Eckrich, R. IgA anaphylactic transfusion reactions. Transfus. Med. Rev. 1995, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, E.; Tadokoro, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Niihara, H.; Maeda, I.; Isa, K.; Moriya, S.; Ashida, T.; Mitsunaga, S.; et al. Anaphylactic transfusion reactions in haptoglobin-deficient patients with IgE and IgG haptoglobin antibodies. Transfusion 2002, 42, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.H.; Nguyen, K.D.; Nguyen, C.D.; Truong, B.Q. A Case of Kounis Syndrome Presenting as Coronary Artery Spasm Associated with Acetaminophen Infusion. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e934190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedasingha, S.; Sarathchandra, C.; Weerawansa, P.; Rathnasekara, T.; Karunarathna, S.; Isbister, G.K.; Silva, A. Kounis syndrome following an anaphylactic reaction to antivenom in a patient with Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) bite: A case report. Toxicon 2022, 218, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogos, C.; Sachpekidis, V.; Moschovidis, V.; Styliadis, I.; Kounis, N.G. Kounis Syndrome in a Covid-19 Patient Following Intravenous Administration of Azithromycin. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 32, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liping, Z.; Bin, H.; Qiming, F. An Extraordinary Case Associated with an Allergic Reaction to Clopidogrel: Coronary Artery Spasm or Kounis Syndrome? Heart Lung. Circ. 2015, 24, e180–e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, K.; Kasama, S.; Funada, R.; Katoh, H.; Tsushima, Y. Kounis syndrome induced by contrast media: A case report and review of literature. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2019, 6, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, R.; Mahmoudi, A.; Carrel, G.; Cook, S. Iodinated contrast media induced Kounis syndrome during coronary angiogram: A life-threatening clinical dilemma. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e245047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusnina, W.; Shehata, M.; Abouzid, M.; Price, M.; Zeid, F. Kounis syndrome secondary to gadolinium contrast agent. Baylor Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2019, 32, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga-Gómez, M.; González-Arroyave, D.; Ardila, C.M. Kounis Syndrome Secondary to Laxative Administration. Case Rep. Med. 2022, 2022, 6087176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyankara, W.D.D.; Manoj, E.M.; Gunapala, A.; Ranaweera, A.G.R.M.A.; Vithanage, K.S.; Sivasubramanium, M.; Snajeeva, E. Cardiogenic Shock due to Kounis Syndrome following Cobra Bite. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2019, 2019, 5185716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, T.; Çaltekin, İ.; Gökçen, E.; Savrun, A.; Yaşar, E. Kounis syndrome due to hirudotherapy (leech therapy) in emergency department; a case report. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliola, R.; Secchi, G.; Brunelli, C. A Dangerous Octopus Fishing: Kounis Syndrome Following an Octopus Bite. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 675–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boni, E.; Incorvaia, C. Near-fatal anaphylaxis with Kounis syndrome caused by Argas reflexus bite: A case report. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2020, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwe, E.E.; Sudnik, P.; Dobrovolschi, C.; Krishnamurthy, M. Kounis Syndrome: An Allergic Acute Coronary Syndrome Due to a Bee Sting. Cureus 2022, 14, e26395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, N.; Yıldırım, T. Acute coronary syndrome because of a scorpion sting in a patient with chronic coronary syndrome: A case report and review of the literature. Turk. Kardiyol. Dern. Ars. 2021, 49, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hangouche, A.J.E.; Lamliki, O.; Oukerraj, L.; Dakka, T.; Doghmi, N.; Zarzur, J.; Cherti, M. Kounis syndrome induced by oral intake of aspirin: Case report and literature review. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 30, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, V.; Çelik, O.; Özlek, B.; Özlek, E.; Çil, C.; Başaran, Ö.; Biteker, M. Allergic myocardial infarction: Type I Kounis syndrome following blue crab consumption. Acta Clin. Belg. 2019, 74, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaina, S.; Chrysohoou, C.; Bonfanti, L.; Kounis, N.G.; Cervellin, G.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Tousoulis, D. Anaphylactic cardiovascular collapse manifesting as myocardial infarction following salad consumption. A case of Kounis variant type I syndrome. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-González, M.; Castellano-Martínez, A. Vasoespasmo coronario en un niño alérgico al látex: Síndrome de Kounis (Coronary vasospasm in a child allergic to latex: Kounis syndrome). Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2019, 117, e514–e518. [Google Scholar]
- Marcoux, V.; Nosib, S.; Bi, H.; Brownbridge, B. Intraoperative myocardial infarction: Kounis syndrome provoked by latex allergy. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2012007581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Ihara, M.; Nojima, Y.; Kurimoto, T.; Nanto, S. Kounis syndrome caused by anaphylaxis without skin manifestations after cefazolin administration. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
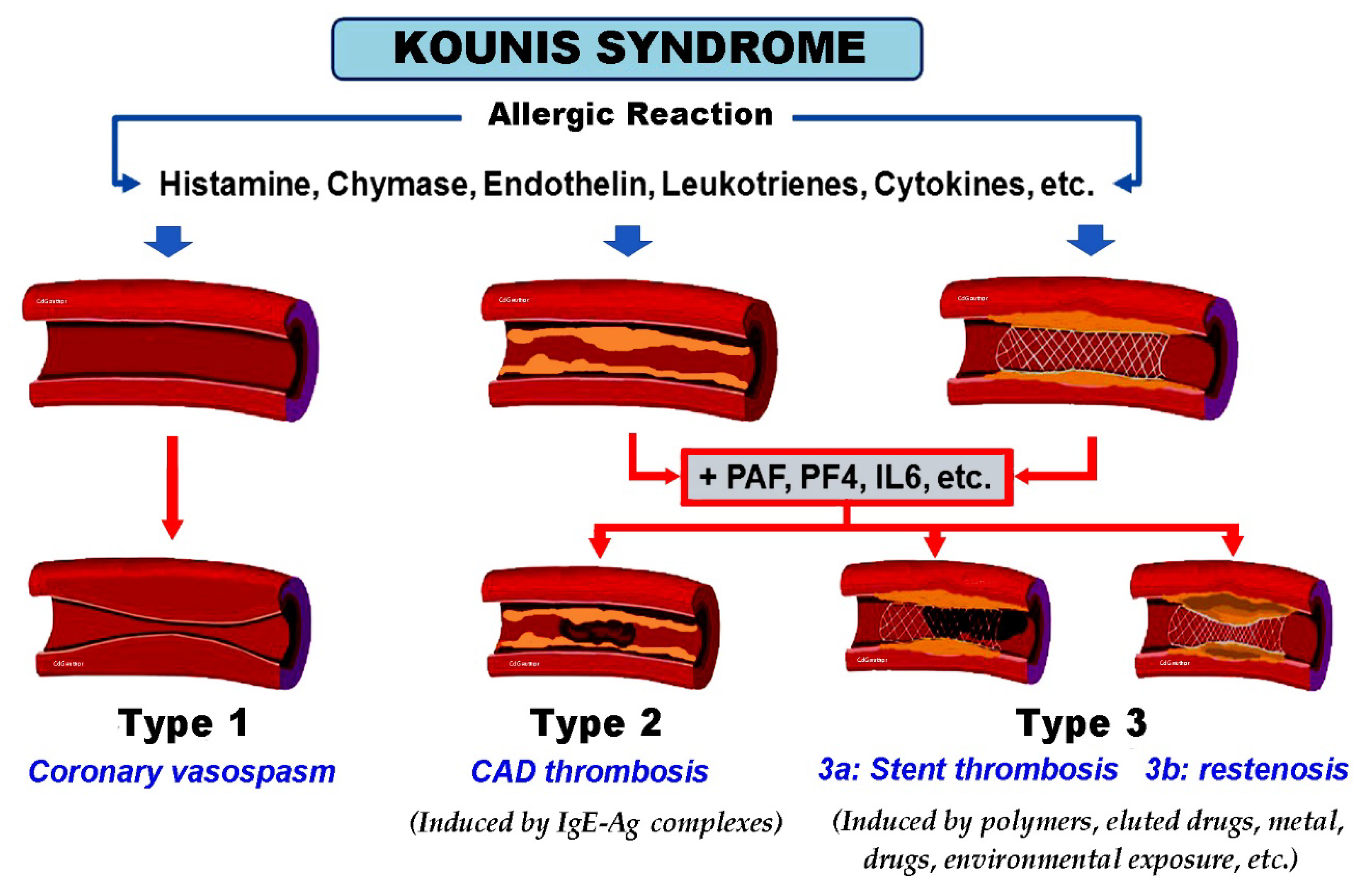
| 1. Antigens crosslinking antigen-specific IgE bound to high affinity FcεR1 (Fragment Crystallizable epsilon Region 1) receptors [17]. |
| 2. Non-IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation via activation of complement C1q, C3a C4, C5a, and Factor B, which are called anaphylatoxins. This pathway involves IL-5 and tryptase and is common in patients who develop renal failure or fatal cerebral events [17]. |
| 3. Low-affinity mas-related G protein-coupled receptor X2 (MRGPRX2) may activate mast cells via non-FcεR1 receptors [18]. |
| 4. Neuropeptides, including the corticotropin-releasing hormone, neurotensin, and substance P via high-affinity receptors during psychological stress conditions [19]. |
| Administrations |
| Acetaminophen Infusion [45] |
| Antivenom administration [46] |
| Azithromycin intravenous administration [47] |
| Clopidogrel administration (drug that treats cardiac ischemia!) [48] |
| Contrast intravenous media [49] |
| Coronary angiogram (iodinated contrast medium) [50] |
| Gadolinium (diagnostic drug for cardiac diseases that contains polyethylene glycol (PEG), an excipient of COVID-19 vaccines) [51] |
| Laxative administration (contains polyethylene glycol (PEG), an excipient of COVID-19 vaccines) [52] |
| Bites and stings |
| Cobra bite (cardiogenic shock) [53] Leech bite therapy [54] |
| Octopus bite [55] |
| Pigeon tick Argas reflexus bite (near-fatal) [56] |
| Bee stings [57] Scorpion sting [58] |
| Consumptions |
| Aspirin consumption [59] |
| Blue crab consumption [60] |
| Salad consumption [61] |
| Latex |
| Latex contact [62] |
| Latex intraoperative [63] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gogos, C.; Stamos, K.; Tsanaxidis, N.; Styliadis, I.; Koniari, I.; Kouni, S.N.; de Gregorio, C.; Kounis, N.G. Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion. Vaccines 2023, 11, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020220
Gogos C, Stamos K, Tsanaxidis N, Styliadis I, Koniari I, Kouni SN, de Gregorio C, Kounis NG. Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion. Vaccines. 2023; 11(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleGogos, Christos, Konstantinos Stamos, Nikolaos Tsanaxidis, Ioannis Styliadis, Ioanna Koniari, Sophia N. Kouni, Cesare de Gregorio, and Nicholas G. Kounis. 2023. "Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion" Vaccines 11, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020220
APA StyleGogos, C., Stamos, K., Tsanaxidis, N., Styliadis, I., Koniari, I., Kouni, S. N., de Gregorio, C., & Kounis, N. G. (2023). Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion. Vaccines, 11(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020220









