COVID-19 Vaccination in Pediatrics: Was It Valuable and Successful?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
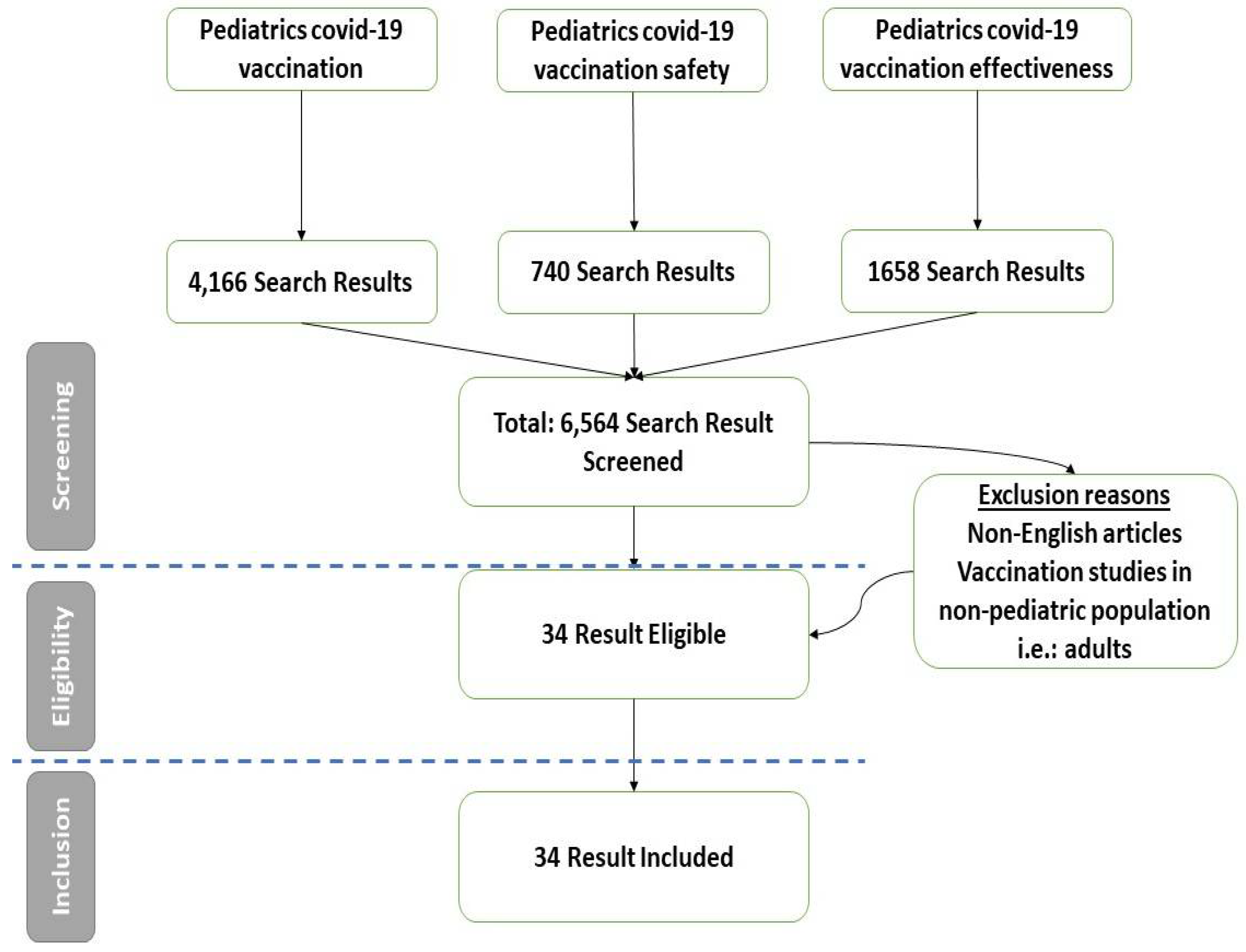
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
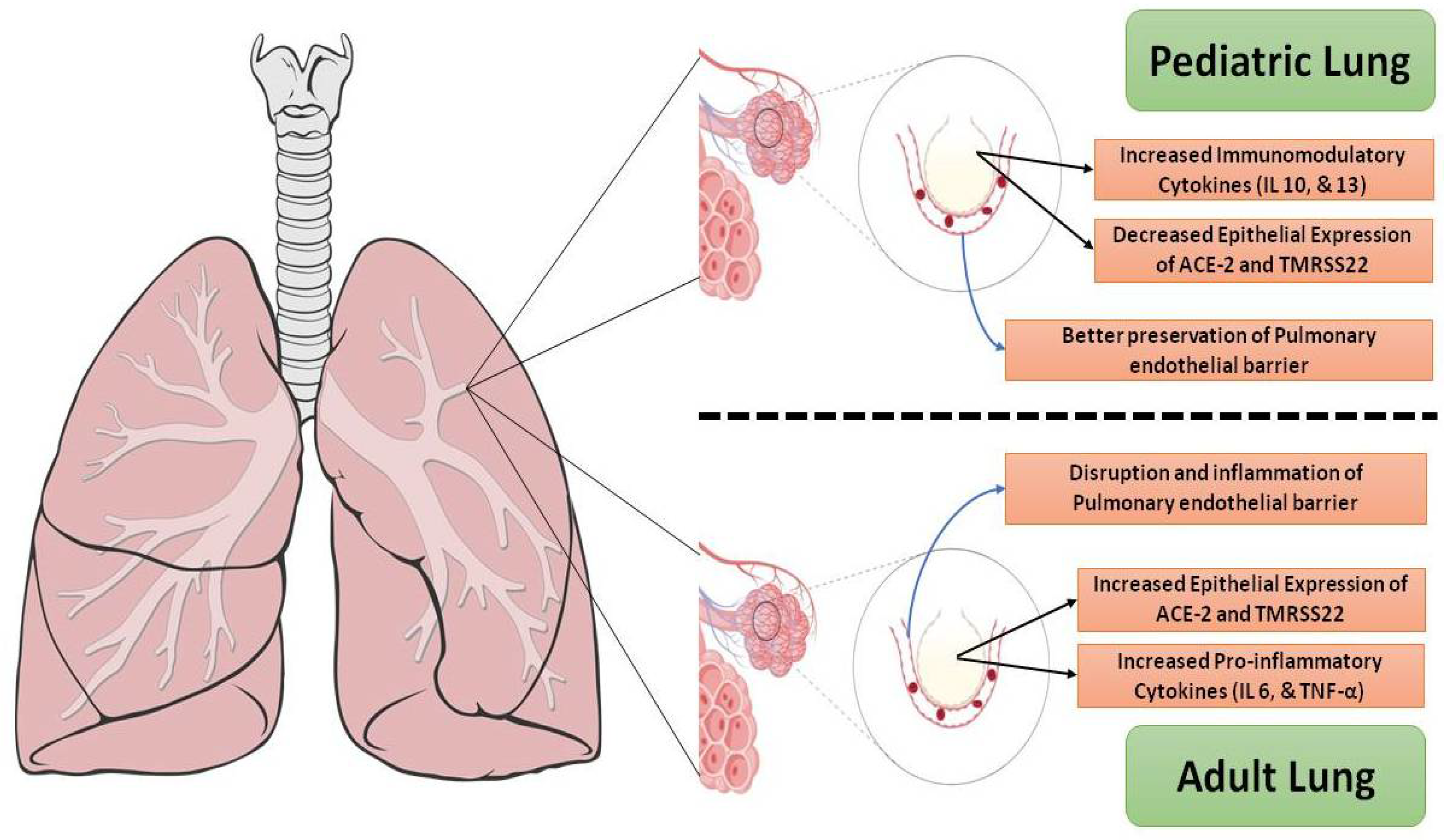
3.1. Disease Incidence, Symptoms, and Complications
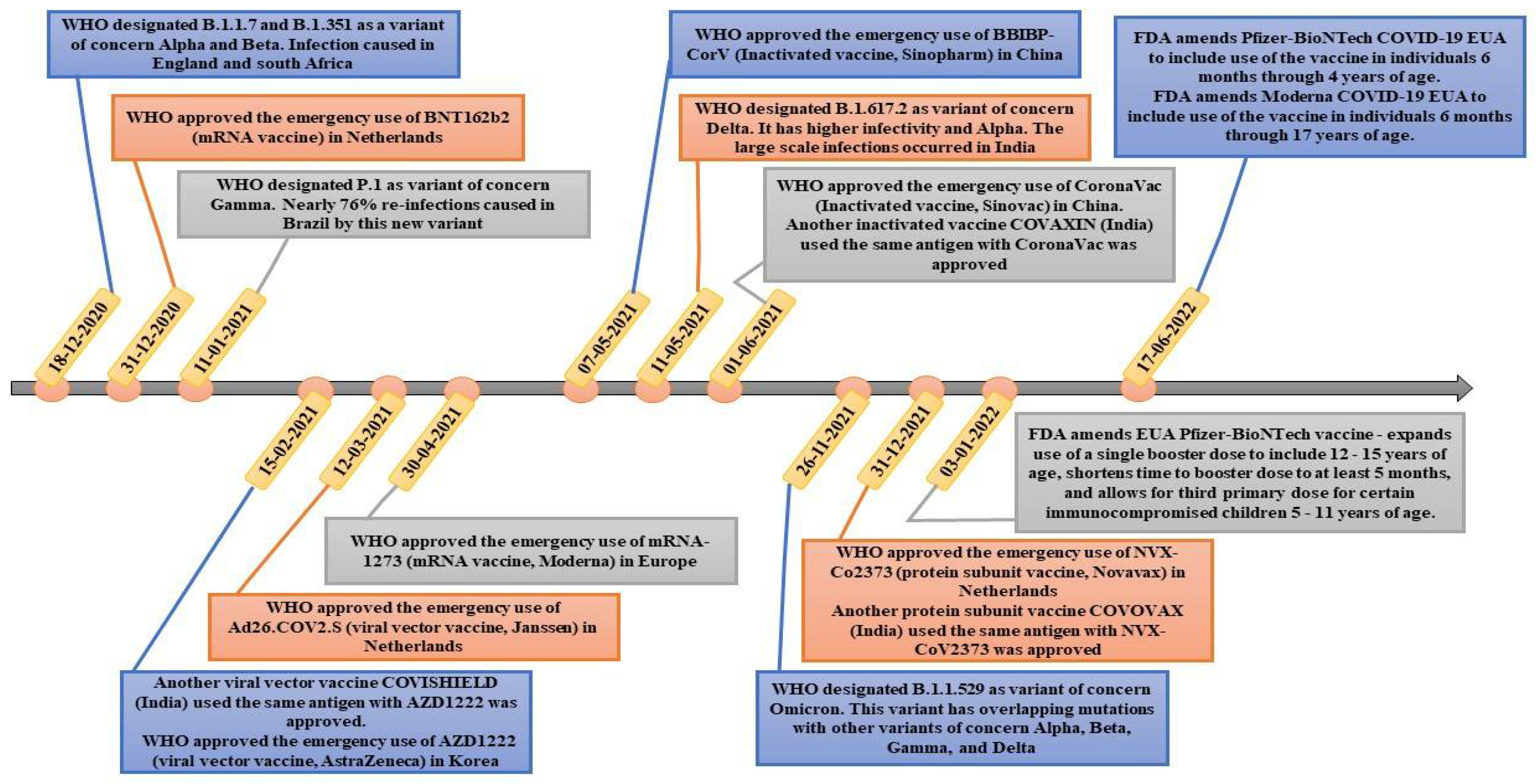
3.2. Different Types of Vaccines
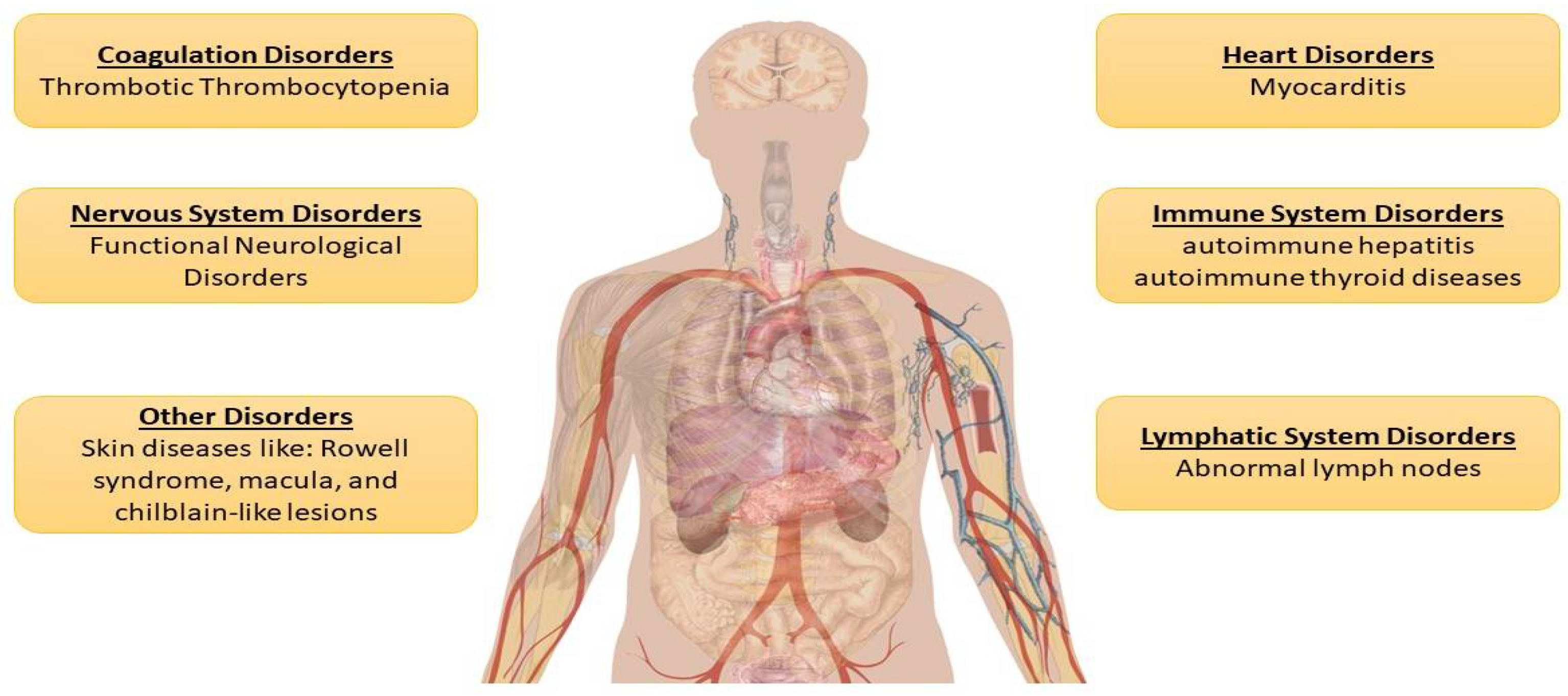
3.3. Post-Vaccination Adverse Reactions
3.4. Were COVID-19 Vaccinations Useful and Successful in Pediatrics?
| Intervention/ Control Groups | Age Range | Follow-Up Duration | Number of Doses and Schedule | Vaccine Name | Vaccine Type | Phase or Study Type | Location | Clinical Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1131 (Intervention) 1129 (Control) | 12–15 years | 4.7 months | 2 doses Days 0 and 21 | BNT162b2 | mRNA vaccine | III | USA | Recipients showed a favorable safety profile and produced stronger immune responses than young adults. The vaccine was highly effective against COVID-19. | [26] |
| 1565 (Intervention) 751 (Control) | 5–11 years | 2.3 months | 2 doses Days 0 and 21 | BNT162b2 | mRNA vaccine | I/II/III | USA, Spain, Finland, and Poland | The vaccine was safe, immunogenic, and efficacious. | [27] |
| 2489 (Intervention) 1243 (Control) | 12–17 years | 4.6 months | 2 doses Days 0 and 28 | mRNA-1273 | mRNA vaccine | II/III | USA | The vaccine showed an acceptable safety profile in adolescents and efficiently prevented COVID-19 | [28] |
| 436 (Intervention) 114 (Control) | 3–17 years | 4.1 months | 2 doses Days 0 and 28 | CoronaVac | Inactivated vaccine | I/II | China | The vaccine was well tolerated and safe and induced humoral responses in children and adolescents. | [29] |
| 755 (Intervention) 252 (Control) | 3–17 years | Not reported | 3 doses Days 0, 28, and 56 | BBIBP-CorV | Inactivated vaccine | I/II | China | The vaccine was safe and well tolerated and elicited robust humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 infection after two doses. | [30] |
| 100 (Intervention) 50 (Control) | 6–17 years | Not reported | 2 doses Days 0 and 56 | Ad5-nCoV | Adenovirus vaccine | IIb | China | A single vaccine dose was safe and induced robust immune responses in children and adolescents. The 56-day booster dose provided limited effect. | [31] |
| 448 (Intervention) 487 (Control) | 12–17 years | 11 months | 3 doses Days 0, 28, and 56 | ZyCov-D | DNA vaccine | III | India | The vaccine was safe, immunogenic, and efficacious. | [32] |
| 468 (Intervention) 156 (Control) | 5–18 years | 6 months | 2 doses Days 0 and 28 | CORBEVAX™ | Protein Sub-unit vaccine | II/III | India | The safety profile of the vaccine in children and adolescents was good. Both humoral and cellular immune responses were comparable to those found in adults. | [33] |
| 118 (Intervention) | 12–18 years | 6 months | 2 doses Days 0, 21, or 42 | BNT162b2 | mRNA vaccine | II | Thailand | Healthy adolescents had good immune responses to the fractional dose regimen of BNT162b2. | [34] |
| 2969 (Intervention) 864 (Control) | 6–11 years | 82 days | 2 doses Days 0 and 28 | mRNA-1273 | mRNA vaccine | II/III | USA, Canada | Two 50 μg doses were safe and effective in inducing immune responses and preventing COVID-19. | [35] |
| 963 (Intervention) | 3–17 years | Short-term follow-up | 2 doses Days 0 and 28 | CoronaVac | Inactivated vaccine | III | Chile | The vaccine was safe and immunogenic against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Neutralizing antibodies were identified against the Delta and Omicron variants. | [36] |
| 39,422 (Test-positive cases) 140,690 (Test-negative controls) | 12–19 years | Short-term follow-up | 2 doses (mRNA vaccine) or 1 dose (Adenovirus vaccine) | BNT162b2, mRNA-1273, and Ad26.COV2.S | mRNA vaccines and Adenovirus vaccine | Test-negative case control | USA | Slightly better protection against the COVID-19 Delta variant than in adults. Booster doses were recommended to enhance time-related mitigated immunization. | [37] |
| 1364 children and adolescents | 5–15 years | Short-term follow-up | 2 doses or 1 dose | BNT162b2 | mRNA vaccine | Prospective cohort study | USA | Two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine were effective in preventing both asymptomatic and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection. | [38] |
3.5. What Are the Risks of COVID-19 Vaccinations in Children and Adolescents?
3.6. Comorbidities and Vaccination Hazards
3.6.1. Children Suffering from the following Allergic Diseases
3.6.2. Children with Asthma
3.6.3. Children with Impaired Immune Function
3.6.4. Children Who Have Been Previously Diagnosed with COVID-19
3.6.5. Children with Cardiovascular Disorders
3.6.6. Children with Renal Disorders
3.6.7. Children with Diabetes
3.7. Children and Vaccine Booster Recommendations
3.8. Readiness of Parents to Vaccinate Themselves and Their Children
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patrucco, F.; Gavelli, F.; Shi, R.; De Vita, N.; Pavot, A.; Castello, L.M.; Ravanini, P.; Balbo, P.E. Coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak. Panminerva Med. 2020, 62, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Progress in COVID-19 pandemic prevention and control. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqfkdt/202111/79103c66c2de404b8e50583816f5e31e.shtml (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Stay Up to Date with COVID-19 Vaccines Including Boosters. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- World Health Organization (WHO). 11 Vaccines Granted Emergency Use Listing (EUL) by WHO. Available online: https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/agency/who/ (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Tian, F.; Yang, R.; Chen, Z. Safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines in children and adolescents: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4644–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Pittet, L.F.; Finn, A.; Pollard, A.J.; Curtis, N. Should children be vaccinated against COVID-19? Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viner, R.M.; Mytton, O.T.; Bonell, C.; Melendez-Torres, G.J.; Ward, J.; Hudson, L.; Waddington, C.; Thomas, J.; Russell, S.; van der Klis, F.; et al. Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adolescents compared with adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezer, H.; Bedir Demirdag, T. Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in children. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.; Whitaker, M.; O’Halloran, A.; Kambhampati, A.; Chai, S.J.; Reingold, A.; Armistead, A.; Kawasaki, B.; Meek, J.; Yousey-Hindes, K.; et al. Hospitalization rates and characteristics of children aged <18 years hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19—COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1-July 25, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, N.S.; Mytton, O.T.; Mullins, E.W.S.; Fowler, T.A.; Falconer, C.L.; Murphy, O.B.; Langenberg, C.; Jayatunga, W.J.P.; Eddy, D.H.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): What do we know about children? A systematic review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, A.J.; Vito, O.; Patel, H.; Seaby, E.G.; Shah, P.; Wilson, C.; Broderick, C.; Nijman, R.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Munblit, D.; et al. Treatment of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.B.F.; Murray, N.; Friedman, K.; Young, C.C.; Newhams, M.M.; Feldstein, L.R.; Loftis, L.L.; Tarquinio, K.M.; Singh, A.R.; Heidemann, S.M.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children—Initial therapy and outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker and Landscape, 23 November 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- COVID-19 Vaccines with WHO Emergency Use Listing. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/vaccines/vaccinescovid-19-vaccine-eul-issued (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Tian, L.; Pang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Huang, T.; Fan, J.; Song, L.; Tong, Y.; Fan, H. COVID-19 vaccine development: Milestones, lessons and prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. C4591001 Clinical Trial Group. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Luo, X.; Shen, Q.; Lei, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, E.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembiński, Ł.; Vieira Martins, M.; Huss, G.; Grossman, Z.; Barak, S.; Magendie, C.; Del Torso, S.; Dornbusch, H.J.; Mazur, A.; Albrecht, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Children and Adolescents-A Joint Statement of the European Academy of Paediatrics and the European Confederation for Primary Care Paediatricians. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 721257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness in Adolescents Aged 12–17 Years and Interim Public Health Considerations for Administration of a Booster Dose. 8 February 2022. Stockholm: ECDC. 2022. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/covid-19-vaccine-effectivenessadolescents-and-interim-considerations-for-booster-dose (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Graff, K.; Smith, C.; Silveira, L.; Jung, S.; Curran-Hays, S.; Jarjour, J.; Carpenter, L.; Pickard, K.; Mattiucci, M.; Fresia, J.; et al. Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e137–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munblit, D.; Simpson, F.; Mabbitt, J.; Dunn-Galvin, A.; Semple, C.; Warner, J.O. Legacy of COVID-19 infection in children: Long-COVID will have a lifelong health/economic impact. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonsenso, D.; Munblit, D.; De Rose, C.; Sinatti, D.; Ricchiuto, A.; Carfi, A.; Valentini, P. Preliminary evidence on long COVID in children. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 2208–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembiński, Ł.; Huss, G.; Radziewicz-Winnicki, I.; Grossman, Z.; Mazur, A.; del Torso, S.; Barak, S.; Sanz, A.C.; Hadjipanayis, A. EAP and ECPCP statement risks for children’s health during the COVID-19 pandemic and a call for maintenance of essential pediatric services. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huss, G.; Magendie, C.; Pettoello-Mantovani, M.; Jaeger-Roman, E. Implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for pediatric primary care practice in Europe. J. Pediatr. 2021, 233, 290–291.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Wang, X.C.; Feng, L.Z.; Xie, Z.D.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, G.; Li, X.W.; Jiang, R.M.; Deng, J.K.; Liu, M.; et al. Expert consensus on COVID-19 vaccination in children. World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Klein, N.P.; Kitchin, N.; Gurtman, A.; Absalon, J.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Walter, E.B.; Senders, S.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 vaccine in adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, E.B.; Talaat, K.R.; Sabharwal, C.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Paulsen, G.C.; Barnett, E.D.; Muñoz, F.M.; Maldonado, Y.; Pahud, B.A.; et al. Evaluation of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 vaccine in children 5 to 11 years of age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Berman, G.; Zhou, H.; Deng, W.; Faughnan, V.; Coronado-Voges, M.; Ding, B.; Dooley, J.; Girard, B.; Hillebrand, W.; et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Lian, X.; Jiao, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy children and adolescents: A double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.Z.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: A randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Jin, P.; Zhu, T.; Wang, W.; Ye, H.; Pan, H.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine with a homologous prime-boost regimen in healthy participants aged 6 years and above: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e783–e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khobragade, A.; Bhate, S.; Ramaiah, V.; Deshpande, S.; Giri, K.; Phophle, H.; Supe, P.; Godara, I.; Revanna, R.; Nagarkar, R.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the DNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (ZyCoV-D): The interim efficacy results of a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in India. Lancet 2022, 399, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuluva, S.; Paradkar, V.; Gunneri, S.; Yerroju, V.; Mogulla, R.R.; Suneetha, P.V.; Turaga, K.; Kyasani, M.; Manoharan, S.K.; Adabala, S.; et al. Safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of Biological E’s CORBEVAX™ vaccine in children and adolescents: A prospective, randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled, phase-2/3 study. Vaccine 2022, 40, 7130–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthanakit, T.; Chantasrisawad, N.; Yoohat, K.; Nantanee, R.; Sophonphan, J.; Meepuksom, T.; Sodsai, P.; Phanthanawiboon, S.; Jantarabenjakul, W.; Hirankarn, N.; et al. Immunogenicity of a Fractional Dose of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine for Primary Series and Booster Vaccination among Healthy Adolescents. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creech, C.B.; Anderson, E.; Berthaud, V.; Yildirim, I.; Atz, A.M.; Melendez Baez, I.; Finkelstein, D.; Pickrell, P.; Kirstein, J.; Yut, C.; et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children 6 to 11 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.A.; Melo-González, F.; Gutierrez-Vera, C.; Schultz, B.M.; Berríos-Rojas, R.V.; Rivera-Pérez, D.; Piña-Iturbe, A.; Hoppe-Elsholz, G.; Duarte, L.F.; Vázquez, Y.; et al. Inactivated Vaccine-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Immunity in Children. mBio 2022, 16, e0131122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, A.; Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Shang, N.; Smith, Z.R.; Dorji, T.; Derado, G.; Accorsi, E.K.; Ajani, U.A.; Miller, J.; Schrag, S.J.; et al. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination With Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Time Since Vaccination and Delta Variant Predominance. JAMA 2022, 327, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowlkes, A.L.; Yoon, S.K.; Lutrick, K.; Gwynn, L.; Burns, J.; Grant, L.; Phillips, A.L.; Ellingson, K.; Ferraris, M.V.; LeClair, L.B.; et al. Effectiveness of 2-Dose BNT162b2 (Pfizer BioNTech) mRNA Vaccine in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Children Aged 5–11 Years and Adolescents Aged 12–15 Years—PROTECT Cohort, July 2021–February 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. 7 Vaccines Approved for Use by WHO. [EB/OL]. (2021-08-17). Available online: https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/agency/who/ (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Transcript of the Press Conference of the Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism of The State Council on June 11, 2021. 2021. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/fkdt/202106/e28487f08ad745c5952356e448a87f13.shtml (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Greish, K.; Alawadhi, A.; Jaradat, A.; Almarabheh, A.; AlMadhi, M.; Jawad, J.; Alsaffar, B.; Alalawi, E.; Alsayyad, A.; Merza, A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of COVID-19 BBIBP-CorV Vaccine in Children 3-12 Years Old. Vaccines 2022, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadrevu, K.M.; Reddy, S.; Jogdand, H.; Ganneru, B.; Mirza, N.; Tripathy, V.N.; Singh, C.; Khalatkar, V.; Prasanth, S.; Rai, S.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (BBV152) in children from 2 to 18 years of age: An open-label, age-de-escalation phase 2/3 study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). The CanSino Biologics Ad5-nCoV-S [recombinant] COVID-19 Vaccine: What You Need to Know. 10 June 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the--cansino-biologics-ad5-ncov-s--recombinant---covid-19-vaccine--what-you-need-to-know (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). The Bharat Biotech BBV152 COVAXIN Vaccine against COVID-19: What You Need to Know. 10 June 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the-bharat-biotech-bbv152-covaxin-vaccine-against-covid-19-what-you-need-to-know (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Fenton, C.; Lamb, Y.N. COVID-19: State of the Vaccination. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2021, 37, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Updated (Bivalent) COVID-19 Vaccines for Children Down to 6 Months of Age. 8 December 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-updated-bivalent-covid-19-vaccines-children-down-6-months (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). The Novavax Vaccine against COVID-19: What You Need to Know. Updated on 28 September 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the-novavax-vaccine-against-covid-19-what-you-need-to-know (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Pandit, T.; Pandit, R.; Goyal, L. Uncommon Side Effects of COVID-19 Vaccination in the Pediatric Population. Cureus 2022, 14, e30276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, M.; Kamińska, H.; Bartoszek, M.; Brzewski, M.; Werner, B. COVID-19-Vaccination-Induced Myocarditis in Teenagers: Case Series with Further Follow-Up. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hause, A.M.; Shay, D.K.; Klein, N.P.; Abara, W.E.; Baggs, J.; Cortese, M.M.; Fireman, B.; Gee, J.; Glanz, J.M.; Goddard, K.; et al. Safety of COVID-19 Vaccination in United States Children Ages 5 to 11 Years. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.H.; Hung, K.F.; Wang, M.L.; Chang, T.J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Chiang, S.H.; Chen, M.F.; Liao, Y.T.; Chiou, S.H.; Yang, D.M. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in children and adolescents: Can immunization prevent hospitalization? J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2022, 85, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hause, A.M.; Baggs, J.; Marquez, P.; Myers, T.R.; Gee, J.; Su, J.R.; Zhang, B.; Thompson, D.; Shimabukuro, T.T.; Shay, D.K. COVID-19 Vaccine Safety in Children Aged 5-11 Years—United States, November 3-December 19, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, N.; Nafissi, N.; Shokri, S.; Fallahpour, M.; Soleimani, S.; Riahi, T.; Kalantari, S.; Javan, A.; Goodarzi, A.; Valizadeh, R. Pediatric and adolescent COVID-19 vaccination side effects: A retrospective cohort study of the Iranian teenage group in 2021. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4890–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Creech, C.B.; Berthaud, V.; Piramzadian, A.; Johnson, K.A.; Zervos, M.; Garner, F.; Griffin, C.; Palanpurwala, K.; Turner, M.; et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 Vaccine in Children 6 Months to 5 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hause, A.M.; Marquez, P.; Zhang, B.; Myers, T.R.; Gee, J.; Su, J.R.; Parker, C.; Thompson, D.; Panchanathan, S.S.; Shimabukuro, T.T.; et al. COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Safety Among Children Aged 6 Months-5 Years—United States, June 18, 2022-August 21, 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, O.; Rizzetto, G.; Molinelli, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Cirioni, O.; D’Errico, M.; Offidani, A. Safety and efficacy of vaccines during COVID-19 pandemic in patients treated with biological drugs in a dermatological setting. Healthcare 2021, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). COVID-19 Vaccines for People Who Are Moderately or Severely Immunocompromised. Updated 22 December 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/immuno.html (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Technical guidelines for vaccination of COVID-19 (version 1). Chin. J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 14, 89–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, O.H.I.; Mui, J.; Chung, C.T.; Radford, D.; Ranjithkumar, S.; Evbayekha, E.; Nam, R.; Pay, L.; Satti, D.I.; Garcia-Zamora, S.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination and carditis in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 111, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Ye, Q. Renal Side Effects of COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.L.; Shenoy, M.; Kalra, P.A.; Chinnadurai, R. Intrinsic Kidney Pathology in Children and Adolescents Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review. Children 2022, 9, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, B.; Pessina, B.; Pezzoli, F.; Casalini, E.; Toni, S. COVID-19 vaccination in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes: Glycemic control and side effects. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Update. Booster Dose of the Pfizer Vaccine for Children 5-11 Years Old. Med. Lett. Drugs Ther. 2022, 64, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, N.P.; Stockwell, M.S.; Demarco, M.; Gaglani, M.; Kharbanda, A.B.; Irving, S.A.; Rao, S.; Grannis, S.J.; Dascomb, K.; Murthy, K.; et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination in Preventing COVID-19-Associated Emergency Department and Urgent Care Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Nonimmunocompromised Children and Adolescents Aged 5-17 Years—VISION Network, 10 States, April 2021-January 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiew, C.J.; Premikha, M.; Chong, C.Y.; Wei, W.E.; Ong, B.; Lye, D.C.; Heng, D.; Lee, V.J.; Tan, K.B. Effectiveness of primary series and booster vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalisation among adolescents aged 12-17 years in Singapore: A national cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, G.X.; Zhao, T.S.; Du, J.; Zhang, W.X.; Xie, M.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; et al. Parents’ willingness to vaccinate themselves and their children with the booster vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A cross-sectional study in Puyang city, China. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.L.; Yang, Y.P.; Mao, H.P.; Hu, W.W.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jiesisibieke, Z.L.; Tung, T.H. Parental hesitancy towards vaccinating their children with a booster dose against COVID-19: Real-world evidence from Taizhou, China. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Vaccine Name/ Manufacturer | Vaccine Type | Date of Approval | Age Group | Protective Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech, USA/Germany) | mRNA vaccine | 14 January 2021 | 6 months to 4 years | 95% |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna, USA) | 3 February 2021 | 6 months to 5 years | 94.1% | |
| Covishield (Serum institute of India, India) | Adenoviral vector vaccine | 1 March 2021 | 18 years and older | 63.09% |
| AZ1222 (AstraZeneca/University of Oxford, UK) | 18 years and older | 63.09% | ||
| Ad26.COV2.S (Johnson & Johnson, USA) | 17 March 2021 | 18 years and older | 66.9% | |
| CONVIDECIA (Ad5-nCoV-S) (CanSino Biologics Inc., China) | 19 May 2022 | 18 years and older | 58 to 92% | |
| BBIBP-CorV (CNBG, China) | Inactivated vaccine | 7 May 2021 | 3 to 12 years | 78.1% |
| CoronaVac (Sinovac, China) | 1 June 2021 | 3 to 17 years | 50.7% | |
| COVAXIN (Bharat Biotech International Ltd., India) | 3 November 2021 | 2 to 18 years | 68 to 93% | |
| Novavax (NVX-CoV2373) (Novavax Inc., USA) | Protein subunit | 20 December 2021 | 12 to 17 years | 80% |
| COVOVAX (Serum institute of India, India) | 17 December 2021 | 12 to 17 years | 86.3 to 89.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raslan, M.A.; Raslan, S.A.; Shehata, E.M.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Sabri, N.A.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Alshammeri, S.; Azevedo, V.; Lundstrom, K.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination in Pediatrics: Was It Valuable and Successful? Vaccines 2023, 11, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020214
Raslan MA, Raslan SA, Shehata EM, Mahmoud AS, Sabri NA, Alzahrani KJ, Alzahrani FM, Alshammeri S, Azevedo V, Lundstrom K, et al. COVID-19 Vaccination in Pediatrics: Was It Valuable and Successful? Vaccines. 2023; 11(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaslan, Mohamed Ahmed, Sara Ahmed Raslan, Eslam Mansour Shehata, Amr Saad Mahmoud, Nagwa A. Sabri, Khalid J. Alzahrani, Fuad M. Alzahrani, Saleh Alshammeri, Vasco Azevedo, Kenneth Lundstrom, and et al. 2023. "COVID-19 Vaccination in Pediatrics: Was It Valuable and Successful?" Vaccines 11, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020214
APA StyleRaslan, M. A., Raslan, S. A., Shehata, E. M., Mahmoud, A. S., Sabri, N. A., Alzahrani, K. J., Alzahrani, F. M., Alshammeri, S., Azevedo, V., Lundstrom, K., & Barh, D. (2023). COVID-19 Vaccination in Pediatrics: Was It Valuable and Successful? Vaccines, 11(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020214









