Dynamics of Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Vaccinees through Multiple Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. RBD and Spike Ectodomain Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. ELISA Detection of Antigen-Specific Antibodies in Serum
2.4. Spike Pseudotyped Virus Production and Neutralization
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Vaccination Induces Durable RBD-Specific Humoral Responses in Serum
3.2. Booster Vaccination Induces IgG4-Switched Ag-Specific Responses in Serum
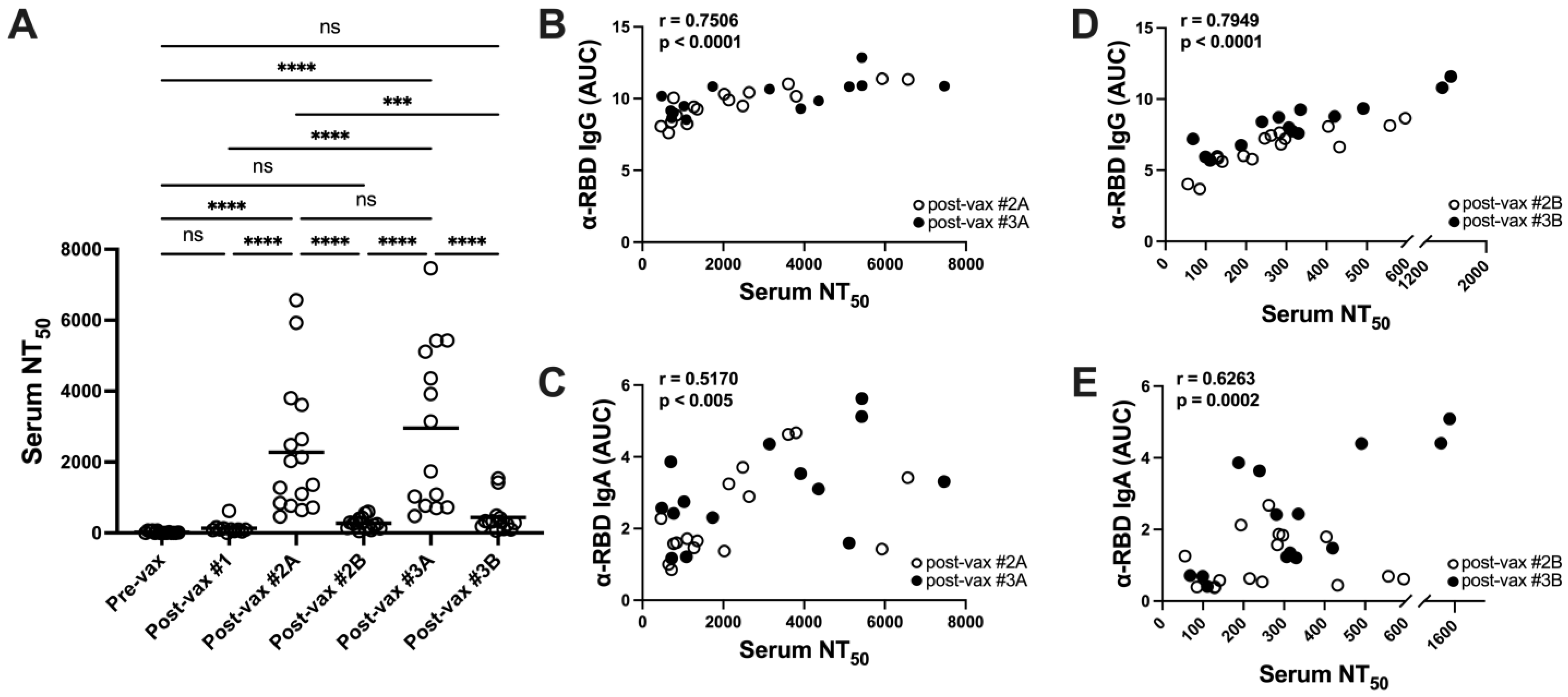
3.3. Vaccination Elicits Potent but Transient Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Serum
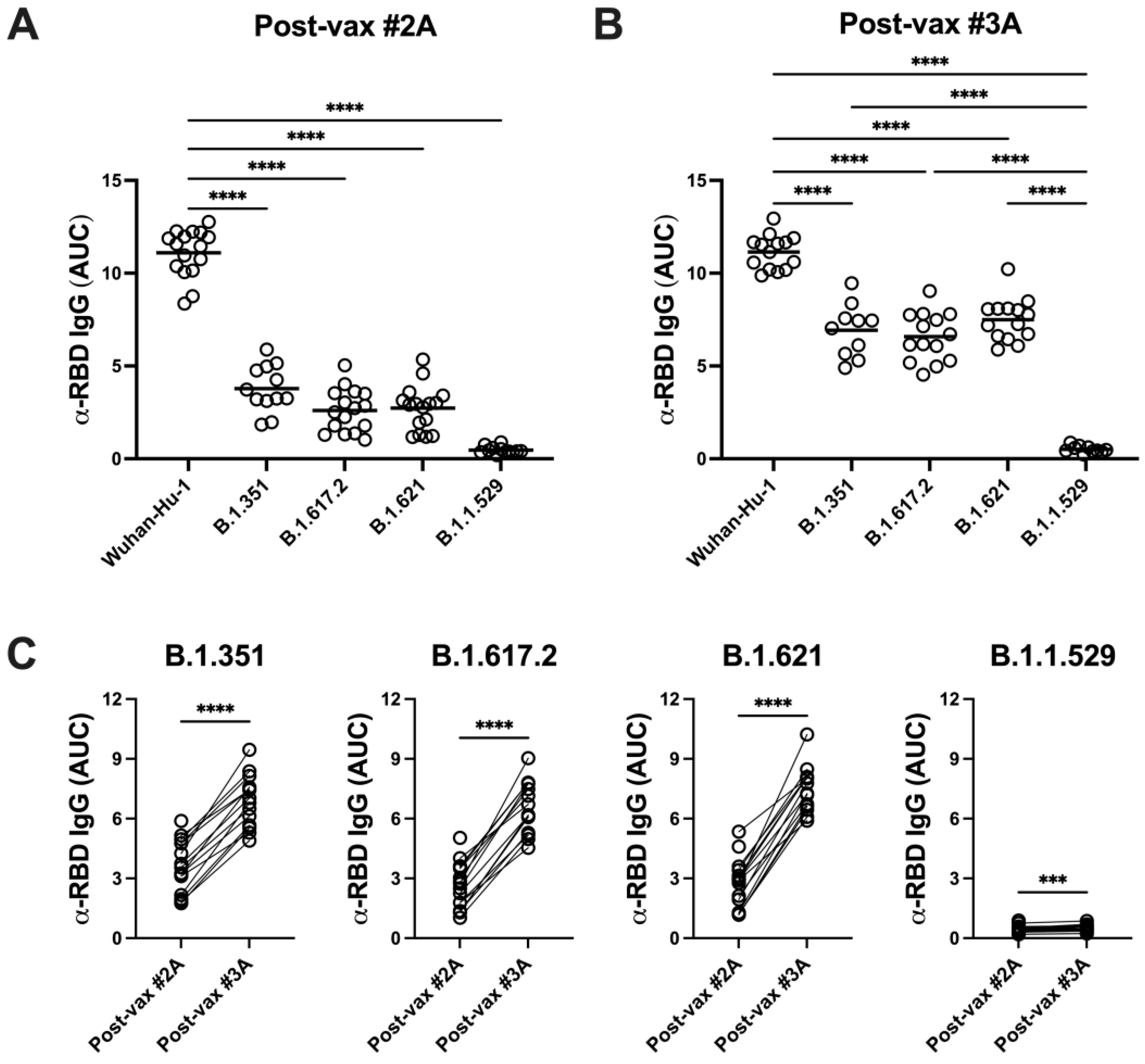
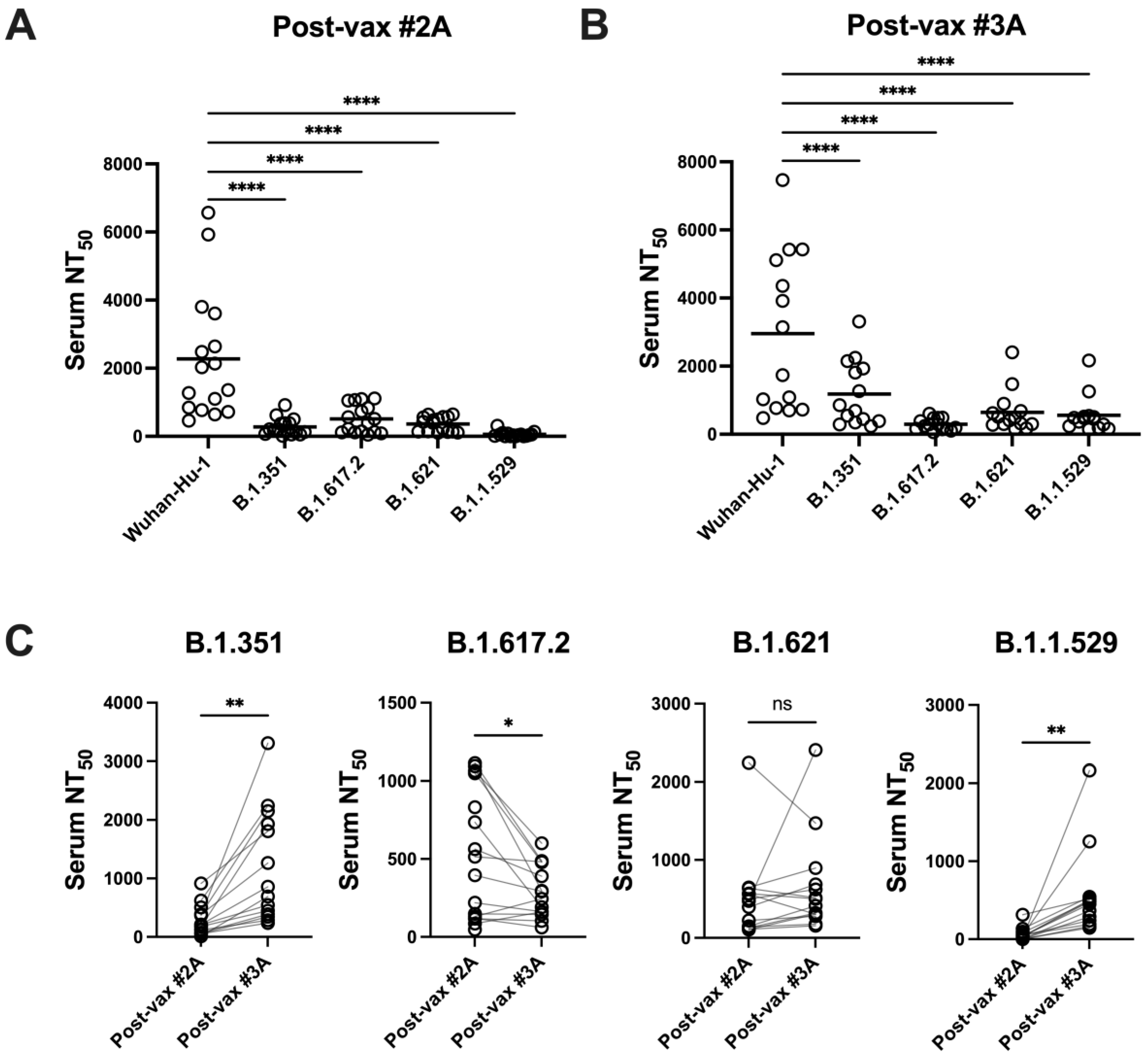
3.4. SARS-CoV-2 Variants Are Resistant to Vaccine-Induced Serum α-RBD Reactivity and Neutralizing Antibody Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson, O.J.; Barnsley, G.; Toor, J.; Hogan, A.B.; Winskill, P.; Ghani, A.C. Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savinkina, A.; Bilinski, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Paltiel, A.D.; Rizvi, Z.; Salomon, J.; Thornhill, T.; Gonsalves, G. Estimating deaths averted and cost per life saved by scaling up mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in low-income and lower-middle-income countries in the COVID-19 Omicron variant era: A modelling study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e061752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development. Nature 2020, 586, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claer, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isho, B.; Abe, K.T.; Zuo, M.; Jamal, A.J.; Rathod, B.; Wang, J.H.; Li, Z.; Chao, G.; Rojas, O.L.; Bang, Y.M.; et al. Persistence of serum and saliva antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 spike antigens in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.G.; et al. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: Results of a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Barnes, C.O.; Finkin, S.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Cipolla, M.; Gaebler, C.; Lieberman, J.A.; et al. mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants. Nature 2021, 592, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Painter, M.M.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Mathew, D.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Lundgreen, K.A.; Reynaldi, A.; Khoury, D.S.; Pattekar, A.; et al. mRNA vaccines induce durable immune memory to SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Science 2021, 374, abm0829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; O’Connell, S.E.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; Talana, C.A.; Lai, L.; Albert, J.; Anderson, E.; Bennett, H.; Corbett, K.S.; et al. Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2021, 373, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, M.; Jawed, A.; Mandal, R.K.; Dailah, H.G.; Janahi, E.M.; Dhama, K.; Somvanshi, P.; Haque, S. Variants of SARS-CoV-2, their effects on infection, transmission and neutralization by vaccine-induced antibodies. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees-Spear, C.; Muir, L.; Griffith, S.A.; Heaney, J.; Aldon, Y.; Snitselaar, J.L.; Thomas, P.; Graham, C.; Seow, J.; Lee, N.; et al. The effect of spike mutations on SARS-CoV-2 neutralization. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, A.P.S.; Janani, L.; Cornelius, V.; Aley, P.K.; Babbage, G.; Baxter, D.; Bula, M.; Cathie, K.; Chatterjee, K.; Dodd, K.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of seven COVID-19 vaccines as a third dose (booster) following two doses of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 or BNT162b2 in the UK (COV-BOOST): A blinded, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2258–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.M.; et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajon, R.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Shen, X.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; McDanal, C.; Feng, W.; Tong, J.; Eaton, A.; Maglinao, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Neutralization after mRNA-1273 Booster Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbel, R.; Hammerman, A.; Sergienko, R.; Friger, M.; Peretz, A.; Netzer, D.; Yaron, S. BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster and Mortality Due to Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesen, M.J.M.; Matson, R.; Puranik, A.; O’Horo, J.C.; Pawlowski, C.; Vachon, C.; Challener, D.; Virk, A.; Swift, M.; Speicher, L.; et al. Third dose vaccination with mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 vaccines improves protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrgang, P.; Gerling, J.; Kocher, K.; Lapuente, D.; Steininger, P.; Habenicht, K.; Wytopil, M.; Beileke, S.; Schafer, S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Class switch toward noninflammatory, spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after repeated SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eade2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhre, J.S.; Pongracz, T.; Kunsting, I.; Lixenfeld, A.S.; Wang, W.; Nouta, J.; Lehrian, S.; Schmelter, F.; Lunding, H.B.; Duhring, L.; et al. mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 induce comparably low long-term IgG Fc galactosylation and sialylation levels but increasing long-term IgG4 responses compared to an adenovirus-based vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1020844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, P.S.; Lai, L.; Samaha, H.; Feng, Y.; Hu, M.; Hui, H.S.; Wali, B.; Ellis, M.; Davis-Gardner, M.E.; Huerta, C.; et al. Durability of immune responses to mRNA booster vaccination against COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e167955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, P.; Faraone, J.N.; Evans, J.P.; Zheng, Y.M.; Yu, L.; Ma, Q.; Carlin, C.; Lozanski, G.; Saif, L.J.; Oltz, E.M.; et al. Durability of Booster mRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 Subvariants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, D.; Bennett, S.J.; Sheehan, J.; Trauth, A.J.; Tso, F.Y.; West, J.T.; Hagensee, M.E.; Ramsay, A.J.; Wood, C. Longitudinal Variations in Antibody Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike Epitopes upon Serial Vaccinations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.J.; Dorfman, T.; Li, W.; Wong, S.K.; Li, Y.; Kuhn, J.H.; Coderre, J.; Vasilieva, N.; Han, Z.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Retroviruses pseudotyped with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein efficiently infect cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10628–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Jia, T.; Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; et al. The Characterization of Disease Severity Associated IgG Subclasses Response in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 632814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.D.; da Costa, H.H.M.; Correa, V.A.; Lima, A.K.d.S.; Lindoso, J.A.L.; De Gaspari, E.; Hong, M.A.; Cunha-Junior, J.P.; Prudencio, C.R. Assessment of avidity related to IgG subclasses in SARS-CoV-2 Brazilian infected patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Dold, C.; Ewer, K.J.; Folegatti, P.M.; Gilbride, C.; Halkerston, R.; Hill, J.; Jenkin, D.; Stockdale, L.; et al. Phase 1/2 trial of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 with a booster dose induces multifunctional antibody responses. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeringa, J.J.; McKenzie, C.I.; Varese, N.; Hew, M.; Bakx, A.; Aui, P.M.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; van Zelm, M.C. Induction of IgG(2) and IgG(4) B-cell memory following sublingual immunotherapy for ryegrass pollen allergy. Allergy 2020, 75, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan-Hammarstrom, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hammarstrom, L. Class switch recombination: A comparison between mouse and human. Adv. Immunol. 2007, 93, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.M.; Walker, B.A.; Wardell, C.P.; Leleu, X.; Davies, F.E.; Morgan, G.J. B-cell malignancies: Capture-sequencing strategies for identification of gene rearrangements and translocations into immunoglobulin gene loci. Blood Lymphat. Cancer 2014, 4, 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, H. Advances in Next-Generation Coronavirus Vaccines in Response to Future Virus Evolution. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, T.; Kennedy, D.A.; Read, A.F.; Gandon, S. Pathogen evolution during vaccination campaigns. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabel, K.G.; Clark, S.A.; Shankar, S.; Pan, J.; Clark, L.E.; Yang, P.; Coscia, A.; McKay, L.G.A.; Varnum, H.H.; Brusic, V.; et al. Structural basis for continued antibody evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Science 2022, 375, eabl6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Guo, S.; Hou, C.; Liao, C.; Shi, L.; Ma, X.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, B.; Fang, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, RBD Mutations, Binding Affinity, and Antibody Escape. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, L.; Dalla Gasperina, D.; Veronesi, G.; Shallak, M.; Ietto, G.; Iovino, D.; Baj, A.; Gianfagna, F.; Maurino, V.; Focosi, D.; et al. Mucosal immune response in BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine recipients. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Israelow, B.; Peña-Hernández, M.A.; Suberi, A.; Zhou, L.; Luyten, S.; Reschke, M.; Dong, H.; Homer, R.J.; Saltzman, M.W.; et al. Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses. Science 2022, 378, eabo2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Sidney, J.; Crotty, S. T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Methot, N.; Yu, E.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Rubiro, P.; Sutherland, A.; Wang, E.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the total CD4+ and CD8+ T cell reactivity in infected or vaccinated individuals. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobano, C.; Santano, R.; Jimenez, A. Immunogenicity and crossreactivity of antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2: Utility and limitations in seroprevalence and immunity studies. Transl. Res. 2021, 232, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walory, J.; Ksiazek, I.; Karynski, M.; Baraniak, A. Twenty-Month Monitoring of Humoral Immune Response to BNT162b2 Vaccine: Antibody Kinetics, Breakthrough Infections, and Adverse Effects. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachmann, N.P.; Miller, J.; Collier, A.Y.; Ventura, J.D.; Yu, J.; Rowe, M.; Bondzie, E.A.; Powers, O.; Surve, N.; Hall, K.; et al. Neutralization Escape by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Iketani, S.; Nair, M.S.; Li, Z.; Mohri, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Bowen, A.D.; Chang, J.Y.; et al. Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5. Nature 2022, 608, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramshaw, I.A.; Ramsay, A.J. The prime-boost strategy: Exciting prospects for improved vaccination. Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.H.; Greenland, M.; Stuart, A.S.V.; Aley, P.K.; Andrews, N.J.; Cameron, J.C.; Charlton, S.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Collins, A.M.; Darton, T.; et al. Persistence of immune response in heterologous COVID vaccination schedules in the Com-COV2 study—A single-blind, randomised trial incorporating mRNA, viral-vector and protein-adjuvant vaccines. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Demographics (n = 16) | Baseline | 1st Vax | 2nd Vax (2A) | 3rd Vax (3A) | 3rd Vax (3B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age|Mean (SD) | 45 (13.6) | - | - | - | - | |
| Sex|Male (Female) | 9 (7) | - | - | - | - | |
| Race|n | W (15), H (1) | - | - | - | - | |
| Vaccination | - | February 2021 | February 2021 | October–December 2021 | - | |
| Sample Collection | May2020–January 2021 | March–April 2021 | March–April 2021 | November 2021 | April 2022 | |
| Antibody | ||||||
| Spike RBD IgG Titer A **, B ****, C ****, D *** | n (%) | |||||
| Below LOD | 13 (81.25%) | 1 (6.25%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Low | 1 (6.25%) | 2 (12.5%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Medium | 2 (12.5%) | 13 (81.25%) | 7 (43.75%) | 0 | 0 | |
| High | 0 | 0 | 9 (56.25%) | 16 (100%) | 16 (100%) | |
| NC IgG Titer | n (%) | |||||
| Below LOD | 12 (75%) | 13 (81.25%) | 12 (75%) | 12 (75%) | 12 (75%) | |
| Low | 4 (25%) | 3 (18.75%) | 3 (18.75%) | 3 (18.75%) | 3 (18.75%) | |
| Medium | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.25%) | 1 (6.25%) | 1 (6.25%) | |
| High | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Neutralization A****, B****, D**** | ||||||
| Serum NT50|mean (SD) | 20.31 (29.14) | 133.33 (166.49) | 2272.11 (1862.06) | 2955.08 (2316.72) | 438.51 (456.66) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheehan, J.; Ardizzone, C.M.; Khanna, M.; Trauth, A.J.; Hagensee, M.E.; Ramsay, A.J. Dynamics of Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Vaccinees through Multiple Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111720
Sheehan J, Ardizzone CM, Khanna M, Trauth AJ, Hagensee ME, Ramsay AJ. Dynamics of Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Vaccinees through Multiple Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine. Vaccines. 2023; 11(11):1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111720
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheehan, Jared, Caleb M. Ardizzone, Mayank Khanna, Amber J. Trauth, Michael E. Hagensee, and Alistair J. Ramsay. 2023. "Dynamics of Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Vaccinees through Multiple Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine" Vaccines 11, no. 11: 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111720
APA StyleSheehan, J., Ardizzone, C. M., Khanna, M., Trauth, A. J., Hagensee, M. E., & Ramsay, A. J. (2023). Dynamics of Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Vaccinees through Multiple Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine. Vaccines, 11(11), 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111720






