A Recombinant Protein XBB.1.5 RBD/Alum/CpG Vaccine Elicits High Neutralizing Antibody Titers against Omicron Subvariants of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Recombinant RBD203-N1 Proteins
2.2. Production of the Five Variant RBD Antigens in Pichia Pastoris X-33
2.3. Vaccine Formulations and Preclinical Study Design
2.4. Serological Antibody Measurements Using ELISA
2.5. Pseudovirus Assay for Determination of Neutralizing Antibodies
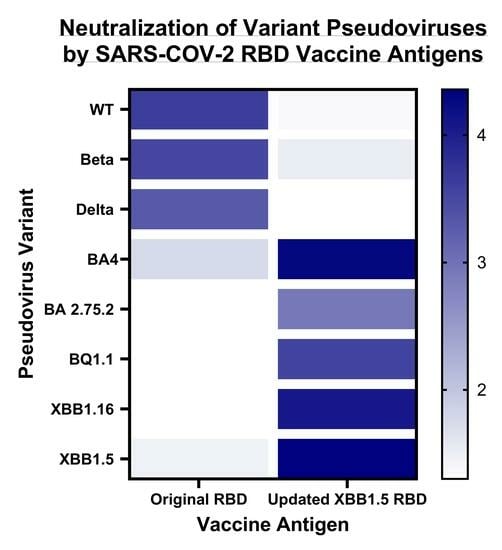
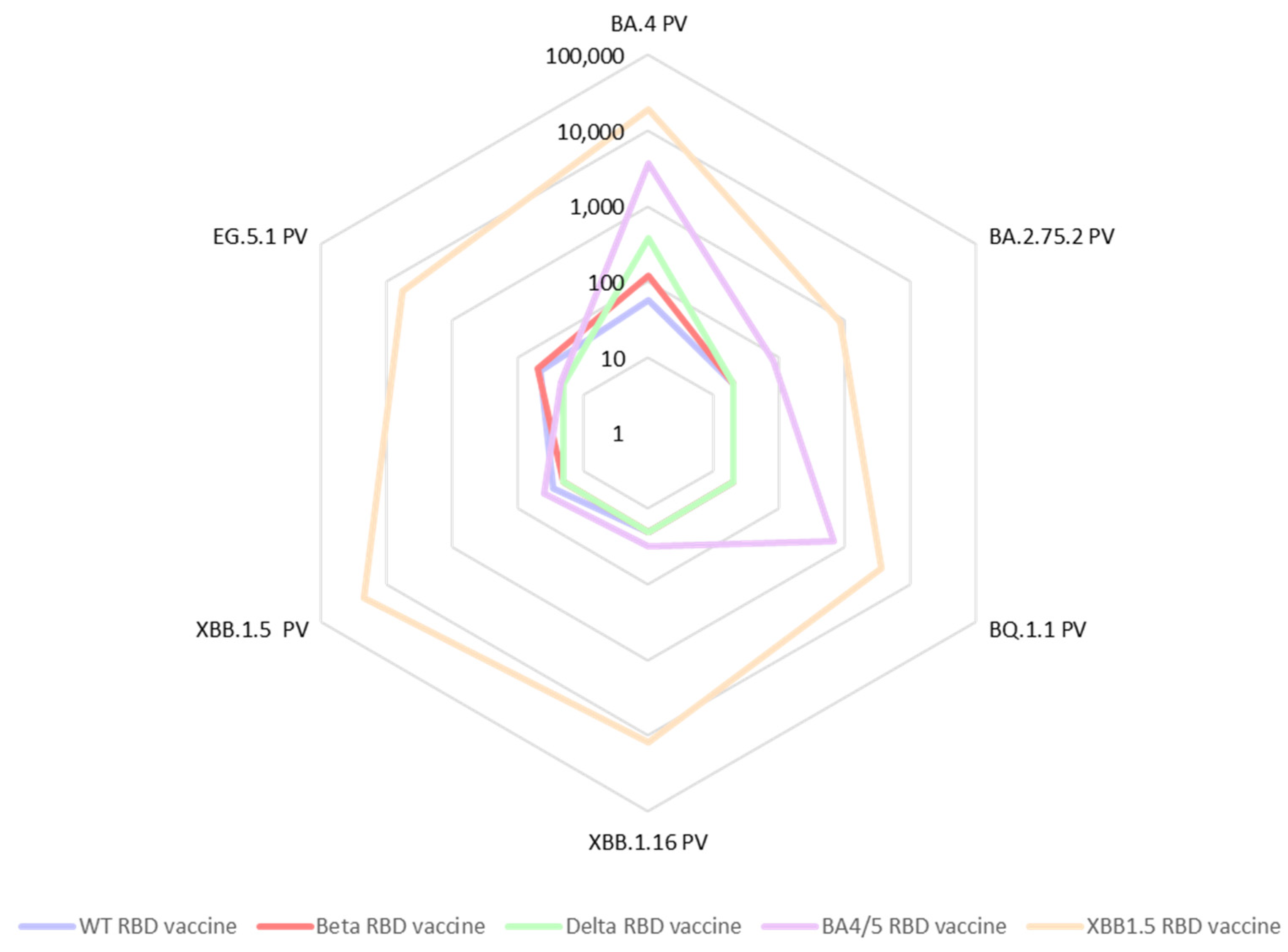
3. Results
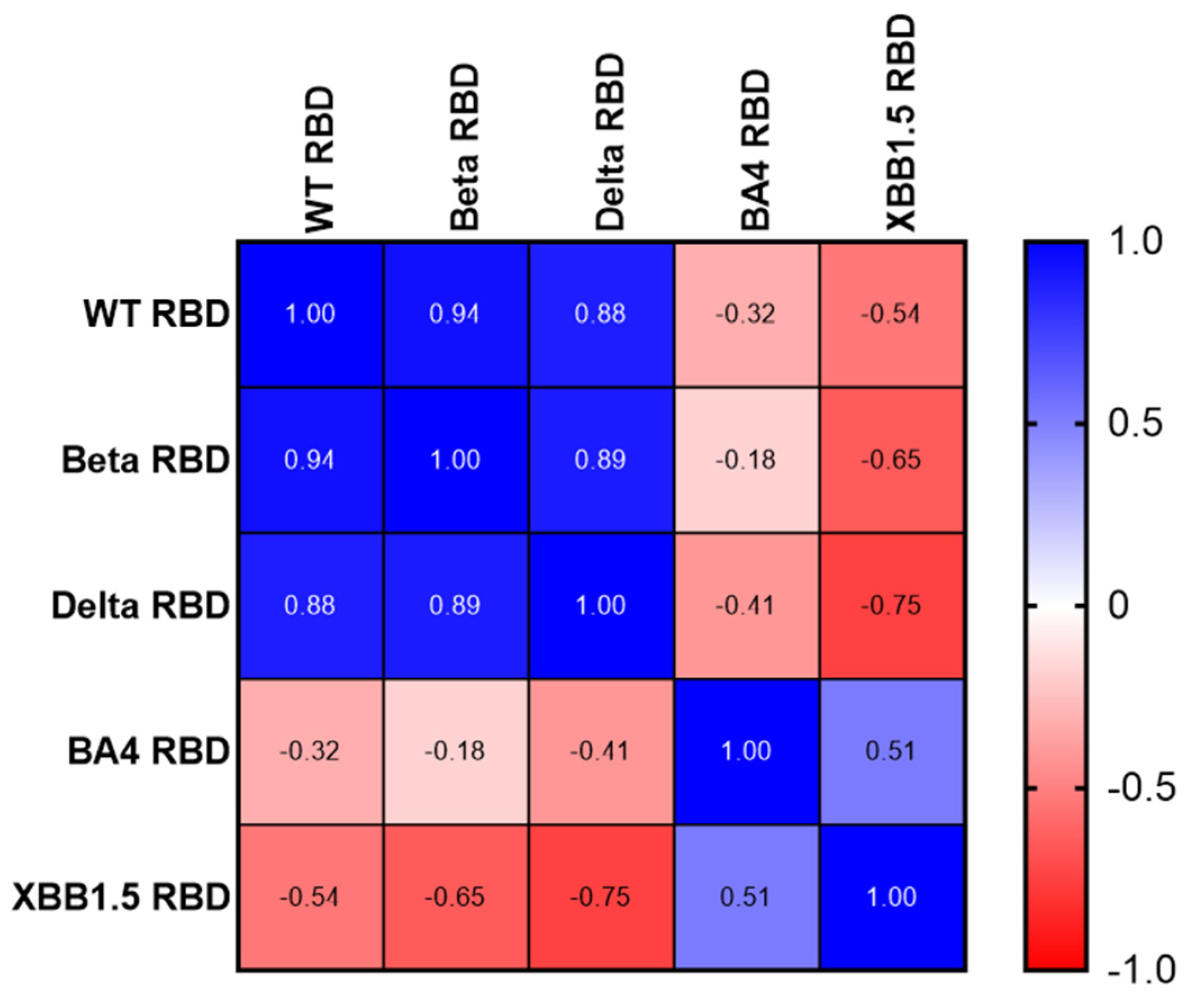
3.1. Expression, Purification, and Characterization of Recombinant Proteins of Different Variants of SARS-CoV-2 RBD203
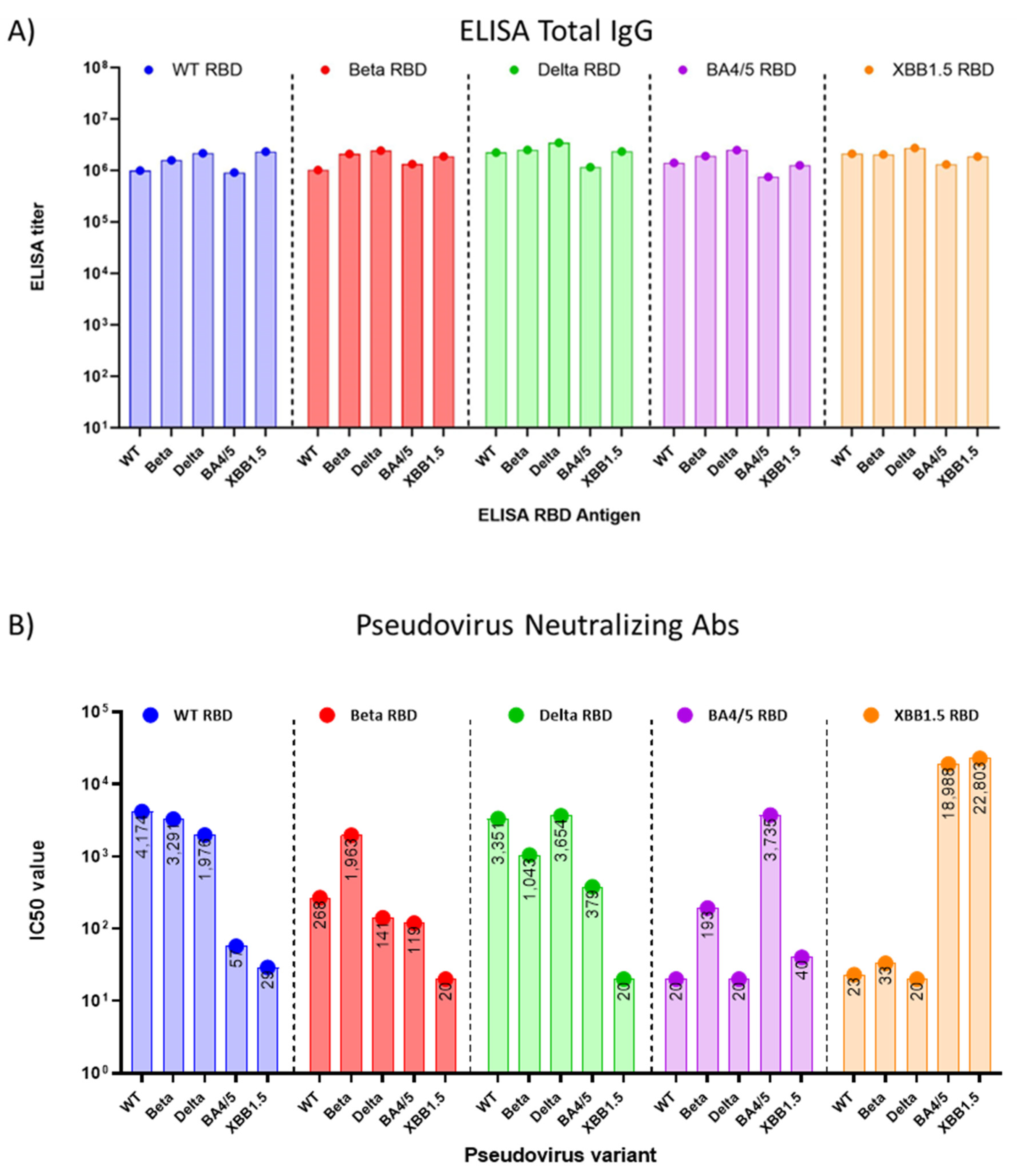
3.2. Immune Response Induced by Adjuvanted RBD Vaccines in Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; Robertson, D.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channabasappa, N.K.; Niranjan, A.K.; Emran, T.B. SARS-CoV-2 variant omicron XBB.1.5: Challenges and prospects–correspondence. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 1054–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardi, V.; Rohaim, M.A.; Naggar, R.F.E.; Atasoy, M.O.; Munir, M. Deep Structural Analysis of Myriads of Omicron Sub-Variants Revealed Hotspot for Vaccine Escape Immunity. Vaccines 2023, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, P.; Faraone, J.N.; Evans, J.P.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Carlin, C.; Anghelina, M.; Stevens, P.; Fernandez, S.; Jones, D.; Panchal, A.R.; et al. Enhanced evasion of neutralizing antibody response by Omicron XBB.1.5, CH.1.1, and CA.3.1 variants. Cell. Rep. 2023, 42, 112443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Alu, A.; Lei, H.; Yang, J.; Hong, W.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Shen, G.; et al. A recombinant spike-XBB.1.5 protein vaccine induces broad-spectrum immune responses against XBB.1.5-included Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. MedComm 2023, 4, e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Duan, M.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, K.; Gao, G.F. Neutralization of BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and XBB with RBD-Dimer Vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1142–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Ito, M.; Kiso, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Uraki, R.; Fukushi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, K.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against Omicron Subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, J.; Strych, U.; Chen, W.-H.; Versteeg, L.; Keegan, B.; Zhan, B.; Wei, J.; Liu, Z.; Lee, J.; Kundu, R.; et al. Receptor-binding domain recombinant protein on alum-CpG induces broad protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Vaccine 2022, 40, 3655–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, J.; Chen, W.-H.; Versteeg, L.; Keegan, B.; Zhan, B.; Wei, J.; Liu, Z.; Lee, J.; Kundu, R.; Adhikari, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RBD219-N1C1: A yeast-expressed SARS-CoV-2 recombinant receptor-binding domain candidate vaccine stimulates virus neutralizing antibodies and T-cell immunity in mice. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, M.; Abid, T.; Ribeiro, S.P.; Edara, V.V.; Floyd, K.; Smith, J.C.; Latif, M.B.; Pacheco-Sanchez, G.; Dutta, D.; Wang, S.; et al. A yeast-expressed RBD-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine formulated with 3M-052-alum adjuvant promotes protective efficacy in non-human primates. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabh3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Adhikari, R.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Gillespie, P.; Islam, N.Y.; Keegan, B.; Kundu, R.T.; Lee, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. From concept to delivery: A yeast-expressed recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccine technology suitable for global access. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2023, 22, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statement on the Antigen Composition of COVID-19 Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/18-05-2023-statement-on-the-antigen-composition-of-covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Lee, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.-H.; Wei, J.; Kundu, R.; Adhikari, R.; Rivera, J.A.; Gillespie, P.M.; Strych, U.; Zhan, B.; et al. Process development and scale-up optimization of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain–based vaccine candidate, RBD219-N1C1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4153–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Pollet, J.; Strych, U.; Lee, J.; Liu, Z.; Kundu, R.T.; Versteeg, L.; Villar, M.J.; Adhikari, R.; Wei, J.; et al. Yeast-expressed recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain RBD203-N1 as a COVID-19 protein vaccine candidate. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 190, 106003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Hao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Nie, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by a pseudotyped virus-based assay. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3699–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannar, D.; Saville, J.W.; Zhu, X.; Srivastava, S.S.; Berezuk, A.M.; Tuttle, K.S.; Marquez, A.C.; Sekirov, I.; Subramaniam, S. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Antibody evasion and cryo-EM structure of spike protein-ACE2 complex. Science 2022, 375, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasoba, D.; Uriu, K.; Plianchaisuk, A.; Kosugi, Y.; Pan, L.; Zahradnik, J.; Ito, J.; Sato, K. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron XBB.1.16 variant. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkias, S.; McGhee, N.; Whatley, J.L.; Essink, B.; Brosz, A.; Tomassini, J.E.; Girard, B.; Wu, K.; Edwards, D.K.; Nasir, A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of XBB.1.5-Containing mRNA Vaccines. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraki, R.; Ito, M.; Furusawa, Y.; Yamayoshi, S.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Adachi, E.; Saito, M.; Koga, M.; Tsutsumi, T.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Humoral immune evasion of the omicron subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hong, W.; Lei, H.; He, C.; Lei, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, T.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; et al. Low levels of neutralizing antibodies against XBB Omicron subvariants after BA.5 infection. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholukh, A.M.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Ford, E.S.; Miner, M.D.; Hou, Y.J.; Tse, L.V.; Kaiser, H.; Zhu, H.; Lu, J.; Madarampalli, B.; et al. Evaluation of Cell-Based and Surrogate SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepler, L.; Rössler, A.; Falch, A.; Volland, A.; Borena, W.; von Laer, D.; Kimpel, J. Comparison of Four SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays. Vaccines 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lusvarghi, S.; Subramanian, R.; Epsi, N.J.; Wang, R.; Goguet, E.; Fries, A.C.; Echegaray, F.; Vassell, R.; Coggins, S.A.; et al. Antigenic cartography of well-characterized human sera shows SARS-CoV-2 neutralization differences based on infection and vaccination history. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1745–1758.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- What to Know About EG.5 (Eris)—The Latest Coronavirus Strain. Yale Medicine. Available online: https://www.yalemedicine.org/news/covid-eg5-eris-latest-coronavirus-strain (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- Parums, D.V. Editorial: A Rapid Global Increase in COVID-19 is Due to the Emergence of the EG.5 (Eris) Subvariant of Omicron SARS-CoV-2. Med. Sci. Monit. 2023, 29, e942244-1–e942244-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

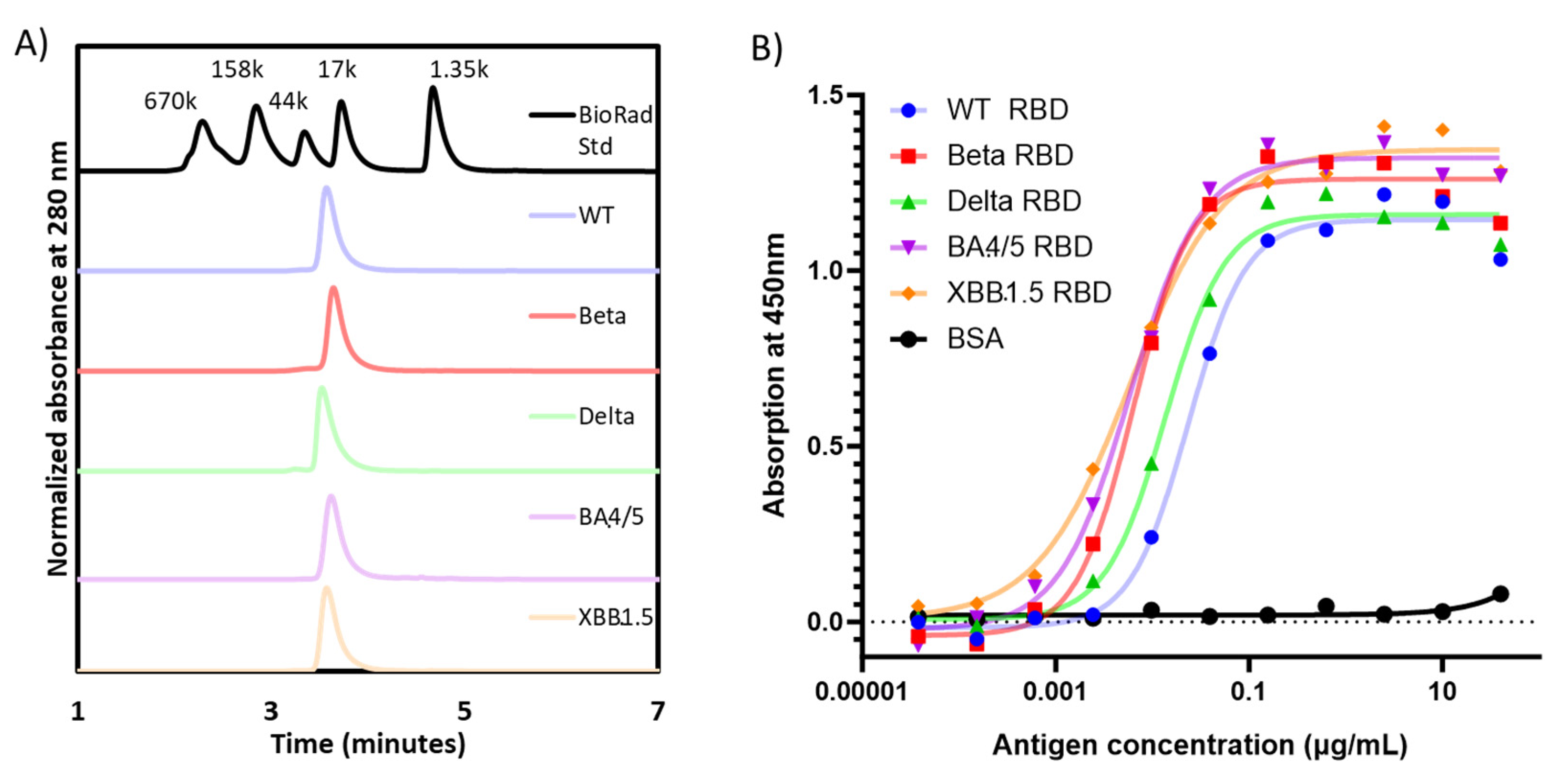
| RBD Variant | Purification Yield [RBD (mg)/Fermentation Supernatant (L)] | SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Blue Staining (Non-Reduced) | Homogeneity via SE-HPLC (%) | Radius via Dynamic Light Scattering (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW (kDa) | Purity (%) | ||||
| WT-RBD | 270.5 | 25.3 | 94.1 | 99.7 | 2.57 ± 0.01 |
| Beta-RBD | 204.3 | 23.8 | 93.2 | 99.7 | 2.63 ± 0.01 |
| Delta-RBD | 294.5 | 25.1 | 93.9 | 98.4 | 2.73 ± 0.02 |
| BA.4/5-RBD | 46.2 | 24.7 | 94.2 | 96.4 | 2.58 ± 0.02 |
| XBB.1.5-RBD | 78.0 | 25.1 | 93.2 | 99.4 | 2.71 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thimmiraju, S.R.; Adhikari, R.; Villar, M.J.; Lee, J.; Liu, Z.; Kundu, R.; Chen, Y.-L.; Sharma, S.; Ghei, K.; Keegan, B.; et al. A Recombinant Protein XBB.1.5 RBD/Alum/CpG Vaccine Elicits High Neutralizing Antibody Titers against Omicron Subvariants of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101557
Thimmiraju SR, Adhikari R, Villar MJ, Lee J, Liu Z, Kundu R, Chen Y-L, Sharma S, Ghei K, Keegan B, et al. A Recombinant Protein XBB.1.5 RBD/Alum/CpG Vaccine Elicits High Neutralizing Antibody Titers against Omicron Subvariants of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines. 2023; 11(10):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101557
Chicago/Turabian StyleThimmiraju, Syamala Rani, Rakesh Adhikari, Maria Jose Villar, Jungsoon Lee, Zhuyun Liu, Rakhi Kundu, Yi-Lin Chen, Suman Sharma, Karm Ghei, Brian Keegan, and et al. 2023. "A Recombinant Protein XBB.1.5 RBD/Alum/CpG Vaccine Elicits High Neutralizing Antibody Titers against Omicron Subvariants of SARS-CoV-2" Vaccines 11, no. 10: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101557
APA StyleThimmiraju, S. R., Adhikari, R., Villar, M. J., Lee, J., Liu, Z., Kundu, R., Chen, Y.-L., Sharma, S., Ghei, K., Keegan, B., Versteeg, L., Gillespie, P. M., Ciciriello, A., Islam, N. Y., Poveda, C., Uzcategui, N., Chen, W.-H., Kimata, J. T., Zhan, B., ... Pollet, J. (2023). A Recombinant Protein XBB.1.5 RBD/Alum/CpG Vaccine Elicits High Neutralizing Antibody Titers against Omicron Subvariants of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines, 11(10), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101557