MDA5 with Complete CARD2 Region Inhibits the Early Replication of H9N2 AIV and Enhances the Immune Response during Vaccination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Strains
2.2. Construction of Expression Vector Containing MDA5 Target Gene
2.3. Cell Infection
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.6. RNA Interference Experiments
2.7. Prokaryotic Expression and Purification of MDA5-1 and MDA5-2 Proteins
2.8. Preparation of Experimental Vaccine
2.9. Chicken Immunization
2.10. Hemagglutination Inhibition Test
2.11. Cell Viability Assay
2.12. Ig Antibody and CD Molecular Detecion
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
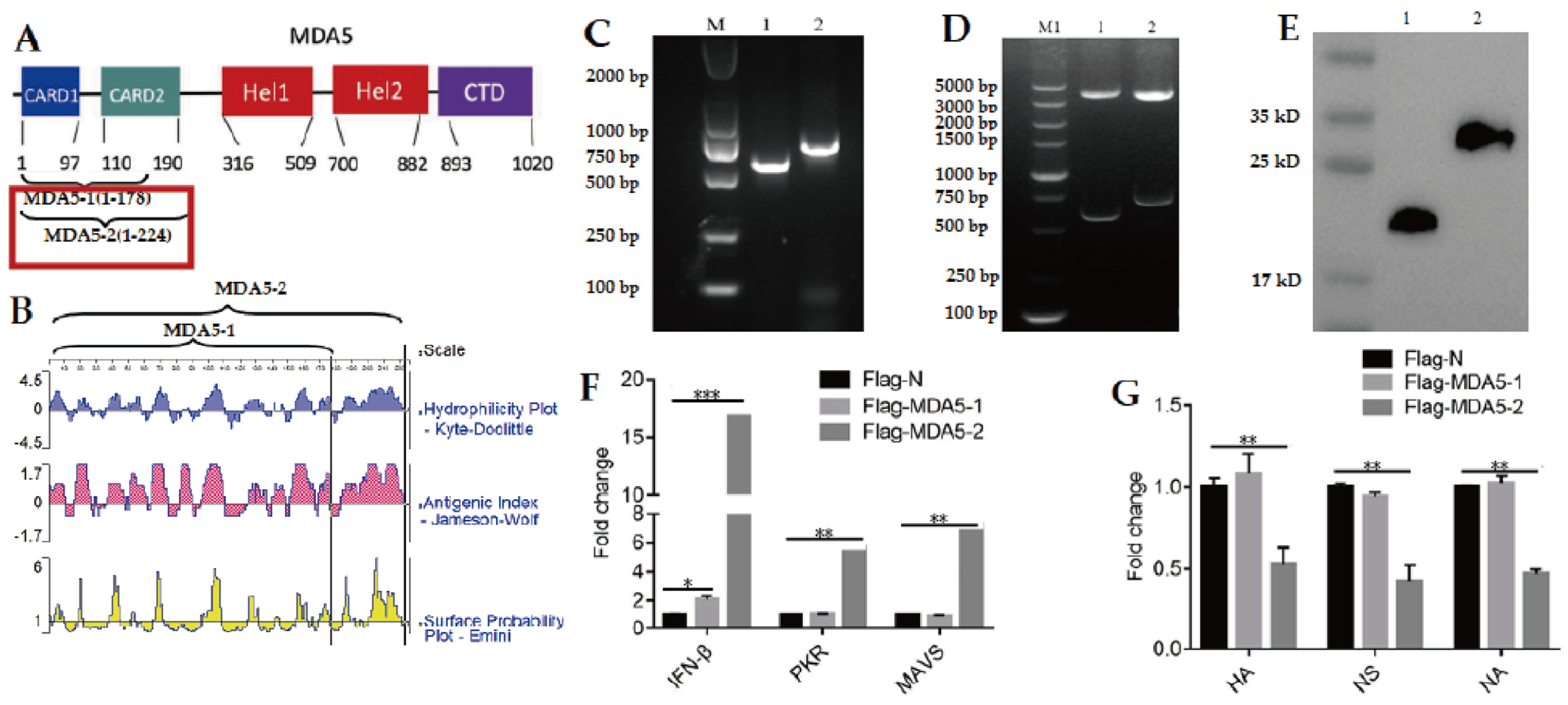
3.1. MDA5-2 Protein with Complete CARD2 Domain Inhibits H9N2 AIV Replication In Vitro
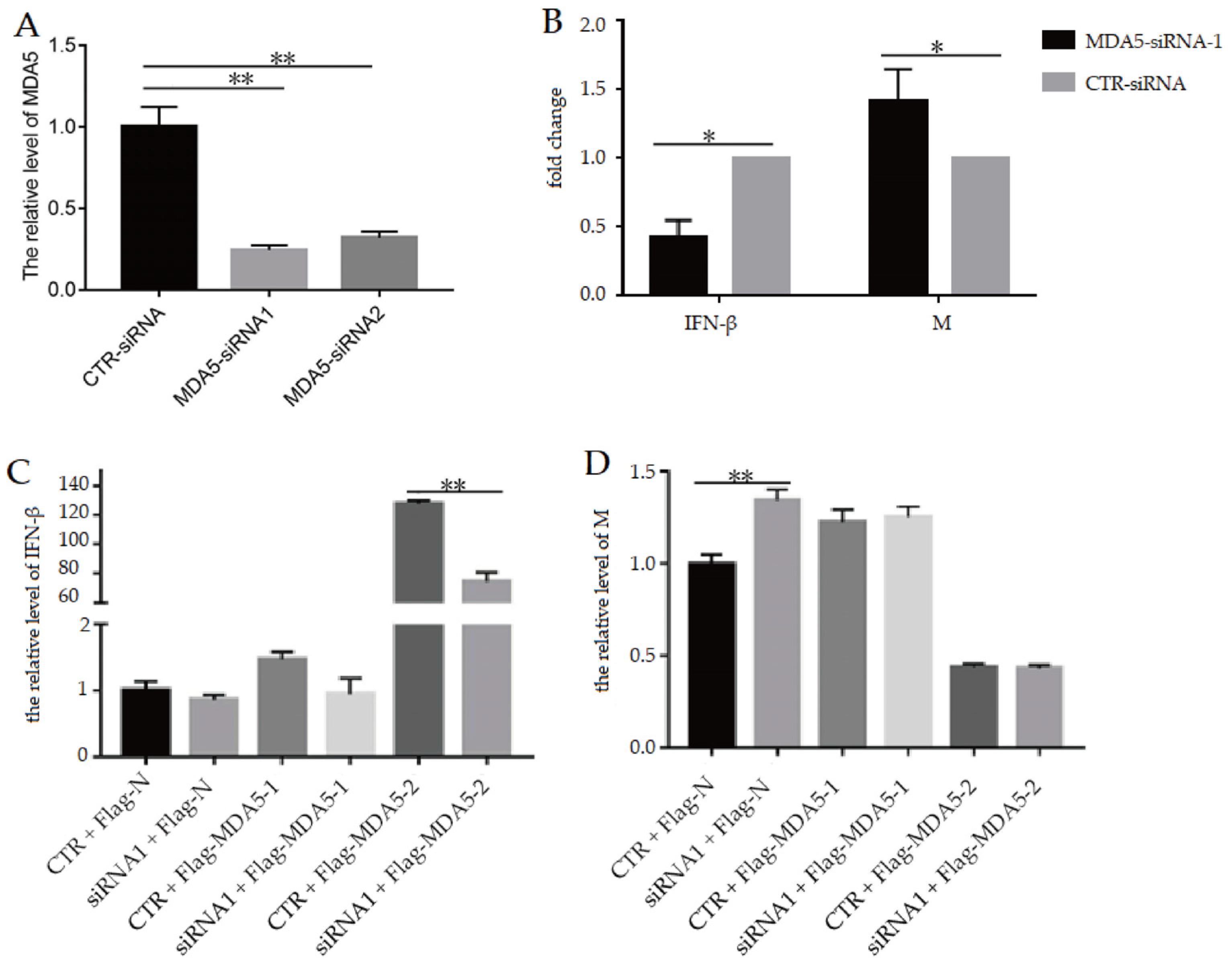
3.2. Knockout of MDA5 Gene Upregulated IFN-β Expression and Downregulated Viral M Gene, and Complementing Flag-MDA5-2 Plasmid Inhibited Replication of H9N2 Virus
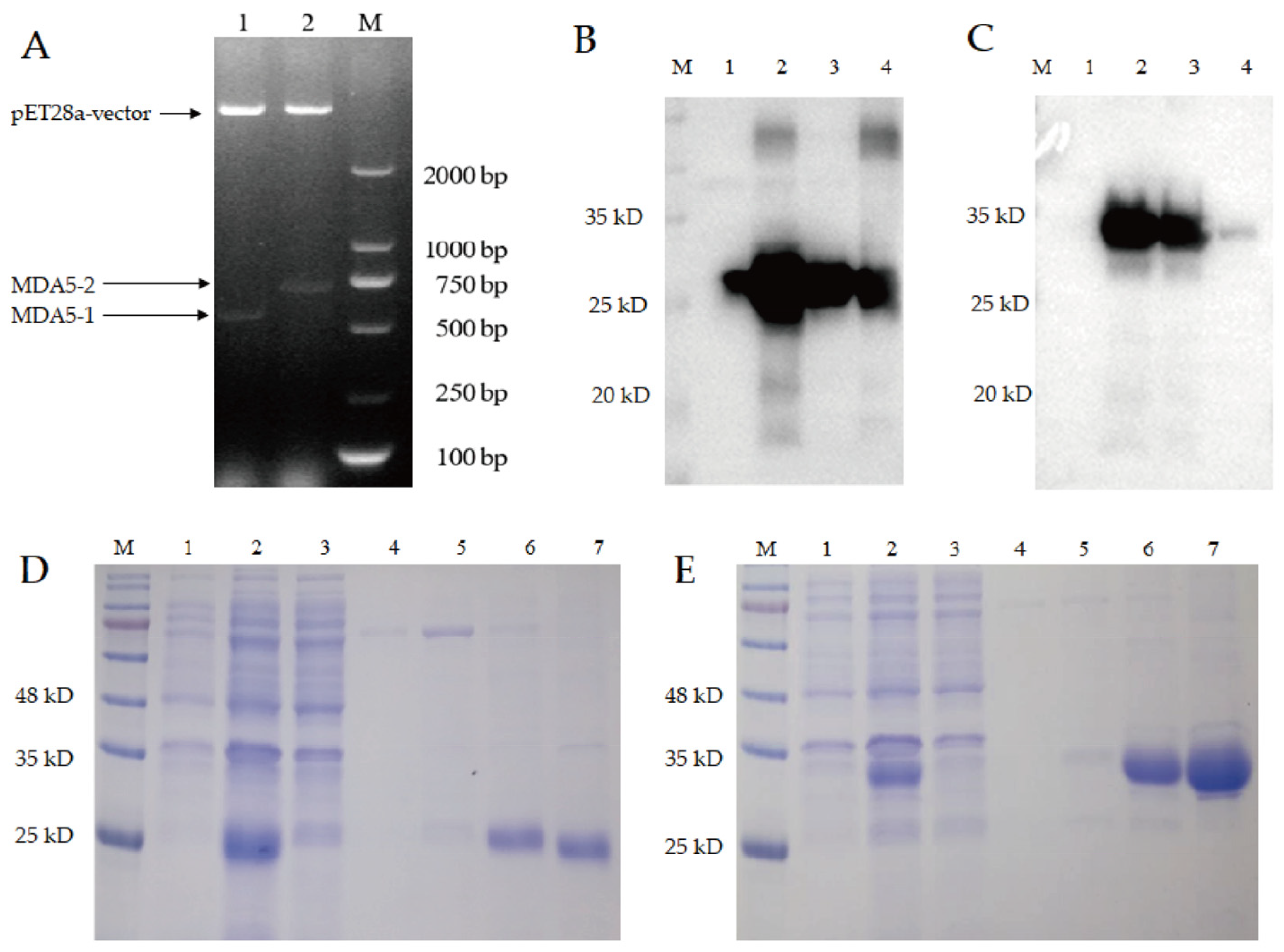
3.3. The Prokaryotic Expression and Purification of MDA5-1 and MDA5-2 Proteins
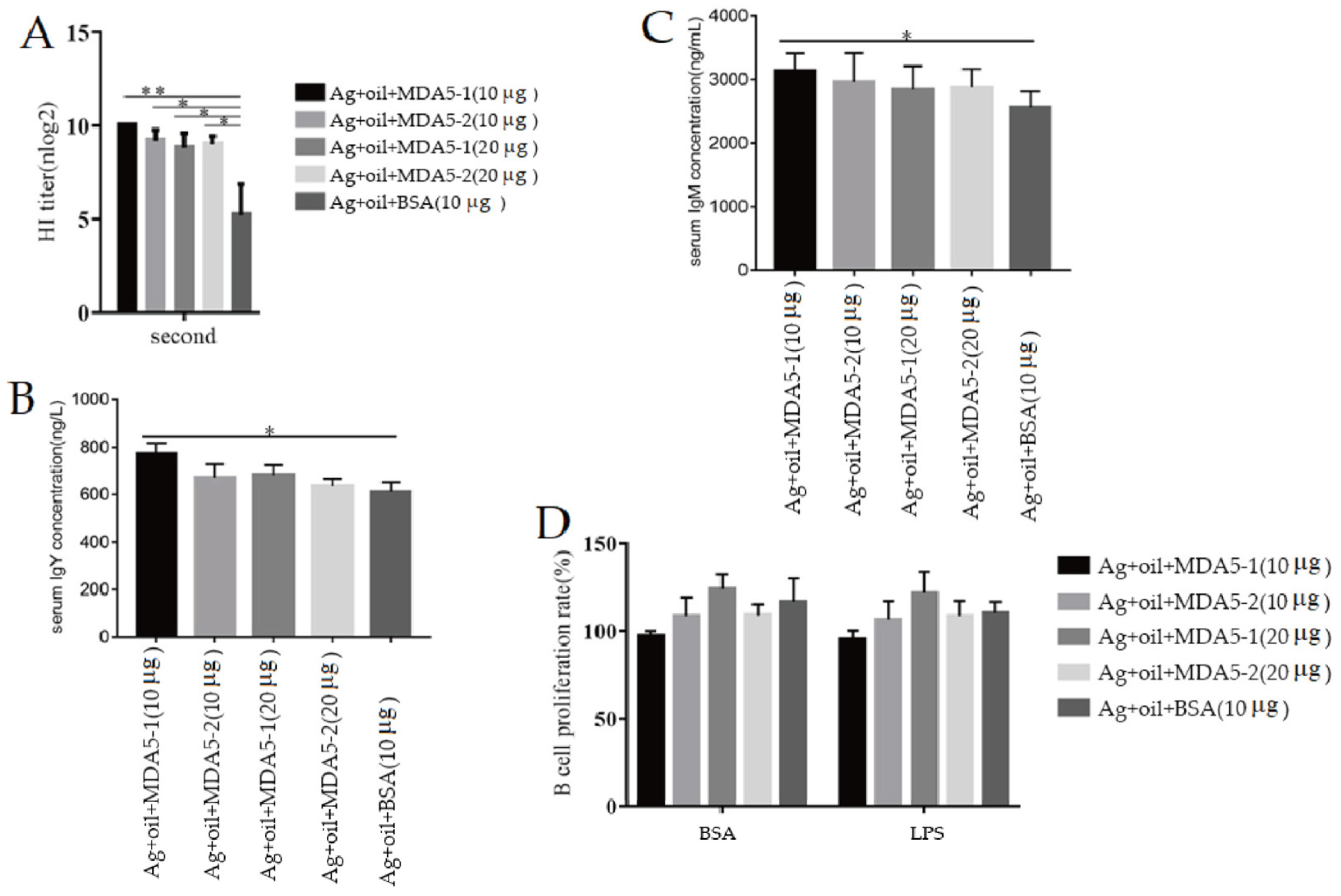
3.4. MDA5 Protein with Complete CARD2 Domain Induced Strong Antibody Production in the Immunized Chickens
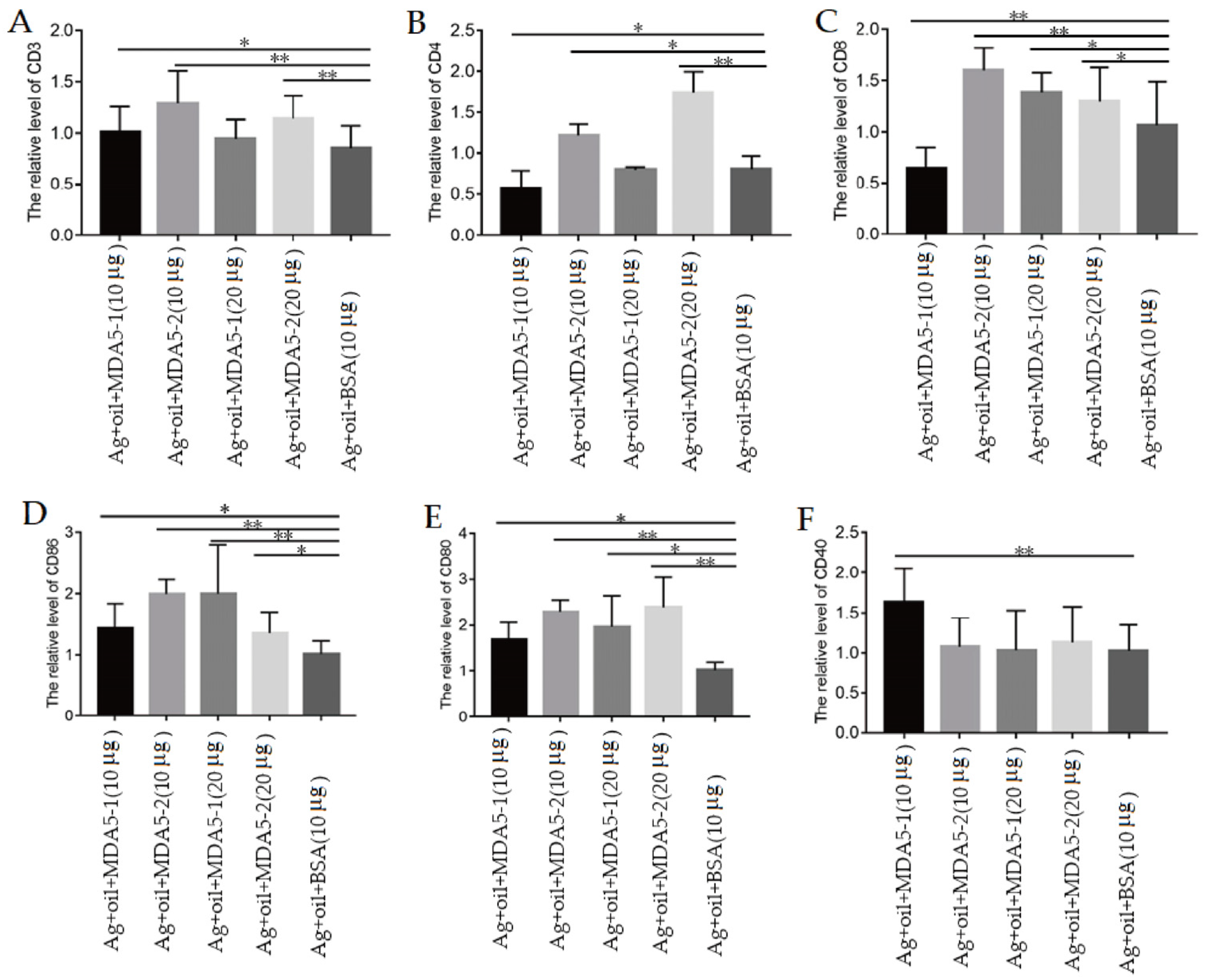
3.5. MDA5 Protein with CARD2 Domain Induced the Increased Expression of Surface Molecules on Lymphocytes during Immunization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1143, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisse, M.; Ly, H. Comparative Structure and Function Analysis of the RIG-I-Like Receptors: RIG-I and MDA5. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, F.; Tan, E.Y.J.; Lei, Y.X.; Song, N.; Han, Y.Q.; Pascal, B.D.; Griffin, P.R.; et al. Ordered assembly of the cytosolic RNA-sensing MDA5-MAVS signaling complex via binding to unanchored K63-linked poly-ubiquitin chains. Immunity 2021, 54, 2218–2230.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgnaoui, S.M.; Paz, S.; Hiscott, J. Orchestrating the interferon antiviral response through the mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS) adapter. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNab, F.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Sher, A.; Wack, A.; O’Garra, A. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzalli, M.H.; Kagan, J.C. Apoptosis and Necroptosis as Host Defense Strategies to Prevent Viral Infection. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweibenz, B.D.; Solotchi, M.; Hanpude, P.; Devarkar, S.C.; Patel, S.S. RIG-I recognizes metabolite-capped RNAs as signaling ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 8102–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Qu, K.; Modis, Y. Cryo-EM Structures of MDA5-dsRNA Filaments at Different Stages of ATP Hydrolysis. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.R.; Aldridge, J.R., Jr.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Association of RIG-I with innate immunity of ducks to influenza. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5913–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liniger, M.; Summerfield, A.; Zimmer, G.; McCullough, K.C.; Ruggli, N. Chicken Cells Sense Influenza A Virus Infection through MDA5 and CARDIF Signaling Involving LGP2. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpala, A.J.; Stewart, C.; McKay, J.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Bean, A.G. Characterization of chicken Mda5 activity: Regulation of IFN-beta in the absence of RIG-I functionality. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5397–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, R.L.; Sher, A.; Seder, R.A. Vaccine adjuvants: Putting innate immunity to work. Immunity 2010, 33, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Suresh, M. Vaccine adjuvants to engage the cross-presentation pathway. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 940047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Wimmers, F.; Pulendran, B. Epigenetic adjuvants: Durable reprogramming of the innate immune systemsy with adjuvants. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2022, 77, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohto, U. Activation and regulation mechanisms of NOD-like receptors based on structural biology. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 953530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicherska-Pawlowska, K.; Wrobel, T.; Rybka, J. Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs), NOD-Like Receptors (NLRs), and RIG-I-Like Receptors (RLRs) in Innate Immunity. TLRs, NLRs, and RLRs Ligands as Immunotherapeutic Agents for Hematopoietic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, G.H.; Lian, B.S.X.; Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Exploration of Pattern Recognition Receptor Agonists as Candidate Adjuvants. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 745016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of Adaptive Immunity by the Innate Immune System. Science 2010, 327, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Koyama, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Cutting edge: Cooperation of IPS-1- and TRIF-dependent pathways in poly IC-enhanced antibody production and cytotoxic T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobiyama, K.; Takeshita, F.; Ishii, K.J.; Koyama, S.; Aoshi, T.; Akira, S.; Sakaue-Sawano, A.; Miyawaki, A.; Yamanaka, Y.; Hirano, H.; et al. A Signaling Polypeptide Derived from an Innate Immune Adaptor Molecule Can Be Harnessed as a New Class of Vaccine Adjuvant. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Qu, X.; Pan, R.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Pan, Z. The virus-induced signaling adaptor molecule enhances DNA-raised immune protection against H5N1 influenza virus infection in mice. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, G.; Zhou, Y. Innate Immune Sensing of Influenza A Virus. Viruses 2020, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.N.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, S.S.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, J.X.; Zong, M.M.; Feng, X.L.; Liu, Q.T. The molecular evolutionary characteristics of new isolated H9N2 AIV from East China and the function of vimentin on virus replication in MDCK cells. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reikine, S.; Nguyen, J.B.; Modis, Y. Pattern Recognition and Signaling Mechanisms of RIG-I and MDA5. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cui, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, F.; Yuan, R.; Gong, L.; Jiao, P.; Liao, M. Duck MDA5 functions in innate immunity against H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infections. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.; Pagano, J.S.; Barber, G.N. IRF7: Activation, regulation, modification and function. Genes. Immun. 2011, 12, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Fang, T.; Li, S.; Meng, K.; Guo, D. Bipartite Nuclear Localization Signal Controls Nuclear Import and DNA-Binding Activity of IFN Regulatory Factor 3. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Watanabe, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Tanikawa, T.; Uchida, Y.; Saito, T. Chicken MDA5 senses short double-stranded RNA with implications for antiviral response against avian influenza viruses in chicken. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciello, N.; Tuosto, L. CD28 costimulatory signals in T lymphocyte activation: Emerging functions beyond a qualitative and quantitative support to TCR signalling. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2016, 28, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, C.; Wang, A.; Gorla, S.R.; Kaithamana, S.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Holterman, M.J. CD80 and CD86 C domains play an important role in receptor binding and co-stimulatory properties. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tippalagama, R.; Chihab, L.Y.; Kearns, K.; Lewis, S.; Panda, S.; Willemsen, L.; Burel, J.G.; Arlehamn, C.L. Antigen-specificity measurements are the key to understanding T cell responses. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1127470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.P.; Moreno, B.; Meraviglia-Crivelli, D.; Nonatelli, F.; Villanueva, H.; Barainka, M.; Zheleva, A.; van Santen, H.M.; Pastor, F. Modulating T Cell Responses by Targeting CD3. Cancers 2023, 15, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.; Cronin, J.G.; Dolton, G.; Panetti, S.; Schauenburg, A.J.; Galloway, S.A.E.; Sewell, A.K.; Cole, D.K.; Thornton, C.A.; Francis, N.J. Metabolic Adaptation of Human CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-Cells to T-Cell Receptor-Mediated Stimulation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neron, S.; Nadeau, P.J.; Darveau, A.; Leblanc, J.F. Tuning of CD40-CD154 interactions in human B-lymphocyte activation: A broad array of in vitro models for a complex in vivo situation. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2011, 59, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, S.P.; Xu, H.; Tadaki, D.K.; Celniker, A.; Burkly, L.C.; Berning, J.D.; Cruzata, F.; Elster, E.A.; Gray, G.; Kampen, R.L.; et al. Combination induction therapy with monoclonal antibodies specific for CD80, CD86, and CD154 in nonhuman primate renal transplantation. Transplantation 2002, 74, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primers | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Flag-MDA5-1 | F: AAGCTTATGTCGGAGGAGTGCCGAGACGAGC (BamH I) |
| R: GTCGACTTACTGAGAGAACCAGTCCTTCTTC (Sal I) | |
| Flag-MDA5-2 | F: AAGCTTATGTCGGAGGAGTGCCGAGACGAGC (BamH I) |
| R: GTCGACTTATACTGGTTGGCTTGCAGCTTCT (Sal I) | |
| His-MDA5-1 | F: GGGATCCATGTCGGAGGAGTGCCGAGACGAGC (BamH I) |
| R: CCAAGCTTTTACTGAGAGAACCAGTCCTTCTTC (Hind III) | |
| His-MDA5-2 | F: CGGGATCCATGTCGGAGGAGTGCCGAGACGAGC (BamH I) |
| R: CCAAGCTTTTATACTGGTTGGCTTGCAGCTTCT (Hind III) | |
| β-actin | F: GAGAAATTGTGCGTGACATCA |
| R: CCTGAACCTCTCATTGCCA | |
| β-IFN | F: CCTCCAGCTCCTTCAGAATAC |
| R: GTGCGGTCAATCCAGTGTT | |
| MAVS | F: CACCCACGAGGTCCATGTG |
| R: TGCTTCATCTGGGACATCATTG | |
| PKR | F: TATGGTACAGGCGTTGGTAAG |
| R: TATGGTACAGGCGTTGGTAAG | |
| HA | F: TTACCCTGTTCAAGACGCCC |
| R: GCCACACTCGTTGTTGTGTC | |
| NS | F: GGTGATGCCCCATTCCTTGA |
| R: TTGCTTTCCCGCACGAGTAG | |
| NA | F: GGCGACACACCAAGAAATGA |
| R: AACCTGAGCGTGAATCCACTT | |
| M | F: TCCTCTCGTTGTTGCAGCAAGTATC |
| R: ATAGACTCAGGCACTCCTTCCGTAG | |
| MDA5-siRNA1 | GCUGCAAGCCAACCAGUAUTT |
| MDA5-siRNA2 | GCAUUUACGAAAGGAGUUUT |
| MAVS-siRNA1 | GCUGUGAGCUCGGAUGUUUTT |
| CTR-siRNA | AGGUAGUGUAAUCGCCUUG |
| ChMDA5 | F: GGACGACCACGATCTCTGTGT |
| R: CACCTGTCTGGTCTGCATGTTATC | |
| ChMAVS | F: CACCCACGAGGTCCATGTG |
| R: TGCTTCATCTGGGACATCATTG | |
| CD3 | F: GGACGCTCCCACCATATCAG |
| R: AAGCTCGTGACATGAGTCCC | |
| CD4 | F: TGTGGAACTGTCACCTCGTG |
| R: CACATGCATGCAAGGCCAAT | |
| CD8 | F: GCTGTACTTCAGCTCGGGAC |
| R: ATGTCCTTGTTGACGTGGCT | |
| CD40 | F: AGGCACCTTCTCCAATGTATC |
| R: GTCCCTTTCACCTTCACCAC | |
| CD80 | F: TGTGACCCTCTTTGTCACCG |
| R: TGTGACCCTCTTTGTCACCG | |
| CD154 | F: TGCAGAAATGTCAGACGGGA |
| R: CAACTCCTCACTGGCTGTCC | |
| CD86 | F: ACCAGCAAGCTGAATATCCCA |
| R: GACTAGCGGCACTGAGACAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Cai, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, R.; Zhou, B.; Feng, X. MDA5 with Complete CARD2 Region Inhibits the Early Replication of H9N2 AIV and Enhances the Immune Response during Vaccination. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101542
Li T, Cai Y, Li C, Huang J, Chen J, Zhang Z, Cao R, Zhou B, Feng X. MDA5 with Complete CARD2 Region Inhibits the Early Replication of H9N2 AIV and Enhances the Immune Response during Vaccination. Vaccines. 2023; 11(10):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101542
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tongtong, Yiqin Cai, Chenfei Li, Jingwen Huang, Jiajing Chen, Ze Zhang, Ruibing Cao, Bin Zhou, and Xiuli Feng. 2023. "MDA5 with Complete CARD2 Region Inhibits the Early Replication of H9N2 AIV and Enhances the Immune Response during Vaccination" Vaccines 11, no. 10: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101542
APA StyleLi, T., Cai, Y., Li, C., Huang, J., Chen, J., Zhang, Z., Cao, R., Zhou, B., & Feng, X. (2023). MDA5 with Complete CARD2 Region Inhibits the Early Replication of H9N2 AIV and Enhances the Immune Response during Vaccination. Vaccines, 11(10), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11101542









