Refocus on Immunogenic Characteristics of Convalescent COVID-19 Challenged by Prototype SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Information
2.2. Specimen Collection and Storage
2.3. Nucleic Acid Extraction and rRT-PCR
2.4. SARS-CoV-2 Humoral IgA, IgG, and IgM Antibodies Test
2.5. Landscape Assay of Coronavirus by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Micro-Neutralization Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings of COVID-19 Convalescent Cases
3.2. Cross-Reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 and Six Other Human Coronaviruses
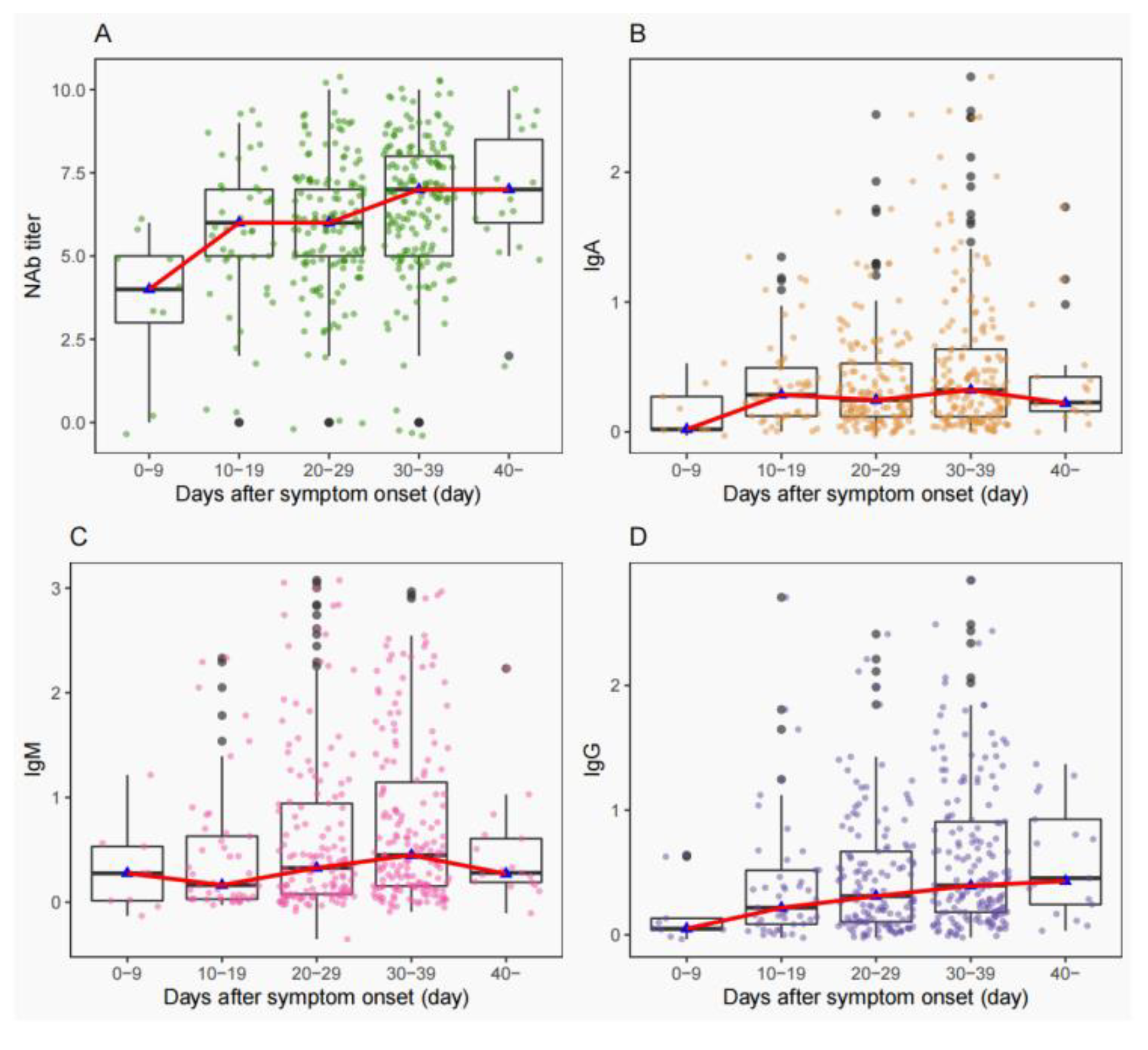
3.3. Consistency of NAbs Titers with IgA/IgM/IgG
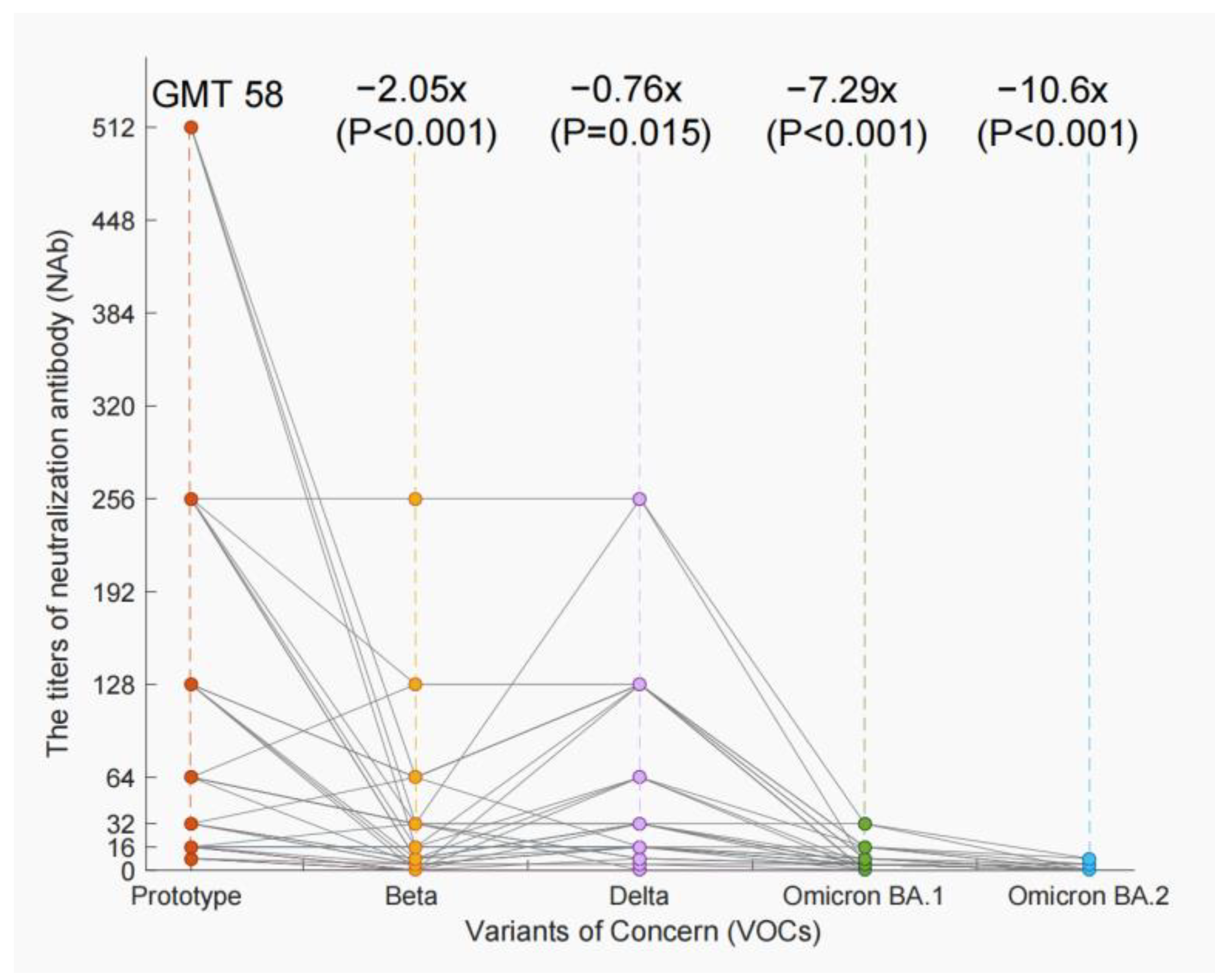
3.4. The Decline of NAb Titers of VOCs
3.5. The Factors Affecting the NAb Titers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. 12 October 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/southeastasia (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Volz, E.; Mishra, S.; Chand, M.; Barrett, J.C.; Johnson, R.; Geidelberg, L.; Hinsley, W.R.; Laydon, D.J.; Dabrera, G.; O’Toole, Á.; et al. Assessing transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Nature 2021, 593, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Thambiraja, T.S.; Karuppanan, K.; Subramaniam, G. Omicron and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2: A comparative computational study of spike protein. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N.R.; Mellan, T.A.; Whittaker, C.; Claro, I.M.; Candido, D.D.S.; Mishra, S.; Crispim, M.A.E.; Sales, F.C.S.; Hawryluk, I.; McCrone, J.T.; et al. Genomics and epidemiology of the P.1 SARS-CoV-2 lineage in Manaus, Brazil. Science 2021, 372, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Smith, D.M. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Shaik Syed Ali, P.; Sheeza, A. Omicron (B.1.1.529)-variant of concern-molecular profile and epidemiology: A mini review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 8019–8022. [Google Scholar]
- Resende, P.C.; Bezerra, J.F.; Teixeira Vasconcelos, R.H.; Arantes, I.; Appolinario, L.; Mendonça, A.C.; Paixao, A.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Silva, T.; Rocha, A.S.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 P.2 Lineage Associated with Reinfection Case, Brazil, June-October 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Elslande, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Vandervoort, K.; Wawina-Bokalanga, T.; Vanmechelen, B.; Wollants, E.; Laenen, L.; André, E.; Van Ranst, M.; Lagrou, K.; et al. Symptomatic Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Reinfection by a Phylogenetically Distinct Strain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.D.; Wang, K.; Roltgen, K.; Nielsen, S.C.A.; Roach, J.C.; Naccache, S.N.; Yang, F.; Wirz, O.F.; Yost, K.E.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 and Failure of Humoral Immunity: A case report. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, R.A.; Nakamura, G.E.K.; de Matos Aquino, B.; Bignardi, P.R. COVID-19 vaccines: Update of the vaccines in use and under development. Vacunas 2022, 23, S88–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; du Plessis, L.; Liu, Z.; Hill, V.; Kang, M.; Lin, H.; Sun, J.; François, S.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Faria, N.R.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Guangdong Province, China. Cell 2020, 181, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, X.; Bai, R.; Liang, C.; Zeng, L.; Lin, H.; Yuan, R.; Zhou, P.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Q.; et al. The kinetics of viral load and antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1690.e1–1690.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anichini, G.; Terrosi, C.; Gandolfo, C.; Gori Savellini, G.; Fabrizi, S.; Miceli, G.B.; Cusi, M.G. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response in Persons with Past Natural Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Matthews, P.C.; Stoesser, N.; Maddox, T.; Lorenzi, L.; Studley, R.; Bell, J.I.; Newton, J.N.; Farrar, J.; Diamond, I.; et al. Anti-spike antibody response to natural SARS-CoV-2 infection in the general population. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D.; Yang, F.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sang, L.; Ye, F.; Ruan, S.; Zhong, B.; Song, T.; Alshukairi, A.N.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, T.; Cooper, B.; Robins, J.M.; Ma, S.; James, L.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Chew, S.K.; Tan, C.C.; Samore, M.H.; et al. Transmission dynamics and control of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science 2003, 300, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.S.; Azhar, E.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Memish, Z.A.; Oh, M.D.; Zumla, A. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: Risk factors and determinants of primary, household, and nosocomial transmission. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e217–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yi, L.; Zou, L.; Zhong, H.; Liang, L.; Song, T.; Song, Y.; Su, J.; Ke, C. Imported case of MERS-CoV infection identified in China, May 2015: Detection and lesson learned. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, J.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Kalish, H.; Shunmugavel, A.; Mehalko, J.; Denson, J.P.; Snead, K.; Drew, M.; Corbett, K.; Graham, B.; et al. Serologic cross-reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 with endemic and seasonal Betacoronaviruses. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.T.; Garcia-Carreras, B.; Hitchings, M.D.T.; Yang, B.; Katzelnick, L.C.; Rattigan, S.M.; Borgert, B.A.; Moreno, C.A.; Solomon, B.D.; Trimmer-Smith, L.; et al. A systematic review of antibody mediated immunity to coronaviruses: Antibody kinetics, correlates of protection, and association of antibody responses with severity of disease. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, J.; Grifoni, A.; Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Ramirez, S.I.; Dan, J.M.; Burger, Z.C.; Rawlings, S.A.; Smith, D.M.; Phillips, E.; et al. Selective and cross-reactive SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes in unexposed humans. Science 2020, 370, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M.; Goodwin, E.C.; Verma, A.; Arevalo, C.P.; Bolton, M.J.; Weirick, M.E.; Gouma, S.; McAllister, C.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Weaver, J.; et al. Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell 2021, 184, 1858–1864.e1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Contant, P.; Embong, A.K.; Kanagaiah, P.; Chaves, F.A.; Yang, H.; Branche, A.R.; Topham, D.J.; Sangster, M.Y. S Protein-Reactive IgG and Memory B Cell Production after Human SARS-CoV-2 Infection Includes Broad Reactivity to the S2 Subunit. mBio 2020, 11, e01991-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrock, E.; Fujimura, E.; Kula, T.; Timms, R.T.; Lee, I.H.; Leng, Y.; Robinson, M.L.; Sie, B.M.; Li, M.Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science 2020, 370, eabd4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudenberg, T.; Pelleau, S.; Anna, F.; Attia, M.; Donnadieu, F.; Gravet, A.; Lohmann, C.; Seraphin, H.; Guiheneuf, R.; Delamare, C.; et al. Humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and seasonal coronaviruses in children and adults in north-eastern France. EBioMedicine 2021, 70, 103495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, M.; Reifler, K.; Rossi, M.; Miller, N.S.; Sinha, P.; White, L.F.; Mizgerd, J.P. Recent endemic coronavirus infection is associated with less-severe COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 143380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenlander, W.R.; Henson, S.N.; Monaco, D.R.; Chen, A.; Littlefield, K.; Bloch, E.M.; Fujimura, E.; Ruczinski, I.; Crowley, A.R.; Natarajan, H.; et al. Antibody responses to endemic coronaviruses modulate COVID-19 convalescent plasma functionality. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e146927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrega, R.; Nelson, D.K.S.; Koval, A.P.; Bond, N.G.; Heinrich, M.L.; Rowland, M.M.; Lathigra, R.; Bush, D.J.; Aimukanova, I.; Phinney, W.N.; et al. Cross-Reactive Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV in Pre-COVID-19 Blood Samples from Sierra Leoneans. Viruses 2021, 13, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Kang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhong, J.; Chen, H.; Ren, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Cross-reactive antibody against human coronavirus OC43 spike protein correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Duan, L.J.; Meng, Q.C.; Jiang, M.D.; Cao, J.; Yao, L.; Zhu, K.L.; Cao, W.C.; Ma, M.J. Susceptibility of Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Variants to Neutralization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2354–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. bioRxiv 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Tang, H.; Pajon, R.; Smith, G.; Glenn, G.M.; Shi, W.; Korber, B.; Montefiori, D.C. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.429 and B.1.351. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2352–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; De Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; Van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addetia, A.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.; Zhu, H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Bloom, J.D.; Greninger, A.L. Neutralizing Antibodies Correlate with Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Humans during a Fishery Vessel Outbreak with a High Attack Rate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02107-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Xiao, C.; Liu, J.; Xue, J.; Lv, Q.; Qi, F.; Gao, H.; Yu, P.; et al. Primary exposure to SARS-CoV-2 protects against reinfection in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 369, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liang, W.; Zhong, H.; He, J.; Chen, Z.; He, G.; Song, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; et al. Risk factors associated with COVID-19 infection: A retrospective cohort study based on contacts tracing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rébillard, R.M.; Charabati, M.; Grasmuck, C.; Filali-Mouhim, A.; Tastet, O.; Brassard, N.; Daigneault, A.; Bourbonnière, L.; Anand, S.P.; Balthazard, R.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2-specific immune alterations in acutely ill patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e145853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; To, K.K.; Chan, K.H.; Wong, Y.C.; Zhou, R.; Kwan, K.-Y.; Fong, C.H.-Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Choi, C.Y.-K.; Lu, L.; et al. High neutralizing antibody titer in intensive care unit patients with COVID-19. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Morishima, C.; Selke, S.; Zamora, D.; McGuffin, S.; Shapiro, A.E.; Campbell, V.L.; McClurkan, C.L.; Jing, L.; Gross, R.; et al. Clinical, laboratory, and temporal predictors of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 among COVID-19 convalescent plasma donor candidates. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e144930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; Elmahi, E.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russell, C.D.; Millar, J.E.; Baillie, J.K. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury. Lancet 2020, 395, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial 9th Edition). China Med. 2022, 17, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
| Basic Characteristics | Clinical Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Gender | Fever | Tracheotomy treatment | |||
| Female | 188 (48.9) | No | 123 (32.0) | No | 381 (99.2) |
| Male | 196 (51.1) | Yes | 261 (68.0) | Yes | 3 (0.8) |
| Age (years) | Cough | ECMO treatment | |||
| ≤39 | 170 (44.3) | No | 201 (52.3) | No | 379 (98.7) |
| 40–59 | 126 (32.8) | Yes | 183 (47.7) | Yes | 5 (1.3) |
| ≥60 | 88 (22.9) | Weakness | ICU treatment | ||
| Occupation | No | 323 (84.1) | No | 350 (91.2) | |
| service | 58 (15.1) | Yes | 61 (15.9) | Yes | 34 (8.8) |
| retire | 147 (38.3) | Dyspnea | CRRT treatment | ||
| worker | 58 (15.1) | No | 356 (92.7) | No | 378 (98.4) |
| student | 37 (9.6) | Yes | 28 (7.3) | Yes | 6 (1.6) |
| other | 84 (21.9) | Muscle pain | Anti-infective drugs treatment | ||
| Highest clinical severity | No | 352 (91.7) | No | 167 (43.5) | |
| Mild | 17 (4.4) | Yes | 32 (8.3) | Yes | 217 (56.5) |
| Moderate | 292 (76.1) | Diarrhea | Vasoactive drug treatment | ||
| Severe | 75 (19.5) | No | 362 (94.3) | No | 378 (98.4) |
| Comorbidity | Yes | 22 (5.7) | Yes | 6 (1.6) | |
| No | 292 (76.0) | Oxygen Inhalation treatment degree | Hormone treatment | ||
| Yes | 92 (24.0) | No | 130 (33.9) | No | 338 (88.0) |
| Hospital stay (days) | 2L | 152 (39.6) | Yes | 46 (12.0) | |
| 0–14 | 59 (15.4) | 3L–4L | 57 (14.8) | Temperature(°C) | |
| 15–28 | 174 (45.3) | 5L–6L | 6 (1.6) | <37.3 | 309 (80.5) |
| 29–42 | 133 (34.6) | High flow | 39 (10.2) | ≥37.3 | 75 (19.5) |
| >42 | 18 (4.7) | Oxyhydrogen atomizer treatment | Respiration(times/min) | ||
| Aggravation of illness during hospitalization | No | 351 (91.4) | ≤20 | 324 (84.4) | |
| No | 327 (85.2) | Yes | 33 (8.6) | >20 | 60 (15.6) |
| Yes | 57 (14.8) | Noninvasive ventilator treatment | Pulse(times/min) | ||
| The re-inspection positive | No | 342 (89.1) | <60 | 5 (1.3) | |
| No | 270 (70.3) | Yes | 42 (10.9) | 60–100 | 329 (85.7) |
| Yes | 114 (29.7) | Tracheal cannula treatment | >100 | 50 (13.0) | |
| No | 372 (96.9) | ||||
| Yes | 372 (3.1) | ||||
| Laboratory test characteristics | |||||
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Neutrophil count (×109/L) | Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | Oxygenation index | |||
| <1.8 | 23 (6.0) | <90 | 2 (0.5) | <400 | 112 (29.2) |
| 1.8–6.3 | 310 (80.7) | 90–139 | 312 (81.3) | 400–500 | 115 (29.9) |
| >6.3 | 36 (9.4) | ≥140 | 58 (15.1) | >500 | 42 (10.9) |
| Unknown | 15 (3.9) | Unknown | 12 (3.1) | Unknown | 115 (29.9) |
| Lymphocyte count (×109/L) | Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | Blood oxygen saturation (%) | |||
| <1.0 | 79 (20.6) | <60 | 8 (2.1) | <95 | 11 (2.9) |
| ≥1.0 | 288 (75.0) | 60–89 | 303 (78.9) | ≥95 | 345 (89.8) |
| Unknown | 17 (4.4) | ≥90 | 60 (15.6) | Unknown | 28 (7.3) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | Unknown | 13 (3.4) | White blood cell count (×109/L) | ||
| <40 | 328 (85.4) | Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | <4 | 55 (14.3) | |
| ≥40 | 36 (9.4) | <70 | 4 (1.0) | 4–10 | 291 (75.8) |
| Unknown | 20 (5.2) | 70–105 | 301 (78.4) | >10 | 21 (5.5) |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | >105 | 66 (17.2) | Unknown | 17 (4.4) | |
| <40 | 300 (75.1) | Unknown | 13 (3.4) | ||
| ≥40 | 64 (16.7) | ||||
| Unknown | 20 (5.2) | ||||
| Median (log2) | β | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| female | 188 (6) | Reference | |
| male | 196 (7) | 0.225 | 0.266 |
| Age | |||
| <40 | 170 (6) | Reference | |
| 40–59 | 126 (7) | 0.566 | 0.020 |
| 60 | 88 (7) | 0.621 | 0.041 |
| Highest clinical severity | |||
| Mild | 17 (6) | Reference | |
| Moderate | 292 (6) | −0.453 | 0.360 |
| Severe | 75 (8) | 0.431 | 0.438 |
| Fare | |||
| no | 123 (5) | Reference | |
| yes | 261 (7) | 1.046 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| no | 292 (6) | Reference | |
| yes | 92 (6) | 0.044 | 0.869 |
| Muscle pain | |||
| No | 352 (6) | Reference | |
| Yes | 32 (7) | 0.389 | 0.293 |
| Oxygen inhalation treatment degree | |||
| No | 130 (6) | Reference | |
| 2L | 152 (6) | 0.310 | 0.212 |
| 3L–4L | 57 (7) | 0.540 | 0.099 |
| 5L–6L | 6 (8.5) | 1.648 | 0.059 |
| High flow | 39 (7) | 0.553 | 0.209 |
| Noninvasive ventilator treatment | |||
| No | 342 (6) | Reference | |
| Yes | 42 (8) | −0.078 | 0.873 |
| ICU treatment | |||
| No | 350 (6) | Reference | |
| Yes | 34 (7) | 0.184 | 0.700 |
| Hormone treatment | |||
| No | 338 (6) | Reference | |
| Yes | 46 (8) | 0.950 | 0.024 |
| Temperature(°C) | |||
| <37.3 °C | 309 (6) | Reference | |
| ≥37.3 | 75 (7) | 0.474 | 0.078 |
| Neutrophil count (×109/L) | |||
| <1.8 | 23 (7) | Reference | |
| 1.8-6.3 | 310 (6) | −0.036 | 0.937 |
| ≥6.3 | 36 (7) | 0.088 | 0.877 |
| Unknown | 15 (7) | — | |
| Lymphocyte count (×109/L) | |||
| <1.0 | 79 (7) | Reference | |
| ≥1.0 | 288 (6) | −0.181 | 0.511 |
| Unknown | 17 (7) | — | |
| Median (log2) | β | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| female | 188 (0.600) | Reference | |
| male | 196 (0.667) | 0.303 | 0.136 |
| Age | |||
| <40 | 170 (0.667) | Reference | |
| 40–59 | 126 (0.613) | 0.692 | 0.005 |
| 60 | 88 (0.571) | 0.661 | 0.030 |
| Highest clinical severity | |||
| Mild | 17 (1.000) | Reference | |
| Moderate | 292 (0.667) | −0.382 | 0.431 |
| Severe | 75 (0.556) | 0.583 | 0.286 |
| Fare | |||
| no | 123 (0.667) | Reference | |
| yes | 261 (0.625) | 1.003 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| no | 292 (0.625) | Reference | |
| yes | 92 (0.667) | −0.070 | 0.795 |
| Muscle pain | |||
| No | 352 (0.625) | Reference | |
| Yes | 32 (0.571) | 0.293 | 0.441 |
| Oxygen treatment degree | |||
| No | 130 (0.667) | Reference | |
| 2L | 152 (0.667) | 0.377 | 0.136 |
| 3L–4L | 57 (0.571) | 0.643 | 0.052 |
| 5L–6L | 6 (0.613) | 1.594 | 0.064 |
| High flow | 39 (0.571) | 0.522 | 0.240 |
| Noninvasive ventilator treatment | |||
| No | 342 (0.625) | Reference | |
| Yes | 42 (0.444) | −0.212 | 0.664 |
| ICU treatment | |||
| No | 350 (0.625) | Reference | |
| Yes | 34 (0.444) | 0.068 | 0.884 |
| Hormone treatment | |||
| No | 338 (0.667) | Reference | |
| Yes | 46 (0.500) | 0.838 | 0.044 |
| Temperature(°C) | |||
| <37.3 | 309 (0.625) | Reference | |
| ≥37.3 | 75 (0.625) | 0.480 | 0.072 |
| Neutrophil count (×109/L) | |||
| <1.8 | 23 (0.625) | Reference | |
| 1.8–6.3 | 310 (0.625) | 0.053 | 0.908 |
| ≥6.3 | 36 (0.667) | 0.066 | 0.907 |
| Unknown | 15 (0.667) | — | |
| Lymphocyte count (×109/L) | |||
| <1.0 | 79 (0.600) | Reference | |
| ≥1.0 | 288 (0.625) | −0.357 | 0.198 |
| Unknown | 17 (0.667) | — | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Liang, C.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Ruan, Q.; Hu, X.; Zeng, L.; Lin, H.; Zhao, W.; et al. Refocus on Immunogenic Characteristics of Convalescent COVID-19 Challenged by Prototype SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2023, 11, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010123
Huang X, Liang C, Li M, Chen H, Li Z, Ruan Q, Hu X, Zeng L, Lin H, Zhao W, et al. Refocus on Immunogenic Characteristics of Convalescent COVID-19 Challenged by Prototype SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines. 2023; 11(1):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010123
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaorong, Chumin Liang, Manman Li, Huimin Chen, Zhaowan Li, Qianqian Ruan, Ximing Hu, Lilian Zeng, Huifang Lin, Wei Zhao, and et al. 2023. "Refocus on Immunogenic Characteristics of Convalescent COVID-19 Challenged by Prototype SARS-CoV-2" Vaccines 11, no. 1: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010123
APA StyleHuang, X., Liang, C., Li, M., Chen, H., Li, Z., Ruan, Q., Hu, X., Zeng, L., Lin, H., Zhao, W., Xiao, J., Sun, L., & Sun, J. (2023). Refocus on Immunogenic Characteristics of Convalescent COVID-19 Challenged by Prototype SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines, 11(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010123




