Effects of Prior Infection with SARS-CoV-2 on B Cell Receptor Repertoire Response during Vaccination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
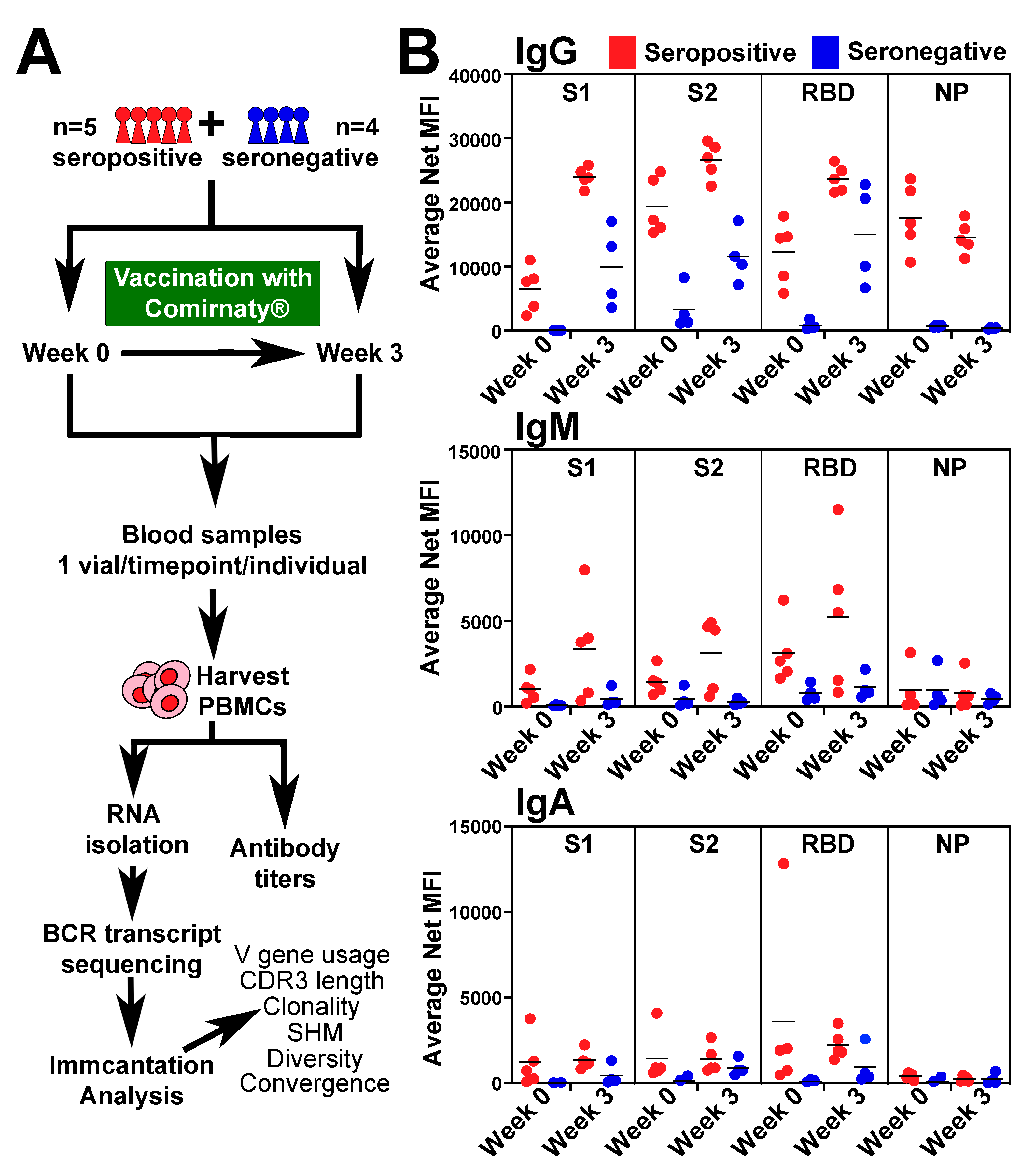
2.1. Individuals and Sample Collection
2.2. Antibody Titers
2.3. RNA Extraction and Library Preparation
2.4. Data Analyses
2.5. Statistical Tests
2.6. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. BCR-seq of Peripheral Blood after COVID-19 Vaccine
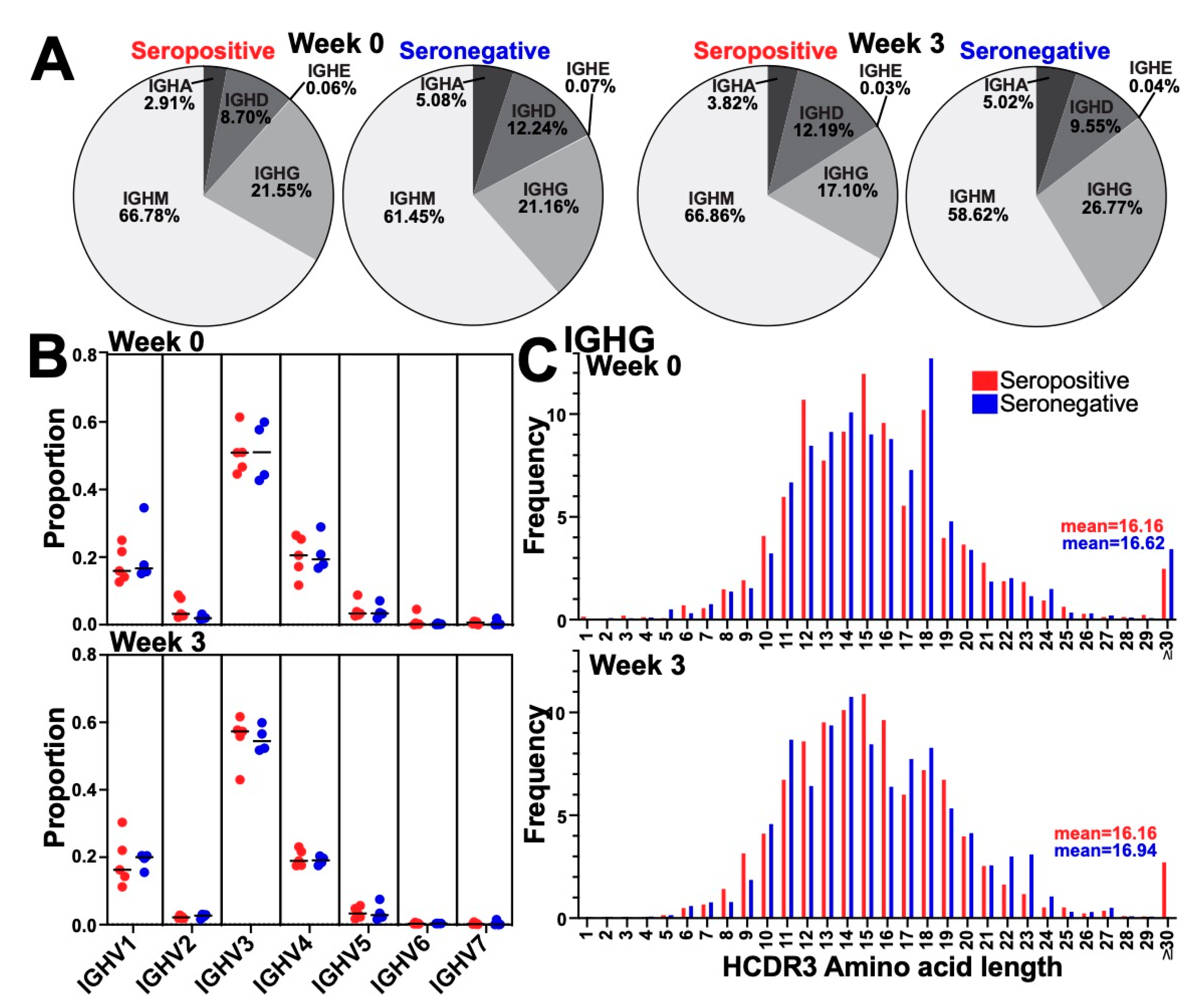
3.2. Immunization Did Not Alter the Global BCR Isotype, Variable Gene Usage, or HCDR3 Length Distribution
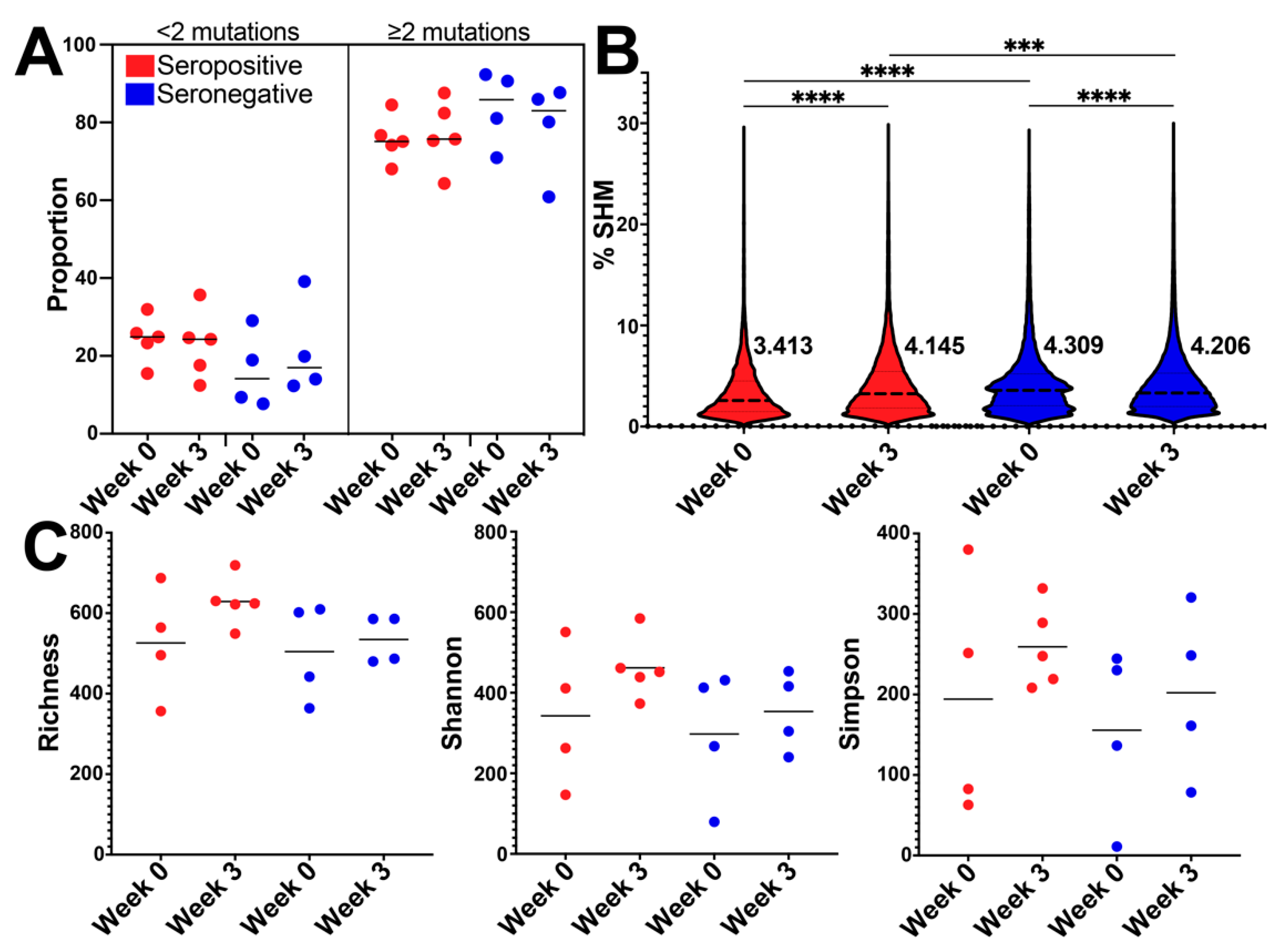
3.3. BCR SHM Increased after Vaccination in the Seropositive Group and Decreased in Seronegative Group
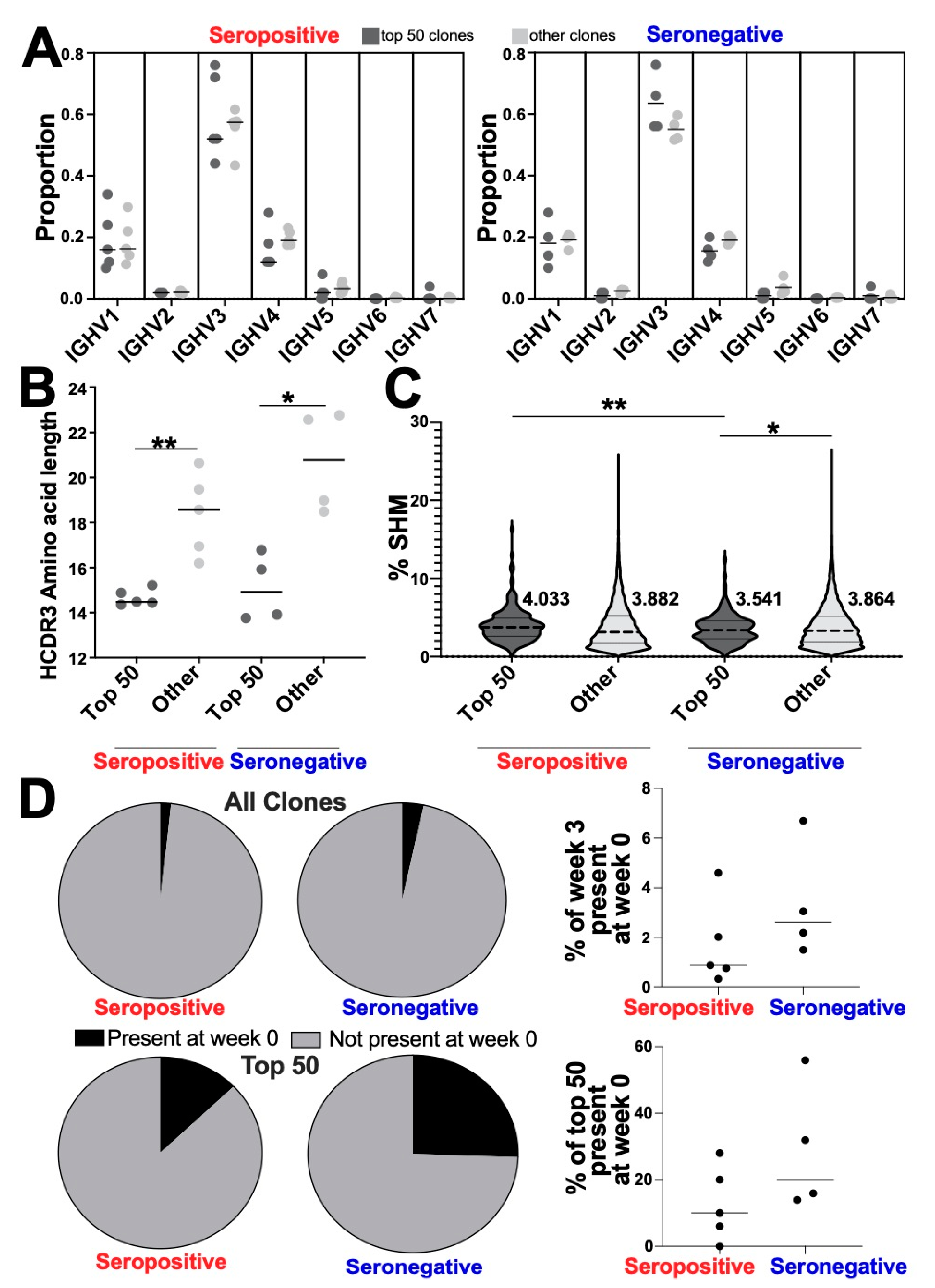
3.4. Altered Genetic Features of the Most Abundant Clonotypes between Seropositive and Seronegative Groups
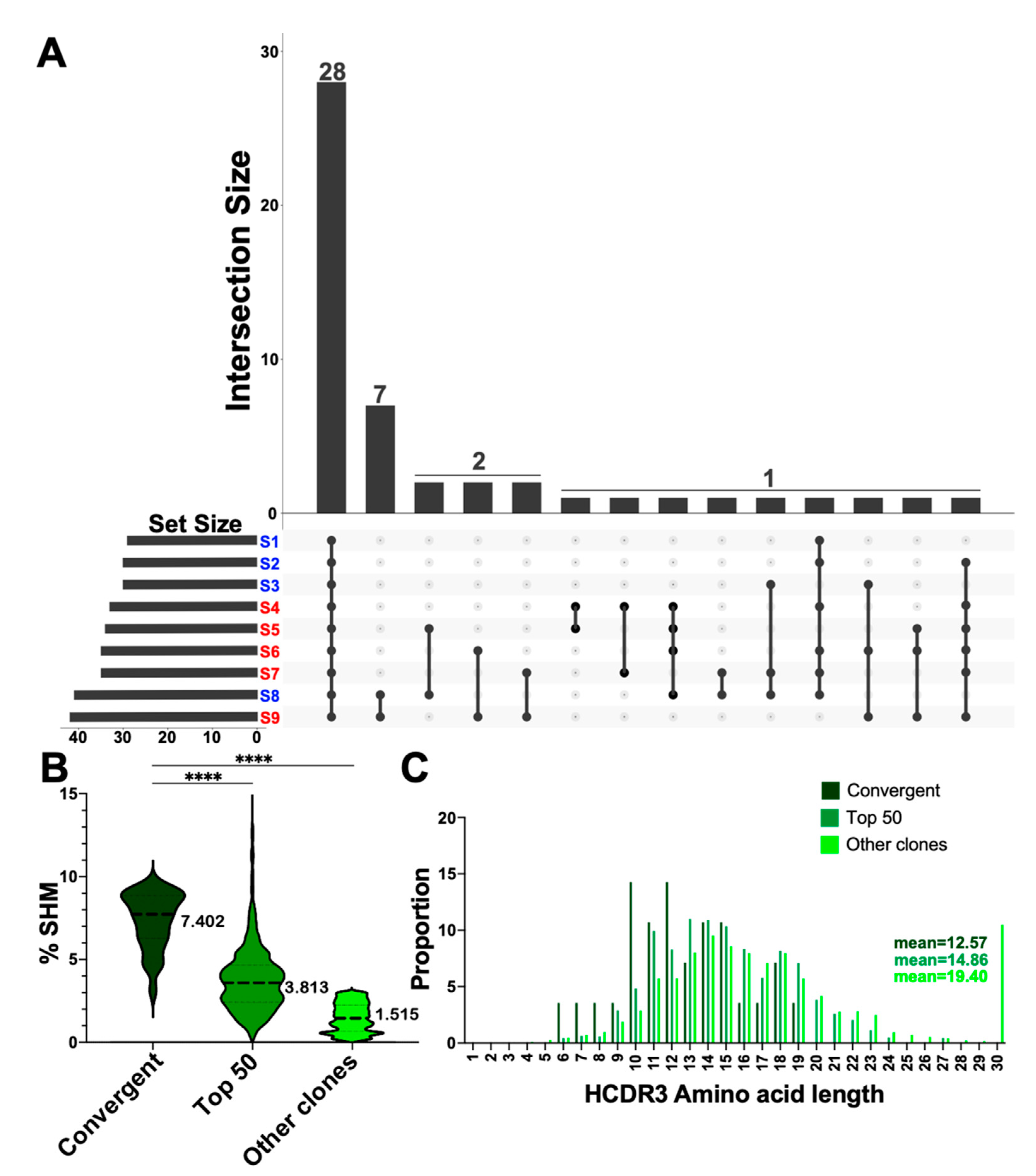
3.5. Convergent Clones Were Observed across Both Serotypes including 28 Clones Present in All Samples in This Study
3.6. Queried Clonotypes Included Matches to the COVID Antibody Database
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.O.; Jette, C.A.; Abernathy, M.E.; Dam, K.A.; Esswein, S.R.; Gristick, H.B.; Malyutin, A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Lee, Y.E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies. Nature 2020, 588, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edara, V.V.; Hudson, W.H.; Xie, X.; Ahmed, R.; Suthar, M.S. Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants After Infection and Vaccination. JAMA 2021, 325, 1896–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 34, 1548p. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, N.; Wesemann, D.R. Analyzing Immunoglobulin Repertoires. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.B. V(D)J Recombination: Mechanism, Errors, and Fidelity. In Mobile DNA III.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kocks, C.; Rajewsky, K. Stepwise intraclonal maturation of antibody affinity through somatic hypermutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8206–8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, G.C.; Jaffee, E.M. Cancer Immunotherapy: Immune Suppression and Tumor Growth, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 22, 655p. [Google Scholar]
- Yaari, G.; Kleinstein, S.H. Practical guidelines for B-cell receptor repertoire sequencing analysis. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotagiri, P.; Mescia, F.; Rae, W.M.; Bergamaschi, L.; Tuong, Z.K.; Turner, L.; Hunter, K.; Gerber, P.P.; Hosmillo, M. B cell receptor repertoire kinetics after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Luo, K.; He, P.; Hou, R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Yi, H.; Liang, H.; Deng, Y.; et al. Analysis of B Cell Receptor Repertoires Reveals Key Signatures of the Systemic B Cell Response after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0160021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultheiss, C.; Paschold, L.; Simnica, D.; Mohme, M.; Willscher, E.; von Wenserski, L.; Scholz, R.; Wieters, I.; Dahlke, C.; Tolosa, E.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing of T and B Cell Receptor Repertoires from COVID-19 Patients Showed Signatures Associated with Severity of Disease. Immunity 2020, 53, 442–455.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.C.A.; Yang, F.; Jackson, K.J.L.; Hoh, R.A.; Roltgen, K.; Jean, G.H.; Stevens, B.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Rustagi, A.; Rogers, A.J.; et al. Human B Cell Clonal Expansion and Convergent Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 516–525.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Nielsen, S.C.A.; Hoh, R.A.; Roltgen, K.; Wirz, O.F.; Haraguchi, E.; Jean, G.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Pham, T.D.; Jackson, K.J.L.; et al. Shared B cell memory to coronaviruses and other pathogens varies in human age groups and tissues. Science 2021, 372, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galson, J.D.; Schaetzle, S.; Bashford-Rogers, R.J.M.; Raybould, M.I.J.; Kovaltsuk, A.; Kilpatrick, G.J.; Minter, R.; Finch, D.K.; Dias, J.; James, L.K.; et al. Deep Sequencing of B Cell Receptor Repertoires From COVID-19 Patients Reveals Strong Convergent Immune Signatures. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raybould, M.I.J.; Kovaltsuk, A.; Marks, C.; Deane, C.M. CoV-AbDab: The coronavirus antibody database. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, T.; Grundberg, E.; Selvarangan, R.; LeMaster, C.; Fraley, E.; Banerjee, D.; Belden, B.; Louiselle, D.; Nolte, N.; Biswell, R.; et al. Antibody Responses after a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, E.; LeMaster, C.; Geanes, E.; Banerjee, D.; Khanal, S.; Grundberg, E.; Selvarangan, R.; Bradley, T. Humoral immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine administration in seropositive and seronegative individuals. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, E.; LeMaster, C.; Khanal, S.; Banerjee, D.; Pastinen, T.; Grundberg, E.; Selvarangan, R.; Bradley, T. Prior infection and age impacts antibody persistence after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, e902–e904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMaster, C.; Geanes, E.S.; Fraley, E.R.; Selvarangan, R.; Bradley, T. Vaccination after SARS-CoV-2 infection increased antibody avidity against the Omicron variant compared to vaccination alone. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, jiac247. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, M.; Ma, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Harding, A.; Min, C.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Yuan, M.; Ji, Q.; et al. Neutralizing Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Selected from a Human Antibody Library Constructed Decades Ago. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2102181. [Google Scholar]
- Rujas, E.; Kucharska, I.; Tan, Y.Z.; Benlekbir, S.; Cui, H.; Zhao, T.; Wasney, G.A.; Budylowski, P.; Guvenc, F.; Newton, J.C.; et al. Multivalency transforms SARS-CoV-2 antibodies into ultrapotent neutralizers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, W.; Luo, M.; Wang, P.; Xu, Z.; Ma, K.; Cao, H.; Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, R.; et al. Global characterization of B cell receptor repertoire in COVID-19 patients by single-cell V(D)J sequencing. Brief Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanshylla, K.; Fan, C.; Wunsch, M.; Poopalasingam, N.; Meijers, M.; Kreer, C.; Kleipass, F.; Ruchnewitz, D.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Gruell, H.; et al. Discovery of ultrapotent broadly neutralizing antibodies from SARS-CoV-2 elite neutralizers. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 69–82.e10. [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Wang, J.J.; Selva, K.J.; Reynaldi, A.; Tan, H.X.; Lee, W.S.; Wragg, K.M.; Kelly, H.G.; Esterbauer, R.; et al. Evolution of immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in mild-moderate COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brinkkemper, M.; Brouwer, P.J.M.; Maisonnasse, P.; Grobben, M.; Caniels, T.G.; Poniman, M.; Burger, J.A.; Bontjer, I.; Oomen, M.; Bouhuijs, J.H.; et al. A third SARS-CoV-2 spike vaccination improves neutralization of variants-of-concern. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydoux, E.; Homad, L.J.; MacCamy, A.J.; Parks, K.R.; Hurlburt, N.K.; Jennewein, M.F.; Akins, N.R.; Stuart, A.B.; Wan, Y.H.; Feng, J.; et al. Analysis of a SARS-CoV-2-Infected Individual Reveals Development of Potent Neutralizing Antibodies with Limited Somatic Mutation. Immunity 2020, 53, 98–105.e5. [Google Scholar]
- Shiakolas, A.R.; Kramer, K.J.; Wrapp, D.; Richardson, S.I.; Schafer, A.; Wall, S.; Wang, N.; Janowska, K.; Pilewski, K.A.; Venkat, R.; et al. Cross-reactive coronavirus antibodies with diverse epitope specificities and Fc effector functions. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, J.; Khan, H.; Rosa, A.; Calvaresi, V.; Graham, C.; Pickering, S.; Pye, V.E.; Cronin, N.B.; Huettner, I.; Malim, M.H.; et al. A neutralizing epitope on the SD1 domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike targeted following infection and vaccination. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111276. [Google Scholar]
- Seydoux, E.; Homad, L.J.; MacCamy, A.J.; Parks, K.R.; Hurlburt, N.K.; Jennewein, M.F.; Akins, N.R.; Stuart, A.B.; Wan, Y.H.; Feng, J.; et al. Characterization of neutralizing antibodies from a SARS-CoV-2 infected individual. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Srivastava, K.; Alshammary, H.; Amoako, A.A.; Awawda, M.H.; Beach, K.F.; Bermudez-Gonzalez, M.C.; Bielak, D.A.; Carreno, J.M.; Chernet, R.L.; et al. Antibody Responses in Seropositive Persons after a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1372–1374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.J.; Pade, C.; Gibbons, J.M.; Butler, D.K.; Otter, A.D.; Menacho, K.; Fontana, M.; Smit, A.; Sackville-West, J.E.; Cutino-Moguel, T.; et al. Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection rescues B and T cell responses to variants after first vaccine dose. Science 2021, 372, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Figueiredo, J.C.; Eyk, J.E.V.; Braun, J.G.; Cheng, S.; Sobhani, K. Prior COVID-19 Infection and Antibody Response to Single Versus Double Dose mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, E.; LeMaster, C.; Banerjee, D.; Khanal, S.; Selvarangan, R.; Bradley, T. Cross-reactive antibody immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in children and adults. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1826–1828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, K.B.; Turner, J.S.; Miller, F.I.; Jiang, R.; Pybus, O.G.; Ellebedy, A.H.; Kleinstein, S.H. Human B cell lineages associated with germinal centers following influenza vaccination are measurably evolving. eLife 2021, 10, e70873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naive and recovered individuals following mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ai, J.; Wang, Y.A.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, C.; Lian, C.; Gao, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; et al. B cell receptor signatures associated with strong and poor SARS-CoV-2 vaccine responses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 452–464. [Google Scholar]
- Galson, J.D.; Truck, J.; Fowler, A.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Munz, M.; Cerundolo, V.; Reinhard, C.; van der Most, R.; Pollard, A.J.; Lunter, G.; et al. Analysis of B Cell Repertoire Dynamics Following Hepatitis B Vaccination in Humans, and Enrichment of Vaccine-specific Antibody Sequences. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Kitaura, K.; Yamashita, H.; Ayabe, H.; Shini, T.; Matsutani, T.; Suzuki, R. Different Somatic Hypermutation Levels among Antibody Subclasses Disclosed by a New Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Antibody Repertoire Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 389. [Google Scholar]
- Bullen, G.; Galson, J.D.; Hall, G.; Villar, P.; Moreels, L.; Ledsgaard, L.; Mattiuzzo, G.; Bentley, E.M.; Masters, E.W.; Tang, D.; et al. Cross-Reactive SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies from Deep Mining of Early Patient Responses. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Clone | Alignment Target | Sequence Match % | Number of Individuals Detected | VDJ Gene | CDR3 Length | Mean SHM % | Neutralizing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #34727 | S-B8 | 80 | 9 | IGHV3-11*06 | 10 | 7.626758896 | Yes |
| #13327 | Fab-368 | 80 | 1 | IGHV3-74*01 | 10 | 1.670646982 | Yes |
| #8269 | XG001 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | R121-3G10 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | R410-3D10 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | PDI-38 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | COVA1-27 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | H712443+K711941 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | R259-1F4 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | CV10 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | H712427+K711927 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | Shiakolas_53181-5 | 100 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | XG002 | 83.33 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | R616-1E6 | 83.33 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | PDI-124 | 83.33 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | R849-3B4 | 83.33 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | R849-1F9 | 83.33 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
| #8269 | PDI-211 | 83.33 | 1 | IGHV4-59*09 | 6 | 0.758942973 | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fraley, E.R.; Khanal, S.; Pierce, S.H.; LeMaster, C.A.; McLennan, R.; Pastinen, T.; Bradley, T. Effects of Prior Infection with SARS-CoV-2 on B Cell Receptor Repertoire Response during Vaccination. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091477
Fraley ER, Khanal S, Pierce SH, LeMaster CA, McLennan R, Pastinen T, Bradley T. Effects of Prior Infection with SARS-CoV-2 on B Cell Receptor Repertoire Response during Vaccination. Vaccines. 2022; 10(9):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091477
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraley, Elizabeth R., Santosh Khanal, Stephen H. Pierce, Cas A. LeMaster, Rebecca McLennan, Tomi Pastinen, and Todd Bradley. 2022. "Effects of Prior Infection with SARS-CoV-2 on B Cell Receptor Repertoire Response during Vaccination" Vaccines 10, no. 9: 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091477
APA StyleFraley, E. R., Khanal, S., Pierce, S. H., LeMaster, C. A., McLennan, R., Pastinen, T., & Bradley, T. (2022). Effects of Prior Infection with SARS-CoV-2 on B Cell Receptor Repertoire Response during Vaccination. Vaccines, 10(9), 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091477






