Analysis of Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines in Spain following Booster Dose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population Study
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Vaccine Schedule
3.3. Adverse Effects after Homologous Vaccination with Pfizer
3.4. Adverse Effects after Homologous Vaccination with AstraZeneca
3.5. Reactogenicity of Pfizer Booster in AstraZeneca-Primed Participants
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meo, S.A.; Bukhari, I.A.; Akram, J.; Meo, A.S.; Klonoff, D.C. COVID-19 vaccines: Comparison of biological, pharmacological characteristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19 Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-vaccines (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Gobierno de España. COVID-19 Vaccination Strategy. Available online: www.vacunacovid.gob.es (accessed on 11 July 2022). (In Spanish).
- Chiu, N.C.; Chi, H.; Tu, Y.-K.; Huang, Y.-N.; Tai, Y.-L.; Weng, S.-L.; Chang, L.; Huang, D.T.-N.; Huang, F.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y. To mix or not to mix? A rapid systematic review of heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccination. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). EMA and ECDC Recommendations on Heterologous Vaccination Courses Against COVID-19: ‘Mix-and-Match’ Approach Can Be Used for Both Initial Courses and Boosters. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-ecdc-recommendations-heterologous-vaccination-courses-against-covid-19-mix-match-approach-can-be (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Possible Side Effects After Getting a COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/expect/after.html (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). What Are the Risks Associated with Vaxzevria? Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/vaxzevria-previously-covid-19-vaccine-astrazeneca (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Ramasamy, M.N.; Minassian, A.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Flaxman, A.L.; Folegatti, P.M.; Owens, D.R.; Voysey, M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Babbage, G.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): A single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 2021, 396, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejczak-Grządko, S.; Czudy, Z.; Donderska, M. Side effects after COVID-19 vaccinations among residents of Poland. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 4418–4421. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). What Are the Risks Associated with Comirnaty? Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/comirnaty (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Laganà, A.S.; Veronesi, G.; Ghezzi, F.; Ferrario, M.M.; Cromi, A.; Bizzarri, M.; Garzon, S.; Cosentino, M. Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey. Open Med. 2022, 17, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez, M.G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menni, C.; Klaser, K.; May, A.; Polidori, L.; Capdevila, J.; Louca, P.; Sudre, C.H.; Nguyen, L.H.; Drew, D.A.; Merino, J.; et al. Vaccine side-effects and SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccination in users of the COVID Symptom Study app in the UK: A prospective observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control Prevention (CDC). Information about the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/pfizer/reactogenicity.html (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS). 15th Pharmacovigilance Report on Vaccines COVID-19. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/informa/boletines-aemps/boletin-fv/2022-fv/15o-informe-de-farmacovigilancia-sobre-vacunascovid-19/#Comirnaty (accessed on 11 July 2022). (In Spanish).
- Center for Disease Control Prevention (CDC). Information about the Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/moderna/reactogenicity.html (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Hause, A.M.; Baggs, J.; Gee, J.; Marquez, P.; Myers, T.R.; Shimabukuro, T.T.; Shay, D.K. Safety Monitoring of an Additional Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine—United States, August 12–September 19, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). AstraZeneca’s COVID-19 Vaccine: EMA Finds Possible Link to Very Rare Cases of Unusual Blood Clots with Low Blood Platelets. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/astrazenecas-covid-19-vaccine-ema-finds-possible-link-very-rare-cases-unusual-blood-clots-low-blood (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Wichova, H.; Miller, M.E.; Derebery, M.J. Otologic Manifestations After COVID-19 Vaccination: The House Ear Clinic Experience. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e1213–e1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.H.; Waseem, S.; Shaikh, T.G.; Qadir, N.A.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Ullah, I.; Waris, A.; Yousa, Z. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated-tinnitus: A review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 75, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS). 11th Pharmacovigilance Report on Vaccines COVID-19. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/informa/boletines-aemps/boletin-fv/2021-boletin-fv/11o-informe-de-farmacovigilancia-sobre-vacunas-covid-19/ (accessed on 11 July 2022). (In Spanish).
- Sapkota, B.; Saud, B.; Shrestha, R.; Al-Fahad, D.; Sah, R.; Shrestha, S.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.F. Heterologous prime-boost strategies for COVID-19 vaccines. J. Travel Med. 2022, 29, taab191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.
bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.
 bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.
bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.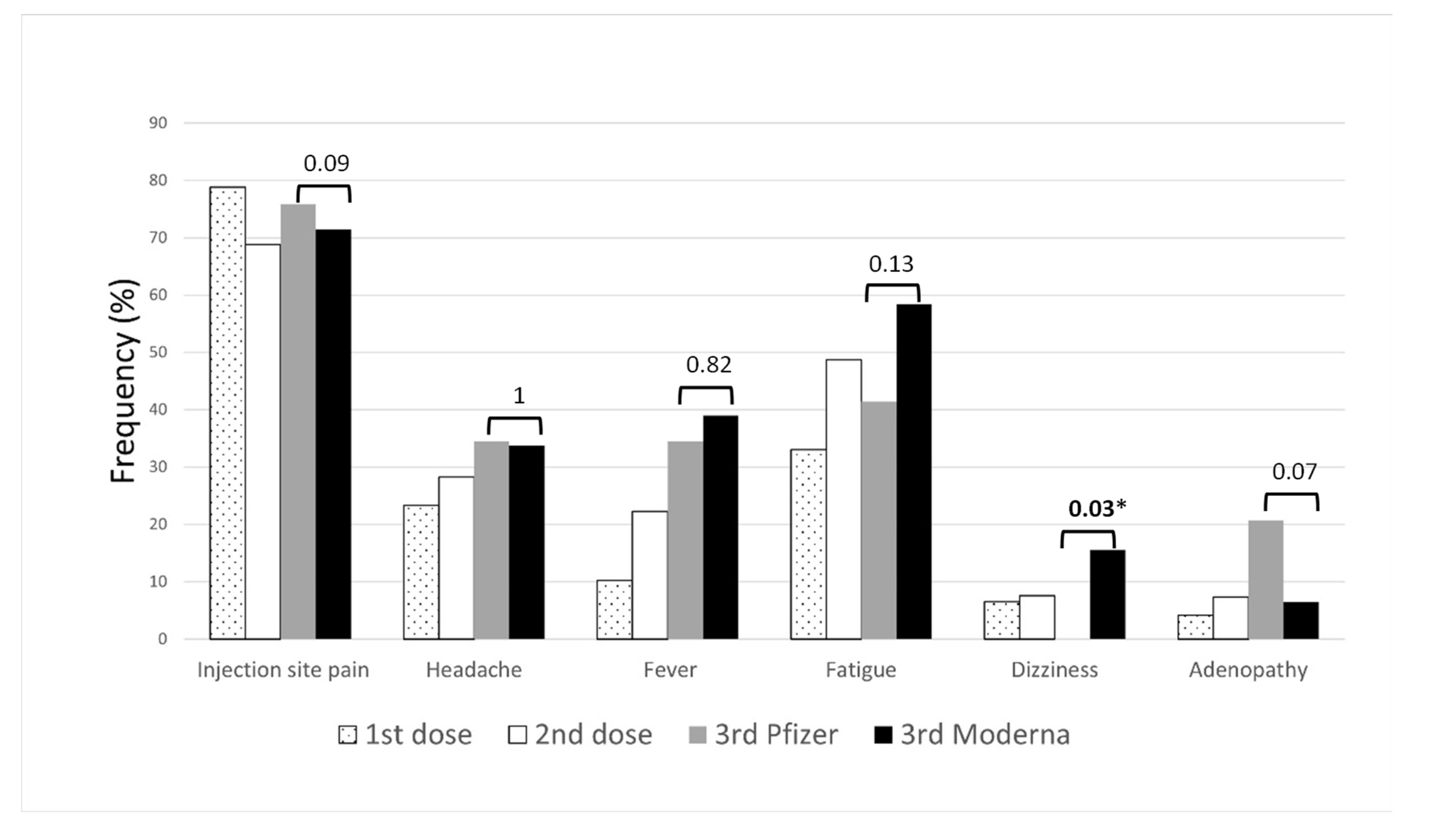
 bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.
bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.
 bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.
bars represent p-values. * p-values < 0.05.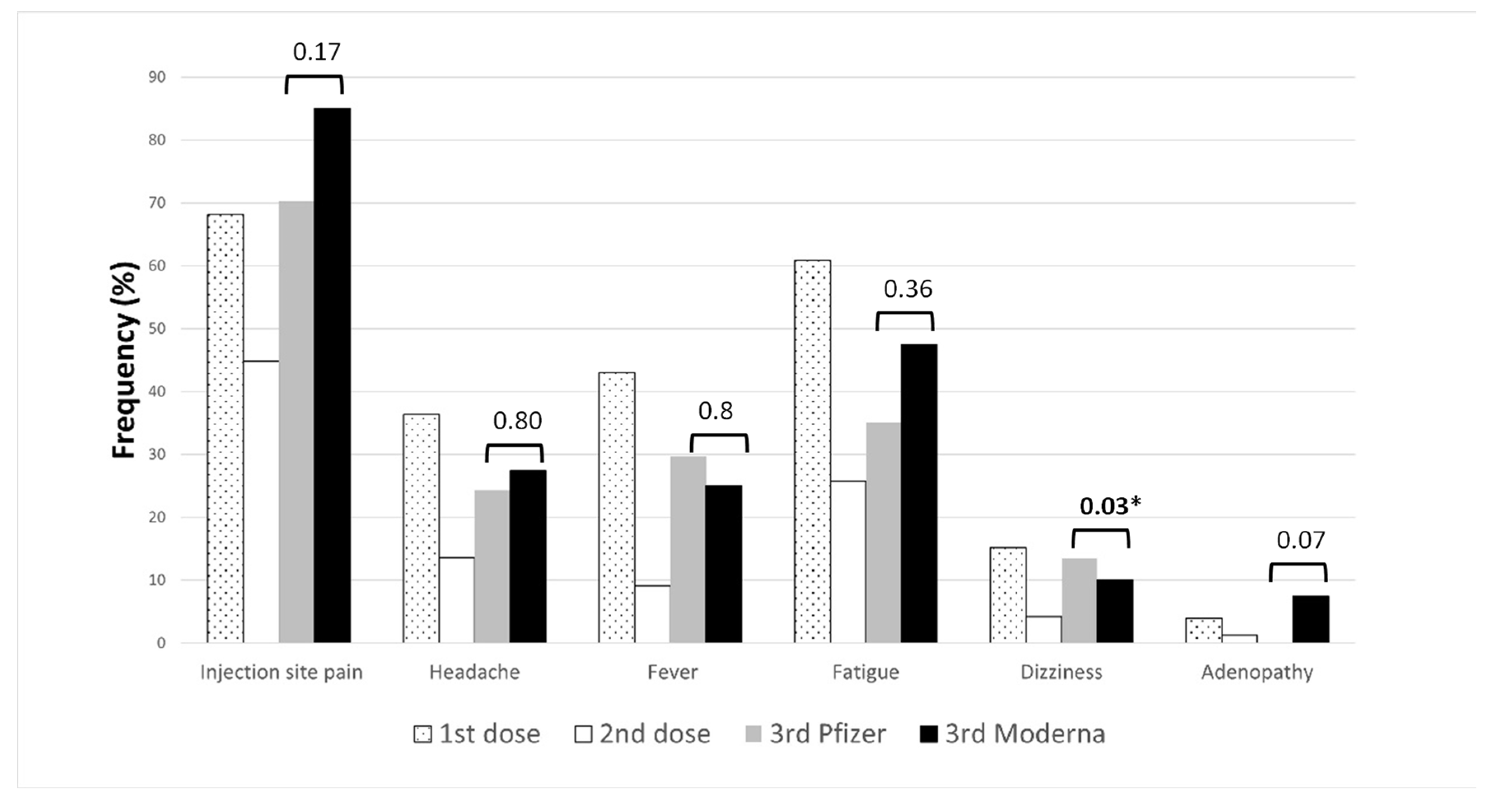

| 1st Dose | 2nd Dose | 3rd Dose | No. of Participants |
|---|---|---|---|
| PZ | PZ | PZ | 29 |
| PZ | PZ | Mo | 77 |
| PZ | PZ | - | 276 |
| PZ | - | - | 1 |
| AZ | AZ | PZ | 37 |
| AZ | AZ | Mo | 40 |
| AZ | AZ | - | 253 |
| AZ | PZ | - | 10 |
| AZ | PZ | PZ | 4 |
| AZ | - | - | 2 |
| Az | - | Mo | 4 |
| AZ/AZ/PF vs. AZ/AZ/Mo | PF/PF/PF vs. PF/PF/Mo | 1st Dose AZ vs. 1st Dose PF | 2nd Dose AZ vs. 2nd Dose PF | 1st Dose AZ vs. 2nd Dose AZ | 1st Dose PF vs. 2nd Dose PF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection site pain | ||||||
| p-value | 0.1699 | 0.0879 | 0.0015 | <0.0001 | < 0.0001 | 0.0023 |
| 95% CI | 0.1363 to 1.276 | 0.4699 to 3.363 | 0.4115 to 0.8081 | 0.2708 to 0.5000 | 1.918 to 3.620 | 1.212 to 2.332 |
| Headache | ||||||
| p-value | 0.7995 | 1 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1365 |
| 95% CI | 0.3047 to 2.357 | 0.4198 to 2.539 | 1.357 to 2.608 | 0.2725 to 0.5889 | 2.459 to 5.325 | 0.5566 to 1.067 |
| Fever | ||||||
| p-value | 0.7985 | 0.8227 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 95% CI | 0.4647 to 3.467 | 0.3378 to 2.013 | 4.468 to 9.876 | 0.2236 to 0.5459 | 4.893 to 11.66 | 0.2637 to 0.5985 |
| Fatigue | ||||||
| p-value | 0.3556 | 0.1312 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 95% CI | 0.2393 to 1.498 | 0.2109 to 1.195 | 2.328 to 4.305 | 0.2660 to 0.5025 | 3.224 to 6.256 | 0.3870 to 0.6951 |
| Dizziness | ||||||
| p-value | 0.7306 | 0.0337 | 0.0002 | 0.0817 | <0.0001 | 0.6723 |
| 95% CI | 0.3472 to 5.695 | 0.005083 to 1.552 | 1.539 to 4.226 | 0.2799 to 1.039 | 2.181 to 7.450 | 0.4894 to 1.485 |
| Adenopathy | ||||||
| p-value | 0.2413 | 0.0666 | 1 | <0.0001 | 0.0462 | 0.0866 |
| 95% CI | 0.007125 to 2.864 | 1.048 to 13.47 | 0.4443 to 1.981 | 0.05382 to 0.4472 | 1.078 to 10.36 | 0.2939 to 1.039 |
| Others | ||||||
| p-value | 0.1891 | 0.6708 | 0.0212 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0088 |
| 95% CI | 0.5031 to 44.42 | 0.04863 to 3.673 | 1.087 to 2.709 | 0.07204 to 0.3022 | 3.076 to 13.19 | 0.3529 to 0.8494 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ríos, E.; Medrano, S.; Martínez, M.; Novella, C.; Marcos, E.; Fernández, J.J.; Delgado-Iribarren, A.; Culebras, E. Analysis of Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines in Spain following Booster Dose. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091397
Ríos E, Medrano S, Martínez M, Novella C, Marcos E, Fernández JJ, Delgado-Iribarren A, Culebras E. Analysis of Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines in Spain following Booster Dose. Vaccines. 2022; 10(9):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091397
Chicago/Turabian StyleRíos, Esther, Sara Medrano, Mercedes Martínez, Consuelo Novella, Esther Marcos, Jose J. Fernández, Alberto Delgado-Iribarren, and Esther Culebras. 2022. "Analysis of Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines in Spain following Booster Dose" Vaccines 10, no. 9: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091397
APA StyleRíos, E., Medrano, S., Martínez, M., Novella, C., Marcos, E., Fernández, J. J., Delgado-Iribarren, A., & Culebras, E. (2022). Analysis of Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines in Spain following Booster Dose. Vaccines, 10(9), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091397







