Genomic Characteristics and E Protein Bioinformatics Analysis of JEV Isolates from South China from 2011 to 2018
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Cells
2.2. Identification of Clinical Materials and Virus Isolation
2.3. Serological Identification, Subculture and Determination of Virus Content
2.4. Analysis of Genomic Characteristics and Genetic Variation of Amino Acids
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
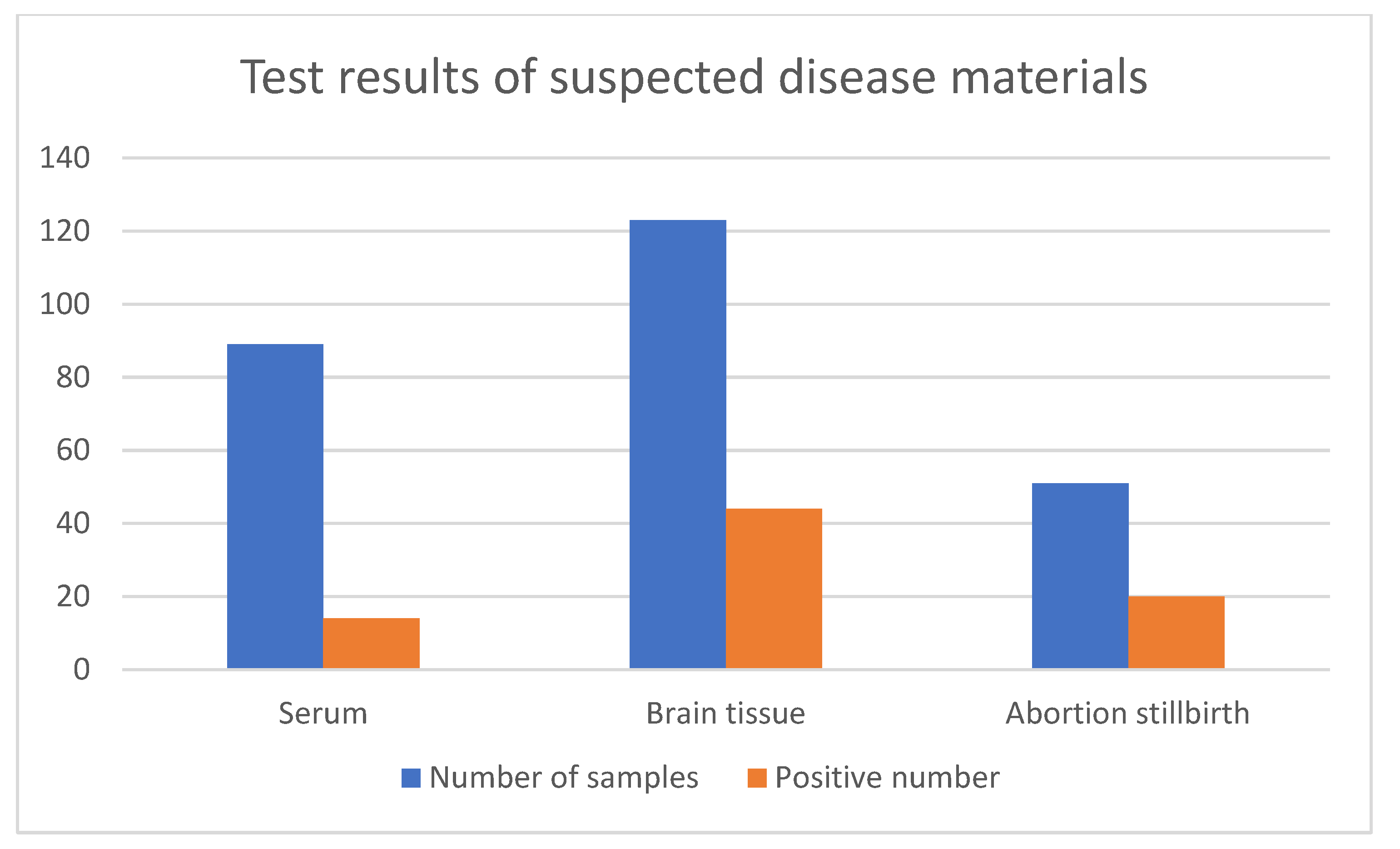
3.1. Clinical Sample Detection and Virus Isolation and Identification
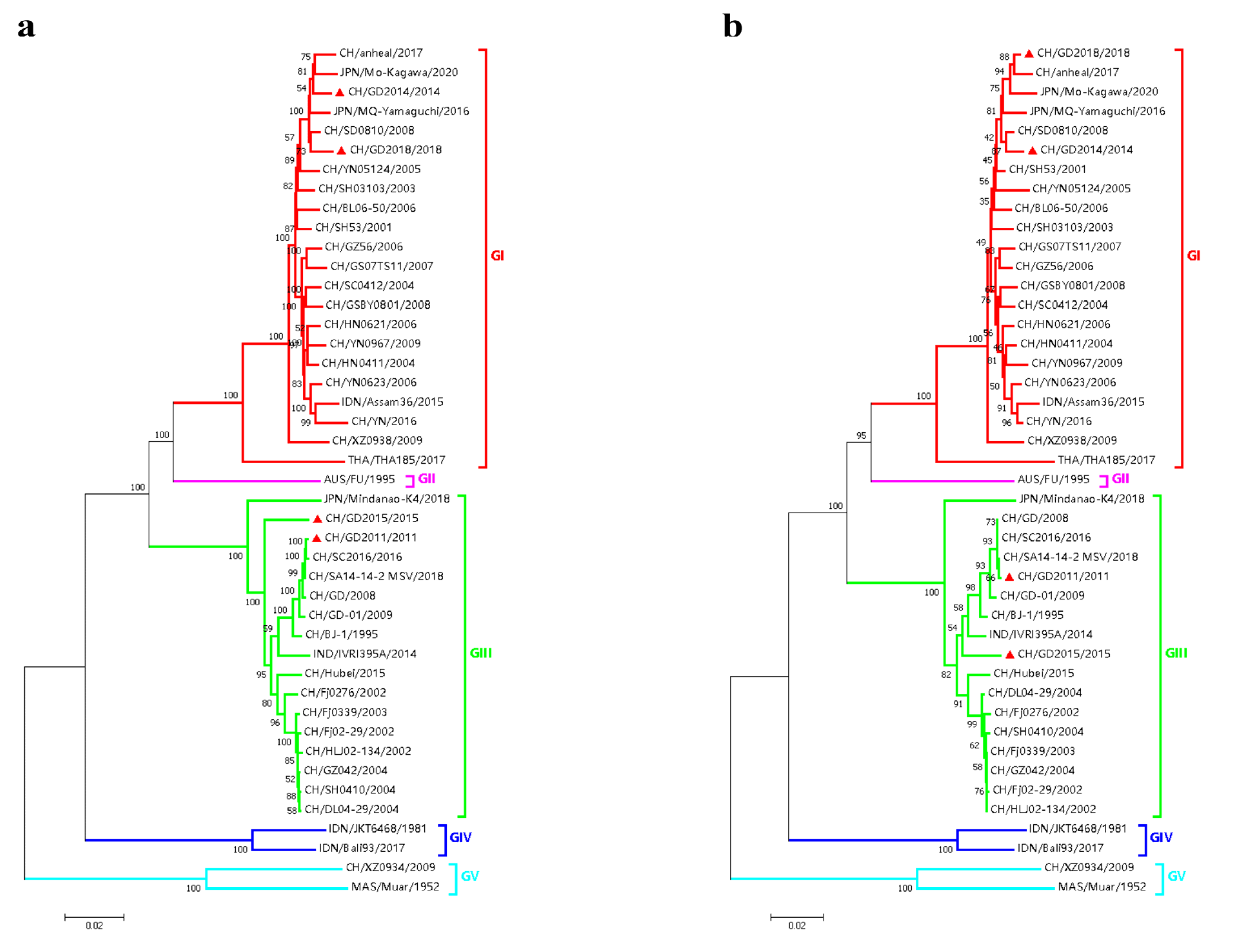
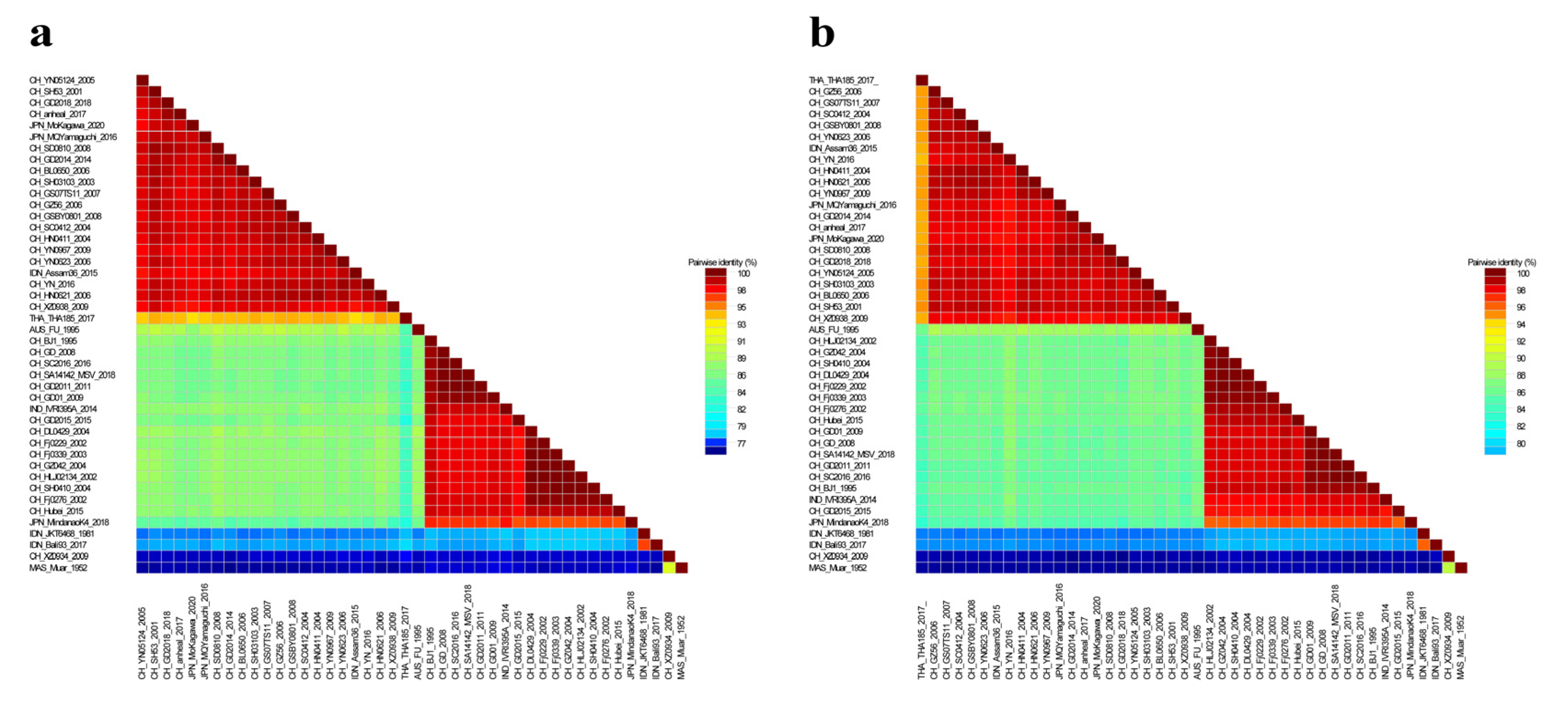
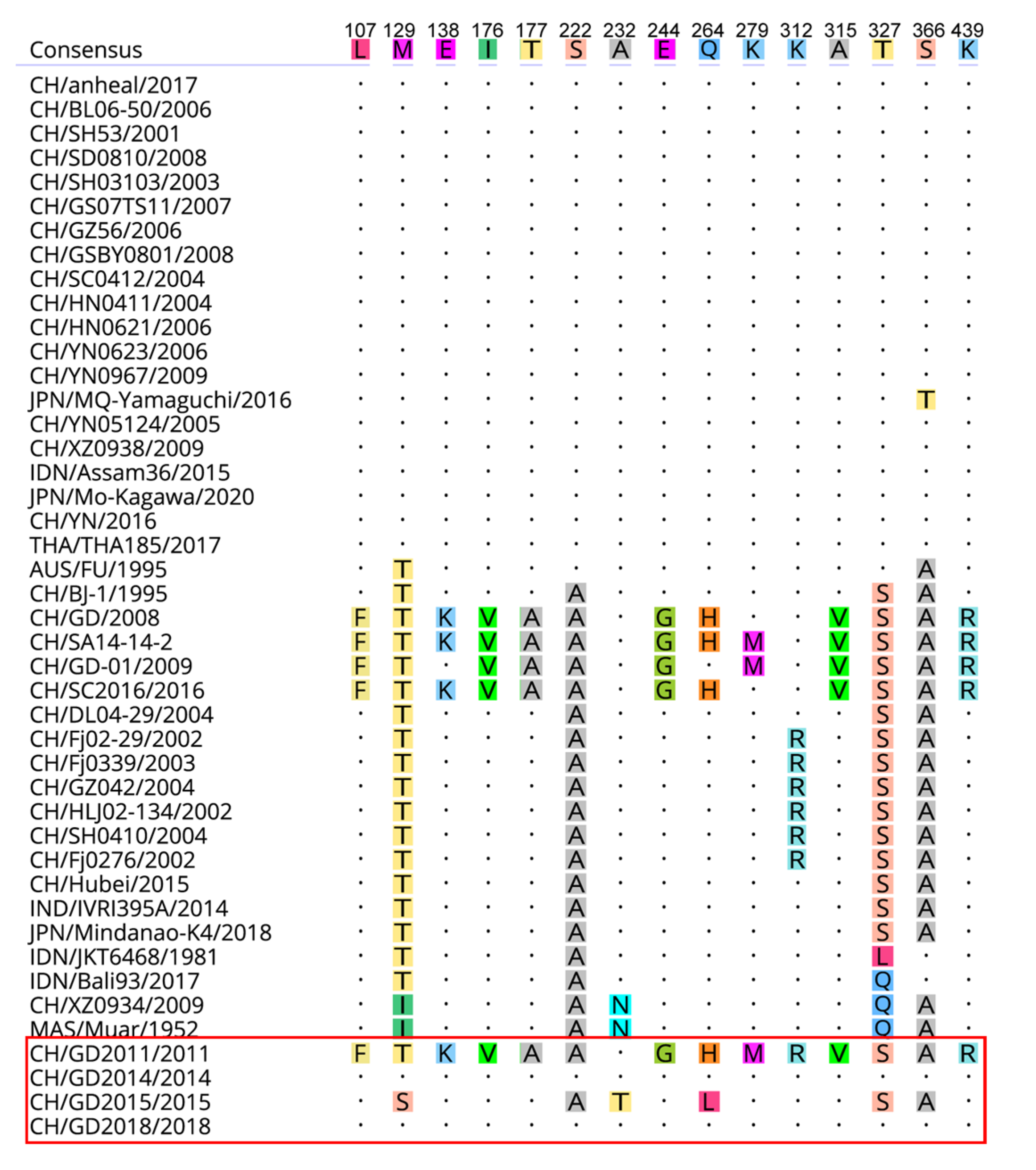
3.2. Nucleotide and Amino Acid Similarity and Genetic Evolution Analysis of JEV Isolates
3.3. Bioinformatics Analysis of E Gene
3.3.1. Glycosylation Site Analysis
3.3.2. Phosphorylation Site Analysis
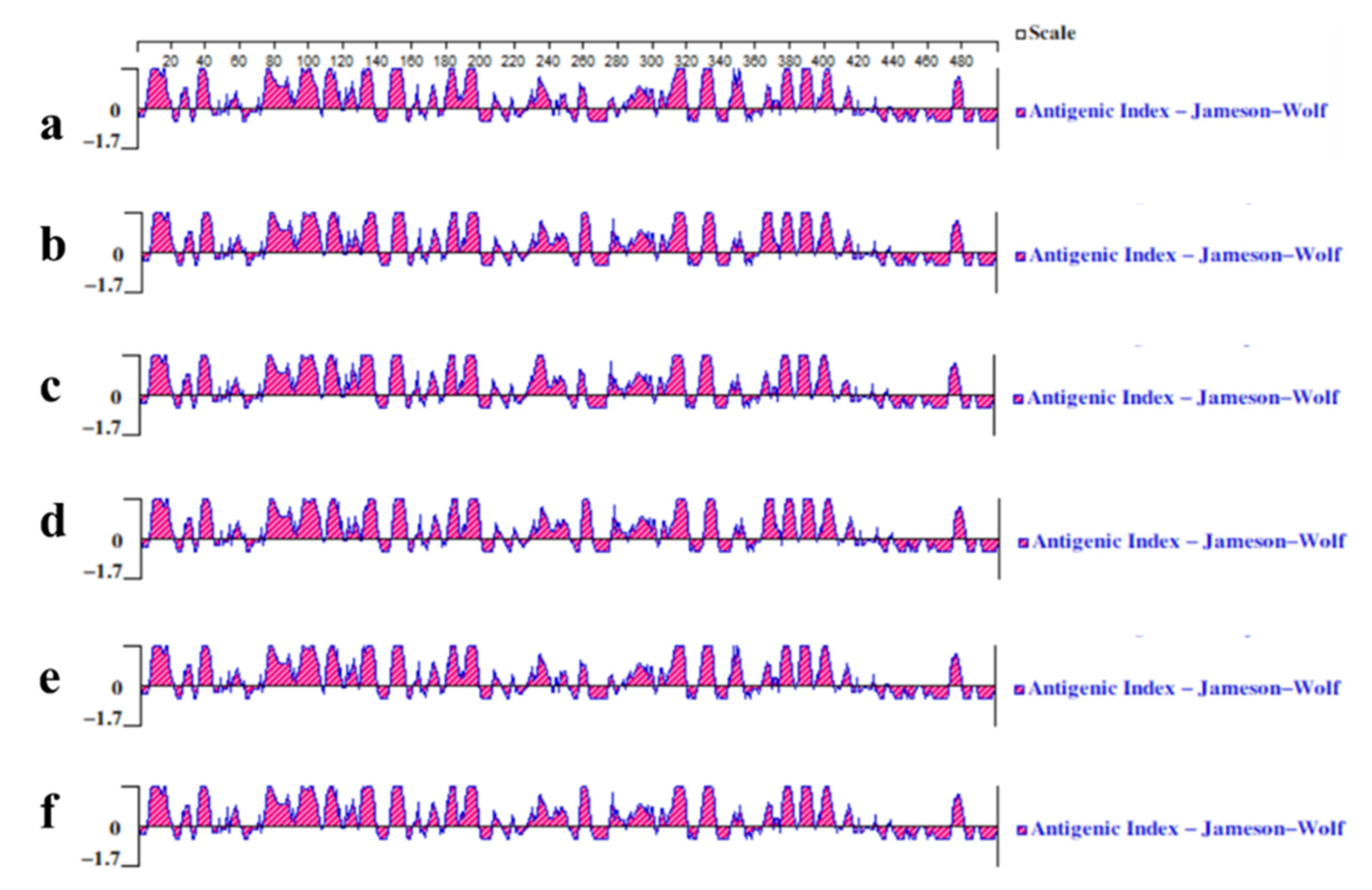
3.3.3. Analysis of Antigenic Epitopes of T/B Cells
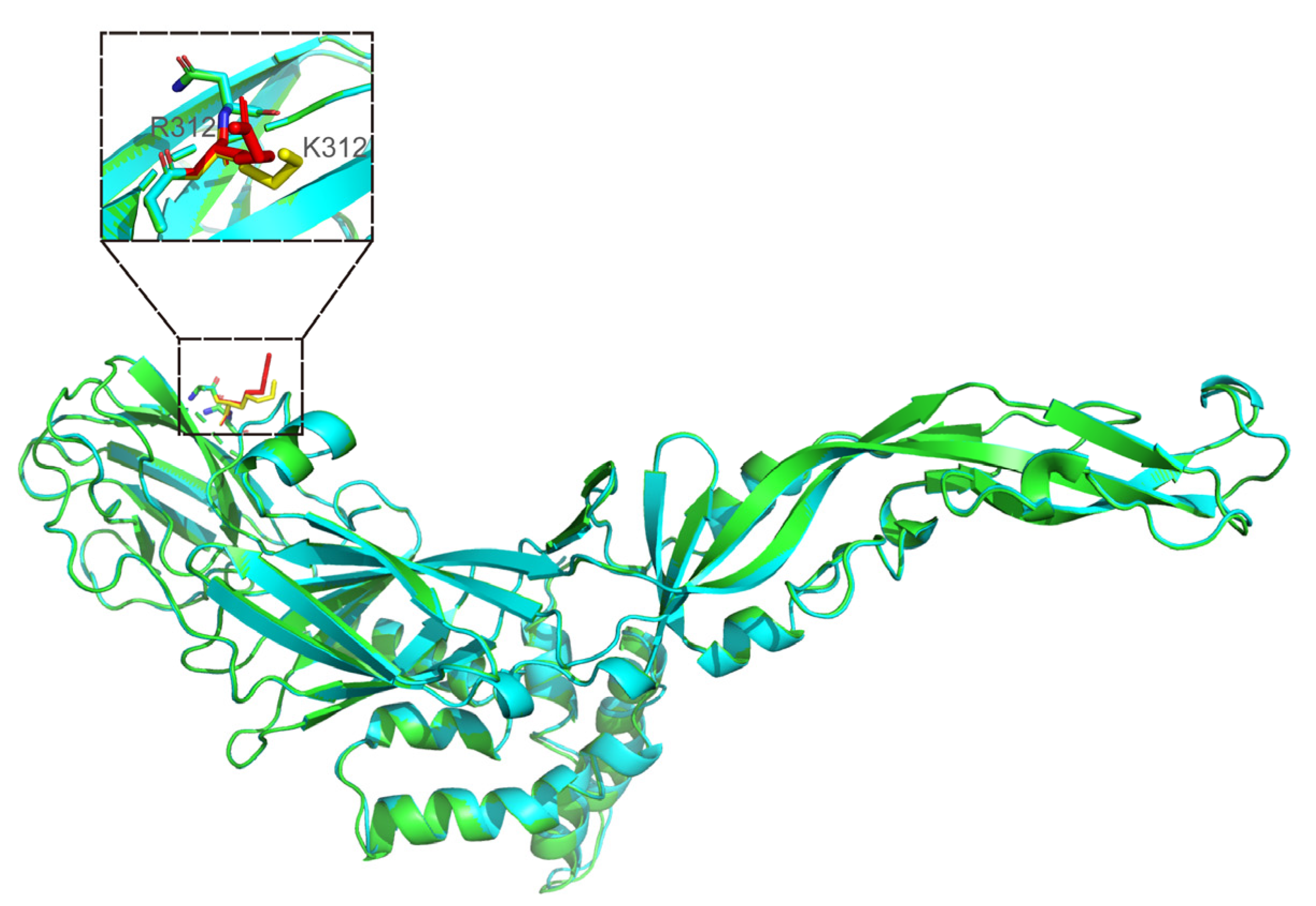
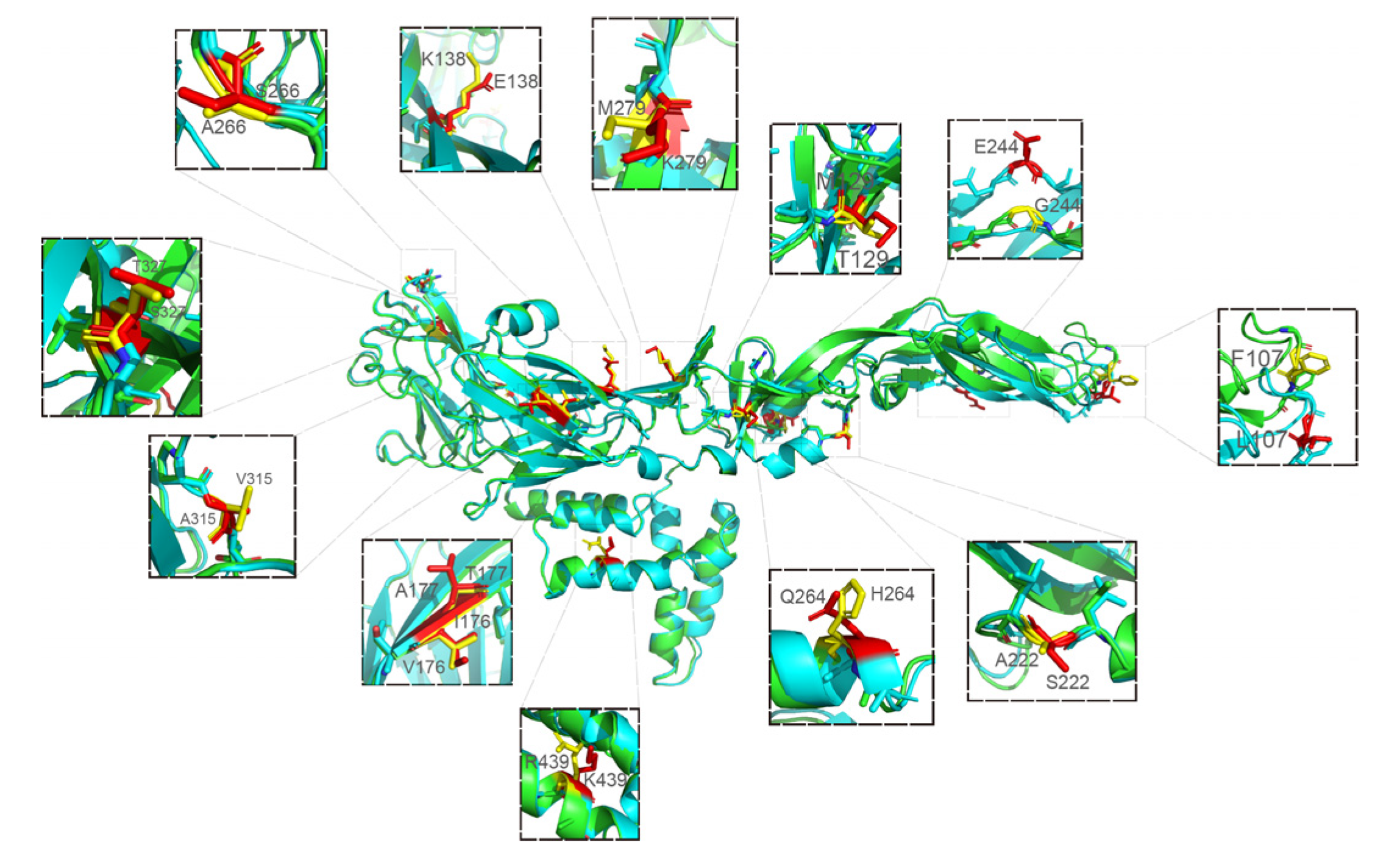
3.3.4. Modeled 3D Structure Analysis of E Protein
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, T.; Ni, H.; Beasley, D.W.; Ekkelenkamp, M.; Cardosa, M.J.; Barrett, A.D. Origin and evolution of Japanese encephalitis virus in southeast Asia. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Casey, C.; Chen, R.T. Promise of new Japanese encephalitis vaccines. Lancet 2007, 370, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Adams, J.; Chen, P.; Guo, Z.Y.; Zhong, X.F.; Fang, W.; Li, N.; Wen, L.; Tao, X.Y.; Yuan, Z.M.; et al. Comparison of genotypes I and III in Japanese encephalitis virus reveals distinct differences in their genetic and host diversity. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11469–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.L.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Hoke, C.H.; Hombach, J.M.; Marfin, A.A.; Solomon, T.; Tsai, T.F.; Tsu, V.D.; et al. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Dung, N.M.; Kneen, R.; Thao, L.T.T.; Gainsborough, M.; Nisalak, A.; Day, N.P.; Kirkham, F.J.; Vaughn, D.W.; Smith, S.; et al. Seizures and raised intracranial pressure in Vietnamese patients with Japanese encephalitis. Brain 2002, 125, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impoinvil, D.E.; Ooi, M.H.; Diggle, P.J.; Caminade, C.; Cardosa, M.J.; Morse, A.P.; Baylis, M.; Solomon, T. The effect of vaccination coverage and climate on Japanese encephalitis in Sarawak, Malaysia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Mehmood, K.; Gui, R.; Li, J. Epidemiology of Japanese Encephalitis in China (2004–2015). Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 28, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P. Molecular phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of Japanese encephalitis virus in China. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.; Holden, K.L.; Edgil, D.; Polacek, C.; Clyde, K. Molecular biology of flaviviruses. In Novartis Foundation Symposium; John Wiley: Chichester, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 277, pp. 23–39, discussion 40, 71–23, 251–253. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Fu, S.H.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, M.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Sun, X.H.; et al. Emergence of genotype I of Japanese encephalitis virus as the dominant genotype in Asia. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9847–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Fu, S.; Cao, L.; Shao, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Lei, W.; et al. Changing Geographic Distribution of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotypes, 1935–2017. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis 2019, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Ward, M.J.; Brown, A.J.; Barrett, A.D. Phylogeography of Japanese encephalitis virus: Genotype is associated with climate. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xue, J.B.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring Mosquito-Borne Arbovirus in Various Insect Regions in China in 2018. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 640993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.L.; Huang, R.; Feng, Y.N.; Peng, L.J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.H. The pre membrane and envelope protein is the crucial virulence determinant of Japanese encephalitis virus. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 148, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Lin, H.; Liu, L.; Ni, Q.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Envelope Protein Mutations L107F and E138K Are Important for Neurovirulence Attenuation for Japanese Encephalitis Virus SA14-14-2 Strain. Viruses 2017, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Bian, P.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Ye, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Lei, Y. Structure-based discovery of antiviral inhibitors targeting the E dimer interface of Japanese encephalitis virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, V.C.; AbiMansour, J.; Nelson, C.A.; Fremont, D.H. Crystal structure of the Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, M.; Abdin, M.Z.; Kalia, M.; Vrati, S. Japanese encephalitis virus invasion of cell: Allies and alleys. Rev. Med. Virol. 2016, 26, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Chou, M.W.; Lin, Y.L. DC-SIGN Binding Contributed by an Extra N-Linked Glycosylation on Japanese Encephalitis Virus Envelope Protein Reduces the Ability of Viral Brain Invasion. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, X.F.; Ye, Q.; Wang, H.J.; Deng, Y.Q.; Zhu, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.H.; Qin, C.F. Characterization of live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine virus SA14-14-2. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Gupta, A.; Khan, S.A.; Kumar, S. Enhanced cytopathic effect of Japanese encephalitis virus strain SA14-14-2: Probable association of mutation in amino acid of its envelope protein. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzi, M. Sampling variation of the fifty percent end-point, determined by the Reed-Muench (Behrens) method. Hum. Biol. 1950, 22, 151–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Yamada, K.D.; Tomii, K.; Katoh, K. Parallelization of MAFFT for large-scale multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2490–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janson, G.; Paiardini, A. PyMod 3: A complete suite for structural bioinformatics in PyMOL. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1471–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Li, G.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Gao, F.; Shan, T.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Acidity/Alkalinity of Japanese Encephalitis Virus E Protein Residue 138 Alters Neurovirulence in Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00108-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravell, J.C.; Matsuda-Lennikov, M.; Chauvin, S.D.; Zou, J.; Biancalana, M.; Deeb, S.J.; Price, S.; Su, H.C.; Notarangelo, G.; Jiang, P.; et al. Defective glycosylation and multisystem abnormalities characterize the primary immunodeficiency XMEN disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, X.; Dias, A.M.; Colombel, J.F.; Vermeire, S.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Callewaert, N.; Pinho, S.S. Protein Glycosylation as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker of Chronic Inflammatory Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Han, W. Protein Post-translational Modifications in Head and Neck Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 571944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T. Why nature chose phosphate to modify proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2513–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umenai, T.; Krzysko, R.; Bektimirov, T.A.; Assaad, F.A. Japanese encephalitis: Current worldwide status. Bull. World Health Organ. 1985, 63, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Liang, G. Japanese encephalitis and Japanese encephalitis virus in mainland China. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desprès, P.; Frenkiel, M.P.; Deubel, V. Differences between cell membrane fusion activities of two dengue type-1 isolates reflect modifications of viral structure. Virology 1993, 196, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.; Guirakhoo, F.; Fenner, S.; Zhang, Z.X.; Monath, T.P.; Chambers, T.J. Molecular basis for attenuation of neurovirulence of a yellow fever Virus/Japanese encephalitis virus chimera vaccine (ChimeriVax-JE). J. Virol. 2001, 75, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhao, Q.; Chang, Y.F.; Wen, X.; Feng, Y.; Huang, X.; Wen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Mutation of I176R in the E coding region weakens Japanese encephalitis virus neurovirulence, but not its growth rate in BHK-21 cells. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Cao, R.; Gu, J. Mutation of putative N-linked glycosylation sites in Japanese encephalitis virus premembrane and envelope proteins enhances humoral immunity in BALB/C mice after DNA vaccination. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechtawewat, T.; Roytrakul, S.; Yingchutrakul, Y.; Charoenlappanit, S.; Siridechadilok, B.; Limjindaporn, T.; Mangkang, A.; Prommool, T.; Puttikhunt, C.; Songprakhon, P.; et al. Potential Phosphorylation of Viral Nonstructural Protein 1 in Dengue Virus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Trincado, J.L.; Gomez-Perosanz, M.; Reche, P.A. Fundamentals and Methods for T- and B-Cell Epitope Prediction. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 2680160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäueler, W.; Bassili, G.; Epplen, C.; Keyl, H.G.; Epplen, J.T. Protein binding to simple repetitive sequences depends on DNA secondary structure(s). Chromosome Res. 1999, 7, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stollar, E.J.; Smith, D.P. Uncovering protein structure. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 649–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Gallo Cassarino, T.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, E.A.; Kahle, K.M.; Mattia, K.; Puffer, B.A.; Pfaff, J.M.; Miller, A.; Paes, C.; Davidson, E.; Doranz, B.J. Atomic-level functional model of dengue virus Envelope protein infectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18662–18667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.H.; Zhu, L.; Nian, Q.G.; Yuan, S.; Gao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Li, X.F.; Xie, D.Y.; et al. Near-atomic structure of Japanese encephalitis virus reveals critical determinants of virulence and stability. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer | Sequence (5′~3′) | Product Length (bp) | Primer Position (nt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JEV-P1-F | TATGCTGAAACGCGGCCTAC | 2836 | 140~2975 |
| JEV-P1-R | ACGGGTTGATGTGATGCCAA | ||
| JEV-P2-F | GAGATATCGCTCAGCCCCAAA | 2840 | 2762~5601 |
| JEV-P2-R | GGGCATTTGAGTCGGGAAAAG | ||
| JEV-P3-F | CCGCACGAGGATACATTGCT | 2835 | 5494~8328 |
| JEV-P3-R | CGTGATTGGAGTTTCGGGAC | ||
| JEV-P4-F | TCTGCCCTTACATGCCCAAG | 2716 | 8227~10,942 |
| JEV-P4-R | GCTACATACTTCGGCGCTCT |
| Number | T-Cell Epitope Sequence | The Starting Point of Amino Acid Position | Confidence Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GNYSAQVGASQAAKF | 153 | 34 |
| 2 | FLATGGVLVFLATNV | 484 | 32 |
| 3 | HATKQSVVALGSQEG | 246 | 28 |
| 4 | GHGTVVIELSYSGSD | 318 | 28 |
| 5 | HALAGAIVVEYSSSV | 264 | 27 |
| 6 | DVRMINIEASQLAEV | 42 | 26 |
| 7 | EGGLHHALAGAIVVE | 259 | 26 |
| 8 | VEYSSSVMLTSGHLK | 272 | 26 |
| 9 | ARDRSIALAFLATGG | 475 | 26 |
| 10 | PCKIPIVSVASLNDM | 334 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhao, F.; Yan, Q.; Li, Y.; Niu, X.; Zeng, W.; Wu, K.; Ling, B.; Fan, S.; et al. Genomic Characteristics and E Protein Bioinformatics Analysis of JEV Isolates from South China from 2011 to 2018. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081303
Sun Y, Ding H, Zhao F, Yan Q, Li Y, Niu X, Zeng W, Wu K, Ling B, Fan S, et al. Genomic Characteristics and E Protein Bioinformatics Analysis of JEV Isolates from South China from 2011 to 2018. Vaccines. 2022; 10(8):1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081303
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yawei, Hongxing Ding, Feifan Zhao, Quanhui Yan, Yuwan Li, Xinni Niu, Weijun Zeng, Keke Wu, Bing Ling, Shuangqi Fan, and et al. 2022. "Genomic Characteristics and E Protein Bioinformatics Analysis of JEV Isolates from South China from 2011 to 2018" Vaccines 10, no. 8: 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081303
APA StyleSun, Y., Ding, H., Zhao, F., Yan, Q., Li, Y., Niu, X., Zeng, W., Wu, K., Ling, B., Fan, S., Zhao, M., Yi, L., & Chen, J. (2022). Genomic Characteristics and E Protein Bioinformatics Analysis of JEV Isolates from South China from 2011 to 2018. Vaccines, 10(8), 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081303






