Intranasal Immunization with a Vaccinia Virus Vaccine Vector Expressing Pre-Fusion Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike Fully Protected Mice against Lethal Challenge with the Heavily Mutated Mouse-Adapted SARS2-N501YMA30 Strain of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Plaque Assay
2.4. Immunization
2.5. Inhibition of RBD/huACE2 Interaction
2.6. SARS2-N501YMA30 Challenge
3. Results
3.1. Generation of NYVAC-KC-pfsSpike
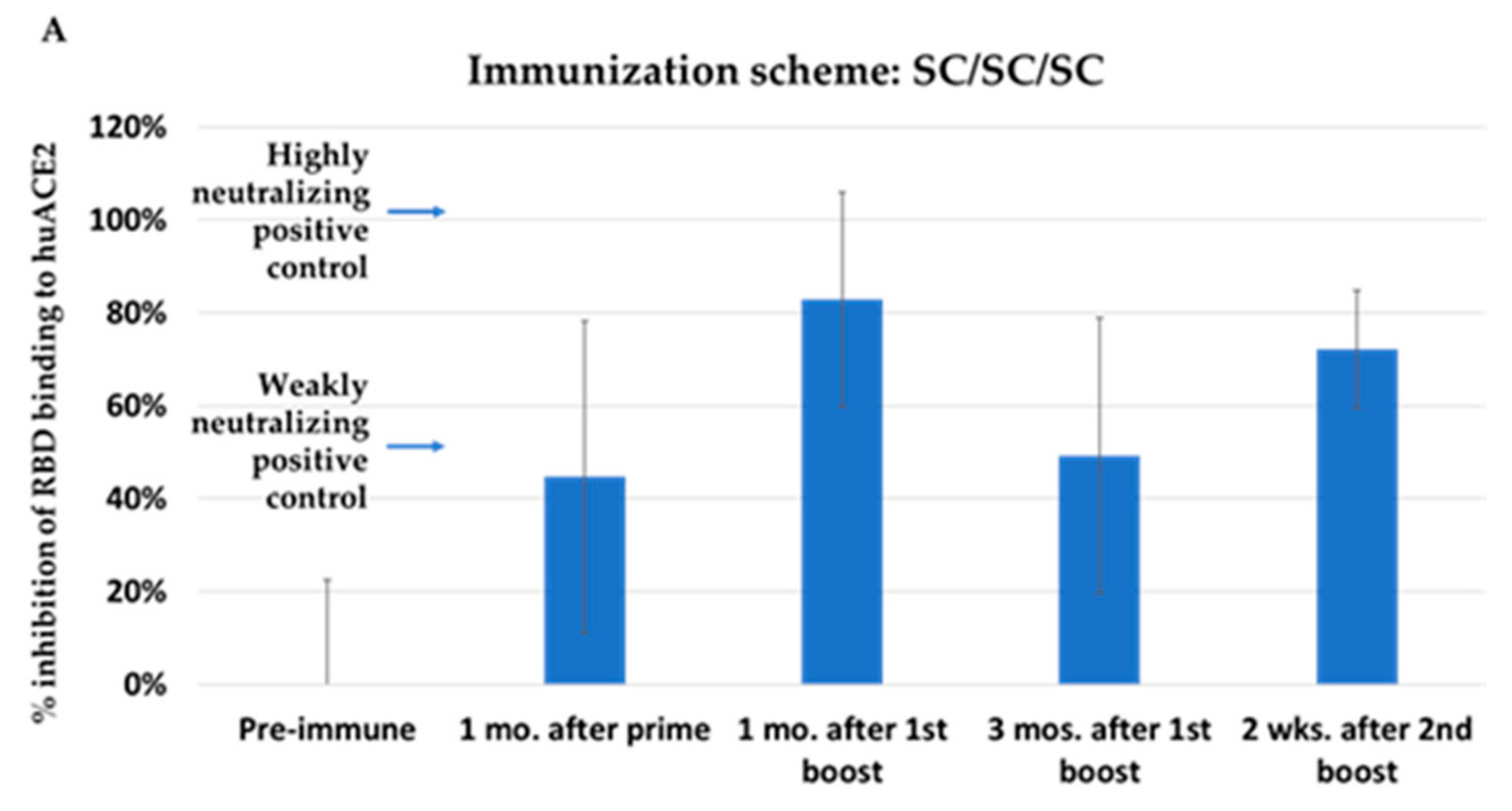
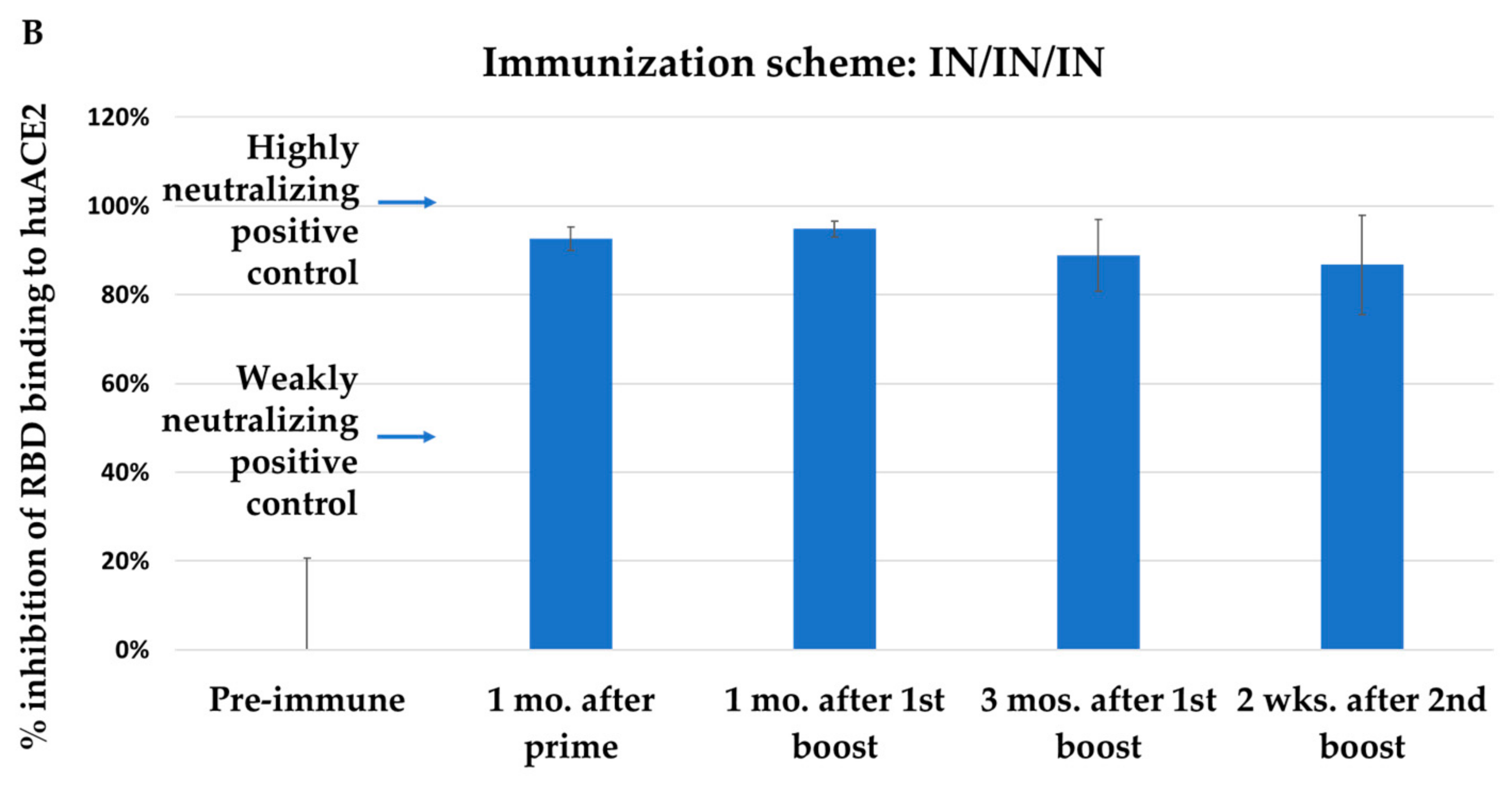
3.2. Immunization with NYVAC-KC
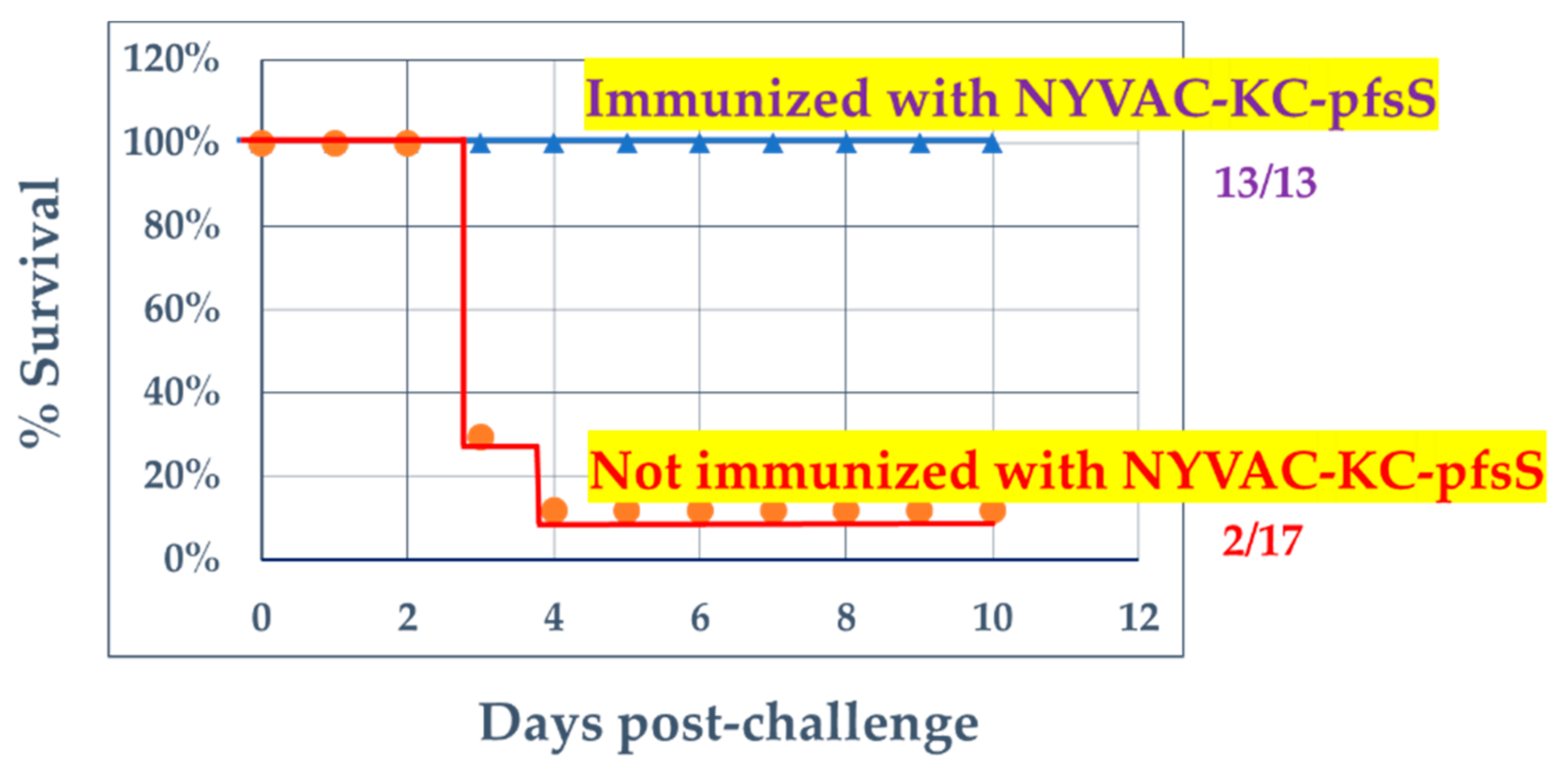
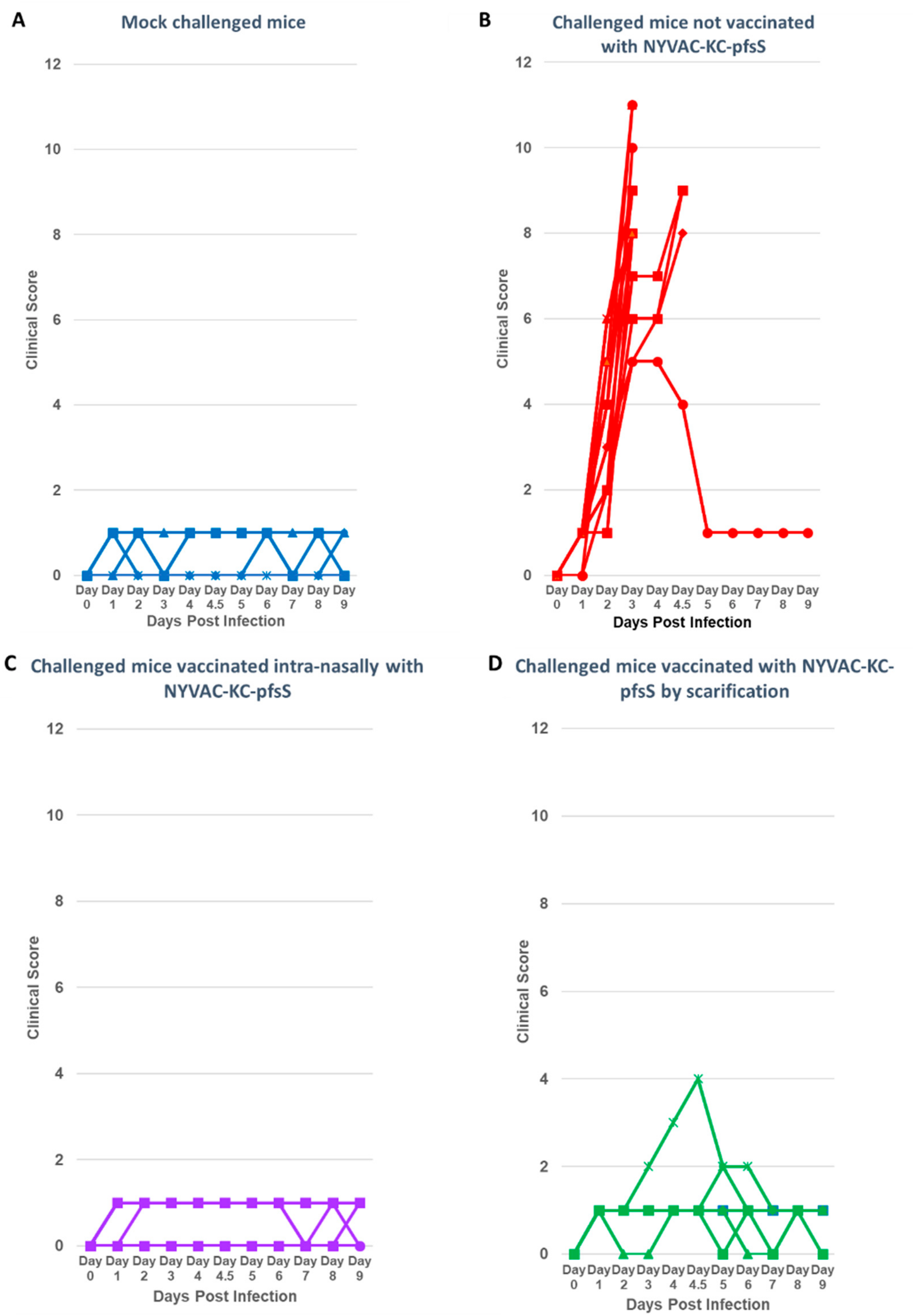
3.3. Challenge with SARS2-N501YMA30
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Chu, A.W.; Zhang, R.R.; Chan, W.M.; Ip, J.D.; Tsoi, H.W.; Chen, L.L.; Cai, J.P.; Lung, D.C.; Tam, A.R.; et al. The impact of spike N501Y mutation on neutralizing activity and RBD binding of SARS-CoV-2 convalescent serum. EBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Addetia, A.; Hannon, W.W.; Choudhary, M.C.; Dingens, A.S.; Li, J.Z.; Bloom, J.D. Prospective mapping of viral mutations that escape antibodies used to treat COVID-19. Science 2021, 371, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. Elife 2020, 9, e61312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibler, K.V.; Gomez, C.E.; Perdiguero, B.; Wong, S.; Huynh, T.; Holechek, S.; Arndt, W.; Jimenez, V.; Gonzalez-Sanz, R.; Denzler, K.; et al. Improved NYVAC-Based Vaccine Vectors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Arriaza, J.; Perdiguero, B.; Heeney, J.; Seaman, M.S.; Montefiori, D.C.; Yates, N.L.; Tomaras, G.D.; Ferrari, G.; Foulds, K.E.; Roederer, M.; et al. HIV/AIDS Vaccine Candidates Based on Replication-Competent Recombinant Poxvirus NYVAC-C-KC Expressing Trimeric gp140 and Gag-Derived Virus-Like Particles or Lacking the Viral Molecule B19 That Inhibits Type I Interferon Activate Relevant HIV-1-Specific B and T Cell Immune Functions in Nonhuman Primates. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02182-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kibler, K.V.; Asbach, B.; Perdiguero, B.; García-Arriaza, J.; Yates, N.L.; Parks, R.; Stanfield-Oakley, S.; Ferrari, G.; Montefiori, D.C.; Tomaras, G.D.; et al. Replication-Competent NYVAC-KC Yields Improved Immunogenicity to HIV-1 Antigens in Rhesus Macaques Compared to Nonreplicating NYVAC. J Virol. 2019, 93, e01513-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perdiguero, B.; Gomez, C.E.; Cepeda, V.; Sánchez-Sampedro, L.; García-Arriaza, J.; Mejías-Pérez, E.; Jiménez, V.; Sánchez, C.; Sorzano, C.O.S.; Oliveros, J.C.; et al. Virological and Immunological Characterization of Novel NYVAC-Based HIV/AIDS Vaccine Candidates Expressing Clade C Trimeric Soluble gp140(ZM96) and Gag(ZM96)-Pol-Nef(CN54) as Virus-Like Particles. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quakkelaar, E.D.; Redeker, A.; Haddad, E.K.; Harari, A.; McCaughey, S.M.; Duhen, T.; Filali-Mouhim, A.; Goulet, J.-P.; Loof, N.M.; Ossendorp, F.; et al. Improved Innate and Adaptive Immunostimulation by Genetically Modified HIV-1 Protein Expressing NYVAC Vectors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurawski, G.; Shen, X.; Zurawski, S.; Tomaras, G.D.; Montefiori, D.C.; Roederer, M.; Ferrari, G.; Lacabaratz, C.; Klucar, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Superiority in Rhesus Macaques of Targeting HIV-1 Env gp140 to CD40 versus LOX-1 in Combination with Replication-Competent NYVAC-KC for Induction of Env-Specific Antibody and T Cell Responses. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01596-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, L.Y.; Zheng, J.; Wilhelmsen, K.; Li, K.; Ortiz, M.E.; Schnicker, N.J.; Pezzulo, A.A.; Szachowicz, P.J.; Klumpp, K.; Aswad, F.; et al. Eicosanoid signaling as a therapeutic target in middle-aged mice with severe COVID-19. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Schaub, J.M.; DiVenere, A.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Javanmardi, K.; Le, K.C.; Wrapp, D.; Lee, A.G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spikes. Science 2020, 369, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D.; Conwell, K.; Langland, J.O.; Jacobs, B.L. Use of a negative selectable marker for rapid selection of recombinant vaccinia virus. BioTechniques 2011, 50, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, S.G.; Cope, T.A.; Hruby, D.E. BiZyme: A Novel Fusion Protein-Mediating Selection of Vaccinia Virus Recombinants by Fluorescence and Antibiotic Resistance. BioTechniques 2002, 32, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shors, T.; Jacobs, B.L. Complementation of Deletion of the Vaccinia Virus E3L Gene by theEscherichia coliRNase III Gene. Virology 1997, 227, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Sisler, J.R.; Moss, B. Compact, Synthetic, Vaccinia Virus Early/Late Promoter for Protein Expression. BioTechniques 1997, 23, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Renner, D.M.; Comar, C.E.; Whelan, J.N.; Reyes, H.M.; Cardenas-Diaz, F.L.; Truitt, R.; Tan, L.H.; Dong, B.; Alysandratos, K.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 induces double-stranded RNA-mediated innate immune responses in respiratory epithelial-derived cells and cardiomyocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022643118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, D.F.; Roeder, A.J.; Kaleta, E.; Jasbi, P.; Pfeffer, K.; Koelbela, C.; Periasamy, S.; Kuzmina, N.; Bukreyev, A.; Grys, T.E.; et al. Development of a rapid point-of-care test that measures neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 145, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, D.; Roeder, A.; Gonzalez-Moa, M.; Koehler, M.; Kaleta, E.; Jasbi, P.; Vanderhoof, J.; McKechnie, D.; Forman, J.; Edwards, B.; et al. Third COVID-19 Vaccine Dose Boosts Neutralising Antibodies in Poor Responders. Commun. Med. 2021, 2, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Challenge of Vaccine Cold Chain Logistics: How a Chemical ‘Casing’ Could Save Lives. Available online: https://globalbiodefense.com/2020/09/04/the-challenge-of-vaccine-cold-chain-logistics-how-a-chemical-casing-could-save-lives/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Ainai, A.; Van Riet, E.; Ito, R.; Ikeda, K.; Senchi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Tamura, S.; Asanuma, H.; Odagiri, T.; Tashiro, M.; et al. Human immune responses elicited by an intranasal inactivated H5 influenza vaccine. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Residue | Beta | Gamma | Delta | Omicron | SARS2-N501YMA30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G339 | G339D | ||||
| S371 | S371L | ||||
| S373 | S373P | ||||
| S375 | S375F | ||||
| K417 * | K417N | K417T | K417N | K417M | |
| N440 * | N440K | ||||
| G446 | G446S | ||||
| L452 | L452R | ||||
| S477 | S477N | ||||
| T478 | T478K | T478K | |||
| E484 * | E484K | E484K | E484A | E484K | |
| Q493 * | Q493K | Q493R | |||
| G496 | G496S | ||||
| Q498 | Q498R | Q498R | |||
| N501 * | N501Y | N501Y | N501Y | N501Y | |
| Y505 | Y505H |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kibler, K.V.; Szczerba, M.; Lake, D.; Roeder, A.J.; Rahman, M.; Hogue, B.G.; Roy Wong, L.-Y.; Perlman, S.; Li, Y.; Jacobs, B.L. Intranasal Immunization with a Vaccinia Virus Vaccine Vector Expressing Pre-Fusion Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike Fully Protected Mice against Lethal Challenge with the Heavily Mutated Mouse-Adapted SARS2-N501YMA30 Strain of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081172
Kibler KV, Szczerba M, Lake D, Roeder AJ, Rahman M, Hogue BG, Roy Wong L-Y, Perlman S, Li Y, Jacobs BL. Intranasal Immunization with a Vaccinia Virus Vaccine Vector Expressing Pre-Fusion Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike Fully Protected Mice against Lethal Challenge with the Heavily Mutated Mouse-Adapted SARS2-N501YMA30 Strain of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines. 2022; 10(8):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081172
Chicago/Turabian StyleKibler, Karen V., Mateusz Szczerba, Douglas Lake, Alexa J. Roeder, Masmudur Rahman, Brenda G. Hogue, Lok-Yin Roy Wong, Stanley Perlman, Yize Li, and Bertram L. Jacobs. 2022. "Intranasal Immunization with a Vaccinia Virus Vaccine Vector Expressing Pre-Fusion Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike Fully Protected Mice against Lethal Challenge with the Heavily Mutated Mouse-Adapted SARS2-N501YMA30 Strain of SARS-CoV-2" Vaccines 10, no. 8: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081172
APA StyleKibler, K. V., Szczerba, M., Lake, D., Roeder, A. J., Rahman, M., Hogue, B. G., Roy Wong, L.-Y., Perlman, S., Li, Y., & Jacobs, B. L. (2022). Intranasal Immunization with a Vaccinia Virus Vaccine Vector Expressing Pre-Fusion Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike Fully Protected Mice against Lethal Challenge with the Heavily Mutated Mouse-Adapted SARS2-N501YMA30 Strain of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines, 10(8), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081172







