Antiviral Activities of HIV-1-Specific Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Are Isotype-Dependent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
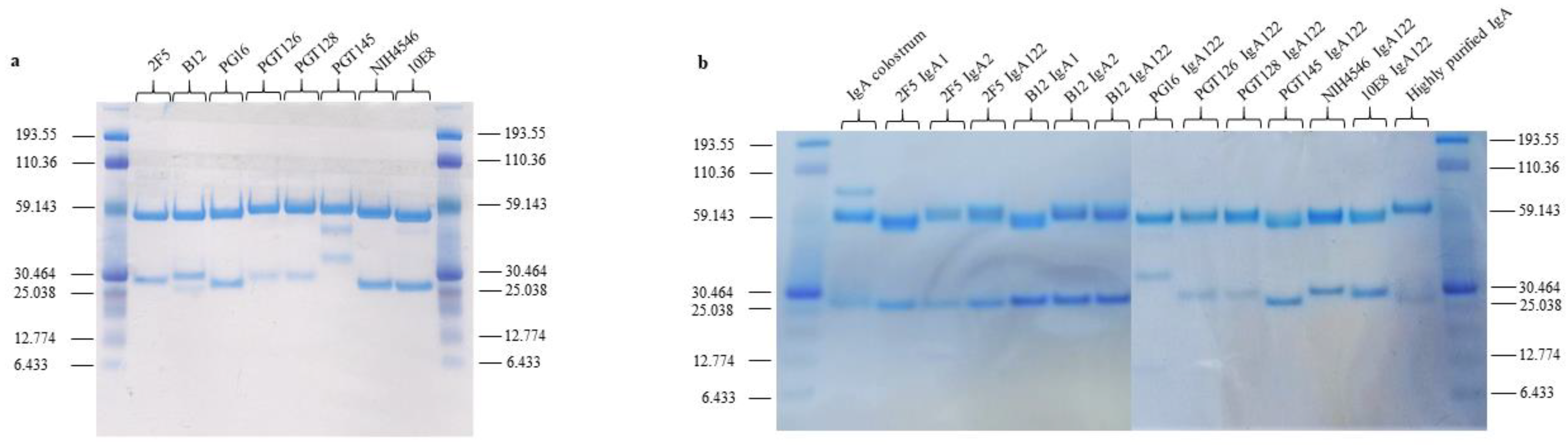
2.2. Construction and Production of Recombinant IgA1, IgA2, IgA122, and IgG
2.3. Analysis of the Specificity of the Different bNAb Isotypes
2.4. HIV-1-Specific Neutralization Assays
2.5. TZMbl/Pseudovirus Assay
2.6. PBMC/Primary Isolate Assay
2.7. HIV-1 Env-Dependent Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)-like Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
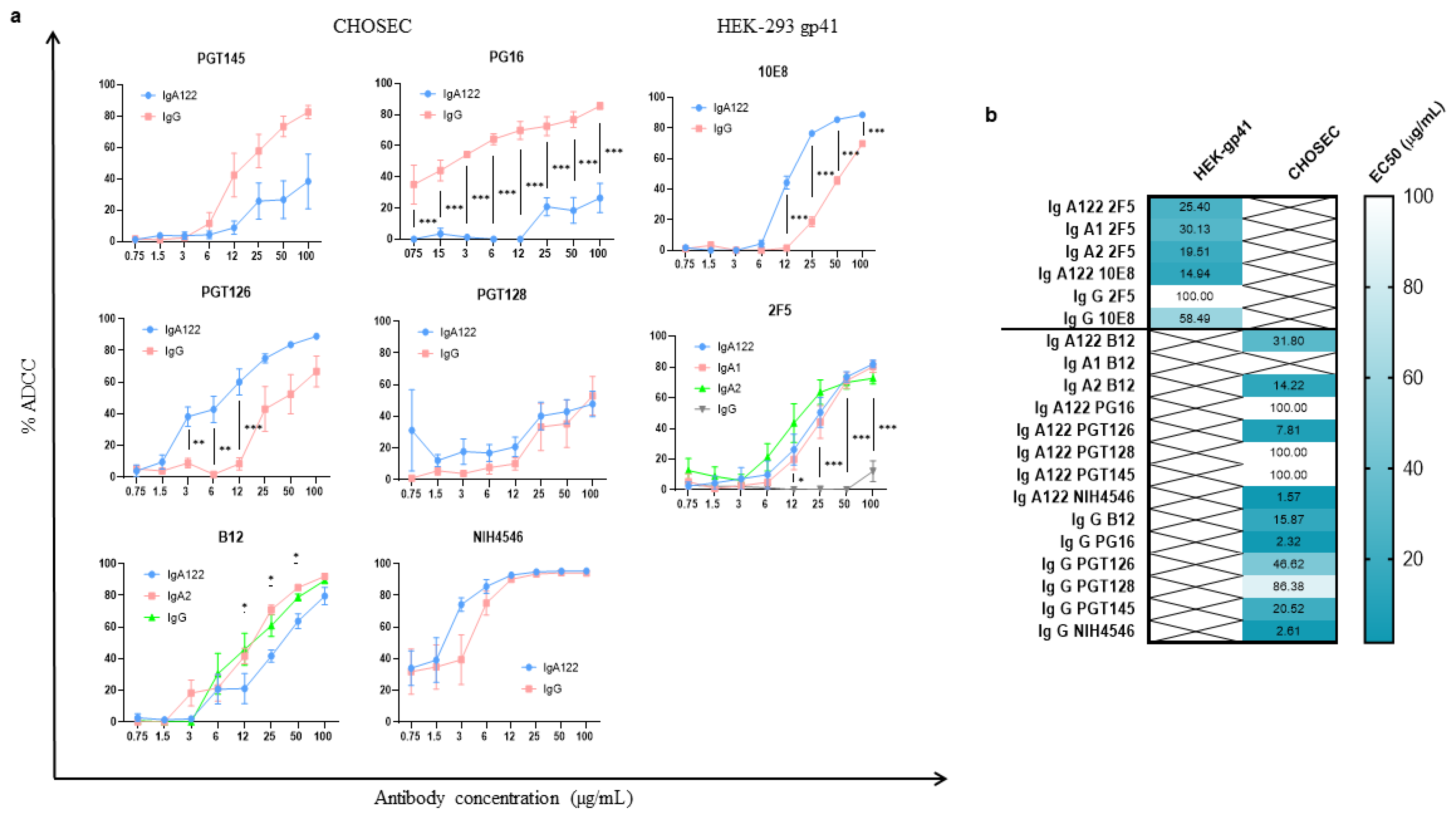
3.1. Development of a New Highly Potent Cellular Assay to Measure the ADCC-like Activity
3.2. ADCC-like Activities of bNAbs Depend on Their Isotypes and Their Specificity
3.2.1. Higher ADCC-like Activity of gp41-Specific IgA Isotypes
3.2.2. Heterogenous gp120-Specific ADCC-like Activity of IgG1 and IgA Isotypes
3.3. Development of a New Highly Potent Cellular Assay to Measure the ADCC-like Activity
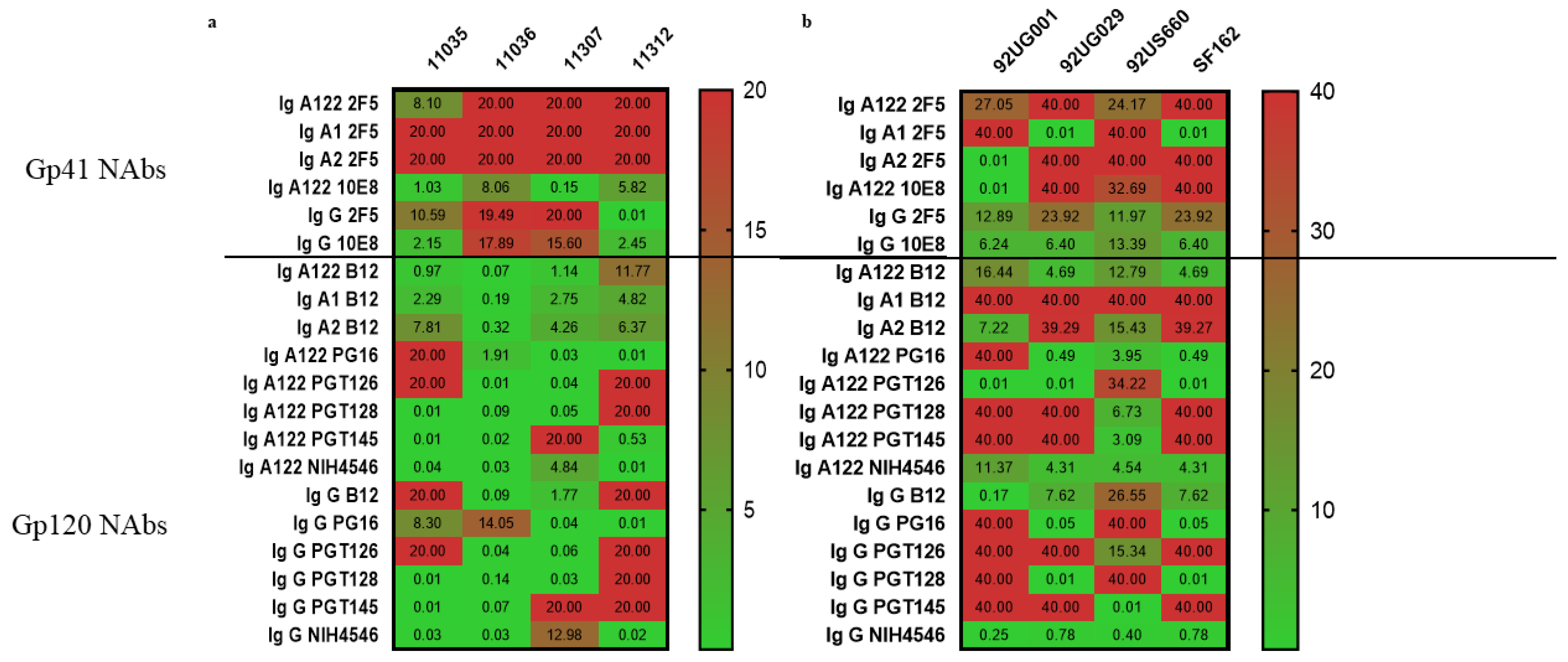
3.3.1. Gp41-Specific IgG1 Has More Potent Neutralizing Activity
3.3.2. Gp120-Specific IgG1 and IgAs Have Similar Neutralization Effect
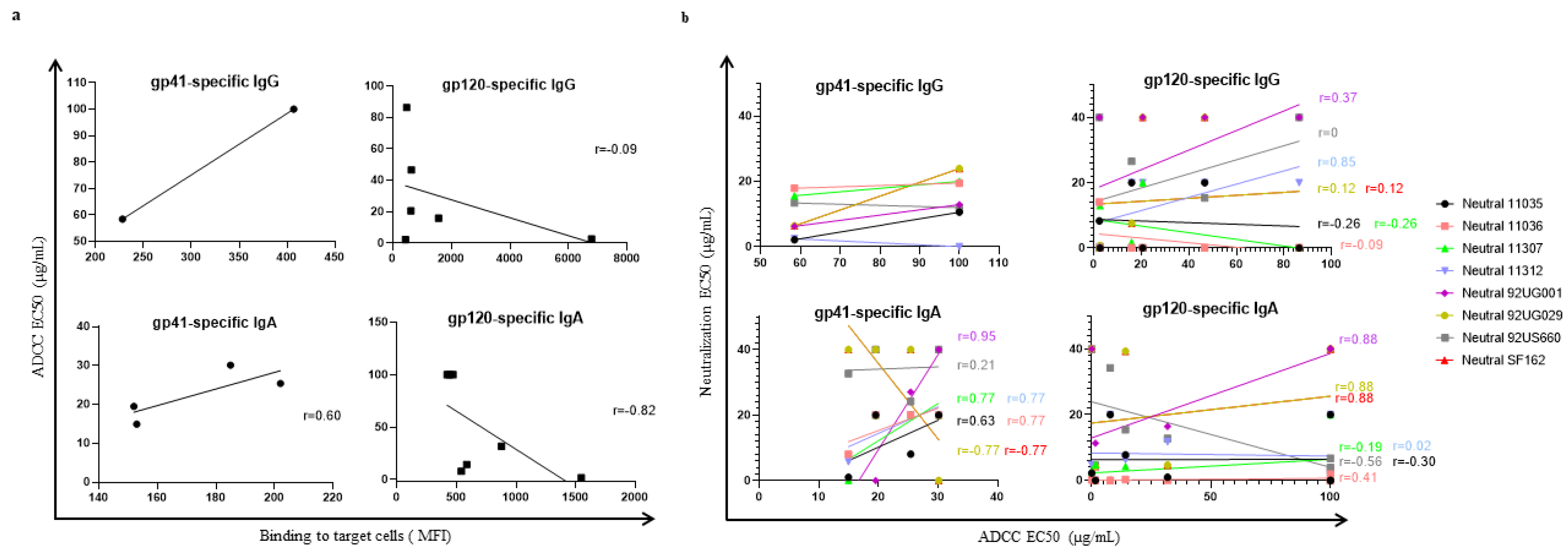
3.4. Correlation between ADCC-like Activity and Virus Neutralization
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouda, G.G.; Eudailey, J.; Kunz, E.L.; Amos, J.D.; Liebl, B.E.; Himes, J.; Boakye-Agyeman, F.; Beck, K.; Michaels, A.J.; Cohen-Wolkowiez, M.; et al. Systemic Administration of an HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Dimeric IgA Yields Mucosal Secretory IgA and Virus Neutralization. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, J.D.; Sholukh, A.M.; Mukhtar, M.M.; Siddappa, N.B.; Lakhashe, S.K.; Kim, M.; Reinherz, E.L.; Gupta, S.; Forthal, D.N.; Sattentau, Q.J.; et al. Anti-HIV IgA Isotypes: Differential Virion Capture and Inhibition of Transcytosis Are Linked to Prevention of Mucosal R5 SHIV Transmission. AIDS 2013, 27, F13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.; Casadevall, A. The Immunoglobulin Constant Region Contributes to Affinity and Specificity. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor, D.; Yu, H.; Maupetit, J.; Drillet, A.S.; Bouceba, T.; Schwartz-Cornil, I.; Lopalco, L.; Tuffery, P.; Bomsel, M. Isotype Modulates Epitope Specificity, Affinity, and Antiviral Activities of Anti-HIV-1 Human Broadly Neutralizing 2F5 Antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12680–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astronomo, R.D.; Santra, S.; Ballweber-Fleming, L.; Westerberg, K.G.; Mach, L.; Hensley-McBain, T.; Sutherland, L.; Mildenberg, B.; Morton, G.; Yates, N.L.; et al. Neutralization Takes Precedence Over IgG or IgA Isotype-Related Functions in Mucosal HIV-1 Antibody-Mediated Protection. EBioMedicine 2016, 14, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbank, S.; Kunert, R.; Stiegler, G.; Katinger, H. Characterization of Human Class-Switched Polymeric (Immunoglobulin M [IgM] and IgA) Anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Antibodies 2F5 and 2G12. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Drelichman, E.R.; Bimczok, D.; Ochsenbauer, C.; Kappes, J.C.; Cannon, J.A.; Tudor, D.; Bomsel, M.; Smythies, L.E.; Smith, P.D. GP41-Specific Antibody Blocks Cell-Free HIV Type 1 Transcytosis through Human Rectal Mucosa and Model Colonic Epithelium. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3648–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantis, N.J.; Palaia, J.; Hessell, A.J.; Mehta, S.; Zhu, Z.; Corthésy, B.; Neutra, M.R.; Burton, D.R.; Janoff, E.N. Inhibition of HIV-1 Infectivity and Epithelial Cell Transfer by Human Monoclonal IgG and IgA Antibodies Carrying the B12 V Region. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bergami, P.L.; Duval, M.; Kuhrt, D.; Posner, M.; Cavacini, L. Expression and Functional Activity of Isotype and Subclass Switched Human Monoclonal Antibody Reactive with the Base of the V3 Loop of HIV-1 Gp120. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2003, 19, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.I.; Lambson, B.E.; Crowley, A.R.; Bashirova, A.; Scheepers, C.; Garrett, N.; Karim, S.A.; Mkhize, N.N.; Carrington, M.; Ackerman, M.E.; et al. IgG3 Enhances Neutralization Potency and Fc Effector Function of an HIV V2-Specific Broadly Neutralizing Antibody. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournazos, S.; Klein, F.; Pietzsch, J.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies Require Fc Effector Functions for in Vivo Activity. Cell 2014, 158, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, L.; Su, B.; Moog, C. Role of Nonneutralizing Antibodies in Vaccines and/or HIV Infected Individuals. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomsel, M.; Tudor, D.; Drillet, A.S.; Alfsen, A.; Ganor, Y.; Roger, M.G.; Mouz, N.; Amacker, M.; Chalifour, A.; Diomede, L.; et al. Immunization with HIV-1 Gp41 Subunit Virosomes Induces Mucosal Antibodies Protecting Nonhuman Primates against Vaginal SHIV Challenges. Immunity 2011, 34, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.H.; Crowley, A.R.; Backes, I.; Chang, C.; Tay, M.; Broge, T.; Tuyishime, M.; Ferrari, G.; Seaman, M.S.; Richardson, S.I.; et al. Hinge Length Contributes to the Phagocytic Activity of HIV-Specific IgG1 and IgG3 Antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, M.; Khamassi, M.; Xu, L.; Tudor, D.; Bomsel, M. IgA Targeting Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Envelope Gp41 Triggers Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Cross-Clade and Cooperates with Gp41-Specific IgG to Increase Cell Lysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, M.; Tudor, D.; Cottignies-Calamarte, A.; Bomsel, M. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis of HIV-1-Infected Cells Is Efficiently Triggered by IgA Targeting HIV-1 Envelope Subunit Gp41. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Liberatore, R.A.; Guo, Y.; Chan, K.W.; Pan, R.; Lu, H.; Waltari, E.; Mittler, E.; Chandran, K.; Finzi, A.; et al. VSV-Displayed HIV-1 Envelope Identifies Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Class-Switched to IgG and IgA. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 963–975.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Plotkin, S.A. Complex Immune Correlates of Protection in HIV-1 Vaccine Efficacy Trials. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, R.; Benjelloun, F.; Pin, J.J.; Kone, A.; Chanut, B.; Jospin, F.; Lucht, F.; Verrier, B.; Moog, C.; Genin, C.; et al. Generation of HIV-1 Potent and Broad Neutralizing Antibodies by Immunization with Postfusion HR1/HR2 Complex. AIDS 2013, 27, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefiori, D.C. Evaluating Neutralizing Antibodies against HIV, SIV, and SHIV in Luciferase Reporter Gene Assays. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2004, 64, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C.D.; White, J.M. Characterization of Stable Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells Expressing Wild-Type, Secreted, and Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-Anchored Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Envelope Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7060–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.; Jelicic, K.; Van Ryk, D.; Rochereau, N.; Cicala, C.; Arthos, J.; Noailly, B.; Genin, C.; Verrier, B.; Laurant, S.; et al. Neutralizing and Targeting Properties of a New Set of A4β7-Specific Antibodies Are Influenced by Their Isotype. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 75, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascola, J.R.; Haynes, B.F. HIV-1 Neutralizing Antibodies: Understanding Nature’s Pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 254, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Ruprecht, R.M. Are Anti-HIV IgAs Good Guys or Bad Guys? Retrovirology 2014, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancera, M.; Shahzad-Ul-Hussan, S.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; McLellan, J.S.; Bailer, R.T.; Dai, K.; Loesgen, S.; Louder, M.K.; Staupe, R.P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Structural Basis for Diverse N-Glycan Recognition by HIV-1-Neutralizing V1-V2-Directed Antibody PG16. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ofek, G.; Laub, L.; Louder, M.K.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Longo, N.S.; Imamichi, H.; Bailer, R.T.; Chakrabarti, B.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Broad and Potent Neutralization of HIV-1 by a Gp41-Specific Human Antibody. Nature 2012, 491, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, A.; Sakamoto, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Osawa, M.; Hiroyama, T.; Eyre, H.J.; Sutherland, G.R.; Endo, Y.; Fujita, T.; et al. Fcα/μ Receptor Mediates Endocytosis of IgM-Coated Microbes. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruel, T.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Amraoui, S.; Malbec, M.; Richard, L.; Bourdic, K.; Donahue, D.A.; Lorin, V.; Casartelli, N.; Noël, N.; et al. Elimination of HIV-1-Infected Cells by Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bredow, B.; Arias, J.F.; Heyer, L.N.; Moldt, B.; Le, K.; Robinson, J.E.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Burton, D.R.; Evans, D.T. Virus Neutralization by HIV-1 Env-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6127–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, G.; Peng, H.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Morelli, M.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, B. A Fusion-Intermediate State of HIV-1 Gp41 Targeted by Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3739–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Frey, G.; Peng, H.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Garrity, J.; Seaman, M.S.; Chen, B. Mechanism of HIV-1 Neutralization by Antibodies Targeting a Membrane-Proximal Region of Gp41. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, R.M.F.; Zwick, M.B.; Stanfield, R.L.; Kunert, R.; Binley, J.M.; Katinger, H.; Burton, D.R.; Wilson, I.A. Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV Antibody 4E10 Recognizes a Helical Conformation of a Highly Conserved Fusion-Associated Motif in Gp41. Immunity 2005, 22, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irimia, A.; Sarkar, A.; Stanfield, R.L.; Wilson, I.A. Crystallographic Identification of Lipid as an Integral Component of the Epitope of HIV Broadly Neutralizing Antibody 4E10. Immunity 2016, 44, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bredow, B.; Andrabi, R.; Grunst, M.; Grandea, A.G., III; Le, K.; Song, G.; Berndsen, Z.T.; Porter, K.; Pallesen, J.; Ward, A.B.; et al. Differences in the Binding Affinity of an HIV-1 V2 Apex- Specific Antibody for the SIV Smm / Mac Envelope Glycoprotein Uncouple Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity From. MBio 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Ferrari, G.; Shen, X.; Alam, S.M.; Liao, H.X.; Pollara, J.; Bonsignori, M.; Moody, M.A.; Fong, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Vaccine-Induced Plasma IgA Specific for the C1 Region of the HIV-1 Envelope Blocks Binding and Effector Function of IgG. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9019–9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamassi, M.; Xu, L.; Rey, J.; Duchemin, M.; Bouceba, T.; Tuffery, P.; Tudor, D.; Bomsel, M. The CH1α Domain of Mucosal Gp41 IgA Contributes to Antibody Specificity and Antiviral Functions in HIV-1 Highly Exposed Sero-Negative Individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepers, C.; Bekker, V.; Anthony, C.; Richardson, S.I.; Oosthuysen, B.; Moyo, T.; Kgagudi, P.; Kitchin, D.; Nonyane, M.; York, T.; et al. Antibody Isotype Switching as a Mechanism to Counter HIV Neutralization Escape. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.S.; Wrin, M.T.; Crawford-Miksza, L.; Potts, B.; Wu, Y.; Weber, P.A.; Alfonso, R.D.; Hanson, C. V Neutralization Sensitivity of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Is Determined in Part by the Cell in Which the Virus Is Propagated. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrin, T.; Loh, T.P.; Vennari, J.C.; Schuitemaker, H.; Nunberg, J.H. Adaptation to Persistent Growth in the H9 Cell Line Renders a Primary Isolate of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Sensitive to Neutralization by Vaccine Sera. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammonds, J.; Chen, X.; Ding, L.; Fouts, T.; De Vico, A.; Zur Megede, J.; Barnett, S.; Spearman, P. Gp120 Stability on HIV-1 Virions and Gag-Env Pseudovirions Is Enhanced by an Uncleaved Gag Core. Virology 2003, 314, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugach, P.; Kuhmann, S.E.; Taylor, J.; Marozsan, A.J.; Snyder, A.; Ketas, T.; Wolinsky, S.M.; Korber, B.T.; Moore, J.P. The Prolonged Culture of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 in Primary Lymphocytes Increases Its Sensitivity to Neutralization by Soluble CD4. Virology 2004, 321, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Target Protein | Epitope * | Antibody | Isotype | MFI | % of Positivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gp41 (HEK-gp41) | MPER | 2F5 | IgG1 | 407 | 93.5% |
| IgA1 | 185 | 55.0% | |||
| IgA2 | 152 | 45.5% | |||
| IgA122 | 202 | 64.5% | |||
| 10E8 | IgG1 | 228 | 41.6% | ||
| IgA122 | 153 | 8.76% | |||
| gp140 (CHOSEC) | CD4 binding site | B12 | IgG1 | 1566 | 99.6% |
| IgA1 | 886 | 98.4% | |||
| IgA2 | 586 | 73.5% | |||
| IgA122 | 878 | 92.3% | |||
| NIH4546 | IgG1 | 6784 | 100% | ||
| IgA122 | 1548 | 99.4% | |||
| V2 glycan | PG16 | IgG1 | 439 | 0.049% | |
| IgA122 | 422 | 0.23% | |||
| PGT145 | IgG1 | 623 | 41.4% | ||
| IgA122 | 471 | 4.34% | |||
| V3 glycan | PGT126 | IgG1 | 638 | 47.6% | |
| IgA122 | 540 | 27.4% | |||
| PGT128 | IgG1 | 476 | 13.2% | ||
| IgA122 | 442 | 1.62% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noailly, B.; Yaugel-Novoa, M.; Werquin, J.; Jospin, F.; Drocourt, D.; Bourlet, T.; Rochereau, N.; Paul, S. Antiviral Activities of HIV-1-Specific Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Are Isotype-Dependent. Vaccines 2022, 10, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060903
Noailly B, Yaugel-Novoa M, Werquin J, Jospin F, Drocourt D, Bourlet T, Rochereau N, Paul S. Antiviral Activities of HIV-1-Specific Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Are Isotype-Dependent. Vaccines. 2022; 10(6):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060903
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoailly, Blandine, Melyssa Yaugel-Novoa, Justine Werquin, Fabienne Jospin, Daniel Drocourt, Thomas Bourlet, Nicolas Rochereau, and Stéphane Paul. 2022. "Antiviral Activities of HIV-1-Specific Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Are Isotype-Dependent" Vaccines 10, no. 6: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060903
APA StyleNoailly, B., Yaugel-Novoa, M., Werquin, J., Jospin, F., Drocourt, D., Bourlet, T., Rochereau, N., & Paul, S. (2022). Antiviral Activities of HIV-1-Specific Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Are Isotype-Dependent. Vaccines, 10(6), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060903






